Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkene and Alcohol Reactions Overview
Uploaded by
Phirun ChengOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkene and Alcohol Reactions Overview
Uploaded by
Phirun ChengCopyright:
Available Formats
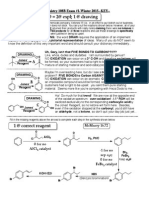
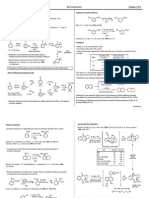
Alkene Rxns
1
Hydrohalogenation
Hydration
Hydration
(with rearrangement)
Addition of Alcohol
Bromination
Bromination in H
2
O
Bromination in Alcohol
Oxymercuration-
Demurcuration
Alkoxymercuration-
Demurcuration
Hydroboration-
Oxidation
Catalytic Hydrogenation
(Catalytic Reduction)
Hydrobromination with
Peroxide
Epoxidation
Anti-Hydroxylation
Syn-Hydroxylation
Syn-Hydroxylation
Ozonolysis under
Reducing Conditions
Ozonolysis under
Oxidizing Conditions
Oxidative Cleavage
Free Radical Halogenation
Free Radical Bromination
(high selectivity)
Free Radical Chlorination
(low selectivity)
Allylic/Benzylic Bromination
Grignard Rxns
Nucleophilic Addition of a
Grignard Reagent to a Ketone
Nucleophilic Addition of a
Grignard Reagent to an Epoxide
(attacks less substituted side)
Nucleophilic Addition of a
Grignard Reagent to CO
2
Protonation of a Grignard
Reagent
(Grignards are protonated in
protic solutions)
2
Alkyne Rxns
Catalytic Hydrogenation
(Catalytic Reduction)
Reduction to cis-alkene
Reduction to trans-alkene
Hydrohalogenation
Hydration of an Internal Alkyne
Hydration (Markovnikov)
Hydration (Anti-Markovnikov)
S
N
2 Addition of an Acetylide
Ion
Addition of an Acetylide Ion to
a Ketone
NaNH
2
O
1.
2. H
2
O
HO
Addition of an Acetylide Ion to
an Epoxide
3
Benzene Rxns
4
Nitration (EAS)
Sulfonation (EAS)
Chlorination (EAS)
Bromination (EAS)
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (EAS)
Cl
AlCl
3
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation (EAS)
(with rearrangement)
Friedel-Crafts Acylation (EAS)
Bromination (EAS)
-NH
2
is an ortho/para director
and doesnt require a catalyst
like FeBr
3
Chlorination (EAS)
-OH is an ortho/para director
OH
OH OH
Cl
Cl
Cl
2
AlCl
3
+
Chlorination (EAS)
-OR is an ortho/para director
Chlorination (EAS)
-CH
3
is an ortho/para director
Chlorination (EAS)
-Br is an ortho/para director
Chlorination (EAS)
Carbonyl is a meta director
Chlorination (EAS)
-NO
2
is a meta director
NO
2
NO
2
Cl
Cl
2
AlCl
3
Chlorination (EAS)
-CN is a meta director
Chlorination (EAS)
-SO
3
H is a meta director
Chlorination (EAS)
-CF
3
is a meta director
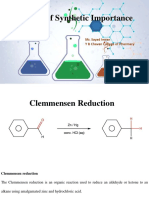
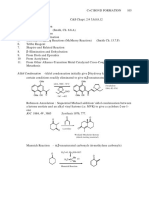
Clemmensen Reduction
O
Zn (Hg)
HCl
Wolff-Kishner Reduction
Side-chain Oxidation
(Benzylic Oxidation)
Side-chain Oxidation
(Benzylic Oxidation)
5
Alcohol Rxns
Conversion to an alkyl iodide
Conversion to an alkyl bromide
Conversion to an alkyl chloride
Conversion to an alkyl chloride
with thionyl chloride
(only for 1 and 2)
Conversion to an alkyl bromide
(only for 1 and 2)
Conversion to a tosylate ester
Acid-catalyzed Dehydration
Chromic Acid Oxidation of a 1
Alcohol (Chromic Acid can also
be written as H
2
CrO
4
or
CrO
3
/H
2
SO
4
)
PCC Oxidation of a 1 Alcohol
Chromic Acid Oxidation of an
Aldehyde
Chromic Acid Oxidation of a 2
Alcohol
PCC Oxidation of a 2 Alcohol
Ether Rxns
Williamson Ether Synthesis
(2
nd
step is S
N
2)
Acid-Catalyzed cleavage of
Ethers
(also works with HI and HCl)
Epoxide Rxns
6
Base-Catalyzed Ring Opening
of an Epoxide
(Attacks less-substituted side)
Acid-Catalyzed Ring Opening
of an Epoxide
(Attacks more-substituted side)
Hydride Reduction Rxns
Reduction of a ketone to a 2
alcohol
Reduction of a aldehyde to a 1
alcohol
Reduction of an acid chloride to
a 1 alcohol
Cl
O
OH
1. LiAlH
4
2. H
3
O
+
Reduction of an ester to two
alcohols
Reduction of a carboxylic acid
to a 1 alcohol
Reduction of an amide to an
amine
Reduction of an ester to an
aldehyde using DIBALH (also
called DIBAH)
DIBALH is diisobutylaluminum
hydride (shown below)
Reduction of an acid chloride to
an aldehyde using tri-t-
butoxyaluminum hydride
Hoffman Rearrangment
Converts an amide to an amine
with the loss of a carbon
(note the difference with
reduction of an amide with
LiAlH
4
where there is no loss of
carbon)
7
Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives (Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
Diels-Alder Rxns
Basic Diels-Alder Rxn
(a 4+2 cycloaddition rxn)
8
Nucleophilic Addition to Ketones and Aldehydes
Addition of water to form a
hydrate
Addition of an alcohol under
basic conditions to form a hemi-
ketal
Addition of 1eq of an alcohol in
acid to form a hemi-ketal and
then a 2
nd
eq to form a ketal
Addition of ethylene glycol to
from a cyclic ketal which
functions as a protecting group
for ketones and aldehydes
H
3
O
+
is used to de-protect
Addition of a 1 amine to form
an imine
(can be reversed with H
3
O
+
)
O
H
+
N
RNH
2
R
H
2
O
H
3
O
+
Addition of a 2 amine to form
an enamine
Forms on less substituted side if
theres a difference
(can be reversed with H
3
O
+
)
O
H
+
N
R
2
NH
R
H
2
O
H
3
O
+
R
9
Wittig Rxn
Addition of a phosphylide to
form an alkene
Formation of a phosphoylide
from an alkyl halide
O
PPh
3
R
2
R
1
R
1
R
2
PPh
3
R
2
R
1
Br
R
2
R
1
PPh
3
PPh
3
R
2
R
1
BuLi
acts as a base
Michael Addition
(also called -addition or
conjugate addition)
Michael Addition with a
lithium dialkylcuprate
O
(CH
3
)
2
CuLi
H
2
O
O
CH
3
10
Alpha Addition Rxns
Self Aldol Condensation
Mixed Aldol Condensation
O
O
H
H
O
H
O
OH
OH
-
Self Claisen Condensation
Mixed Claisen Condensation O
O
OEt
1. LDA
2.
3. H
2
O
O O
Malonic Ester Synthesis
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
EtO
O O
EtO
O O
O 1. NaOEt
2.
Br
3. NaOEt
4.
Br
H
3
O
+
CO
2
11
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry All ReactionsDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry All ReactionsWaseem Alkakoz100% (4)
- Reagent and The Reactions They CauseDocument3 pagesReagent and The Reactions They CauseChip Timmons100% (8)
- Undergraduate organic reactions summaryDocument41 pagesUndergraduate organic reactions summaryKathyNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesVersiform89% (9)
- Organic Chemistry II Reactions SummaryDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II Reactions SummaryRicky Fontaine100% (9)
- Go Diane you can do itDocument3 pagesGo Diane you can do itDiane Malaso80% (10)
- Summary of Organic ReactionsDocument6 pagesSummary of Organic ReactionsAbudi Alsagoff100% (5)
- Summary of All Reactions For Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesSummary of All Reactions For Organic Chemistryfoodytang91% (23)
- Organic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFcztinu88% (50)
- Cheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet For Organic Chemistry Midterm 1 2015 - 1Norma Leticia Ramos33% (3)
- Organic Reactions Summary SheetDocument2 pagesOrganic Reactions Summary Sheetthacheee64% (11)
- Organic Chemistry IDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Iscribblerofnonsense80% (5)
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Document1 pageOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet For Midterm2015Norma Leticia Ramos100% (5)
- Chemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction SchemeDocument19 pagesChemistry - Organic Chemistry Reaction Schemehelixate94% (16)
- Organic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsDocument120 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsLoveena Steadman100% (8)
- Problems in Organic ChemistryDocument408 pagesProblems in Organic ChemistryGowri Shankar100% (11)
- Chem 108 Exam 2 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChem 108 Exam 2 Cheat SheetStarrx714100% (2)
- 86 Tricks To Ace Organic ChemistryDocument164 pages86 Tricks To Ace Organic Chemistryjinzo8892% (12)
- Organic ChemistryDocument334 pagesOrganic ChemistryCristiano Hamdiansyah Sempadian100% (16)
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- Organic Chemistry Reactions BookDocument56 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reactions BookKeith Philippe100% (10)
- Chemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistry - Overview of Aliphatic Organic Chemistryhelixate100% (5)
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms - A Step by Step Approach, Second EditionDocument517 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms - A Step by Step Approach, Second Editionmehrdad63100% (8)
- Chemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003Document717 pagesChemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003ramik100% (23)
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument15 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundsapi-1986055092% (24)
- Organic Chemistry Question BankDocument92 pagesOrganic Chemistry Question BankGpg Subhash100% (7)
- Organic Chem Midterm 1 Multi+keyDocument1 pageOrganic Chem Midterm 1 Multi+keyNorma Leticia RamosNo ratings yet
- Stereochem Test BankDocument19 pagesStereochem Test BankCarmela Liria100% (15)
- Stereochemistry Basic Concepts, Useful Notes For StudentsDocument26 pagesStereochemistry Basic Concepts, Useful Notes For StudentsATUL R BENDALE89% (45)
- General Chemistry Reference Sheet GuideDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reference Sheet Guidedadadabababa100% (8)
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Stereochemistry: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandStereochemistry: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Syntheses Based on Name Reactions: A Practical Guide to Over 800 TransformationsFrom EverandOrganic Syntheses Based on Name Reactions: A Practical Guide to Over 800 TransformationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Organic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Concepts and Applications for Medicinal ChemistryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Student's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzFrom EverandStudent's Solutions Manual to Accompany Organic Chemistry: Organic Chemistry by Weininger and StermitzRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (12)
- Experimental Organic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualFrom EverandExperimental Organic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Nomenclature and Chemistry of Three to Five Membered HeterocyclesFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Heterocycles: Nomenclature and Chemistry of Three to Five Membered HeterocyclesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Enantioselective Chemical Synthesis: Methods, Logic, and PracticeFrom EverandEnantioselective Chemical Synthesis: Methods, Logic, and PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Introduction to Co-Ordination Chemistry: International Series of Monographs in Inorganic ChemistryFrom EverandAn Introduction to Co-Ordination Chemistry: International Series of Monographs in Inorganic ChemistryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Pericyclic Reactions: A Mechanistic and Problem-Solving ApproachFrom EverandPericyclic Reactions: A Mechanistic and Problem-Solving ApproachRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- The Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: Applications in Everyday LifeFrom EverandAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry: Applications in Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Update your DMV address onlineDocument1 pageUpdate your DMV address onlinePhirun ChengNo ratings yet
- DMV 14Document1 pageDMV 14aloknsinghNo ratings yet
- DMV 14Document1 pageDMV 14aloknsinghNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear Structure and Periodic TrendsDocument15 pagesAtomic and Nuclear Structure and Periodic TrendsPhirun ChengNo ratings yet
- Pooh Search WordDocument1 pagePooh Search WordPhirun ChengNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Organic Compounds Containing HalogensDocument3 pagesRevision Notes On Organic Compounds Containing HalogensSUSHMANo ratings yet
- Name Reactions - Chemistrypage PDFDocument12 pagesName Reactions - Chemistrypage PDFManojNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalidesDocument46 pagesAlkyl HalidesIndahNo ratings yet
- 12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFDocument13 pages12 Pericyclic Rxns 2 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Rules For Organic Chemical ConversionsDocument4 pagesRules For Organic Chemical ConversionsKamran Maqsood78% (9)
- Nitration of Methyl Benzoate: Cooch Cooh CH OH H SODocument29 pagesNitration of Methyl Benzoate: Cooch Cooh CH OH H SOsyedmuhammadtariqueNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument1 pageGujarat Technological UniversityShubham KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: SN1 and SN2 ReactionsDocument29 pagesOrganic Chemistry: SN1 and SN2 ReactionsSUBHAM SAGARNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PortalDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry PortalULFA TUFFAHATINo ratings yet
- Reaction Road MapDocument2 pagesReaction Road MapBenedick Jayson MartiNo ratings yet
- Alkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewDocument11 pagesAlkene and Alcohol Reactions OverviewPhirun Cheng97% (29)
- Name Reaction 3569Document38 pagesName Reaction 3569Ashish AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution DPPDocument35 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution DPPAsif Hoda0% (1)
- Substitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument71 pagesSubstitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDaniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- 14-Pericyclic Rxns 4 HarvardDocument12 pages14-Pericyclic Rxns 4 HarvardLinda RubioNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions-McqDocument3 pagesElimination Reactions-Mcqirudayajyothi67% (3)
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution PDFDocument5 pagesNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution PDFKaz TongNo ratings yet
- Chem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSDocument1 pageChem 345 - Organic Reactions Chapter 17: Prepared by José Laboy, MSsridhar ramanaNo ratings yet
- Leaving Group Ability and Factors That Impact ItDocument7 pagesLeaving Group Ability and Factors That Impact ItSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonDocument46 pagesNucleophilic Substitution at Saturated CarbonAhmed AtefNo ratings yet
- Dehalogenation Process OverviewDocument26 pagesDehalogenation Process Overviewvnikhar123100% (1)
- Homework Assignments Chapter-6: Alkyl Halides-Substitution and Elimination ReactionsDocument14 pagesHomework Assignments Chapter-6: Alkyl Halides-Substitution and Elimination ReactionsandrewNo ratings yet
- DPP 02 - Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - pdf-11Document7 pagesDPP 02 - Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - pdf-11JeetNo ratings yet
- The Stork Synthesis ofDocument2 pagesThe Stork Synthesis ofChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chem 215 Myers: Birch ReductionDocument7 pagesChem 215 Myers: Birch ReductionPrasanna AndojuNo ratings yet
- Bamberger RearrangementDocument2 pagesBamberger RearrangementJohn EspiqueNo ratings yet
- Chemistry III (Organic) : An Introduction To Reaction Stereoelectronics LECTURE 5 Neighbouring Group ParticipationDocument12 pagesChemistry III (Organic) : An Introduction To Reaction Stereoelectronics LECTURE 5 Neighbouring Group ParticipationSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions and MechanismDocument51 pagesOrganic Reactions and MechanismAbhay Kumar Nayak75% (8)
- C=C Bond Formation Reaction OverviewDocument12 pagesC=C Bond Formation Reaction Overviewaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet