Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Application of Enzymes in Health Care Industry
Uploaded by
Joan Christie WijayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Application of Enzymes in Health Care Industry
Uploaded by
Joan Christie WijayaCopyright:
Available Formats
Joan Christie W.
(11320120002)
Ong. Nicky Alexander (11320120006)
Aristya Wismoyo (11320120017)
Danika Augusta S. (11320120019)
Overview : Enzyme
Are naturally occurring bio-catalysts found in the living organisms
Combine molecules to produce new products or break molecule into smaller parts
Require specific conditions for efficient functioning like optimal temperature, pH,
concentration.
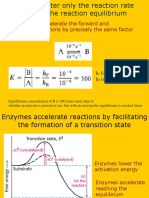
Lower activation energy (amount of energy required for reaction to occur)
Without enzymes, reactions would not occur fast enough to sustain life
Will only bind with certain substrates. Active site is where chemical reaction
occurs
Overview : Sources of Enzymes
Enzymes can be attained from animals (chimosin, pepsin, trypsin), plants (ficin, papain,
bromelain), or microorganisms (pectinases, glucoamylase, alpha amylase).
The reason for a tendency to use microbial enzymes on industrial scale :
plentiful supplied and producer can control all phases of the enzyme production
commercial enzyme preparation is well standardized
can often produce several different enzymes producer can operate the fermentation plant to shift
the production to one enzyme in detriment of the others coping with the market fluctuations
presents high growing capability huge amounts of enzyme can be produced in a
short period of time
can be genetically manipulated DNA recombinant technique to improve its enzyme
production capability
Overview : Enzyme Production
Commercially valuable enzymes are usually produced through processes such as
extraction from adequate sources, filtration, centrifugation, precipitation, purification,
drying, stabilization, standardization, and packaging
In biotechnology, all unit operations comprised between filtration and packaging are
generally said downstream processing
Enzymes of animal and plant origin are produced through maceration of tissues,
organs, leaves, and fruits - followed by extraction with water or organic solvent
Differently, microbial enzymes are attained from either prokaryotic
(bacteria) or eukaryotic (yeasts, fungi, mainly) cells cultured in a
liquid or semi-solid medium, carried out in a special reactor called
fermenter, being the process known as fermentation
Enzymes and Health Care Industries
Health care (medical) industry as generally consisting of :
hospital activities
medical and dental practice activities
other human health activities such as acupuncture and music therapy
health care equipment and services; and
pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and related life sciences.
Development of medical applications for enzymes have been at least as extensive
as those for industrial applications, reflecting the magnitude of potential rewards.
Variety of enzymes and their potential therapeutic applications are
considerable
At present, the most successful applications are extracellular : purely
topical uses, removal toxic substances and treatment of life-threatening
disorders within the blood circulation.
Topical Medication Uses
Enzymes is used in skin care products and especially used for exfoliation and
anti-inflammation.
For exfoliation :
Certain enzymes are effective exfoliants and can be gentler than other methods like scrubs
and microdermabrasion.
The upper layer of your skin is mostly made of dead skin cells containing keratin protein.
The enzymes work by specifically breaking down the keratin protein, resulting in smoother skin.
Enzymes can also penetrate the skin to help cleanse pores and improve skin tone and texture.
Look for fruit enzymes like papain (papaya), pineapple or blueberry.
Medical Application of Enzymes
There are four different types of uses for enzymes in medical case :
Analytical
Manipulative
Therapeutic
Industrial
With those uses, the treatment of pharmaceutical enzymes range from
detection to defection
Used in supplements and medication
There are both good and bad side-effect
Analytical Uses
Enzymes used as detector :
Enzymes can be used to detect and measure amounts of glucose in blood
Amount of glucose in blood and urine is an indicator for diagnosis of diabetes
Detected by using enzyme glucose oxidase
Catalyzes reaction between glucose and oxygen to form gluconic acid
Biosensor measures the produced gluconic acid and then indicated by a color change.
Enzymes used to diagnose disorders :
Enzymes of liver, kidney and other types leak into blood during related disorders.
Thus the corresponding enzyme presence in high levels in blood than normal
range indicates the specific disorder.
Enzyme Use
Aldolase muscle disorders
Glutamate oxalo acetate transfrerase myocardial infarction
Iso-citrate dehydrogenase acute hepatitis
Acid phosphatase prostate cancer
Manipulative Uses
The goal : make an enzyme that has improved properties to improve health
Changes created through : exchange of amino acids, modifications in enzymes
structure, and adding short peptide domains (that stabilize the enzyme and target
the cell membrane or DNA).
Most common genetic alterations are with the creation of enzymes; introducing
point mutations, exchanging protein domains, and changing the structure
Enzymes can also be manipulated by :
engineering fusion proteins
enzyme hybrids
recruit established functions and properties from existing enzymes and
incorporate them into the engineered enzyme.
Creation of hybrid enzymes can expand the potential uses of natural enzymes.
Enzymes, or fragments of enzymes, could potentially serve as building blocks for
proteins capable of catalyzing reactions not observed in nature
Therapeutic Uses
Enzymes used to treat disorders :
In some disorders like low blood pressure, head or spinal injuries, there are chances of
formation of blood clots due to stagnation of blood inside the blood vessels.
These clots can be life threatening as they can get stuck in small vessels of brain and obstruct
blood flow.
These clots can be removed only by dissolution by enzymes that can break them such as
Streptokinase or Urokinase.
Enzymes used to assist metabolism :
In old patients, digestive capacity is low due to low secretion of digestive enzymes
Hence their digestive system cannot metabolize some food materials efficiently.
In such cases they can experience malnutrition, constipation etc.
To aid digestion, enzymes like Papain are administered orally after food for easier
digestion.
Therapeutic Uses
Enzyme supplements for enzyme deficiencies :
Many of us suffer from milk intolerance mainly due to a genetic lack of the correct enzyme
secretion.
Milk intolerance usually relates to an inability to digest lactose (milk sugar).
Prolactazyme contains lactase and other milk digesting enzymes treats lactose intolerance.
Enzymes used to assist drug delivery :
Some drugs need to penetrate deeper tissues for better action.
For this some enzymes are used along with drugs in intra-muscular injection
forms to help proper penetration of tissues.
One of such enzyme is Hyaluronidase (a natural human enzyme present in human
sperm to help sperm penetrate uterine tissue and fertilize with ova).
The same enzyme is manufactured by rDNA technology and administered along with
drugs to enable efficient drug delivery to the target site.
Some Important Therapeutic Enzymes
Factors Severely Reduces Potential Utility of Enzymes as
Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
They are too large to be distributed simply within the body's cells
This is why enzymes have not yet been successful applied to large number of human genetic
diseases
To overcome this problem : ex : enzymes covalently coupled to target-specific monoclonal
antibodies are being used to avoid non-specific side-reactions
Their effective lifetime within circulation may be only a matter of minutes
To overcome this problem : disguise using covalent modification, entrapment
of enzyme within artificial liposomes, synthetic microspheres, and red blood
cell ghosts
Although these methods are efficacious at extending the circulatory lifetime of
enzymes, they often cause increased immunological response and additionally
may cause blood clots
Factors Severely Reduces Potential Utility of Enzymes as
Therapeutic Agents for Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
Being generally foreign proteins to the body, they are antigenic and
can elicit an immune response which may cause severe and life-
threatening allergic reactions, particularly on continued use
To overcome this problem : disguising the enzyme as an apparently non-proteinaceous
molecule by covalent modification
Asparaginase, modified by covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol, has been shown
to retain its anti-tumour effect whilst possessing no immunosgenicity
Clearly the presence of toxins, pyrogens and other harmful materials within a
therapeutic enzyme preparation is totally forbidden
Effectively, this encourages the use of animal enzymes, in spite of their
high cost, relative to those of microbial origin
Application of Enzyme in Cancer Treatment
Asparaginase treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia
Tumor cells are deficient in aspartate-ammonia ligase activity, which restricts their ability
to synthesize the normally non-essential amino acid L-asparagine. Therefore, they are
forced to extract it from body fluids
Action of the asparaginase doesnt affect functioning of normal cells which are able to
synthesize enough for their own requirements, but reduce free exogenous concentration
and so induces a state of fatal starvation in susceptible tumor cells
A 60% incidence of complete remission has been reported in a study of almost 6000
cases of acute lymphocytic leukaemia
The enzyme is administered intravenously
It is only effective in reducing asparagine levels within the bloodstream,
showing a half-life of about a day (in a dog)
This half-life may be increased 20-fold by use of polyethylene glycol-modified
asparaginase
Industrial Uses Drug Manufacture
Immobilized enzymes are used in manufacture of many drugs and antibiotics
This is possible as enzymes convert the pro-drug molecules to drugs or starting
material to drugs
In production of Antibiotics:
Immobilized pencillinase is used in converting Pencillin-G or V to 6-amino pencillinic acid.(6-
APA).
From this 6-APA Ampicillin is produced using immobilized enzyme pencillamidase.
Other examples include: Bacitracin, tyrosine, nikkomycin are manufactured using
suitable immobilized enzymes.
In Production of Steroids:
Prednisolone is produced from cortisone using immobilized enzyme obtained
from curcuria lanata.
Industrial Uses Drug Manufacture
To produce amino acids:
Immobilised L-aspartase-4-decarboxylase enzyme helps in conversion of L-Aspartic acid to L-
Alanine an amino acid.
In production of L-DOPA:
L-DOPA is a drug used in treatment of Parkinsonism. This can be produced by
using immobilized enzyme -tyrosinase.
In production of : Co-enzyme-A (Vit-B5), Pro-insulin, interleukin-2,
prostaglandins, monoclonal anti-bodies.
To produce medicinal plant derivatives like anthraquinone
(a glycoside to relieve constipation).
References
Bheem. 2014. 12 Applications of Enzymes in Medicine, Food, & Other Industries. Retrieved
from : http://www.rajaha.com/applications-enzymes-role/ (7 September 2014).
Chaplin, M. 2014. Enzyme Technology : Medical applications of enzymes. Retrieved from :
http://www1.lsbu.ac.uk/water/enztech/medical.html (7 September 2014).
Madison, Michelle, Nancy, Peter and Vivian. 2014. Applications of Enzymes in the
Pharmaceutical Industry. Retrieved from : http://www.loreescience.ca/site/SBI4U/bioch
emistry/Applications%20of%20Enzymes%20in%20the%20Pharmaceutical%20Industry
.pdf (7 September 2014).
Nixon, A. E., Ostermeier, M., & Benkovic, S. J. 1998. Hybrid enzymes: manipulating enzyme
design. Trends in Biotechnology, 16 : 258 - 264.
Vitolo, M. 2012. Industrial Uses of Enzymes. Retrieved from : http://www.eolss.net/sample-
chapters/c17/e6-58-05-12.pdf (7 September 2014).
You might also like
- Biosynthesis of CarbohydratesDocument31 pagesBiosynthesis of CarbohydratesDaniella Pasilbas Sabac100% (2)
- Glycogenesis: DR Nazakat HussainDocument16 pagesGlycogenesis: DR Nazakat HussainMuhammad Jamal100% (1)
- Carbohydrates Lecture 1Document52 pagesCarbohydrates Lecture 1hafsaharshadNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: CarbohydrateDocument10 pagesBiochemistry: CarbohydrateAsif Hasan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Lysosomal Storage DiseaseDocument37 pagesLysosomal Storage Diseasehoria96No ratings yet
- Nature of Enzymes ClassificationDocument13 pagesNature of Enzymes ClassificationAbraham Oluwatimilehin IsaacNo ratings yet
- Protein TransportDocument13 pagesProtein TransportvmshanesNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes Speed Up Biochemical ReactionsDocument16 pagesHow Enzymes Speed Up Biochemical ReactionsZEE zee100% (2)
- Cell MembraneDocument100 pagesCell MembranephyMedza AppNo ratings yet
- Western BlottingDocument13 pagesWestern BlottingAshfaq Fazal100% (1)
- Difference between alpha and beta glucose structuresDocument3 pagesDifference between alpha and beta glucose structuresLeyla MajundaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Topic 3 (Part 1) Cell BiologyDocument71 pagesBiology: Topic 3 (Part 1) Cell BiologyHo Chung Yin100% (1)
- Mutations: Causes, Types and Genetic DisordersDocument18 pagesMutations: Causes, Types and Genetic DisordersSushanthNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDocument38 pagesTransport Across Cell MembraneViswadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Module 6 in BiochemistryDocument19 pagesModule 6 in BiochemistryjeromeNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED BIOCHEMISTRYDocument70 pagesADVANCED BIOCHEMISTRYCik Syin100% (1)
- Biomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeDocument49 pagesBiomolecules: Dr. Vishwajeet S. GhorpadeVishwajeet GhorpadeNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & ApoptosisDocument20 pagesThe Cell Cycle & ApoptosisSathiyaraj100% (4)
- BIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Document13 pagesBIO307 Lecture 3 (Introduction To Enzymes)Phenyo MmerekiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate FilamentsDocument4 pagesIntermediate FilamentsSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Protein Notes PDFDocument38 pagesProtein Notes PDFLUi Anne Mateo LatogNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument39 pagesProteinNICHOLE MOJELLO100% (1)
- Biochem Introduction A PDFDocument107 pagesBiochem Introduction A PDFDaevy Toribio AmdosNo ratings yet
- Reducing and Non-Reducing SugarDocument4 pagesReducing and Non-Reducing SugarAyunee ZulhasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Document16 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument14 pagesEnzymesLudho MadridNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument23 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismMSc Biotech/MicroNo ratings yet
- Signal TransductionDocument38 pagesSignal Transductionjuju100% (2)
- Lecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: CarbohydrateDocument24 pagesLecture Two: Carbohydrate Lecture Two: Carbohydratesaacid bashirNo ratings yet
- Cot CurveDocument16 pagesCot CurveVidyasagar Deshpande100% (1)
- Week 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument34 pagesWeek 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryPaula LouiseNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Document11 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Life Science: Biology's Core ConceptsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Life Science: Biology's Core ConceptsMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Affinity ChromatographyDocument3 pagesAffinity ChromatographyNithya Ram100% (1)
- LipidsDocument13 pagesLipidsalianaNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument25 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwaydyologsbaboyguyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intorduction To BiochemistryDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Intorduction To BiochemistryAnonymous cCCibZnQ1No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymesSanchit Dhyani100% (1)
- BIOC 307 Old Exam 1Document17 pagesBIOC 307 Old Exam 1Katie RoseNo ratings yet
- Western Blotting MicrsoftDocument45 pagesWestern Blotting MicrsoftSoNu de Bond100% (2)
- Endocrine System (Lecture)Document79 pagesEndocrine System (Lecture)roselle legsonNo ratings yet
- Glycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVDocument34 pagesGlycoproteins and Proteoglycans TTVcraigNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Document12 pagesSyllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Yuri PaderesNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDocument107 pagesGastrointestinal DrugsRezzmah Alicia Tomon KhadrawyNo ratings yet
- Lysosomes PresentationDocument53 pagesLysosomes PresentationCaroline Stephenson50% (2)
- BIO307 Lecture 5 (Enzyme Kinetics I)Document11 pagesBIO307 Lecture 5 (Enzyme Kinetics I)Phenyo Mmereki100% (1)
- Bacterial Resistance To AntibioticsDocument37 pagesBacterial Resistance To Antibioticscristi69230% (1)
- DNA Manipulative EnzymesDocument17 pagesDNA Manipulative EnzymesZain Ul AbedienNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ProteinsRegine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Practical Proteins and Amino Acids Identification PDFDocument23 pagesPractical Proteins and Amino Acids Identification PDFFarahDeebaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationDocument35 pagesEnzymes: A Protein With Catalytic Properties Due To Its Power of Specific ActivationAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial DisorderDocument55 pagesMitochondrial DisorderRaja DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDocument12 pagesLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Structure and Function: The Fluid Mosaic ModelDocument75 pagesCell Membrane Structure and Function: The Fluid Mosaic Modelvinay chaudhary100% (1)
- Carbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUDocument85 pagesCarbohydrates Slide-2 PHARM-D, SALUShahid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument23 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- Lipids Classification and FunctionsDocument37 pagesLipids Classification and FunctionsAngelica de TorresNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody InteractionsDocument8 pagesAntigen-Antibody InteractionsChong Aiklong0% (1)
- 4 ProteinsDocument23 pages4 Proteinsshibhi100% (1)
- Induced expression strategies and protocols for recombinant proteinsDocument61 pagesInduced expression strategies and protocols for recombinant proteinsAbhi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Hem Lab Microhematocrit F15Document10 pagesHem Lab Microhematocrit F15Joan Christie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Identification Flowcharts Bacteria - Bergey'sDocument8 pagesIdentification Flowcharts Bacteria - Bergey'sMicro BioNo ratings yet
- 221 Payment Procedures For New Student 1208301356Document10 pages221 Payment Procedures For New Student 1208301356Joan Christie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Am J Clin Nutr 2013 Kien 689 97Document20 pagesAm J Clin Nutr 2013 Kien 689 97Joan Christie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar 2014Document3 pagesAcademic Calendar 2014Joan Christie WijayaNo ratings yet
- Gabapantin and PregabalinDocument23 pagesGabapantin and PregabalinayushiNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Times Europe (2022-Feb)Document38 pagesOphthalmology Times Europe (2022-Feb)Erick CoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Questionnaire 2Document51 pagesPlumbing Questionnaire 2mcpayod100% (1)
- Combo Versus MonotherapyDocument44 pagesCombo Versus MonotherapyMihai Eugen FilipNo ratings yet
- Ocular Trauma: State of Illinois Trauma Nurse Specialist ProgramDocument38 pagesOcular Trauma: State of Illinois Trauma Nurse Specialist ProgramMayuha SaidNo ratings yet
- DRDDS 23Document8 pagesDRDDS 23Rockson SamuelNo ratings yet
- Nimesulide ODTDocument10 pagesNimesulide ODTMihai SebastianNo ratings yet
- Surgical Staplers: Circular / Linear / PPH / Linear CutterDocument24 pagesSurgical Staplers: Circular / Linear / PPH / Linear CutterRino KefasNo ratings yet
- Ohi Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageOhi Graphic Organizerapi-278298083No ratings yet
- BDD Module 2 - Maintenance2 PDFDocument14 pagesBDD Module 2 - Maintenance2 PDFHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Category-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.Document5 pagesCategory-Wise Opening & Closing Rank-Ayur - BHU Int.srikanth PosaNo ratings yet
- Budwig Cancer GuideDocument101 pagesBudwig Cancer Guidedora.oreiro9920No ratings yet
- 07 Lamp. VII ALAT KESEHATAN 2 PDFDocument19 pages07 Lamp. VII ALAT KESEHATAN 2 PDFDinan Bagja NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument46 pagesAcute PancreatitisLew NianNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument9 pagesAnxiety DisorderSatish KujurNo ratings yet
- Jaycees® Andjaycee® Women Care ... : Have Special Reason ToDocument6 pagesJaycees® Andjaycee® Women Care ... : Have Special Reason ToDianne BishopNo ratings yet
- Harbor City Behavioral Health Center BrochureDocument2 pagesHarbor City Behavioral Health Center BrochureAlfredo GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Enviro-Flo, Inc. Enviro-Chlor Tablet Chlorinator: Installation & Owner'S ManualDocument7 pagesEnviro-Flo, Inc. Enviro-Chlor Tablet Chlorinator: Installation & Owner'S ManualSteve DennisNo ratings yet
- 09 SterilizationDocument34 pages09 Sterilizationitung2350% (2)
- Perioperative Nursing Care PhasesDocument5 pagesPerioperative Nursing Care PhasesanjieNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal CystsDocument4 pagesThyroglossal CystsCondurache Ilie-AndreiNo ratings yet
- Health & Nutrition Classification of FoodDocument10 pagesHealth & Nutrition Classification of Foodg20kpNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Waste ManagementDocument14 pagesBiomedical Waste ManagementdivyeshkpatelNo ratings yet
- India Travel Health Guide for CliniciansDocument9 pagesIndia Travel Health Guide for CliniciansRumana AliNo ratings yet
- Practical Radiotherapy Planning, Fourth EditionDocument477 pagesPractical Radiotherapy Planning, Fourth EditionMehtap Coskun100% (12)
- Case Analysis SchizophreniaDocument2 pagesCase Analysis Schizophreniamark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Funcional Properties of Bioctive Peptides Derived From MeatDocument22 pagesFuncional Properties of Bioctive Peptides Derived From MeatJohanna RomeroNo ratings yet
- Case #2: Group CDocument27 pagesCase #2: Group CKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Administration of An Oxytocin Receptor Antagonist Attenuates SexualDocument7 pagesAdministration of An Oxytocin Receptor Antagonist Attenuates SexualAtlamaltaNo ratings yet
- What Is Malnutrition?: WastingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Malnutrition?: WastingĐoan VõNo ratings yet