Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Types of Tissue
Uploaded by
JamesMarcoM100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
250 views6 pagesTissue's function, location and features.
Original Title
Different types of tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTissue's function, location and features.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
250 views6 pagesDifferent Types of Tissue
Uploaded by
JamesMarcoMTissue's function, location and features.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
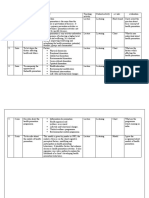
Simple Squamous Epithelial
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
DESCRITION: Single layer of flattened cells with disc
shape central nuclei
FUNCTION: Filtration and Diffusion
LOCATION: Nasal Cavity, Skin, and Lungs
Simple Cuboidal epithelium (x/s Human kidney)
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of cube like cells with large
spherical central nuclei
FUNCTION: Secretion
LOCATION: Thyroid gland, Kidney, and Ovaries
Simple Columnar ciliated epithelium (x/s Large intestine)
SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Single layer of tall cells with oval nuclei;
some cells bear cilia; some cells bear goblet cells
FUNCTION: Absorption
LOCATION: Gastrointestinal tract and Stomach
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Single layer cell of different height;
nuclei seen at different levels; may contain goblet cells
and bear cilia
FUNCTION: Secretion, particularly mucus
LOCATION: Trachea
Stratified Keratinized Squamous Epithelium (Skin)
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Composed of several cells layer; basal
cells are cuboidal and columnar; surface cells are
flattened (squamous)
FUNCTION: Protection
LOCATION: Esophagus
Statified non-keratinized squamous epithelium (Esophagus)
STRATIFED CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Generally two layers of cube like cells
FUNCTION: Protection
LOCATION: Sweat glands and Salivary glands
STRATIFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Several cell layers; basal cells usually
cuboidal; superficial cells elongated and columnar
FUNCTION: Protection and Secretion
LOCATION: Male Urethra
Transitional Epithelium TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM
DESCRIPTION: Resembles both stratified squamous
and stratified cuboidal; basal cells cuboidal and
columnar; surface cells dome shape or squamous like
FUNCTION: Stretches readily and permits distension of
urinary organ
LOCATION: Urinary bladder and Urethra
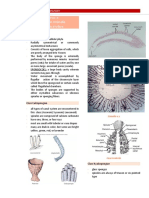
Areolar Connective Tissue
AREOLAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE (LOOSE)
DESCRIPTION: Gel like matrix with all three fiber
types: fibroblast, mast cell and macro phalanges
FUNCTION: Wraps and cushions
LOCATION:
Adipose Tissue (adipocyte circle with dot)
ADIPOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE (LOOSE)
DESCRIPTION: Closely packed adipocytes, or fat cells;
have nucleus pushed to the side by large fat droplet
FUNCTION: Provides reserve food fuel
LOCATION: Under the skin and Breast
Reticular Tissue
RETICULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE (LOOSE)
DESCRIPTION: Network of reticular fibers in a typical
loose ground substance
FUNCTION: Supports other cells
LOCATION: Spleen and bone marrow
Tendon dense-regular
DENSE REGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE (DENSE)
DESCRIPTION: Primarily parallel collagen fibers; major
cell type is the fibroblast
FUNCTION: Attaches muscles to the bone
LOCATION: Tendons
DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE (DENSE)
DESCRIPTION: Primarily irregularly arranged collagen
fibers; major cell type is the fibroblast
FUNCTION: Provides structural strength
LOCATION: Fibrous capsules
ELASTIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE (DENSE)
DESCRIPTION:
FUNCTION:
LOCATION:
Hyaline Cartilage
HYALINE CARTILAGE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Amorphous but firm matrix collagen
fibers form an imperceptible network
FUNCTION: Support and reinforce
LOCATION: Cartilages of the Nose, Trachea and Larynx
Fibrocartilage
FIBROCARTILAGE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Matrix similar to but less firm than in
hyaline cartilage; thick collagen fibers predominate
FUNCTION: Absorb comprehensive shock
LOCATION: Knee joint and intervetebral discs
Elastic Cartilage
ELASTIC CARTILAGE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Similar to hyaline cartilage but more
elastic fibers in matrix
FUNCTION: Maintains shape and flexibility
LOCATION: Ear - Pinna
BONE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Hard, calcified matrix containing many
collagen fibers; osteocytes lie in the lacuna
FUNCTION: Support and Protection
LOCATION: Bone
Cross section of spinal cord; focused: monopolar neuron
Cross section of spinal cord; focused:multipolar neuron and
bipolar neuron
Cross section of the spinal cord
BLOOD TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Red and white blood cells in a fluid
matrix (plasma)
FUNCTION: Transport
LOCATION: Blood Vessel
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Long cylindrical, multinucleated cell;
obvious striations
FUNCTION: Voluntary movement
LOCATION: Skeletal muscle attached to the skin
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Branching, striated and uninucleated
cells that integrated at specialized junction
FUNCTION: Propels blood
LOCATION: Walls of the heart
Smooth Muscle Tissue
SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Spindle shape cells with central nuclei;
no striations; cells are arranged closely to form a sheet
FUNCTION: Voluntary movement
LOCATION: Hollow walls of organs
Striated Muscle Tissue
STRIATED MUSCLE TISSUE
Cross section of the Nerve NERVOUS TISSUE
DESCRIPTION: Neurons are branching cells; Cell body
with quite long neuron processes
FUNCTION: Transmit electrical signals
LOCATION: Brain, Spinal Cord, and nerves
NODES OF RANVIER
You might also like
- Anatomy of Human EyeDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Human EyeCarly MelachioNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Document5 pagesUnit Plan B.Sc. (Nursing) I Year Nutrition (Proteins)Abhilasha SolomonNo ratings yet
- Final Review of LiteratureDocument25 pagesFinal Review of LiteratureNilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- 1 Year B.SC Nursing Psychology (QP - Code-1758) Question Bank Unit - I: IntroductionDocument9 pages1 Year B.SC Nursing Psychology (QP - Code-1758) Question Bank Unit - I: IntroductionShri Nidhi100% (1)
- Jabalpur (M.P.) : Subject - Management Nursing Assignment ONDocument9 pagesJabalpur (M.P.) : Subject - Management Nursing Assignment ONNikkiNo ratings yet
- Mental Health IntroDocument11 pagesMental Health IntroAnonymous 0C4OZmRNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Phsiology PDFDocument8 pagesAnatomy Phsiology PDFRitika TandonNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Pranayama On Stress Among The BSC - Nursing 1st Year Students in Selected Nursing Colleges of Jabalpur CityDocument6 pagesA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Pranayama On Stress Among The BSC - Nursing 1st Year Students in Selected Nursing Colleges of Jabalpur CityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument41 pagesSyllabusPradeep BossNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plane On Health Promotion.Document6 pagesLesson Plane On Health Promotion.Topeshwar TpkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Human AnatomyDavid HamalalaNo ratings yet
- Applied AnatomyDocument7 pagesApplied AnatomySridevi DevarajNo ratings yet
- Foundation First Sem TheoryDocument6 pagesFoundation First Sem TheoryNandita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Report of Anp Icu PostingDocument5 pagesReport of Anp Icu PostingsimonjosanNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument9 pagesBody TissuesBlaine RogalskiNo ratings yet
- Martha RogersDocument6 pagesMartha RogersPewDiePie JuniorNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Respiration 2018Document48 pagesMechanism of Respiration 2018MomentaNo ratings yet
- Neuman's Taxonomy PDFDocument12 pagesNeuman's Taxonomy PDFHafizh MulyaNo ratings yet
- Seasonal Changes of FoodDocument47 pagesSeasonal Changes of FoodalkaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Research Process by Kamini Chaudhary56788Document9 pagesAssignment On Research Process by Kamini Chaudhary56788kamini ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pathology: Sunilkumar.P Haematology & Transfusion Medicine ST - John's Medical College Hospital BangaloreDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Pathology: Sunilkumar.P Haematology & Transfusion Medicine ST - John's Medical College Hospital BangalorefahdabdNo ratings yet
- 1st Year BSC Master RotationDocument5 pages1st Year BSC Master RotationbijoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CounsellingDocument26 pagesIntroduction To CounsellingSufanah Sabr100% (1)
- Introduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToAesthethic finds100% (1)
- 2 5 17 991Document6 pages2 5 17 991Science JournalNo ratings yet
- Lab DetailsDocument12 pagesLab DetailssangeetachatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Early Clinical Exposure (Ece)Document30 pagesEarly Clinical Exposure (Ece)sandeepNo ratings yet
- Lab ParticularsDocument57 pagesLab ParticularssaranyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document19 pagesChapter - 1Precilla C. StephenNo ratings yet
- A Study of Assessment Menopausal Symptoms and Coping Strategies Among Middle Age Women of North Central IndiaDocument8 pagesA Study of Assessment Menopausal Symptoms and Coping Strategies Among Middle Age Women of North Central Indiaanil agarwalNo ratings yet
- Important Health Days: S.N. Month Date Observed AsDocument1 pageImportant Health Days: S.N. Month Date Observed AsSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Course Plan Post BasicDocument30 pagesCourse Plan Post Basicsumitgupta2391No ratings yet
- Vmscon MRPDocument6 pagesVmscon MRPSrijana GurungNo ratings yet
- BSC & PB BSC - New FormatDocument24 pagesBSC & PB BSC - New FormatNiranjan RajNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology LESSON PLANDocument9 pagesPathophysiology LESSON PLANLokesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Planning PBBSC Second Year Mental Health NursingDocument8 pagesCurriculum Planning PBBSC Second Year Mental Health NursingSAGAR ADHAONo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Comulative - Record - Basic - BSC - NSG - 271210Document3 pagesTopic 11 Comulative - Record - Basic - BSC - NSG - 271210Simran JosanNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (Cabg) :: Case Study ReportDocument83 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Grafting (Cabg) :: Case Study ReportSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Polysiphonia: Powerpoint Templates Powerpoint TemplatesDocument19 pagesPolysiphonia: Powerpoint Templates Powerpoint TemplatesA SASIKALANo ratings yet
- Nursing Manikins As Per IncDocument54 pagesNursing Manikins As Per IncRahul KashyapNo ratings yet
- Indian Health Care System-Weaknesses, Schemes and The Way AheadDocument16 pagesIndian Health Care System-Weaknesses, Schemes and The Way AheadGaurav Prabhaker0% (1)
- What Is Human Body Tissue PDFDocument3 pagesWhat Is Human Body Tissue PDFEng Abdulahi Haji100% (1)
- Introduction To Health and WellnesDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Health and WellnesZgama Abdulrahman100% (1)
- MSC Nursing SyllabusDocument196 pagesMSC Nursing SyllabusShivani100% (2)
- Skeleton MusclesDocument68 pagesSkeleton MusclesMuhammad AFiq Abd RashidNo ratings yet
- IJPHRD February - 2020 PDFDocument2,663 pagesIJPHRD February - 2020 PDFzaenab anissaNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Q.P. CODE: 2601Document1 pageRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Karnataka: Q.P. CODE: 2601VISHNU RAJ VNo ratings yet
- 3Document232 pages3Dipeshwari ThakreNo ratings yet
- Syllab Abus and Regulations NS: P Post Basic B.Sc. NursingDocument4 pagesSyllab Abus and Regulations NS: P Post Basic B.Sc. NursingmuthukumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology No.1Document38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology No.1Ken Marco SalipsipNo ratings yet
- Chetan CV ForDocument3 pagesChetan CV ForchetankumarbhumireddyNo ratings yet
- Borrowed Theories Used by NursesDocument24 pagesBorrowed Theories Used by Nursesmelaipwu0% (1)
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument21 pagesMedical Surgical NursingSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- Affiliation PDFDocument13 pagesAffiliation PDFAdnan SyedNo ratings yet
- Nursing Foundation Word FileDocument12 pagesNursing Foundation Word FileDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- M.SC Nursing RequirementsDocument3 pagesM.SC Nursing RequirementsSDx Sujay Daliya100% (1)
- Orientation To Student Placements: Needs and Benefits: EducationDocument3 pagesOrientation To Student Placements: Needs and Benefits: EducationthomasNo ratings yet
- Infection and Infectious ProcessDocument44 pagesInfection and Infectious Processpandey omkarNo ratings yet
- Tissue TableDocument4 pagesTissue TableMarcie BooneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Document53 pagesLesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Dump Acc 2No ratings yet
- Socio AntroDocument4 pagesSocio AntroJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Karyotyping Activity: Patient A's KaryotypeDocument2 pagesKaryotyping Activity: Patient A's KaryotypeJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- University of Santo TomasDocument2 pagesUniversity of Santo TomasJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- American History XDocument1 pageAmerican History XJamesMarcoM100% (1)
- Specific Heat of MetalsDocument1 pageSpecific Heat of MetalsJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- By Angela Manalang-Gloria: Original: To The Man I MarriedDocument4 pagesBy Angela Manalang-Gloria: Original: To The Man I MarriedJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Approaches in Studying LiteratureDocument21 pagesApproaches in Studying LiteratureJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Opening RemarksDocument1 pageOpening RemarksJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Kinematics UstDocument67 pagesKinematics UstJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Christian MoralityDocument41 pagesChristian MoralityJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- Physiology and Anatomy ApparatusDocument4 pagesPhysiology and Anatomy ApparatusJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- MaterialismDocument31 pagesMaterialismJamesMarcoM100% (1)
- KS4 The Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument49 pagesKS4 The Heart and Circulatory SystemjtNo ratings yet
- Body Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleDocument2 pagesBody Map: Smooth or Visceral MuscleFani Try Utami BoedaxRed'waterzzNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Text 1Document9 pagesBahasa Inggris: Text 1Josua SitumeangNo ratings yet
- Nnewfile 2Document2 pagesNnewfile 2mahariyaNo ratings yet
- 319 ReptilesDocument121 pages319 ReptilesJihan NurainiNo ratings yet
- Sociality - WikipediaDocument10 pagesSociality - WikipediaRobxn GrciaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Chart With Pictures Answers-Option ADocument3 pagesHuman Body Systems Chart With Pictures Answers-Option AJamie Sims100% (2)
- Marine Test On Reptiles and Birds3Document3 pagesMarine Test On Reptiles and Birds3Mavel Madih KumchuNo ratings yet
- Evolution Essay 1Document3 pagesEvolution Essay 1api-251804834No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue NotesDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissue NotesJustine May S. ColicoNo ratings yet
- Fake Research of Haruko ObokataDocument1 pageFake Research of Haruko ObokataNaeem YounisNo ratings yet
- Bot 307 Comparative Plant Anatomy 1Document62 pagesBot 307 Comparative Plant Anatomy 1Kennedy Samuel BanjaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Qs - Part #2 M.TawalbehDocument15 pagesImmunology Qs - Part #2 M.TawalbehMohamed Tawalbe100% (6)
- Learning Objectives - Embryology Lecture 2Document3 pagesLearning Objectives - Embryology Lecture 2kep1313No ratings yet
- Butterfly PDFDocument3 pagesButterfly PDFAmarjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 - Tissues and Herbaceous Stems PrelabDocument16 pagesExercise 4 - Tissues and Herbaceous Stems Prelab施美拉No ratings yet
- Biology of AmphibiansDocument621 pagesBiology of AmphibiansRAILANo ratings yet
- Class 9 ICSE SKIN Jack of All TradesDocument4 pagesClass 9 ICSE SKIN Jack of All TradesArpan Kaur100% (1)
- Discussion Details: Module 3 TopicDocument13 pagesDiscussion Details: Module 3 TopicMatttNo ratings yet
- Lecture Guide: Consciousness, Sleep Patterns & Sleep TheoriesDocument2 pagesLecture Guide: Consciousness, Sleep Patterns & Sleep Theoriesapi-300762638No ratings yet
- BAI Registered Poultry Farms As of August 31 2021Document43 pagesBAI Registered Poultry Farms As of August 31 2021Caren Ss123No ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument5 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyNeha ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Document33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- Kingdom Animalia Phylum Profera: Systematics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesKingdom Animalia Phylum Profera: Systematics LaboratorySIlverNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Dogs and CatsDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast Dogs and CatsReine AmashaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument41 pagesMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaNo ratings yet
- Rory Cinta Naya (Respiratory System)Document2 pagesRory Cinta Naya (Respiratory System)Rory Cinta NayaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Frog DissectionDocument12 pagesLab 1 - Frog DissectionCherry Ann MacalmaNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development of ChickenDocument33 pagesEmbryonic Development of ChickenArsh RizviNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - 4Document71 pagesEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.No ratings yet