Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aspirin
Uploaded by
Angelica Cassandra Villena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesdrug study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdrug study
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views2 pagesAspirin
Uploaded by
Angelica Cassandra Villenadrug study
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Republic of the Philippines
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
(CvSU)
Don Severino Delas Alas Campus
Indang, Cavite
(046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012
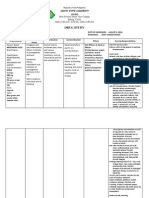
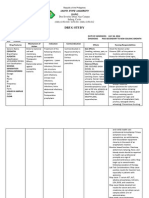
DRUG STUDY
NAME OF PATIENT: CM DATE OF ADMISSION: AUGUST 20, 2014
AGE: 64 YEARS OLD DIAGNOSIS: CVD PROB. INFRACT HPN
SEX: MALE
Drug Features
Mechanism of
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Effects Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name:
Aspirin
Brand Name:
Scheerin
Classification:
antipyretics,
nonopioid
analgesics
Sub
Classification:
Salicylates
Dosage:
80 mg
Route:
PO
Frequency:
OD
Form:
Tablet
Color:
White
Produce
analgesia and
reduce
inflammation
and fever by
inhibiting the
production of
prostaglandins.
Decreases
platelet
aggregation.
Therapeutic
Effects:
Analgesia.
Reduction of
inflammation.
Reduction of
fever.
Decreased
incidence of
transient
ischemic
attacks and MI.
Inflammator
y disorders
including:
Rheumatoid
arthritis,
Osteoarthrit
is. Mild to
moderate
pain. Fever.
Prophylaxis
of transient
ischemic
attacks and
MI.
Unlabelled
Use:
Adjunctive
treatment
of Kawasaki
disease.
Contraindicated
in:
Hypersensitivity
to aspirin or
other salicylates;
Cross-sensitivity
with other
NSAIDs may exist
(less with
nonaspirin
salicylates);
Bleeding
disorders or
thrombocytopeni
a; Pedi: May
increase risk of
Reyes syndrome
in children or
adolescents with
viral infections.
Use Cautiously
in: History of GI
bleeding or ulcer
disease; Chronic
Side Effects &
Adverse
Effects
EENT: tinnitus.
GI: GI
BLEEDING,
dyspepsia,
epigastric
distress,
nausea,
abdominal
pain,
anorexia,
hepatotoxicity
, vomiting.
Hemat:
anemia,
hemolysis.
Derm: rash,
urticaria.
Misc:
ALLERGIC
REACTIONS
INCLUDING
ANAPHYLAXIS
Check for Doctors order
Observe 10Rs of the patient in medicine administration
Assessment:
Patients who have asthma, allergies, and nasal polyps or who are allergic to
tartrazine are at an increased risk for developing hypersensitivity
reactions.
Pain: Assess pain and limitation of movement; note type, location, and
intensity before and at the peak (see Time/Action Profile) after
administration.
Fever: Assess fever and note associated signs (diaphoresis, tachycardia,
malaise, chills).
Lab Test Considerations: Monitor hepatic function before antirheumatic
therapy and if symptoms of hepatotoxicity occur; more likely in patients,
especially children, with rheumatic fever, systemic lupus erythematosus,
juvenile arthritis, or pre-existing hepatic disease. May cause serum
AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase, especially when plasma
concentrations exceed 25 mg/100 mL. May return to normal despite
continued use or dose reduction. If severe abnormalities or active liver
disease occurs, discontinue and use with caution in future.
Monitor serum salicylate levels periodically with prolonged high-dose therapy
to determine dose, safety, and efficacy, especially in children with
Kawasaki disease.
May alter results of serum uric acid, urine vanillylmandelic acid (VMA),
protirelin-induced thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), urine
hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) determinations, and radionuclide
thyroid imaging.
Prolongs bleeding time for 47 days and, in large doses, may cause prolonged
alcohol
use/abuse;
Severe hepatic or
renal disease;
OB: Salicylates
may have
adverse effects
on fetus and
mother and
should be
avoided during
pregnancy,
especially during
the 3rd
trimester;
Lactation: Safety
not established;
Geri: risk of
adverse reactions
especially GI
bleeding; more
sensitive to toxic
levels.
AND
LARYNGEAL
EDEMA.
prothrombin time. Monitor hematocrit periodically in prolonged high-
dose therapy to assess for GI blood loss .
Toxicity and Overdose: Monitor for the onset of tinnitus, headache,
hyperventilation, agitation, mental confusion, lethargy, diarrhea, and
sweating. If these symptoms appear, withhold medication and notify
physician or other health care professional immediately.
Patient Teaching
Instruct patient to take salicylates with a full glass of water and to remain in
an upright position for 1530 min after administration.
Advise patient to report tinnitus; unusual bleeding of gums; bruising; black,
tarry stools; or fever lasting longer than 3 days.
Caution patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol with this medication to
minimize possible gastric irritation; 3 or more glasses of alcohol per day may
increase the risk of GI bleeding. Caution patient to avoid taking concurrently
with acetaminophen or NSAIDs for more than a few days, unless directed by
health care professional to prevent analgesic nephropathy.
Teach patients on a sodium-restricted diet to avoid effervescent tablets or
buffered-aspirin preparations.
Tablets with an acetic (vinegar-like) odor should be discarded.
Advise patients on long-term therapy to inform health care professional of
medication regimen before surgery. Aspirin may need to be withheld for 1 wk
before surgery.
Pedi: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention warns against giving aspirin
to children or adolescents with varicella (chickenpox) or influenza-like or viral
illnesses because of a possible association with Reyes syndrome.
Transient Ischemic Attacks or MI: Advise patients receiving aspirin
prophylactically to take only prescribed dose. Increasing the dose has not
been found to provide additional benefits.
SUBMITTED BY: ANGELICA CASSANDRA P. VILLENA CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR: EDERLYN P. DESTURA RN, MAN
YEAR & SEC. GRP: BSN 3 1 GRP 1
DATE: AUGUST 23, 2014
You might also like
- Sepsis in Older PatientsDocument8 pagesSepsis in Older PatientsFajar WasilahNo ratings yet
- 8.-ANATOMY and Physiology GIDocument12 pages8.-ANATOMY and Physiology GIAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Elective ShockDocument40 pagesElective ShockAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument5 pagesSeptic ShockAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Marcos Administration: Capv, Bsa 2-6Document2 pagesMarcos Administration: Capv, Bsa 2-6Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Physical Activity: Key FactsDocument4 pagesPhysical Activity: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument2 pagesBibliographyAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- F Table 1Document8 pagesF Table 1Talha IdreesNo ratings yet
- JanuaryDocument2 pagesJanuaryAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Observation A Skill Worth DevelopingDocument30 pagesPsychiatric Observation A Skill Worth DevelopingAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- CETIRIZINEDocument2 pagesCETIRIZINEAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (10)
- Sustainability in NursingDocument18 pagesSustainability in NursingAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Mental Health ActDocument9 pagesMental Health ActAngelica Cassandra Villena100% (1)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Lcohol: Key FactsDocument4 pagesLcohol: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Lcohol: Key FactsDocument4 pagesLcohol: Key FactsAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Article 5Document21 pagesArticle 5Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Art 8Document27 pagesArt 8Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Department of Health: History, Policy, Budget, Programs For HealthDocument57 pagesDepartment of Health: History, Policy, Budget, Programs For HealthAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Cavite (046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012Document1 pageDrug Study: Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Cavite (046) 4150-010 / 4150-011 (046) 4150-012Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument2 pagesAspirinAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- EvaluationDocument2 pagesEvaluationAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- United States of America National AnthemDocument1 pageUnited States of America National AnthemGaco Costa RicaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Document2 pagesDrug Study: Cavite State University (Cvsu)Angelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- CEFTRIAZONEDocument2 pagesCEFTRIAZONEAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- CEFRADINEDocument2 pagesCEFRADINEAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- HISTORYDocument3 pagesHISTORYAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- CefoxitinDocument3 pagesCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Campanile (Vol 90, Ed 2), Published Oct 22, 2007Document24 pagesThe Campanile (Vol 90, Ed 2), Published Oct 22, 2007The CampanileNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Fa'iz Annur: Daftar Hasil Studi Dan Yudisium (Dhsy)Document1 pageMuhammad Fa'iz Annur: Daftar Hasil Studi Dan Yudisium (Dhsy)osamafania nadiumaraNo ratings yet
- Digital Fabrication in Architecture PDFDocument192 pagesDigital Fabrication in Architecture PDFAndrada Iulia NeagNo ratings yet
- Faith Confession SheetDocument5 pagesFaith Confession SheetArjel Jamias100% (1)
- Contoh Writing AdfelpsDocument1 pageContoh Writing Adfelpsmikael sunarwan100% (2)
- Application of Schiff Base Ligamd ComplexDocument7 pagesApplication of Schiff Base Ligamd Complexrajbharaths1094No ratings yet
- Data Sheet (English) - 8036 Industrial ControlsDocument44 pagesData Sheet (English) - 8036 Industrial ControlsNabil ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Oracle Partitioned TablesDocument38 pagesOracle Partitioned TablesshahbazbNo ratings yet
- Manila Jocky Club Vs CADocument20 pagesManila Jocky Club Vs CAryusuki takahashiNo ratings yet
- Eniserver Quickstart EDocument14 pagesEniserver Quickstart EYESSER CHANNANo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Marketing 12th Edition LambDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Marketing 12th Edition Lambangelascottaxgeqwcnmy100% (39)
- Food and Medicine Label 1-50Document11 pagesFood and Medicine Label 1-50Muthia KumalaNo ratings yet
- XM 301 StudDocument594 pagesXM 301 StudNarendar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1Funio KhanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Culture - Chapter 13Document11 pagesEntrepreneurial Culture - Chapter 13bnp guptaNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Vector: The Standard Representation ExamplesDocument4 pagesCoordinate Vector: The Standard Representation ExamplesAtikshaNo ratings yet
- 03 9609 12 MS Prov Rma 08022023111718Document18 pages03 9609 12 MS Prov Rma 08022023111718Kalsoom SoniNo ratings yet
- Startup-Shutdown Oracle LinuxDocument4 pagesStartup-Shutdown Oracle LinuxJosé Florencio de QueirozNo ratings yet
- Effective Leadership Case Study AssignmentDocument5 pagesEffective Leadership Case Study AssignmentAboubakr Soultan67% (3)
- Cytomegalovirus in Primary ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 pagesCytomegalovirus in Primary ImmunodeficiencyAle Pushoa UlloaNo ratings yet
- Catherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaDocument7 pagesCatherine The Great: Catherine II, Empress of RussiaLawrence James ParbaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Batching and MixingDocument8 pagesConcrete Batching and MixingIm ChinithNo ratings yet
- Narcissistic ParentDocument5 pagesNarcissistic ParentChris Turner100% (1)
- The Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Job Performance of Myanmar School TeachersDocument16 pagesThe Relationship Between Emotional Intelligence and Job Performance of Myanmar School TeachersAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteNo ratings yet
- Vampire Lord Strategy - FinalDocument8 pagesVampire Lord Strategy - FinalMarco RadiciNo ratings yet
- 25 - A Hard Days NightDocument2 pages25 - A Hard Days NightBruno GovernatoriNo ratings yet
- "The Sacrament of Confirmation": The Liturgical Institute S Hillenbrand Distinguished LectureDocument19 pages"The Sacrament of Confirmation": The Liturgical Institute S Hillenbrand Distinguished LectureVenitoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Science1Document23 pagesPsychological Science1Jatin RaghavNo ratings yet
- 1955 Fujita - The Magnitude and Distribution of Residual StressDocument25 pages1955 Fujita - The Magnitude and Distribution of Residual StressAKNo ratings yet
- Principles and Methods of Effective TeachingDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Methods of Effective TeachingerikaNo ratings yet