Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMDC Motor
Uploaded by
Adnan KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMDC Motor
Uploaded by
Adnan KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
PMDC Motor
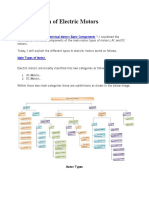
Basic configuration
Permanent magnet DC brushed motors (PMDC motors) consist of permanent magnets, located in
the stator, and windings, located in the rotor.
The ends of the winding coils are connected to commutator segments, that make slipping contact
with the stationary brushes. Brushes are connected to DC voltage supply across motor terminals.
Change of direction of rotation can be achieved by reversal of voltage polarity.
The current flow through the coils creates magnetic poles in the rotor, that interact wthe
permanent magnet poles. In order to keep the torque generation in same direction, the current
flow must be reversed when the rotor north pole passes the stator south pole.
For this the slipping contacts are segmented. This segmented slip ring is called commutator. Left
picture shows angular position just before commutation of rotor winding current, right picture
after it.
Real DC motors have more than two windings and commutator segments, for generation of a
more constant torque
Advantages of DC motors:
Speed control over a wide range both above and below the rated speed:
The attractive feature of the dc motor is that it offers the wide range of speed
control both above and below the rated speeds. This can be achieved in dc shunt
motors by methods such as armature control method and field control method.
This is one of the main applications in which dc motors are widely used in fine
speed applications such as in rolling mills and in paper mills.
High starting torque: dc series motors are termed as best suited drives for
electrical traction applications used for driving heavy loads in starting conditions.
DC series motors will have a staring torque as high as 500% compared to normal
operating torque. Therefore dc series motors are used in the applications such as
in electric trains and cranes.
Accurate steep less speed with constant torque: Constant torque drives is
one such the drives will have motor shaft torque constant over a given speed
range. In such drives shaft power varies with speed.
Quick starting, stopping, reversing and acceleration
Free from harmonics, reactive power consumption and many factors which
makes dc motors more advantageous compared to ac induction motors.
Disadvantages of DC motors:
High initial cost
Increased operation and maintenance cost due to presence of commutator and
brush gear
Cannot operate in explosive and hazard conditions due to sparking occur at
brush ( risk in commutation failure)
You might also like
- Brushless DC Motor Working Principle and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesBrushless DC Motor Working Principle and ApplicationsMd Samee MNo ratings yet
- Ac and DC MotorDocument6 pagesAc and DC MotorKhairunnisa ZakiriNo ratings yet
- Motor Drive and ActuatorsDocument47 pagesMotor Drive and ActuatorsSayeda Asma NoorNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of DC MotorDocument6 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of DC MotorMuhd Izwan Ikhmal RosliNo ratings yet
- Hercules M. Biacoraelectrical-MachinesDocument8 pagesHercules M. Biacoraelectrical-MachinesBiacora Manalo HerculesNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument3 pagesDC MotorShubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsDocument6 pagesThe Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsGalco IndustrialNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument12 pagesDC MotorsJamie Ray DalisayNo ratings yet
- The Basic DC MotorDocument22 pagesThe Basic DC MotortamilselviNo ratings yet
- Classification of MotorSDocument17 pagesClassification of MotorSHumaid Shaikh50% (2)
- DC MotorDocument5 pagesDC MotorMuhamad ZamaniNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument12 pagesDC Motorsmuletola7No ratings yet
- Classification of Electric Motors: Electrical Motors Basic ComponentsDocument89 pagesClassification of Electric Motors: Electrical Motors Basic ComponentsSarada Sankar DasNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument3 pagesDC MotorAhmad AzizudinNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument45 pagesDC MotorRayz C.ONo ratings yet
- Motor Control OverviewDocument7 pagesMotor Control OverviewSaul Mendez ElizondoNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument6 pagesDC MotorUjjawal ParasarNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor: Types of MotorsDocument8 pagesElectric Motor: Types of MotorsPlutoNo ratings yet
- Castillo Gemelene M IelecDocument4 pagesCastillo Gemelene M IelecMeg CastleNo ratings yet
- Ev Engine ResearchDocument15 pagesEv Engine ResearchAnshul YadavNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On DC Motor:-: Name:-Deepshikha Verma Roll No: - RK6003B56 Section: - RK6003 Reg No: - 11011921Document16 pagesTerm Paper On DC Motor:-: Name:-Deepshikha Verma Roll No: - RK6003B56 Section: - RK6003 Reg No: - 11011921Deepshikha VermaNo ratings yet
- Topic: DC Motor Using Mechanical Application: New Era University College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument13 pagesTopic: DC Motor Using Mechanical Application: New Era University College of Engineering and TechnologyMAr Lon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lec # 26 Brushless DC MotorDocument12 pagesLec # 26 Brushless DC MotorBuriro HayatNo ratings yet
- PMBLDCDocument25 pagesPMBLDCYash DeoliaNo ratings yet
- DCMotors DesignGuideDocument12 pagesDCMotors DesignGuidenaruto256No ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet DC MotorDocument7 pagesPermanent Magnet DC MotorJesse Jones Seraspe100% (1)
- DC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Lec # 24 Universal MotorsDocument15 pagesLec # 24 Universal MotorsBuriro HayatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - DC Motor DrivesDocument61 pagesModule 2 - DC Motor DrivesMohammad Amirul ShafiqNo ratings yet
- PBL MotorDocument10 pagesPBL MotorAdam AriffNo ratings yet
- What Is A DC Motor?Document5 pagesWhat Is A DC Motor?Misael CabansagNo ratings yet
- BLDC MotorsDocument45 pagesBLDC Motorswicked_not_meNo ratings yet
- 4.1 DC Motor SpecificationDocument6 pages4.1 DC Motor SpecificationAsgher KhattakNo ratings yet
- Machine Tool DrivesDocument21 pagesMachine Tool DrivesChaitanyaSrivastava100% (1)
- DC and AC Motor ControlDocument6 pagesDC and AC Motor Controldes tosNo ratings yet
- What Is A Compound DC MotorDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Compound DC MotorIan Rafael DeGuzman ReyesNo ratings yet
- What Is DC MotorDocument38 pagesWhat Is DC Motoralvin dalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Types of MotorsDocument12 pagesTypes of MotorsMatin Inamdar100% (1)
- Universal Motor 28th Apr 2020Document5 pagesUniversal Motor 28th Apr 2020Sourav KumarNo ratings yet
- ECEL LAB#3 AngeladaDocument19 pagesECEL LAB#3 AngeladaAlehamarie AngeladaNo ratings yet
- Robotic Trolley For Material HandlingDocument46 pagesRobotic Trolley For Material HandlingSaggy ChhataniNo ratings yet
- PHILMOR ReportDocument3 pagesPHILMOR Reportpmor57409No ratings yet
- IDS NewDocument128 pagesIDS NewShahbaz Ali100% (1)
- BDLC MotorDocument8 pagesBDLC MotorArun VijayNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Brushless DC PDFDocument12 pagesConstruction and Working of Brushless DC PDFaswardi8756No ratings yet
- FLUX Brushless Motors FLUX Pumps CorpUSA BarreltafseogszkDocument2 pagesFLUX Brushless Motors FLUX Pumps CorpUSA Barreltafseogszkpolohouse8No ratings yet
- Machine DC MotorsDocument31 pagesMachine DC Motorsahtisham shahNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 6Document7 pagesAssignment # 6Jay Ey100% (1)
- DC Motors InformationDocument9 pagesDC Motors InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- BLDCDocument4 pagesBLDCmechtex Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Overhead CraneDocument45 pagesFabrication of Overhead CraneWORLD360No ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Robot Drive MechanisamDocument82 pagesUNIT-3 Robot Drive MechanisamChetuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102Document7 pagesElectrical Science-2: Term Paper of Ele102shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Types of Motor Motor TypesDocument17 pagesTypes of Motor Motor TypesGokulThalaNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- AC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAC Electric Motors Control: Advanced Design Techniques and ApplicationsFouad GiriNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingFrom EverandDynamometer: Theory and Application to Engine TestingNo ratings yet
- Conditions Required For ParallelingDocument1 pageConditions Required For ParallelingAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Faraday LawsDocument2 pagesFaraday LawsAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Phasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadDocument3 pagesPhasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Phasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadDocument3 pagesPhasor Diagrams For Transformer On LoadAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Losses in TransformerDocument2 pagesLosses in TransformerAdnan KhanNo ratings yet