Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endodontic Procedures
Uploaded by
Gienit Love BalangyaoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endodontic Procedures
Uploaded by
Gienit Love BalangyaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Clinical conference for Endodontic Procedure Monorooted Case
A. First appointment
Pre-treatment procedure
Diagnosis
B. Second appointment
Access Preparation and Pulp Extirpation
1. Tooth crown build-up
Materials:
4 basic instruments
High-speed Handpiece
Composite syringe light curing unit
Burs
Needle
Composite trimmer
Celluloid strips
Etchant
Applicator tips
Saliva ejector
Lidocanaine
Bonding agent
Plastic filling instrument
Procedure:
a. Remove the caries of the involved tooth
b. Inject anaedthetic solution of the patient cannot resist pain
c. Re-contour the tooth by using composite
2. Access preparation
Materials:
4 basic instruments high-speed handpiece
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Clamp holder
Rubber dam puncher
Burs (carbide #4 and #2)
Procedure:
a. Isolate the tooth using the rubber dam
b. Using the #4 bur start the access prep
c. De-roof the chamber walls to establish a straight line access to the can
al orifice
d. Check the access preparation for the presence of undercats using an eplo
rer
e. Smoothen the preparation
3. Pulp extirpation
Materials:
4 basic instruments
Smooth broach
Irrigating solution
2 disposable syringe
Barbed broach
Glass-bead sterilizer
Procedures:
a. Use a smooth broach to separate the pulp tissue to the canal walls
b. Use a barbed broach to extirpate the pulp tissue completely from the can
al
c. Make sure all instruments inserted into the canal have been sterilized u
sing the glass bead
d. Irrigate the canal with the irrigating solution, then aspirate properly
to remove the debris of the canal
4. Temporization
Materials:
4 basic instruments
Cotton pellets
Woodson filling instrument
Eugenol
Fermin
Paper points
Procedure:
a. After properly drying the canal dipped the cotton pellet at the eugenol
b. Squeeze-out the excess liquid properly
c. Place it into the canal
d. Place a sterilized cotton at the canal orifice
e. Pack the access preparation with fermin, it should be 3mm thick from the
canal orifice to the outer surface of the tooth contour and remove excess
f. Remove the rubber dam isolation
C. Third appointment
Canal preparation
1. Working length determination
Materials:
4 basic instruments
Diagnostic wire
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Clamp holder
Rubber dam puncher
Burs (carbide #4and #2)
Dental floss
Ruler 2 disposable syringe
Rubber stopper
x-ray films
hemostat
irrigating solution
paper points
Procedures:
a. Isolate the tooth
b. Irrigate the canal to flush out debris and then aspirate
c. Insert the diagnostic wire with a rubber stopper in one of the canal the
n take a radiograph
d. Compute for the working length
e. Compute for the working length
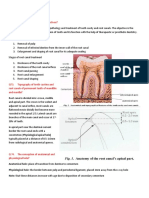
*AWL= measurement from the tip of the file/ diagnostic wire to the rubber stoppe
r, outside of the tooth
*TLI=measured on the radiograph, from the external reference point to the apex o
f the tooth
*SW=measured on the radiograph, from the tip of the file or diagnostic wire to t
he rubber stopper
* It always required using the safety factor since the DCJ is located 0.5 to 1 m
m below the radiographic apex
f. Get a ruler to measure the diagnostic wire and image of the radiograph
g. Record the working length
2. Canal enlargement
4basic instrument
Irrigating solution
Cotton pellet
3 disposable syringes
Pro-taper files
Glass-bead sterilizer
Woodson filling instrument
Fermin
Eugenol
Ruler
Paper point
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Clamp holder
Rubber dam puncher
Procedure:
a. Designate the WL on each pro-taper files using the rubber stopper
b. Enlarge the canal with pro-taper
c. Irrigate with sodium hypochlorite solution and then file once trhen aspi
rate to flush out thr debris
d. When a certain pro-taper reach the WL radiograph with the pro-taper insi
de the canal. This will be the ABI or apical binding instrument
e. Every time you file use the step: irrigate, file and aspirate
f. The last instrument (from abi the 3rd file) which can be enlarge the can
al enough is the MAF or master apical file
g. Irrigate the canal properly and aspirate/ dry the canal properly before
closing
h. Put the temporization
i. Remove the isolation
D. Fourth appointment
Check the canal status/ irrigate & aspirate
Materials:
4 basic instruments
Fermin
Rubber dam sheet
Clamp holder
Rubber dam puncher
Glass-bead sterilizer
Irrigating solution
Poaper points
2 disposable syringe
Procedure
a. Isolate the tooth
b. Prepare sterilized paper points mark the WL of the canal
c. Remove temporary filling
d. Insert the paper point one at a time to check the canal status. Observe
whether it is wet or dry, presence of pus, blood, sticky subs, foul odor
e. Irrigate and aspirate the canal
f. Temporization
g. Remove the isolation
E. Fifth appointment
Bacteriologic examination
Materials
4 basic instruments
Dental floss
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Clamp holder
Rubber dam puncher
Cotton pellets
Glass bead
3 disposable syringes
Fermin
Eugenol
Irrigating saolution
Paper points
Test tube
Media-broth
Petri dish
Procedure:
a. Isolate the tooth
b. Prepare sterilized paper points mark the WLK of the canal
c. Remove the temporary fiolling
d. Insert the paper point one at the time to check the canal status. Observ
e whether iut is wet, dry, presence of pus, blood, stricky subs, foul odor.
e. On the third paper point after placing and removing ot on thr canal inse
rt it on 1 of the test tube (all containing media)
f. Place them on the incubator for 24hrs
g. Irrigate and aspirate thje canal
h. Temporization
i. Remove the isolation
F. Sixth appointment
Obturation
1. Evaluation for obturation.
Procedure:
a. Check the test tube for change in color or presence of precipitate, if a
ll dont have any change obturation follows
2. Obturation
Materials:
4 basic instruments gutta percha
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Rubber dam puncher
Clamp holder
Denatured alcohol
Glass bead sterilizer
Woodson filling instruments
ZOE cement
Glass slab
Cement spatula
Dental floss
Alcohol lamp
Lentullo filler
X-ray film
Procedure:
a. Choose the size of the master cone size of the MAF at it WL
b. A tug-back should be felt as the gutta percha have reached the WL in ord
er to do this reduce the length of the gutta percha by cutting 1mm to its end un
til a tug-backis achieve
c. Radiograph the tooth to check if gutta percha have reached the apex
d. Lateral condensation technique:
e. Mix ZOE (slow setting) on a glass slab dip the lentullo filler on the ce
ment and spread it on the canal
f. Insert the next possible size of the gutta perch apt into the canal
g. Use the finger spreader to condense the gutta percha
h. Continue until the canal is completely filled with gutta percha pts
i. Take a radiograph to see if there is still a space inside the canal
j. Do the same procedure to other canals
k. If it iscompletley sealed, cut the excess gutta percha using a headted w
oodson filling instrument
l. Heat the spoon excavator to get the excess gutta percha. The gutta perch
a should be at the level of canal orifice
m. Temporization
n. Remove the isolation
G. Seventh appointment
Canal impression
1. Apical cone reduction
Material:
4 basic instrument
2 disposable syringe
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Rubber dam puncher
Clamp holder
Chloroform
Irrigating solution
x-ray films
k-files
fermin
cotton pellets
procedure:
a. Remove the isolation
b. From the WL minus 5 and designate it on the smallest K-file by using a r
ubber stopper
c. Place a cotton on the K-file
d. Dip the file on the chloroform and proceed to reducing the set gutta-per
cha
e. Do this until it reaches the rubber stopper
f. Radiograph the tooth to check if the reduction is enough
g. If the reduction is already finished irrigate the canal with the irrigat
ing solution to remove excess chloroform
h. Properly dry the canal by aspirating properly and placing paper points
2. Canal impression
Materials:
4 basic instrument
Tooth pick
Rubber dam sheet
Rubber dam frame
Rubber dam puncher
Clamp holder
Dropper lentullo-filler
Self-cured acrylic resin
Glass slab
Petroleum jelly
Procedure:
a. If tooth build-up has been done (G.I. or composite) remove it
b. Prepare the tooth (same as how to prepare the tooth for a jacket crown)
c. From the radiograph designate the width of the tooth pick so that it can
be inserted into the canal and also have the sufficient space for the acrylic t
o be placed
d. Using a lentullo-filler place a petroleum jelly into the canal so that t
he acrylic would not sick and the impression can be removed easily. Petroleum je
lly also on the tooth surface
e. Insert the trimmed tooth pick into the canal carefully
f. Using salt and pepper techniques place acrylic on the tooth-pick and whe
n in the sticky stage insert it into the canal for it to be in the rubber stage
so upon removal the impression would still have the impression of the canal
g. After the canal impression is finished, if the build-up of tooth has bee
n done and removed restoration but it should be shape as a P.F.J.C
h. Remove the impression check for excess and if there is place again on th
e tooth and remove and smoothen it
i. Remove the impression
j. Insert the temporary crown and adjust it so that there is no contact dur
ing bitting
k. Place a dry cotton pellet into the orifice of the canal
l. Place temporary cement on the crown and insert it properly, remove exces
s and check the bite again
H. Eight appointment
Crown restoration
1. Post and core
2. Porcelain jacket crown
I. Final appointment
Recall system
1. Recall
2. A. the patientis advice to return after a montyh for the recall.
(make sure you pray, and ask God to convince your patient to come backheheheheheh
)
You might also like
- Root Canal Treatment TechniquesDocument11 pagesRoot Canal Treatment TechniquesJailan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Isolation in Endodontics: Moisture Control and Soft Tissue RetractionDocument9 pagesIsolation in Endodontics: Moisture Control and Soft Tissue RetractionBlack Hack HakerNo ratings yet
- Endodontic Review ExamDocument1 pageEndodontic Review ExamShoyo HinataNo ratings yet
- Rubber Dam: Presented By: Cheng Yung Yew P11132Document38 pagesRubber Dam: Presented By: Cheng Yung Yew P11132lupusebastianNo ratings yet
- Special TrayDocument35 pagesSpecial TraypragatiNo ratings yet
- Impressions for Fixed Partial DenturesDocument53 pagesImpressions for Fixed Partial DenturespragatiNo ratings yet
- حDocument30 pagesحZakria Al-HadadNo ratings yet
- 3 - Taping Technique ProtocolDocument65 pages3 - Taping Technique ProtocolAlexis Nacionales AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- RUBBER DAM PRESENTATIONDocument38 pagesRUBBER DAM PRESENTATIONphil wuNo ratings yet
- N116-Skills Performance Checklist: Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesN116-Skills Performance Checklist: Tracheostomy CareAlessandra Dominique MarianoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning and Shaping TechniquesDocument26 pagesCleaning and Shaping TechniquesRohan Bhagat100% (1)
- Tracheostomy CareDocument4 pagesTracheostomy CareEriel Custodio Quijada100% (2)
- Endodontics: Obturation of Root Canal SystemsDocument5 pagesEndodontics: Obturation of Root Canal SystemsAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Isolation TechniquesDocument2 pagesIsolation TechniquesVinceNo ratings yet
- Endo ObturationDocument83 pagesEndo ObturationBețiu CornelNo ratings yet
- ACCESS CAVITY PREPARATION GUIDELINESDocument35 pagesACCESS CAVITY PREPARATION GUIDELINESShaheen Aboobacker Reniya ShaheenNo ratings yet
- Impression Tech in FPDDocument51 pagesImpression Tech in FPDDrGagandeep Singh100% (3)
- PRS NGTDocument7 pagesPRS NGTMika Marielle TrincheraNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF EndodonticsDocument23 pagesPRINCIPLES OF EndodonticsDexter BraveNo ratings yet
- Flasking ProcedureDocument5 pagesFlasking ProcedureAlma Mutiarani100% (1)
- Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesTracheostomy CareKate Chavez100% (1)
- Sample Prometric Dental MCQ BookletDocument12 pagesSample Prometric Dental MCQ BookletMrunal Doiphode80% (15)
- Conservative Adhesive Resin Restoration (CAR) Is An Updated Term Given ToDocument3 pagesConservative Adhesive Resin Restoration (CAR) Is An Updated Term Given ToSanchit RaoNo ratings yet
- DHA April-2019 DentalDocument3 pagesDHA April-2019 DentalSubhajit SahaNo ratings yet
- BDS Final Professional Exam MCQs on Operative Dentistry and EndodonticsDocument11 pagesBDS Final Professional Exam MCQs on Operative Dentistry and Endodonticsammarstein89No ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care: Surgical Ward Matalines - Mua - Rangas - Tan.SDocument15 pagesTracheostomy Care: Surgical Ward Matalines - Mua - Rangas - Tan.SMARIANN JEAN ANDREA CULANAG MATALINESNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13Document2 pagesExperiment 13the horxNo ratings yet
- Exercise 10Document2 pagesExercise 10triciaNo ratings yet
- Impression in FPDDocument9 pagesImpression in FPDAmar Bhochhibhoya100% (1)
- 3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeDocument3 pages3 Assisting in A Crown or BridgeVNo ratings yet
- The Prosthodontic Management of Endodontically Treated Teeth - A Literature Review. Part II. MaintDocument3 pagesThe Prosthodontic Management of Endodontically Treated Teeth - A Literature Review. Part II. MaintkochikaghochiNo ratings yet
- Ravi Varma Sir PublicationDocument9 pagesRavi Varma Sir PublicationSharas GovindoolNo ratings yet
- Biosand Filter CAWST Part6Document10 pagesBiosand Filter CAWST Part6alang_businessNo ratings yet
- KAYAK MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR GUIDEDocument5 pagesKAYAK MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR GUIDEScott NelsonNo ratings yet
- Q72. Endodontics, Its Goal and Objectives?Document12 pagesQ72. Endodontics, Its Goal and Objectives?jimmyNo ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6badr abdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Sample Only Nso - Tracheostomy CareDocument5 pagesSample Only Nso - Tracheostomy CareNader Abdurasad100% (1)
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledMashkat AbdelwahabNo ratings yet
- Sampling and testing lime proceduresDocument44 pagesSampling and testing lime proceduresLucio Rodriguez SifuentesNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy CareDocument41 pagesTracheostomy CareBautista Aubergine100% (2)
- LABREP 7a - DAVIDDocument13 pagesLABREP 7a - DAVIDKristina DavidNo ratings yet
- Non Surgical RetreatmentDocument6 pagesNon Surgical Retreatmentمحمد صلاحNo ratings yet
- Dental Instrument Identification and Tray Setup GuideDocument69 pagesDental Instrument Identification and Tray Setup GuideIndrani Das100% (2)
- EndoPerio 006Document9 pagesEndoPerio 006kapawenkNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Tle 7 Nail Care ServicesDocument3 pagesSummative Test in Tle 7 Nail Care ServicesRAE SEAN CATANNo ratings yet
- How to Take a Sample for Luminescence DatingDocument3 pagesHow to Take a Sample for Luminescence DatingqzxvNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy CareDocument8 pagesTracheostomy CareAlvin L. RozierNo ratings yet
- Tissue Management and Impression MakingDocument55 pagesTissue Management and Impression MakingRamya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Isolation in Restorative DentistryDocument49 pagesIsolation in Restorative DentistrySusan100% (1)
- Dr. Raed Pedodontics Partial PulpectomyDocument2 pagesDr. Raed Pedodontics Partial PulpectomyhusseinNo ratings yet
- Sampling Bituminous Mixture From Behind The Paver: 1. GeneralDocument2 pagesSampling Bituminous Mixture From Behind The Paver: 1. GeneralDilhara WickramaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Providing Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesProviding Tracheostomy CareMitul Peter100% (1)
- Suctioning Techniques and ProceduresDocument12 pagesSuctioning Techniques and ProceduresHannah Clarissa Faith AguilarNo ratings yet
- Impression Tech in FPDDocument50 pagesImpression Tech in FPDDrGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Try inDocument18 pagesChapter 06 Try inمحمد حسنNo ratings yet
- Cementum in Health and Disease: Dr. Anjali Kapoor Prof. & Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral Implantology GDC, JaipurDocument98 pagesCementum in Health and Disease: Dr. Anjali Kapoor Prof. & Head Dept. of Periodontology and Oral Implantology GDC, JaipurlkjhgfdsalkNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Three-Dimensional Analysis ofDocument11 pagesPreliminary Three-Dimensional Analysis ofAndrea Cárdenas SandovalNo ratings yet
- اسئلة امتحان الفصل الاول حشوات الجذورDocument7 pagesاسئلة امتحان الفصل الاول حشوات الجذورJowan EmadNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment Planning: From Problem List To Specific PlanDocument69 pagesOrthodontic Treatment Planning: From Problem List To Specific PlanAtika Iftikhar Mir50% (2)
- RPD QuestionsDocument77 pagesRPD QuestionsDontoNo ratings yet
- Rubber DamDocument15 pagesRubber DamSara MahmoudNo ratings yet
- UK Dental Plan GuideDocument2 pagesUK Dental Plan GuideAlexandra GaborNo ratings yet
- Ap, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayDocument30 pagesAp, Lrrsisal of Roentgenograph, Ic: I SsayMindaugasStacevičiusNo ratings yet
- Molar Distalization: Presenter R.Harshitha II Year PGDocument91 pagesMolar Distalization: Presenter R.Harshitha II Year PGVijay ChinthaNo ratings yet
- Tratment of The Plaque-Induced GingivitisDocument10 pagesTratment of The Plaque-Induced GingivitisPragita Ayu SaputriNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Document143 pagesAtlas of Oral Histology 2nbsped 9788131254844 8131254844Dhikra PikaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2018Document9 pagesJurnal 2018Rizqa MahdynaNo ratings yet
- Cons Endo Long AnsDocument72 pagesCons Endo Long AnssamikshaNo ratings yet
- Ojsadmin, 228Document7 pagesOjsadmin, 228Dr Tarak ChavadaNo ratings yet
- Manual Bio Art 4000sDocument22 pagesManual Bio Art 4000sArchitNo ratings yet
- Retention and Resistance of Preparations For Cast RestorationsDocument19 pagesRetention and Resistance of Preparations For Cast RestorationsMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- 2005 - Stavridakis - Immediate Dentin Sealing of Onlay Preparations - Thickness of Pre-Cured Dentin Bonding Agent and Effect of Surface CleaningDocument11 pages2005 - Stavridakis - Immediate Dentin Sealing of Onlay Preparations - Thickness of Pre-Cured Dentin Bonding Agent and Effect of Surface CleaningAndreea BorislavschiNo ratings yet
- Prezzano 1951Document10 pagesPrezzano 1951Rockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fractured Root Tips During Dental Extractions and Retained Root Fragments. A Clinical Dilemma?Document7 pagesFractured Root Tips During Dental Extractions and Retained Root Fragments. A Clinical Dilemma?DrAshish KalawatNo ratings yet
- Determination of Occlusal Vertical Dimension For Complete Dentures Patients: An Updated ReviewDocument12 pagesDetermination of Occlusal Vertical Dimension For Complete Dentures Patients: An Updated ReviewJohnNo ratings yet
- Immediate Dentin Sealing Supports Delayed Restoration PlacementDocument9 pagesImmediate Dentin Sealing Supports Delayed Restoration PlacementclaudiaNo ratings yet
- EXODONTIADocument80 pagesEXODONTIAcity9848835243 cyber67% (3)
- Biomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethDocument13 pagesBiomechanical Considerations For The Restoration of Endodontically Treated TeethSoraya BouchammaNo ratings yet
- Dental CementsDocument46 pagesDental CementsHammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes 2.0Document56 pagesNotes 2.0ploy_sciNo ratings yet
- 16 MFDS Reading ListDocument3 pages16 MFDS Reading ListMohamed Vandetta100% (1)
- DENTAL FORM Teaching and Non Teaching 2Document2 pagesDENTAL FORM Teaching and Non Teaching 2Connie JusosNo ratings yet
- Removable Partial Dentures (Olcay Sakar) PDFDocument282 pagesRemovable Partial Dentures (Olcay Sakar) PDFRakan Rabi100% (1)
- Tissue ConditioningDocument3 pagesTissue ConditioningNiska DarliantiNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (32)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)