Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ST 40
Uploaded by
ray72roOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ST 40
Uploaded by
ray72roCopyright:
Available Formats
Stomach Channel
1
INDICATIONS
Copious phlegm, fullness, oppression and pain of the
chest, stabbing pain of the chest, cutting pain of the
abdomen, swelling of the face, dizziness, headache,
wind-phlegm headache, plumstone qi (globus hys-
tericus), swelling and pain of the throat, throat
painful obstruction with sudden loss of voice.
Damp body, slackness and heaviness of the body.
Cough and shortness of breath, cough with copious
phlegm, wheezing, dyspnoea, asthma.
Mania-depression, mad laughter, great happiness,
desires to ascend to high places and sing, discards
clothing and runs around, restlessness, seeing ghosts,
indolence, epilepsy, hypertension.
Constipation, difficulty in passing urine and stools.
Atrophy disorder and painful obstruction of the
lower limb, pain of the knee and leg, difficulty in
flexing and extending the knee, lack of control of the
legs, withering of the lower legs.
COMMENTARY
Fenglong ST-40 is the single most important acupuncture
point to transform phlegm in the body, whatever its
origin. Phlegm may be formed when i. stagnation of Liver
qi impairs the circulation of fluids which then congeal into
phlegm, ii. excess or deficiency heat condense body fluids
(phlegm is known as the substantial part of fire, and fire
the non-substantial part of phlegm) or iii. any or all of the
three zang responsible for fluid transformation and trans-
portation are deficient (the Lung in the upper jiao, the
Spleen in the middle jiao and the Kidneys in the lower
jiao). Of all these, disharmony of the transportation and
transformation function of the Spleen is clinically the
most important, thus the Essential Questions
39
says The
Spleen is the origin of phlegm and When water, grain
and body fluids do not flow, they will accumulate and
form phlegm-fluid (tanyin). When the Spleen transpor-
tation and transformation function is impaired, therefore,
body fluids collect and over time transform to phlegm,
which may then transmit to other zangfu and regions of
the body. Furthermore, it is a general treatment principle
that the Spleen should be regulated in the treatment of
phlegm of any aetiology, to assist in its transformation.
Fenglong ST-40 is the point from which the Stomach luo-
connecting channel connects with its associated Spleen
channel. The Guide to the Classics of Acupuncture states the
luo-connecting points are located between two channels
... if they are punctured, symptoms of the interiorly-
exteriorly related channels can be treated
40
. Traditionally,
Fenglong ST-40 has been used to treat any accumulation
of phlegm, especially affecting the Lung, Heart, throat
and head.
FENGLONG ST-40
Abundant Bulge
Luo-Connecting point of the Stomach channel
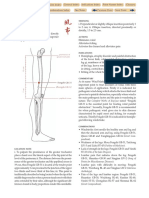
LOCATION
On the lower leg, midway between the tibiofemoral joint
line (level with the popliteal crease) and the lateral malleo-
lus, two finger-breadths lateral to the anterior crest of the
tibia (i.e. one finger-breadth lateral to Tiaokou ST-38).
NEEDLING
Perpendicular or oblique insertion 1 to 1.5 cun.
ACTIONS
Transforms phlegm and dampness
Benefits the chest
Clears phlegm from the Lung and alleviates
cough and wheezing
Clears phlegm from the Heart and calms the spirit
Activates the channel and alleviates pain
8
c
u
n
prominence of the
lateral malleolus
tibio femoral
joint line
8
c
u
n
Tiaokou ST-38
Fenglong ST-40
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Lung
L. Intestine
Stomach
Spleen
Heart
S. Intestine
Bladder
Kidney
Pericardium
Sanjiao
Gall Bladder
Liver
Conception
Governing
Extra Points
See Notes
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Stomach Channel 2
qi (globus hystericus) a sensation of throat blockage which
worsens or ameliorates according to fluctuations in the
emotional state and which is normally associated with
stagnation of qi and phlegm.
A great variety of disorders affecting any region of the
body may be caused by phlegm. This is expressed in the
Chinese medicine sayings There is no place that phlegm
cannot reach, The hundred diseases all pertain to
phlegm, Strange diseases often involve phlegm, and
Chronic disease often involves phlegm. Whatever the
manifestations, if phlegm is a component of the pathol-
ogy, Fenglong ST-40 is indicated.
Like many points of the foot yangming Stomach chan-
nel which is abundant in qi and blood, Fenglong ST-40 is
indicated for channel disorders such as atrophy disorder
and painful obstruction of the lower leg. Due to its ability
to transform phlegm, Fenglong ST-40 is especially indi-
cated in the treatment of hemiplegia due to wind-phlegm
in the channels.
Finally the Great Compendium of Acupuncture and Moxi-
bustion gives specific indications for excess and deficiency
of the luo-connecting points. In the case of Fenglong ST-40,
these are mania-depression (excess); lack of control of the
legs and withering of the lower legs (deficiency).
COMBINATIONS
All phlegm disease, head wind, dyspnoea and cough,
all types of phlegm-fluid (tanyin): Fenglong ST-40
and Zhongwan REN-12 (Outline of Medicine).
Cough with phlegm: Fenglong ST-40 and Feishu
BL-13 (Ode of the Jade Dragon).
Vomiting phlegm and watery saliva, dizziness that
does not cease: Fenglong ST-40, Yangxi L.I.-5, Gongsun
SP-4 and Shanzhong REN-17 (Complete Collection).
Stabbing pain of the chest: Fenglong ST-40 and
Qiuxu GB-40 (Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Headache that is difficult to endure: Fenglong ST-40
and Qiangjian DU-18 (One Hundred Symptoms).
Head wind and dizziness: Fenglong ST-40, Hegu L.I.-4,
Jiexi ST-41 and Fengchi GB-20 (Great Compendium).
Facial swelling: Fenglong ST-40, Tianshu ST-25,
Lidui ST-45, Xiangu ST-43 and Chongyang ST-42
(Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Mania disorder with rash behaviour, desires to as-
cend to high places and sing, discards clothing and
runs around: Fenglong ST-40 and Chongyang ST-42
(Thousand Ducat Formulas).
Loss of voice: Fenglong ST-40, Tiantu REN-22, Rangu
KID-2, Yingu KID-10, Fuliu KID-7 and Lingdao HE-4
(Illustrated Supplement).
According to a saying of Chinese medicine, The Spleen
is the origin of phlegm and the Lung is the container of
phlegm. When phlegm obstructs the descent of Lung qi,
or when Lung qi deficiency is unable to descend the
fluids, there may be coughing, wheezing and asthma
characterised by copious expectoration of phlegm. When
cold predominates, the phlegm will be clear or white,
whilst when heat predominates, the phlegm will be yel-
low, green or brown. Whether cold or hot, Fenglong ST-40
is an essential point to transform phlegm in the Lung.
Both the primary and sinew channels of the Stomach
pass through the chest, and Fenglong ST-40 has long been
considered a pre-eminent point in the treatment of chest
pain. If phlegm obstructs the free movement of qi and
blood in the chest there may be fullness, oppression and
stabbing pain. Such is its affinity for the chest, however, that
Fenglong ST-40 may be used in the treatment of any kind of
chest pain including sprain and injury of the chest muscles.
The pattern of phlegm or phlegm-fire misting or de-
ranging the Heart and spirit principally occurs when
severe emotional depression leads to stagnation of qi.
Stagnant qi can no longer distribute body fluids, which
coagulate to form phlegm. Phlegm then obstructs the
portals of the Heart, disrupting the spirit. Pronounced or
prolonged stagnation of qi and phlegm may transform
into fire resulting in phlegm-fire, which may be further
complicated by over-consumption of greasy and spicy
food and alcohol. When the fire aspect of phlegm-fire is
intense, the patient suffers from kuang, or mania disor-
der, with such symptoms as mad laughter and wild and
intense behaviour. When the phlegm aspect predomi-
nates, with relatively less fire, the patient suffers from
dian, characterised by mental confusion, lethargy and
stupor. The ability of Fenglong ST-40 to transform phlegm,
combined with the fact that the Stomach divergent chan-
nel connects with the Heart, and the Stomach primary
channel with the Governing vessel (and thus the brain) at
Shenting DU-24 and Renzhong DU-26, renders it particu-
larly suitable in treating these disorders.
The Stomach luo-connecting channel from Fenglong
ST-40 joins with all the yang channels in the head region.
If phlegm-damp obstructs the upper jiao and the head, it
may impair the ascent of clear yang to the head and
sensory orifices, giving rise to dizziness and headache
characterised by a heavy and clouded sensation. If inte-
rior wind rushes upwards, carrying phlegm with it, this is
known as wind-phlegm and may give rise to such symp-
toms as epilepsy and severe dizziness. The Stomach
luo-connecting channel terminates at the throat, and if
stagnant qi impairs the ability of the Lung and Stomach to
descend the fluids, phlegm is formed and combines with
stagnant qi to obstruct the throat, giving rise to plumstone
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
Combinations Index
Points Index General Index Indications Index Point Names Index Glossary
Next Point Previous Point
CONTENTS
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Da Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year SpiritsDocument2 pagesDa Liu Ren: Hour Day Month Year Spiritsray72roNo ratings yet
- Instructions Ffmpeg WinDocument3 pagesInstructions Ffmpeg Winray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 14 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 14 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Emotions Essential Oils 6th EnlightenDocument271 pagesEmotions Essential Oils 6th Enlightenray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 10 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 10 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Instructions Ffmpeg MacDocument3 pagesInstructions Ffmpeg Macray72roNo ratings yet
- Gui NotesDocument18 pagesGui Notesffmbdrng100% (8)
- DLR 2021 04 18 06 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 06 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 08 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 08 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Yang Earth Joye Yap PDFDocument18 pagesYang Earth Joye Yap PDFSerenity Serenity100% (3)
- Yi Notes PDFDocument19 pagesYi Notes PDFEe6803100% (1)
- GB 38 PDFDocument2 pagesGB 38 PDFray72roNo ratings yet
- DLR 2021 04 18 02 00Document3 pagesDLR 2021 04 18 02 00ray72roNo ratings yet
- Jiang Notes PDFDocument19 pagesJiang Notes PDFffmbdrngNo ratings yet
- Notes: Gall Bladder ChannelDocument1 pageNotes: Gall Bladder Channelray72roNo ratings yet
- FourSacredSeasons EbookDocument19 pagesFourSacredSeasons EbookLouis Lee Hires100% (3)
- BaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengDocument18 pagesBaZi - Notes On Yang Metal, GengMoses YeeNo ratings yet
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDocument2 pagesZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roNo ratings yet
- The Gall Bladder Channel of Foot ShaoyangDocument6 pagesThe Gall Bladder Channel of Foot Shaoyangray72roNo ratings yet
- Zhongdu Gb-32: Middle DitchDocument1 pageZhongdu Gb-32: Middle Ditchray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 39Document2 pagesGB 39ray72roNo ratings yet
- Guangming Gb-37: Bright LightDocument2 pagesGuangming Gb-37: Bright Lightray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 36Document1 pageGB 36ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 34Document3 pagesGB 34ray72roNo ratings yet
- Zulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of TearsDocument2 pagesZulinqi Gb-41: Foot Governor of Tearsray72roNo ratings yet
- Yangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageYangjiao Gb-35: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 31Document2 pagesGB 31ray72roNo ratings yet
- Juliao Gb-29: Stationary CreviceDocument1 pageJuliao Gb-29: Stationary Creviceray72roNo ratings yet
- GB 30Document2 pagesGB 30ray72roNo ratings yet
- Toulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageToulinqi Gb-15: Gall Bladder Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Fuchs S Et Al. Pediatrics. 2016 138Document10 pagesFuchs S Et Al. Pediatrics. 2016 138Esteban RamosNo ratings yet
- Complications Druing HemodialysisDocument30 pagesComplications Druing HemodialysisMD Hajj83% (6)
- Comprehensive Nclex Notes - Easy To ReadDocument97 pagesComprehensive Nclex Notes - Easy To ReadBilal Yousuf98% (58)
- Internal Diseases Propedeutics Part I. Diagnostics of Pulmonary Diseases PDFDocument94 pagesInternal Diseases Propedeutics Part I. Diagnostics of Pulmonary Diseases PDFYashwanth vNo ratings yet
- NCP TahbsoDocument18 pagesNCP TahbsoUzziah Dharambai GurbuxaniNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet - Sodium Fluoride MSDSDocument6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet - Sodium Fluoride MSDSGodIsTruthNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical Medicine MCQ Set ADocument2 pagesIntroduction To Clinical Medicine MCQ Set AHimanshu Karmacharya100% (9)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument86 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Document5 pagesPart 2 Nclex Question and Answer 2020Joyce Corpuz100% (1)
- Clinical Methods in MedicineDocument556 pagesClinical Methods in MedicineVLd ADd100% (2)
- ATSHMADocument16 pagesATSHMAEgie Nugraha Fitriyan ApriyadiNo ratings yet
- Australian Triage ScaleDocument5 pagesAustralian Triage ScaleRhenty NarusNo ratings yet
- Shortness of BreathDocument17 pagesShortness of BreathChingHuaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- NP1 Dec 2012Document8 pagesNP1 Dec 2012Tatiana's CoutureNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisMelody B. Miguel0% (1)
- Report On COVID-19 Virus OutbreakDocument16 pagesReport On COVID-19 Virus OutbreakSara GuptaNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Indicators Guidance PaperDocument4 pagesPrognostic Indicators Guidance PaperirfanyNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange - NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange - NCPJaye DangoNo ratings yet
- KR 2003Document22 pagesKR 2003ruchipickleNo ratings yet
- OSCE NotesDocument4 pagesOSCE NotesHighschool AudiobooksNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaderic93% (60)
- Nishant Respiratory SecondDocument10 pagesNishant Respiratory SecondNishantNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationGiddel Guerra PapellerasNo ratings yet
- ABCDE Medical Student Session 10th May 2011Document42 pagesABCDE Medical Student Session 10th May 2011gedepambudi0% (1)
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Neil YoungNo ratings yet
- Acute Dyspnoea and Haemoptysis My Notes Add Jimmy's PDF Notes On & OrganiseDocument171 pagesAcute Dyspnoea and Haemoptysis My Notes Add Jimmy's PDF Notes On & OrganisewwwrgrobinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disease - A Case Study Approach To Patient Care PDFDrive PDFDocument536 pagesRespiratory Disease - A Case Study Approach To Patient Care PDFDrive PDFБ.ХалиунNo ratings yet
- NCP ThoracostomyDocument3 pagesNCP ThoracostomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Kombinasi Pursed-Lip Breathing Dan Guided Imagery Music TerhadapDocument7 pagesPengaruh Kombinasi Pursed-Lip Breathing Dan Guided Imagery Music TerhadapFaisal AmirNo ratings yet