Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Scheme of First Trial Examination 2014
Uploaded by
Chin Chin YipCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Scheme of First Trial Examination 2014
Uploaded by
Chin Chin YipCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer scheme of First Trial
Examination 2014
Q Rubric Marks
1 (a) Saponification 1
(b) P1 Detergent
P2 Sea water contains calcium ion and magnesium ion that will not
form scum with detergent
1
1
(c) Detergent is more effective in hard water compared soap
Detergent is more effective in acidic water.
1
(d) Biological enzymes / whitening agent 1
(e) Concentrated potassium hydroxide solution 1
(f) (i) Expiry date 1
(ii) Cause hair fall / allergy 1
(g)
Type of medicine Name of medicine
Antibiotics Streptomycin
Penicillin
Psychotherapeutics Chloropromazine
Amphetamine
1
1
Subtotal
10
Q Rubric Marks
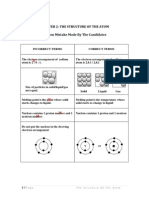
2 (a) A: 2.8.2
B: 2.8.6
1
1
(b) (i) Ionic bond 1
(ii) P1 Atom A donates 2 valence electrons to form A
2+
ion.
P2 Atom B accepts 2 electrons from atom A to form B
2-
ion.
P3 Two oppositely charged ions, A
2+
and B
2-
are attracted by strong
electrostatic force.
1
1
1
(c)
2
(d) High melting point and boiling point//
Can dissolve in water but can dissolve in organic solvent//
Can conduct electricity in molten state or aqueous solution.
1
(e) (i) CB
2
1
(ii) Relative molecular mass
=12+32x2
=76
1
Subtotal 11
Q Rubric Marks
3 (a) (i) Silver 1
(ii) Silver nitrate solution 1
2+ 2-
(b) Ag
+
+ e Ag 1
(c) The blue intensity increase
The concentration of copper (II) ion in copper(II) sulphate increase.
1
1
(d) (i) Z, Y, X, W 1
(ii) X.
X is less electropositive than Z
1
1
(iii) 0.6 V 1
Subtotal 9
Q Rubric Marks
4 (a) (i) Zinc chloride solution 1
(ii) Lead (II) chloride 1
(b) (i) 2HCl + ZnCO
3
ZnCl
2
+ CO
2
+ H
2
O 1
(ii) Number of moles of HCl
= 20x1/1000
=0.02mol
2 mol HCl 1 mol CO
2
0.02 mol HCl 0.01 mol CO
2
Volume of carbon dioxide
= 0.01 x 24
= 0.24 dm
3
1
1
1
(c) (i) Double decomposition / Precipitation 1
(ii) Filter the mixture.
The residue is dried by pressing between two pieces of filter paper.
1
1
Subtotal 9
Q Rubric Marks
5 (a) (i) Hydrogenation 1
(ii) 180 C
Nickel as catalyst
1
1
(iii) C
3
H
6
+ H
2
C
3
H
8
1
(iv) P1 Channel the propene and propane into the each test tube containing
2 cm
3
of bromine water / acidified potassium manganate (VII)
solution.
P2 Propene will decolourise the brown bromine / purple acidified
KMnO
4
but propane cannot.
1
1
(b) Bromine water 1
(c) Hydration 1
(d) (i)
Propyl methanoate
1
1
(ii) Sweet smell/ fragant smell 1
Subtotal 11
Q Rubric Marks
6 (a) (i) Brown / yellow 1
(ii) P1 Add sodium hydroxide solution into the test tube until in excess
P2 Brown precipitate is formed.
1
1
(b) +2 +3 1
(c) Acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution 1
(d) Chlorine water / acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution 1
(e) (i) To allow the movement of ions to complete the circuit. 1
(ii) Reduction 1
(iii) X + 4(-2) = -1
X = +7
1
(iv) 2I
-
I
2
+ 2e 1
Subtotal 10
Q Rubric Marks
7 (a) P1 Potassium hydroxide is a strong alkali while ammonia is a
weak alkali
P2 Potassium hydroxide dissociates completely in water to
produce high concentration of hydroxide ions.
P3 Ammonia dissociates partially in water to produce low
concentration of hydroxide ions
P4 The concentration of hydroxide ion in potassium hydroxide
is higher than ammonia solution.
P5 The higher the concentration of hydroxide ions, the higher the
pH value.
Any four
1
1
1
1
1
Max 4
(b) (i) One mole of ethanoic acid ionizes in water to produce one mole of
hydrogen ion
CH
3
COOH CH
3
COO
-
+ H
+
1
(ii) P1 Glacial ethanoic acid remains as molecules only
P2 Aqueous ethanoic acid ionizes in water to produce free
moving ions that carry electrical charge.
1
1
(c)
Mg + 2 CH
3
COOH Mg(CH
3
COO)
2
+ H
2
No of moles of hydrogen gas
= 48 /24000
= 0.002mol
2 mol CH
3
COOH 1 mol of hydrogen
0.004 mol CH
3
COOH 0.002 mol of hydrogen
0.004 = M x 50 / 1000
M = 0.08 mol dm
-3
1
1
1
1
(d) Number of moles of acid
38.4 /192 = 0.2 mol
Concentration of acid
= 0.2 / ( 100/1000)
= 2 mol dm
-3
1
1
(e) Compound T is ammonia solution
P1 In condition III, bacteria will produce lactic acid/ H
+
ions
which neutralize negative charge of the protein membrane
P2 The rubber molecules will be collide with each other and
cause the protein membrane broken.
1
1
1
P3 Rubber polymer are released and lump together/ coagulate
P4 In condition II, hydroxide ions from compound T will
neutralize H
+
produced by acid.
P5 The proteins membrane remains negative charged
P6 The rubber particle repel each others / the rubber polymers
cannot combine and coagulate
1
1
1
1
Max 6
Subtotal 20
Q Rubric Marks
8 (a) Source:
P1 sulphur dioxide release from factory.
P2 toxic waste from factory
Process:
P1 Sulphur dissolved in rain water and produce acid rain
P2 toxic waste goes to drain/ lake. Combine with water in the drain /
lake
Effect
P1 Corrode the building
P2 Increase the pH of lake / soil
1
1
1
1
1
1
(b) (i) Material: Copper block and bronze block
Apparatus: steel bearing, 1 kg weight, clamp , ruler, cellotape, thread
Procedure
1. Clamp a meter rule to a retort stand and place a piece of
copper clock on the base of the retort stand.
2. Place a steel ball bearing on the copper block and use a piece
of cellotape to hold the ball bearing in place.
3. Hang 1 kg weight at a height of 50cm above the copper block.
4. The weight is released onto the ball bearing which place on
the copper block
5. Measure the diameter of diameter of the dent made by ball
bearing.
6. Repeat the experiment 3 times using different areas on the
surface of the copper block
7. Calculate the average diameter of the dent
8. Repeat step 1-7 by using a piece of bronze block to replace the
copper block.
Type of
block
Diameter of dent/cm Average /
cm 1 2 3
Copper
Bronze
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
(ii) Explanation
1. In copper metal, the atoms of same size are arranged in order.
2. When the force is applied, the layers of metal atom will slide
easily
3. In bronze, the presence of tin atom of different size
4. Disrupt the orderly arrangement of atoms in copper
5. reduce the layer of metal atoms to slide one another easily
1
1
1
1
Subtotal 20
Q Rubric Marks
9 (a) P1 The total energy content of reactants is lower the total energy
content of products in Reaction I
P2 The Reaction I is endothermic reaction
P3 The total energy content of reactants is higher than the total
energy content of products in Reaction II
P4 The Reaction II is exothermic reaction.
1
1
1
1
(b) (i) Acid P : Ethanoic acid
Acid Q : Hydrochloric acid
1
(ii) P1 Monoprotic acid P is a weak acid
P2 which dissociates partially in water to produce low concentration of
hydrogen ions
P3 some of the ethanoic acid still remains as molecules
P4 Some heat given out during neutralisation is absorbed to ionize the
ethanoic acid molecules completely
1
1
1
(iii) No of moles of acid P
= 100 x1.0 /1000
= 0.1 mol
H
+
+ OH
-
H
2
O
1 mol of H
+
reacts with 1 mol of OH
-
to form 1 mol of H
2
O.
0.1 mol of H
+
reacts with 0.1 mol of OH
-
to form 0.1 mol of H
2
O.
H = - H / n
55000 = H / 0.1
H = 5500 J
5500 = (100 +100) x 4.2 x
= 6.5 C
1
1
1
(iv)
1. 100 cm
3
of 1.0 mol dm
-3
hydrochloric acid is measured using a
measuring cylinder.
2. Pour the solution into a plastic cup.
3. 100 cm
3
of 1.0 mol dm
-3
sodium hydroxide solution is
measured using another measuring cylinder.
4. Pour the solution into a plastic cup.
5. A thermometer is placed into each solution and the initial
temperature of sodium hydroxide solution and hydrochloric
acid are recorded.
6. The hydrochloric acid is poured quickly and carefully into the
sodium hydroxide solution.
7. The mixture is stirred using a thermometer and the highest
temperature reached by the mixture is recorded.
Method
8. Initial temperature of hydrochloric acid = T
1
o
C
9. Initial temperature of NaOH = T
2
o
C
10. Average initial temperature =( T
1
+ T
2
)/2 = T
a
o
C
11. Highest temperature = T
b
o
C
12. Heat given out, H = mc = 200 x 4.2 x ( T
b
T
a
)
13. Number of moles = 100 x 1.0 / 1000
14. Heat of neutralisation = - H / 0.1 = - A kJ mol
-1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max =8
Subtotal
20
Q Rubric Mar
ks
10 (a) P1 Reaction I is not a redox reaction
P2 No change in oxidation number for all the elements before and after
the reaction
HCl + NaOH NaOH + H
2
O
Oxidation no. +1 -1 +1 -2 +1 +1 -2 +1 +1 -2
P3 Reaction II is not a redox reaction
P4 Oxidation number of magnesium increase from 0 +2
Oxidation number of copper decrease from +2 0
Mg + CuSO
4
Mg SO
4
+ Cu
0 +2 +2 0
1
1
1
1
(b) (i) Oxidation number of copper in CuO = +2
Oxidation number of copper in Cu
2
O = +1
1
1
(ii) Copper (II) oxide
Copper (I) oxide
They have different oxidation number.
1
1
1
(c) Step Chemicals used Observation
I
Any suitable oxidizing
agent/
e.g: Copper(II) sulphate
solution
Correct corresponding
observation/
Blue solution of
Copper(II) sulphate
solution becomes paler or
colourless
II
Any suitable reducing
agent/
e.g: zinc powder
Correct corresponding/
zinc powder dissolves//
brown colour of iron(III)
ions becomes pale green
1+1
1+1
(d) P : chlorine / bromine
Q : bromine / iodine
Set I
P1 P is more electronegative [than iodine]// iodine is less electronegative
[than P]
P2 P is reduced to P
-
ion / P undergoes reduction to P
-
P3 I
-
ion is oxidised to iodine/ I
-
ion undergoes oxidation
P4 P
2
+ 2e
-
2P
-
P5 2I
-
I
2
+ 2e
Set II
P6 Q is less electronegative/ Chlorine is more electronegative
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
=7
Subtotal
20
End of Answer Scheme
You might also like
- Module The MoleDocument44 pagesModule The MoleChin Chin YipNo ratings yet
- Modul X-A Plus 1 - EditedDocument21 pagesModul X-A Plus 1 - EditedChin Chin YipNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument12 pages2.1 Classes of FoodChin Chin YipNo ratings yet
- Structure and Phenomena of the SunDocument9 pagesStructure and Phenomena of the SunThiran VinharNo ratings yet
- 2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2Document28 pages2013 Yearly Plan For Science f2Jesseca Siew Wey ChanNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The Basicskent_tam611980% (5)
- Midyear Exam Revision Set 1 Form 2Document8 pagesMidyear Exam Revision Set 1 Form 2Lim Wai Wai SmktpNo ratings yet
- Modulejpn Chapter2Document18 pagesModulejpn Chapter2Mohd Sukri RamlyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument20 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionKaoru AmaneNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument5 pagesRocksangelic dailyNo ratings yet
- Indoor Environmental Quality Factors for Comfort and HealthDocument42 pagesIndoor Environmental Quality Factors for Comfort and HealthSyed Imtiaz Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- AFT ChempakDocument2 pagesAFT ChempakbtjajadiNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant activity of phenolic pigments from cocoa hullsDocument6 pagesAntioxidant activity of phenolic pigments from cocoa hullsdjguevara1No ratings yet
- 1984 WhiteheadDocument19 pages1984 WhiteheadAnita yuliyantiNo ratings yet
- ProBlue 15, 30 and 50 Liter MeltersDocument2 pagesProBlue 15, 30 and 50 Liter MeltersNordson Adhesive Dispensing SystemsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Phase EquilibriaDocument53 pagesIntroduction to Phase EquilibriaEko Putra BayuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- Production of Insulating Refractory Bricks From Kankara Kaolin Using AchaDocument150 pagesProduction of Insulating Refractory Bricks From Kankara Kaolin Using AchaSAMUEL PSALMNo ratings yet
- MSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline FlangesDocument52 pagesMSS SP-44-2016 Steel Pipeline Flangesarnoldbatista55100% (2)
- My New ResumeDocument4 pagesMy New ResumeSurajNo ratings yet
- CALF Centre for Analysis and Learning in Livestock and FoodDocument21 pagesCALF Centre for Analysis and Learning in Livestock and FoodK.L. YadavNo ratings yet
- Carbon Black ProcessDocument4 pagesCarbon Black ProcessAnonymous azD9vQD100% (1)
- Extra BMP Unit 1Document40 pagesExtra BMP Unit 1V R SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 1 MergedDocument8 pages1 MergedNo NameNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 Mainspanu oanaNo ratings yet
- Studies On Degradation of Synthetic Polymer Nylon 6 by FungusDocument8 pagesStudies On Degradation of Synthetic Polymer Nylon 6 by FungusTiten PinastiNo ratings yet
- SDS - Penguard Topcoat - Comp. A With LC - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United KingdomDocument8 pagesSDS - Penguard Topcoat - Comp. A With LC - Marine - Protective - English (Uk) - United KingdomNPTNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic InsertsDocument28 pagesOphthalmic InsertsShendi SuryanaNo ratings yet
- All India Aakash Test Series For NEET - 2021 TEST - 6 (Code-C)Document32 pagesAll India Aakash Test Series For NEET - 2021 TEST - 6 (Code-C)Kavyatharsheni S XI-B 46No ratings yet
- Unit Iv Photochemistry and Spectroscopy: Part A 1. Define PhotochemistryDocument18 pagesUnit Iv Photochemistry and Spectroscopy: Part A 1. Define PhotochemistryKrithigasri MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Bio Based Thermosetting Resins For FuturDocument34 pagesBio Based Thermosetting Resins For Futursatish kumarNo ratings yet
- Spray Application of Belzona 2009Document4 pagesSpray Application of Belzona 2009Mounir BoutaghaneNo ratings yet
- Indowud Brochure Revised PDFDocument10 pagesIndowud Brochure Revised PDFsurabhi narangNo ratings yet
- Mooring Line Management SNAME 1994Document8 pagesMooring Line Management SNAME 1994Peyman MznNo ratings yet
- EP0070932B1Document5 pagesEP0070932B1bayuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDDocument9 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Himalaya Health CareDocument38 pagesHimalaya Health Careactive1cafeNo ratings yet
- Jitorres Forster Cycle ReconsideredDocument12 pagesJitorres Forster Cycle ReconsideredNataliaRiveroArenasNo ratings yet