Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SISTEM_INFORMASI_DASAR
Uploaded by
Dedy KurniawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SISTEM_INFORMASI_DASAR
Uploaded by
Dedy KurniawanCopyright:
Available Formats
Dosen:
Budiyono, S. Kom
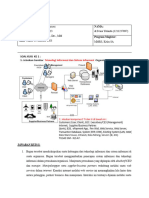
Konsep dan Definisi Sistem Informasi
Evolusi Sistem Informasi
Klasifikasi Sistem Informasi
Contoh Sistem Informasi
Lingkungan komputasi modern
Sistem berbasis web
Terbentuknya Lingkungan komputasi
Memanajemen Sumber daya Informasi
Membedakan antara infrastruktur teknologi informasi dan
arsitektur teknologi informasi
Mendeskripsikan komponen-komponen dari sistem Informasi
berbasis komputer
Mendeskripsikan beraneka ragam sistem informasi dan
evolusinya
Sistem Berbasis Mainframe, Sistem Client Server dan Peer to
peer.
Mengidentifikasi sistem pendukung internal utama tiap level
organisasi
Mendeskripsikan Tipe Utama dari Sistem Informasi berbasi
web dan memahami fungsinya.
Mendeskripsikan terbentuknya lingkungan komputasi.
Mendeskripsikan bagaimana sumberdaya informasi
dimanajemen dan peranan departemen sistem informasi dan
pemakai akhir (End User).
Arsitektur Teknologi Informasi: Peta Besar atau
rincian Informasi yang dimiliki organisasi,
yang mana mengatur jalannya operasi dan
yang menjadi cetak biru (blue print) untuk
tujuan dimasa depan.
Dalam menyiapkan arsitektur Teknologi
Informasi, Desainer membutuhkan informasi
yang akurat, yang dapat dibagi menjadi 2
bagian:
Informasi yang dibutuhkan untuk Bisnis
Teknologi Informasi terkini dan rencana kedepan
serta aplikasi organisasi.
Fasilitas fisik, Komponen Teknologi Informasi, Layanan (Service)
Teknologi Informasi, dan Manajemen Teknologi Informasi yang
mendukung organisasi yang bersangkutan.
Komponen Teknologi Informasi diantaranya adalah Hardware,
Software dan Teknologi Komunikasi yang digunakan untuk
menghasilkan layanan.
Layanan Teknologi Informasi termasuk pembangunan sistem
manajemen data, sistem keamanan data pada tempat-tempat yang
rawan.
Infrastruktur Teknologi Informasi termasuk sumberdaya yang ada
maupun kelengkapan (integrity), pelaksanaan (operation),
dokumentasi, perawatan dan manajemennya.
Secara umum, kesatuan kumpulan dari
sumberdaya informasi, pemakainya, dan
manajemen yang membawahinya; Termasuk
infrastruktur Teknologi Informasi dan sistem
informasi lainnya dalam suatu organisasi.
Sistem Informasi: Suatu proses yang berfungsi
untuk mengumpulkan, memproses,
menyimpan, menganalisa, dan
mendistribusikan informasi untuk suatu tujuan
tertentu.
CBIS: Sistem Informasi yang menggunakan
teknologi komputer untuk menjalankan
beberapa atau semua tugas Sistem Informasi.
Program komputer yang dirancang untuk
mendukung suatu tugas khusus, proses bisnis
atau kegiatan lainnya.
Kumpulan program aplikasi pada satu
departemen biasanya disebut sebagai Sistem
Informasi Departemen.
Data items. Deskripsi dasar tentang sesuatu, kejadian,
aktifitas, dan peristiwa yang direkam, dikelompokkan,
dan disimpan, tetapi tidak terorganisasi sehingga tidak
memiliki arti.
Informasi. Data yang telah teroganisasi sehingga
memiliki arti dan nilai bagi penerimanya.
Pengetahuan. Data dan informasi yang teorganisasi dan
diproses untuk dapat dimengerti, dijalankan,
dikumpulkan untuk dipelajari, dan diterapkan para
ahli untuk mengatasi masalah atau untuk menjalankan
aktifitas saat ini.
Aplikasi bisnis komputer pertama kali kurang
berkembang (tahun 50-an). Komputer hanya
untuk transaksi yang berkapasitas tinggi.
Komputer ketukan angka-angka (crunched
numbers) meringkas dan mengorganisasi
traksaksi dan data akuntansi, keuangan dan
sumberdaya manusia. Sistem tersebut secara
umum disebut sistem proses transaksi
(transaction processing systems-TPSs)
Management Information Systems (MIS): sistem ini
mengakses, mengorganisasi, menyimpulkan dan
menampilkan informasi untuk menunjang pembuatan
keputusan rutin pada bidang yang membutuhkan.
Office Automation Systems( OASs): seperti sistem
pemroses kata (Microsoft Word, Excel, Powerpoint,
Access) yang mana dikembangkan untuk mendukung
kantor dan pegawai perkantoran.
Sistem Penunjang keputusan: Dikembangkan untuk
menyediakan penunjang keputusan berbasis komputer
untuk keputusan yang tidak rutin dan rumit.
End- user computing: Pengembangan sistem
informasi dengan tujuan pengguna tertentu
contohnya adalah Sistem Analis, Sistem
Manajer, Sistem Architech, Sistem Desain
Grafis, Sistem Animasi dan kegiatan
profesional lainnya.
Intelligent Support System (ISSs): Termasuk
sistem pakar yang mana menyediakan
simpanan pengetahuan pakar untuk non-
pakar, dan jenis baru dari sistem pakar adalah
mesin dengan kemampuan belajar yang dapat
belajar dari kasus sejarah.
Knowledge Management Systems: Mendukung
pembuatan, pengumpulan, pengorganisasian,
penggabungan dan penyebarluasan
pengetahuan.
Data Warehousing: Database yang dirancang
untuk mendukung DSS (Decission Support
Systems-Sistem Penunjang Keputusan), ESS
aktifitas analisis serta pengguna akhir lainya.
Mobile Computing: Sistem Informasi yang
mendukung karyawan yang bekerja dengan
pelanggan atau mitra bisnis diluar batas
perusahaanya; dapat dijalankan melalui jalur
kaber atau jaringan tanpa kabel.
Pada umumnya dibagi menjadi 2 jenis:
Berdasarkan dukungan aktifitas
Berdasarkan tingkat organisasi
Jenis Sistem Informasi yang mengikuti struktur hirarki
organisasi diantaranya departemen perusahaan
keseluruhan dan antar organisasi.
Sistem Informasi Fungsional mengatur sekitar
departemen tradisional.
Sistem Informasi perusahaan melayani beberapa
bepartemen atau perusahaan yang bersangkutan.
Sistem Antar Organisasi menghubungkan dua atau lebih
organisasi.
Organisasi An organizations supply chain describe the
flow of materials , information money and service from
raw material suppliers through factories and warehouses
to the end customers.
IT provide two major types of software solution for
managing supply chain activities . First enterprise
resource planning ( ERP), Second Supply Chain
Management (SCM)
The typical enterprise is organized
hierarchically, from the clerical and office
worker layer, to the operational layer, the
managerial layer, the knowledge worker layer
and finally the strategic layer.
Clerical workers constitute a large class of
employee who support managers at all levels
of the company. Among clerical workers, those
who use, manipulate, or disseminate
information are referred to as data workers.
These employee include bookkeepers,
secretaries who work with word processors,
electronic file clerks, and insurance claim
processors.
Operational, or first- line managers deal with
the day-to day operations of the organization,
making routine decision, which deal in general
with activities such as short- term planning,
organizing, and control
They act as advisors and assistants to both top
and middle management and are often subject-
area experts. Many of these professional
workers are classified as knowledge workers,
people who create information and knowledge
as part of their work and integrate it into the
business.
Top-level or strategic managers( the executive)
make decision that deal with situation that may
significantly change the manner in which
business is done.
Computing Environment: The way in which an
organizations information technologies (
hardware, software, and communications
technology) are organized and integrated for
optimal efficiency and effectiveness.
Legacy system: Older systems, typically those
that process an organizations high-volume
transactions, that are central to the operations
of a business.
Computing architecture that divides the
processing work between two or more
computers, using a network for connection,
also called distributed processing.
A type of distributed architecture that divides
distributed computing units into two major
categories, clients and servers, connected by a
network .
Client .A computer ( such as a PC attached to a
network ) that is used to access shared network
resources.
Server. A computer that is attached to a
client/server network and provides clients
with variety of services.
Enterprise wide computing. Computing
environment in which each client/ server
architecture is used throughout an
organization.
Peer- to Peer (P2P). A distribute computing
network in which each client/ server computer
shares files or computer resources directory
with others but not through a central service
(as in traditional client/ server architecture).
Web based systems: Applications or service
that are resident on a server that is accessible
using a web browser and is therefore accessible
from anywhere via the internet.
Internet ( the Net): a world wide system of
computer a network of networks; a public,
cooperative and self- sustaining facility
accessible to hundreds of millions of people
worldwide.
Information Superhighway. A national fiber-
optic- based network and wireless
infrastructure that will connect all internet
users in a country
An application that uses the transport
functions of the Internet; has universally
accepted standards for storing, retrieving
formatting, and displaying information via a
client/server architecture
A private network, usually within one
enterprise that uses web technologies such as
browsers and internet protocols separated from
the Internet by a security gateway such as a
firewall
A secured network that connects several
intranet via the Internet; allows two or more
enterprise to communicate and collaborate in a
controlled fashion .
Web site that provide the gateway to corporate
information from a single point of access.
Electronic Storefront: The web- equivalent of a
showroom or a physical store through which
an e-business can display and/or sell its
products.
Electronic market: A network of interaction
and relationships over which information,
products service and payments are exchanged.
Electronic exchange: A web based public
electronic market in which many buyer and
many sellers interact electronically .
Mobile commerce: The buying and selling of
goods and services in a wireless environment.
Location based commerce: Mcommerce
transaction targeted to customers in specific
locations at specific times.
Enterprise Web: An open environment for
managing and delivering web application by
combining service from different vendors in a
technology layer that spans platform and
business systems.
Utility computing: Unlimited computing
power and storage capacity that, like electricity
and water services, can be obtained on demand
from virtual utilities around the globe.
Subscription computing: A type of utility
computing that puts the pieces of a computing
platform together as services, rather than as a
collection of separately purchase component .
Grid computing: The use of networks to
harness unused processing cycles of various
computers in order to create powerful
computing capabilities.
Pervasive computing: invisible, everywhere
computing that is embedded in objects
around us.
Web services: Universal, prefabricated
business process software modules,
delivered over the Internet that users can
select and combine through almost any
device enabling disparate system to share
data and services.
You might also like
- Bab IiDocument41 pagesBab Iiputri prihandayaniNo ratings yet
- PERMENPAN NO 37 TAHUN 2020 TTG JFT Analis SDM-dikonversiDocument189 pagesPERMENPAN NO 37 TAHUN 2020 TTG JFT Analis SDM-dikonversiKaswandiAl-MakassariNo ratings yet
- Dupak Prakom Ahli PertamaDocument9 pagesDupak Prakom Ahli PertamaRisqon KhasaniNo ratings yet
- JUDULDocument39 pagesJUDULsquidwordNo ratings yet
- MANAJEMEN KESEHATAN GIGIDocument19 pagesMANAJEMEN KESEHATAN GIGIRefo Prima EfradinataNo ratings yet
- Arsiparis Ahli Pertama2023Document506 pagesArsiparis Ahli Pertama2023Sufriyah SufNo ratings yet
- Tata Kelola Pemerintahan dan MSDMDocument16 pagesTata Kelola Pemerintahan dan MSDMadit mamasNo ratings yet
- Perka Anri No 17 Tahun 2011 Tentang Pedoman Klasifikasi Keamanan Akses Arsip DinamisDocument39 pagesPerka Anri No 17 Tahun 2011 Tentang Pedoman Klasifikasi Keamanan Akses Arsip Dinamisindra agustina100% (1)
- Sap 1 Partai Politik Dan Sistem KepartaianDocument14 pagesSap 1 Partai Politik Dan Sistem KepartaianMesiani ElfrideNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan DataDocument3 pagesPengolahan DataMiftah Al-bughuryNo ratings yet
- Elektronik Voting (E-Voting)Document17 pagesElektronik Voting (E-Voting)Amalia DewiNo ratings yet
- KodeEtikPustakawanDocument18 pagesKodeEtikPustakawanFadhilatul HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Pengelolaan Arsip Di Dinas Perpustakaan Dan Kearsipan Provinsi Sulawsi SelatanDocument9 pagesPengelolaan Arsip Di Dinas Perpustakaan Dan Kearsipan Provinsi Sulawsi SelatannurimanafajrinaNo ratings yet
- Kompak Gesi Strategy Keadilan Gender Dan Inklusi Sosial 2017Document32 pagesKompak Gesi Strategy Keadilan Gender Dan Inklusi Sosial 2017Abah JufriNo ratings yet
- Laboratorium SMK Negeri 2 KaranganyarDocument46 pagesLaboratorium SMK Negeri 2 KaranganyarTri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Basis DataDocument223 pagesPerancangan Basis DataDODY FAIZALNo ratings yet
- BAB 10. Evolusi Strategi Integrasi Sistem InformasiDocument20 pagesBAB 10. Evolusi Strategi Integrasi Sistem InformasiRivando Al RasyidNo ratings yet
- My PortofolioDocument1 pageMy PortofolioFedy JuniansyahNo ratings yet
- DS, BD, dan AI: Konsep, Konteks, dan AplikasiDocument26 pagesDS, BD, dan AI: Konsep, Konteks, dan Aplikasivito 98No ratings yet
- Contoh Proposal: Sistem Informasi Rumah Sakit (SIRS)Document22 pagesContoh Proposal: Sistem Informasi Rumah Sakit (SIRS)Ridwan FauziNo ratings yet
- Evolusi Sistem InformasiDocument13 pagesEvolusi Sistem Informasiaisyah fadhillaNo ratings yet
- SMKI-DJPDocument18 pagesSMKI-DJPhidayatNo ratings yet
- Modul 12 - Audit Teknologi InformasiDocument34 pagesModul 12 - Audit Teknologi Informasiharish sabarNo ratings yet
- Ekspose Percepatan SPBE Kearsipan 26 Nov 2020Document22 pagesEkspose Percepatan SPBE Kearsipan 26 Nov 2020naonsih100% (1)
- SimpegDocument13 pagesSimpegChui ⊱▬▬▬▬◊⋙ ChaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri Manajemen ProyekDocument7 pagesTugas Mandiri Manajemen ProyekKristian JuniantoNo ratings yet
- Peran Kecerdasan Buatan Pada Kehidupan Manusia Dan MekanismenyaDocument11 pagesPeran Kecerdasan Buatan Pada Kehidupan Manusia Dan MekanismenyaFebria Erliana100% (1)
- SPBE KearsipanDocument16 pagesSPBE KearsipannaonsihNo ratings yet
- OPTIMASI REGULASIDocument108 pagesOPTIMASI REGULASIDEDY KURNIAWANNo ratings yet
- 01-Konsep Sistem InformasiDocument64 pages01-Konsep Sistem Informasikomersial bandhajpNo ratings yet
- Buku Panduan Standar Pelayanan Publik Bapas Surakarta PDFDocument34 pagesBuku Panduan Standar Pelayanan Publik Bapas Surakarta PDFSuprapto Teguh100% (1)
- Partai PolitikDocument3 pagesPartai PolitikVelia MonicaNo ratings yet
- E-VOTING MENGGUNAKAN FINGERPRINT DAN WEBDocument6 pagesE-VOTING MENGGUNAKAN FINGERPRINT DAN WEBAde Gumilar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Interoperabilitas Sistem Perpustakaan DigitalDocument220 pagesInteroperabilitas Sistem Perpustakaan DigitalMuhammad IkhsanNo ratings yet
- C2 - 2.6 - 1 - 1625013976-Laporan Manajemen Resiko Uin Raden Fatah PalembangDocument12 pagesC2 - 2.6 - 1 - 1625013976-Laporan Manajemen Resiko Uin Raden Fatah PalembangMuhammad Trian PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Esai Tentang Penyelamatan Arsip Melalui Media DigitalDocument7 pagesEsai Tentang Penyelamatan Arsip Melalui Media DigitalIta WahyuNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penataan Arsip Di MAN 5 Pasaman BaratDocument144 pagesAnalisis Penataan Arsip Di MAN 5 Pasaman BaratFebriantiNo ratings yet
- Renstra UBSI 2018-2023Document90 pagesRenstra UBSI 2018-2023Joseph AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Pencegahan Kebocoran Data Dari Ancaman InternalDocument10 pagesPencegahan Kebocoran Data Dari Ancaman InternalArinaSeissaSutedjoNo ratings yet
- Cara Mengelompokkan Data (Grouping) Pada Pivot Table Excel - Kelas ExcelDocument13 pagesCara Mengelompokkan Data (Grouping) Pada Pivot Table Excel - Kelas ExcelJati DajaNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Aplikasi E-Gov KominfoDocument153 pagesBlueprint Aplikasi E-Gov KominfoIrena SusantiNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Dokumen & Dokumentasi: Disusun Dari Beberapa sumber/UU KearsipanDocument25 pagesPengertian Dokumen & Dokumentasi: Disusun Dari Beberapa sumber/UU KearsipanBane Beben100% (1)
- Analisis Sistem Informasi Persediaan Obat Pada Apotek MutiaraDocument49 pagesAnalisis Sistem Informasi Persediaan Obat Pada Apotek MutiaraAtika100% (3)
- Materi 1 SisumakerDocument9 pagesMateri 1 SisumakerDeki AstriantoNo ratings yet
- Makalah Sistem Basis DataDocument28 pagesMakalah Sistem Basis DataRianNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Sistem Informasi KesehatanDocument21 pagesManajemen Sistem Informasi KesehatanBEM IST Buton100% (1)
- Makalah Arsitek EnterpriseDocument35 pagesMakalah Arsitek EnterpriseRaden ZakaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Manajemen KearsipanDocument29 pagesKonsep Manajemen Kearsipanlenny gurningNo ratings yet
- Digitalisasi Arsip Penting dalam Manajemen KearsipanDocument5 pagesDigitalisasi Arsip Penting dalam Manajemen Kearsipanahyana yusmar100% (1)
- Sistem Administrasi Keuangan Negara IDocument108 pagesSistem Administrasi Keuangan Negara IDinnar Kusumawati SunaryaNo ratings yet
- KUIS - MMRS - 8A - Dr. Ivana YolandaDocument14 pagesKUIS - MMRS - 8A - Dr. Ivana YolandaIvana YolandaNo ratings yet
- 8669 - 5049 - Rangkuman Chapter 4Document13 pages8669 - 5049 - Rangkuman Chapter 4Erina OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Bab 1. Peranan Sistem Informasi Dalam BisnisDocument16 pagesBab 1. Peranan Sistem Informasi Dalam Bisnismitra fotocopyNo ratings yet
- MANAJEMEN_INFORMASIDocument44 pagesMANAJEMEN_INFORMASIRani SukmadewiNo ratings yet
- MaklhDocument15 pagesMaklhFujhieNuryanie Phutri KimiNicholasNo ratings yet
- RMK 1 Desain AkDocument6 pagesRMK 1 Desain AkBilqist Nabila ZahraNo ratings yet
- SISTEM INFORMASI DIGITALDocument16 pagesSISTEM INFORMASI DIGITALNia Azura SariNo ratings yet
- Sistem Maklumat PengurusanDocument4 pagesSistem Maklumat PengurusanAizu Aziz50% (2)
- Catatan DsiDocument6 pagesCatatan Dsi03-agnes veronikaNo ratings yet
- SISTEM INFORMASIDocument29 pagesSISTEM INFORMASIMay RizaNo ratings yet
- TA Andi NuriaDocument37 pagesTA Andi NuriaDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- TA Andi NuriaDocument37 pagesTA Andi NuriaDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Nomenklatur Prodi Akademik 27 Agustus 2017 RevDocument33 pagesLampiran Nomenklatur Prodi Akademik 27 Agustus 2017 RevJaya SutejaNo ratings yet
- Pesan Media SosialDocument150 pagesPesan Media SosialDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction GISDocument46 pagesIntroduction GISNurhidayatNo ratings yet
- CARA BELAJAR PUKULANDocument2 pagesCARA BELAJAR PUKULANDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pelamar Lulus Seleksi Administrasi Cpns 2018 FinalDocument12 pagesDaftar Pelamar Lulus Seleksi Administrasi Cpns 2018 FinalDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Sorting PopulerDocument8 pagesAlgoritma Sorting PopulerDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Dan Dokumentasi Prose Sekolahyok!! PDFDocument30 pagesSpesifikasi Dan Dokumentasi Prose Sekolahyok!! PDFDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- REI Ebook ManajemenSistemInformasiDocument276 pagesREI Ebook ManajemenSistemInformasiAhmad Soleh Afif100% (1)
- 21hb05072014kim MedanDocument1 page21hb05072014kim MedanDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- MENGENALDocument11 pagesMENGENALDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- ANALISIS_STRATEGIDocument42 pagesANALISIS_STRATEGIDedy Kurniawan75% (4)
- 22 PDFDocument1 page22 PDFDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Strategi Bisnis Toko Buku OnlineDocument10 pagesAnalisis Strategi Bisnis Toko Buku OnlineDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Soal Select SD CartesianDocument3 pages2 Soal Select SD CartesianDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Manajemen StrategisDocument15 pagesManajemen StrategisDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- FileDocument3 pagesFilewildan_rifqiNo ratings yet
- Pengertian MVCDocument23 pagesPengertian MVCDedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Keyword SMS Versi 4-12Document1 pageKeyword SMS Versi 4-12Dedy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- FileDocument3 pagesFilewildan_rifqiNo ratings yet