Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Start by Patient Profile Position: Thyroid Lump Examination
Uploaded by
Mahmoud AbuAwad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views8 pagessurgery
Original Title
thyriod
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsurgery
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views8 pagesStart by Patient Profile Position: Thyroid Lump Examination
Uploaded by
Mahmoud AbuAwadsurgery
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
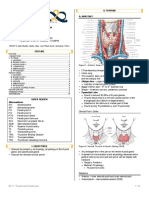
thyroid lump examination
Start by patient profile
Position : the patient is sitting & slightly hyper extending his neck
( if the patient were fatty then ask him to push his hands from behind against
his head ; pizillo's method )
Inspection :
1. size &shape of the lump
2. site : according to : 1- sternoclidiomastoid muscle / triangles
2- to midline: on one side both sides or in midline
3- suprasternal notch : if there is extension
3. surface : 1- smooth (nodular) >> multinodular goiter , simple
hyperplasic goiter
2-bosselated >> colloid goiter
4. skin over it : 1- redness , edema , tenderness >> inflammation
2- Scar >> previous thyroid surgery
3- Sinuses >> thyroglossal fistula with mucous discharge
4- Dilated veins >> the mass is obstructing thoracic inlet
5. pulsatility : inspect for seconds to check if its pulsatile & use your
hand at palpation
6. movement with swallowing ( deglutination ) : ask the patient to
swallow , movement indicate that lump is attached to pretracheal
fascia which is attached to thyroid cartilage
swellings that moves while swallowing :
1- thyroid & thyroglossal cyst
2- pretrachal lymph node
3- subhyoid bursa
4- extrinsic ca of larynx
if not moved and in anterior triangle :
1- lipoma
2- carotid body tumor
3- bracial cyst
4- lymph gland
7. movement with tongue protrusion : if +ve its thyroglossal cyst
ask the patient to protrude his tongue and look to the lump ; this
occurs because of cyst attachment to tongue by hyoid bone
palpation :
1. palpate for temperature & tenderness
2. palpate during swallowing & tongue protrusion : put your hand on the
midline then palpate
3. palpate thyroid gland ( normally not palpable )
4. asses borders , edges , consistency , surface
5. composition : 1- soft (cystic) : colloid goiter
2- solid : a- firm : multinodular goiter b- hard: ca thyroid
6. trachea : feel it over jugular notch if not palpable look for thyroid
cartilage deviation if else , look for retrosternal extension by palpation
during swallowing & by percussion later on
7. if the swelling involve the hole gland , one lobe or isthmus only
8. feel for thrill especially at upper lope : if +ve its primary toxic goiter
9. pinch the skin : looking for fixity of it to the swelling
10. carotid artery pulsation : against transverse process of C6 between
posterior border of thyroid and sternoclideomastoid muscle
*if the lump is on one side feel normal side pulsation then affected
side if the lump is benign it will push carotid but it still palpable , but if
its malignant it will be absent or week ( berrys +ve test )
11. lymph nodes : palpate looking for any enlargement
percussion :
over maniburum sterni : to asses lump extension . normally its resonant due
to trachea presence , but with lump extension + tracheal deviation it
becomes dull .
auscultation :
over swelling , especially over horns , for bruits which is diagnostic of primary
toxic goiter , because of increase in gland vascularity
Thyroid diseases
A- in general
By system Hyper thyroidism hypothyroidism
Metabolic -weight loss / thin
hands &face / increase
appetite
- looking hot / sweating
even in cold / likes cold
weather / dislike hot
weather
- Tiredness / weakness
/mental and physical
lethargy
-feels cold / likes hot
weather / dislikes cold
weather
- poor appetite &weight
gain
CVS -Palpitation / SOB with
exercise / extra-systoles
+AF ( irregular
irregularity ) /Tiredness
-bruies & thrills ( on
thyroid gland )
-Breathlessness
-ankle swelling
CNS & PNS -Nervousness
/irritability / insomnia /
depression / excitement
Hyper asthenia
- headaches
vertigo / hand &tounge
tremor
-Difficulty in thinking,
,speaking quickly&
clearly
-Hallucinations /
dementia & myxodema
madness ( myxodema
coma ; in sever cases )
GIT & GUS -Weight loss , incease
appetite / diarrhea
-Ammenoria or
reduction of menses in
females
-Weight gain , decrease
appetite / constipation
-Menorragia ( if
myxodema occurs
before menopause)
B- hands :
1- pulse ( tachycardia / AF / extrasystoles ; thyrotoxicoses , bradycardia
; hypothyroidism )
2- palms ( moist /sweaty; thyrotoxicoses , dry ; hypothyroidism )
3- tremor in hands and tongue ; thyrotoxicoses
4- hands thinar & hypothinar wasting ; thyrotoxicoses
C- eye
a- hypothyroidism : 1- eyes are normal
2- eye lids become swollen and heavy
3- hair of 1/3 out brow full down
b- Hyperthyroidism :
1- Lid retraction & led lag
2- Exophthalmia / difficulty in convergence / abscent forhead
wrinkling ( when looking upward )
3- Opthalmoplagia he cant look outward & upward ( superior rectus
&inferior oblique muscles are mostly involved )
4- chemoses
D- OTHERS :
1- Peritibial myxodema (red blochy raised skin over the shin ) in
hyperthyroidism
2- Wasted muscles & tip finger enlarged hyperthyroidism
3- Delayed deep tendon reflexes & horsiness of voice hypothyroidism
Important notes:
Borders of thyroid lumps : sternoclidiomastoid muscle >> lateral border
supraternal notch >> inferior border
location : according to lobe ( RT , LF , isthmus )
is the rest of the gland is palpaple or not
is it single or multiple
the isthmus is the only part which is normally palpable and it covers the 2
nd
,
3
rd
,4
th
tracheal rings
consistency :
1- cystic , soft ,smooth : ear lobule
2- rubbery : cheeks
3- hard , firm : nose
4- bony hard : frontal bone
old say : solid lumps are cystic __ cystic feels solid >>> in thyroid lumps
about thyroglossal cyst :
1- site : midline chin and 2
nd
tracheal ring either suprahyoid , subhyoid or
pretrachial
2- firm hard & maybe transilluminent .
3- if infected : red , tender and hot / if not : normal overlying skin
thyroid diseases notes :
in 1ry thyrotoxicoses CNS & eye signs are more important than CVS signs
although tachycardia is present .
in 2ry thyrotoxicoses CVS is the more prominent one .
lymph nodes to be examined are ( IF YOU FIND ENLARGMENT COMMENT ON
SITE, SIZE , CONSESTANCY , MOTILITY , TEMPRETURE & TENDERNESS ) :
A - head
1- occipital = base of skull
2- post auricular = over mastoid process
3- pre auricular = front of ear
4- parotid & tonsils = angle of mandible
5- submandibular = half way between angle & tip of mandible
6- submental
B- neck
1- superficial cervical = at SCM muscle
2- posterior cervical = anterior border of trapezius muscle
3- deep cervical = deep to SMC muscle
4- supraclavicular
- in tremor
a- hand : we extend elbow , wrist & separate fingers ; fine &fast tremor appears
by nicked eyes or paper on paitents hand
b- tongue : protrude for 30 seconds
eye signs of thyrotoxicoses " all of them may be unilateral or bilateral " :
1- eye led retraction " stare : by inspection , upper margin of cornea is not covered
by the eye led ( so the white upper sclera is exposed ) upper lid is higher than
normal ; occers due to over activity of the involuntary muscle part of lavetar
palpeprae superioris muscle
2- extra ocular muscle weakness , " opthalmoplagia " : presented as double vision ,
during H of eye muscles
3- lid lag , " von-graefe's sign " : immobility or lagging " dont keep pace with eyeball
movement " of upper eyelid on downward rotation movement of the eye , if
unilateral its called " pseudo-vongraefes"
4- exopthalmous " proptosis " : it is bulging of the eye anteriorly ( bulging out of the
orbit ) , seen by looking at the eyes from above , while being behind of the patient "
naffziger's sign
5- chemosis : edema of the conjunctiva , it appears at redness of the eyes & you may
find ulcers
diagnosis of neck swellings :
A- multiple lumps : lymph nodes
B- single lumps :
1- anterior triangle and moves with swallowing :
# solid :
a- thyroid gland
b- thyroid isthmus lymph node
# cystic :
Thyroglossal cyst " moves with tongue protruding "
2- anterior triangle without swallowing movement
#solid :
a- a lymph gland
b- carotid body tumor
# cystic :
a- cold abscess
b- brachial cyst
3- posterior triangle without swallowing movement :
#solid
A lymph gland
# cystic :
a- cystic hygroma
b- pharyngeal pouch
c- secondary deposit of papillary thyroid carcinoma
# pulsatile :
Subclavian aneurysm
Sings of retrosternal extension :
1- inspect upper chest for dilated veins , it become congested by thoracic inlet
occlusion by a mass
2- palpate trachea & suprasternal notch during swallowing
3- percussion of maniburuim sterni ; if dull its positive for extension
Look for horner's syndrome :
1- ptosis
2- construction pupil
3- exopthalmous
4- abscent alio-spinal reflex
5- anhydrosis " loss of sweeting on the affected side of the body "
Which occurs with : 1- retrosternal goiter
2- malignant goiter affecting " cervical sympathetic nerves "
Sings of metastasis :
1- lymph nodes movement " cervical LN "
2- hard nodule in the skull
3- long bone metastasis
4- nodular liver & ascites
5- chest effusion & consolidation
Investigations :
1- radioactive iodine 131
2- SERUM T3 , T4 , TSH
3- FNA /US / laryngoscope
You might also like
- Basic Anatomy of The NeckDocument79 pagesBasic Anatomy of The NeckAlyssa GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- OSCE / PEDITRICS Review NotesDocument38 pagesOSCE / PEDITRICS Review NotesEbn Seena71% (17)
- Pediatric Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument13 pagesPediatric Cervical LymphadenopathyShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesClinical ExaminationMavra zNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal CystsDocument4 pagesThyroglossal CystsCondurache Ilie-AndreiNo ratings yet
- Neck Lumps, (Cervical Masses) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNeck Lumps, (Cervical Masses) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Examination FiryaLDocument3 pagesThyroid Examination FiryaLFiryal Balushi100% (1)
- 11 - Part1.Neck MassesDocument51 pages11 - Part1.Neck MassesRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Medical Facts and Mcq's Pediatric Surgery MCQDocument34 pagesMedical Facts and Mcq's Pediatric Surgery MCQMohammed Kassim Abdul Jabbar100% (3)
- Pediatric Surgical Handbook PDFDocument139 pagesPediatric Surgical Handbook PDFNia LahidaNo ratings yet
- Wasting of Small Muscles of HandDocument38 pagesWasting of Small Muscles of HandSumit Khare75% (4)
- 05.11.02 Thyroid and ParathyroidDocument10 pages05.11.02 Thyroid and Parathyroidbo gum parkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Head Neck EMRCS MCQDocument23 pagesAnatomy Head Neck EMRCS MCQTowhid HasanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pediatrics MsMMaMDocument40 pagesClinical Pediatrics MsMMaMGoha Basha100% (3)
- Larynx Wrote by DR Nassem TalaatDocument38 pagesLarynx Wrote by DR Nassem TalaatAbouzr Mohammed ElsaidNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck TumorsDocument14 pagesHead and Neck TumorsBarda GulanNo ratings yet
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCarpal Tunnel Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- General Examination..Document6 pagesGeneral Examination..zaid100% (2)
- INGUINAL-SCROTAL SWELLINGS GUIDEDocument23 pagesINGUINAL-SCROTAL SWELLINGS GUIDEAzmyza Azmy100% (1)
- 8 PACES CasesDocument14 pages8 PACES CasesManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Indications and ContraindicationsDocument7 pagesIndications and ContraindicationsMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Indications and ContraindicationsDocument7 pagesIndications and ContraindicationsMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Post Op HXDocument3 pagesPost Op HXMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Post Op HXDocument3 pagesPost Op HXMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Best Pediatric Neck MassesDocument116 pagesBest Pediatric Neck MassesOmar PeterNo ratings yet
- CVS, GIS, and RS Exam SimplifiedDocument13 pagesCVS, GIS, and RS Exam SimplifiedMuhammad SyarmineNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Skin DiseasesDocument33 pagesEpidemiology of Skin DiseasesMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam Internal FINALDocument27 pagesPhysical Exam Internal FINALMohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid History and Physical Examination Key PointsDocument49 pagesThyroid History and Physical Examination Key PointsAbeer RadiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideDocument6 pagesThyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideKeen RunnerNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Status ExaminationDocument10 pagesThyroid Status ExaminationamilaNo ratings yet
- Medicine NeckDocument102 pagesMedicine NeckMukesh KhatiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid ExaminationDocument5 pagesThyroid Examinationjackfruit5887No ratings yet
- Thyroid Status ExaminationDocument5 pagesThyroid Status ExaminationCaliph IVNo ratings yet
- thyroidDocument11 pagesthyroideiuj497No ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminatiionDocument68 pagesClinical Examinatiionahmed mokhtarNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument107 pagesAbdominal Examinationaxmedfare138No ratings yet
- Thyroid Examination SchemeDocument3 pagesThyroid Examination SchemeUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical Principles of Patient: General SurgeryDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Principles of Patient: General SurgeryMohammed Yousif AbdualjabbarNo ratings yet
- Med Final Exam Hints: Cardio, Neuro, CVS CasesDocument6 pagesMed Final Exam Hints: Cardio, Neuro, CVS Casesmyolie wuNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Examination: by DR Ali Bel KheirDocument10 pagesNeonatal Examination: by DR Ali Bel KheirMohammed AlzergiNo ratings yet
- Sec 2Document44 pagesSec 2Mohamed SolimanNo ratings yet
- Respi DisorderDocument14 pagesRespi DisorderErika ArceoNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins-1Document39 pagesVaricose Veins-1Shruti KandulaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery Physical ExaminationDocument14 pagesGeneral Surgery Physical ExaminationDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument11 pagesAbdominal Examinationibra100% (1)
- HEALTH ASSESSMENT (Head & Neck)Document38 pagesHEALTH ASSESSMENT (Head & Neck)April Mae Magos Labrador100% (1)
- A2 Note Part1Document34 pagesA2 Note Part1Osama KilaniNo ratings yet
- Surg Osce SummaryDocument7 pagesSurg Osce SummaryShatha AlgahtaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Health AssessmentDocument10 pagesChapter 14 - Health Assessmentannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- Preskas Bedah IngDocument19 pagesPreskas Bedah Ingandriana wijayaNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Zain Eldein - Examination of Large RuminantDocument33 pagesMohamed Zain Eldein - Examination of Large RuminantYaserAbbasiNo ratings yet
- 4- Poor feedingDocument8 pages4- Poor feedingZeineddin EtkaidekNo ratings yet
- Surgery: 4 StageDocument73 pagesSurgery: 4 StageAnsares SultanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Chapter SummaryDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Chapter SummaryAmit Kiran RathNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Syatem: January 2009Document19 pagesRespiratory Syatem: January 2009aarti devNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument59 pagesAcute AbdomenMohamed MubarkNo ratings yet
- Basics Steps and Approach For PACESDocument5 pagesBasics Steps and Approach For PACESRebecca Teng Siew YanNo ratings yet
- Assessing The NeckDocument18 pagesAssessing The NecksrslytrdNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DseDocument14 pagesCongenital Heart DseJedzRNNo ratings yet
- Neurological Sheet: A. HistoryDocument18 pagesNeurological Sheet: A. HistorysivaNo ratings yet
- Case Write UpDocument9 pagesCase Write UpAsraf LatifNo ratings yet
- Historiaaaaa ClinicaaaaaaaaDocument7 pagesHistoriaaaaa Clinicaaaaaaaadavidvilla0104No ratings yet
- Branchial Anomalies: David Gleinser, MD Harold Pine, MDDocument51 pagesBranchial Anomalies: David Gleinser, MD Harold Pine, MDDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet
- Stagiaire's Guide To General Surgery OSCEsDocument36 pagesStagiaire's Guide To General Surgery OSCEsMawNo ratings yet
- Notes On Physical Examination of AbdomenDocument6 pagesNotes On Physical Examination of AbdomenMarwa Al-AzzawiNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideDocument20 pagesThyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideemmaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ExaminationDocument4 pagesAbdominal Examinationdileepa madurangaNo ratings yet
- Chest ExaminationDocument34 pagesChest Examinationwr48f26rjmNo ratings yet
- KURSK STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY CASE HISTORY MODELDocument9 pagesKURSK STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY CASE HISTORY MODELManushi HenadeeraNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument37 pagesCase PresentationRevan NasirNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics RemarksDocument62 pagesPediatrics RemarksGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- Mrcs-A Sep 2012 RecallDocument6 pagesMrcs-A Sep 2012 RecallMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Defeating Dementia - PathologyDocument7 pagesDefeating Dementia - PathologyMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Basic Surgical PrinciplesDocument2 pagesBasic Surgical PrinciplesMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Fluids - WMDocument10 pagesFluids - WMMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- BB-4 4Document59 pagesBB-4 4Mahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- 7+8 Abdominal ExaminationDocument43 pages7+8 Abdominal ExaminationMahmoud AbuAwad100% (1)
- Sche DualDocument3 pagesSche DualMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Physical ExamDocument53 pagesPhysical ExamMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Group B Seminars For 6th Year Medical StudentsDocument5 pagesGroup B Seminars For 6th Year Medical StudentsMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Daily Attendance Sheet for Surgery StudentsDocument2 pagesDaily Attendance Sheet for Surgery StudentsMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument48 pagesIntestinal ObstructionMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Sugery LecturesDocument2 pagesSugery LecturesMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- 7+8 Abdominal ExaminationDocument43 pages7+8 Abdominal ExaminationMahmoud AbuAwad100% (1)
- Sche DualDocument3 pagesSche DualMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument15 pagesIntestinal ObstructionMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument11 pagesAcute AppendicitisMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument1 pageNotesMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- 7+8 Abdominal ExaminationDocument43 pages7+8 Abdominal ExaminationMahmoud AbuAwad100% (1)
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1Mahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Exams SchedualDocument1 pageExams SchedualMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Gall Bladder DiseaseDocument15 pagesGall Bladder DiseaseMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Atls Initial Management: Dr. Khalid Abdulwahid CABS, FRCS (England) Al Bashir Teaching HospitalDocument21 pagesAtls Initial Management: Dr. Khalid Abdulwahid CABS, FRCS (England) Al Bashir Teaching HospitalMahmoud AbuAwadNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentDocument7 pagesThyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentTasia RozakiahNo ratings yet
- MrcsDocument7 pagesMrcskelly_ann23100% (1)
- Thyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideDocument20 pagesThyroid Status Examination OSCE GuideemmaNo ratings yet
- Revision - of - Surgery - by - Medad - Team سؤال و اجابه و حالات محلولهDocument45 pagesRevision - of - Surgery - by - Medad - Team سؤال و اجابه و حالات محلولهRehab EL NahasNo ratings yet
- Case Sudy:: Thyroglossal Duct CystDocument21 pagesCase Sudy:: Thyroglossal Duct CystHope SerquiñaNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst StudyDocument7 pagesThyroglossal Duct Cyst StudyAurel OctavianNo ratings yet
- First Aid Q&A EmbryologyDocument13 pagesFirst Aid Q&A EmbryologyzyadNo ratings yet
- Pre Exam Surgical Notes 2Document166 pagesPre Exam Surgical Notes 2flor vickyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Soft Tissue Lesions: Andres Pinto, DMDDocument18 pagesPediatric Soft Tissue Lesions: Andres Pinto, DMDHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- Cba Ospe RevisedDocument11 pagesCba Ospe RevisedSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- Cysts of the Neck: Identification and TreatmentDocument4 pagesCysts of the Neck: Identification and TreatmentgimamrNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of A Neck Mass - UpToDate PDFDocument16 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of A Neck Mass - UpToDate PDFDr.Anurag FursuleNo ratings yet
- Kita Duktus TiroglosusDocument5 pagesKita Duktus TiroglosusbarbiemeNo ratings yet
- Final CP ThyroidDocument31 pagesFinal CP ThyroidSovitJungBaralNo ratings yet
- 2 - Endocrine Assessment 2023Document5 pages2 - Endocrine Assessment 2023Mohned AlhababiNo ratings yet
- Key points on fluid and electrolyte management, preoperative preparations, and common postoperative complicationsDocument176 pagesKey points on fluid and electrolyte management, preoperative preparations, and common postoperative complicationsAdams AdamNo ratings yet
- Kongenitalne Ciste I Fistule VrataDocument2 pagesKongenitalne Ciste I Fistule VrataRoppeNo ratings yet
- The Sistrunk ProcedureDocument4 pagesThe Sistrunk ProcedureDrTarek Mahmoud Abo Kammer100% (1)
- Neck MassDocument13 pagesNeck MassY3153NSNo ratings yet
- General Surgery Two-1Document3 pagesGeneral Surgery Two-1Abhishek NaikNo ratings yet