Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQs
Uploaded by
Dr.TawheedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQs
Uploaded by
Dr.TawheedCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Desmoglein 1 is the antigen in which of the following autoimmune diseases of the skin:
1
Pemphigus foliaceus
2
Bullous impetigo
3
Dermatitis herpetiformis
4
Bullous pemphigoid
5
Pemphigoid gestationis
Q/Q(M)-482410 Report a Problem
Desmoglein 1 is the antigen in which of the following autoimmune diseases of the skin:
1
Pemphigus foliaceus
The antigen implicated in pemphigus foliaceus is Desmoglein 1. Desmoglein 1 is targeted in bullous
impetigo, but this is an infectious condition, not an autoimmune disease. The antigen in dermatitis
herpetiformis is transglutaminase 3. The antigens for both bullous pemphigoid and pemphigoid
gestationis are BPAG1 and BPAG2.
Q/Q(M)-482410 Report a Problem
What is the major component of the anchoring fibril?
1
Type I Collagen
2
Type III Collagen
3
Type IV Collagen
4
Type VII Collagen
5
Laminin 5
Q/Q(M)-478596 Report a Problem
What is the major component of the anchoring fibril?
4
Type VII Collagen
Anchoring fibrils are made of Type VII collegen. Anchoring plaques are made of Type IV collagen,
and interact with a network of Type I And Type III collagen fibers in the dermis.
Q/Q(M)-478596 Report a Problem
Red or blonde hair pigmentation primarily results from:
1
The presence of eumelanin
2
The absence of melanin
3
The presence of pheomelanin
4
The reduced activity of tyrosinase
5
The reduced activity of DOPA dehydroxylase
Q/Q(M)-474173 Report a Problem
2
Red or blonde hair pigmentation primarily results from:
3
The presence of pheomelanin
Hair color is determined by melanocytes. The melanocytic activity of follicular melanocytes is
coupled to anagen hair is only pigmented when it is growing. Pigment is produced in the matrix
area of follicle, above the follicular papilla. Eumelanin is the pigment of brown/black hairs, and
pheomelanin is the pigment of red/blonde hairs. Intensity of color is proportional to the amount of
pigment. The absence of pigment produces white hair, and markedly reduced pigment produces gray
hair.
Q/Q(M)-474173 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true in or associated with Apert Syndrome?
1
Secondary to a mutation in FGFR3
2
AR
3
Acne localized to buttocks and thighs
4
Cutaneous/ocular depigmentation
5
Synostoses
Q/Q(M)-482768 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true in or associated with Apert Syndrome?
5
Synostoses
Apert Syndrome is an AD syndrome secondary to a mutation in FGFR2. Also known as
acrocephlosyndactyly, this condition includes synostoses of the hands, feet, back and skull as well as
generalized acne. Mosaicism of this gene causes nevus comedonicus. There is associated cutaneous
and ocular hypopigmentation.
Q/Q(M)-482768 Report a Problem
Darier's sign is described as:
1
When an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface
2
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla
3
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin
4
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed along its margins
5
Disappearance of color when the lesion is pressed
Q/Q(M)-482673 Report a Problem
Darier's sign is described as:
3
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin is referred to Darier's sign and can be seen in systemic
mastocytosis or urticaria pigmentosa. Nikolsky sign can be seen when an intact epidermis shears away
from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface (seen in pemphigus vulgaris, staphylococcus
3
scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), and toxic epidermal necrosis). Spreading bulla phenomenon with
pressure on an intact bulla is referred to as Asboe-Hansen sign, commonly seen with pemphigus
vulgaris. Central depression within a lesion when squeezed is referred to as the dimpling sign and is
seen in dermatofibromas. Disappearance of color or blanching when the lesion is pressed is commonly
found on vascular lesions
Q/Q(M)-482673 Report a Problem
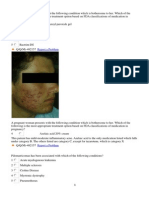
A salt split skin DIF is performed on a biopsy taken adjacent to the skin lesions shown. Where would
you expect staining to be seen?
1
Epidermal side
2
Dermal side
3
Epidermal and Dermal sides equally
4
In the lamina densa
5
In the anchoring plaques
Q/Q(M)-478135 Report a Problem
A salt split skin DIF is performed on a biopsy taken adjacent to the skin lesions shown. Where would
you expect staining to be seen?
1
Epidermal side
The image shown is bullous pemphigoid. On salt split skin DIF exams, deposits are seen on the
epidermal side of the split. If dermal deposits are seen, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita or anti-epiligrin
pemphigoid are potential diagnoses.
Q/Q(M)-478135 Report a Problem
During hair follicle development, the WNT signaling pathway is one of the earliest molecular
pathways involved in hair follicle initiation. What is the downstream mediator of WNT signaling?
1
Smoothened
2
Beta-catenin
3
Keratin 16
4
p53
5
HLA-B27
Q/Q(M)-482425 Report a Problem
4
During hair follicle development, the WNT signaling pathway is one of the earliest molecular
pathways involved in hair follicle initiation. What is the downstream mediator of WNT signaling?
2
Beta-catenin
Beta-catenin is the downstream mediator of WNT signaling. Through a series of signals, WNT
proteins inhibit the degradation of beta-catenin in the cytoplasm. After being translocated to the
nucleus, beta-catenin then forms a complex with LEF/TCF transcription factors, which ultimately
results in expression of downstream genes. Activation of this pathway is necessary for epithelium to
have the potential to develop a hair follicle.
Q/Q(M)-482425 Report a Problem
Which of the following glands is not under neural control?
1
Sebaceous glands
2
Apocrine glands
3
Eccrine glands
4
Salivary glands
5
Ceruminous glands
Q/Q(M)-476519 Report a Problem
Which of the following glands is not under neural control?
1
Sebaceous glands
Sebum is secreted continuously on the skin under hormonal glands. It contains squalene, cholesterol,
cholesterol esters, wax, and triglycerides.
Q/Q(M)-476519 Report a Problem
Regarding dermal-epidermal junction, which of the following statements is true:
1
There are no anchoring filaments in lamina lucida
2
Lamina fibroreticularis lies above lamina densa
3
Lamina fibroreticularis comprises of anchoring fibrils and the elastic microfibrils
4
Blood vessels cross the dermal-epidermal junction to reach the epidermis
5
Lamina lucida is an electron-dense layer
Q/Q(M)-481901 Report a Problem
Regarding dermal-epidermal junction, which of the following statements is true:
3
Lamina fibroreticularis comprises of anchoring fibrils and the elastic microfibrils
Lamina fibroreticularis comprises of anchoring fibrils and the elastic microfibrils. Lamina
fibroreticularis lies below lamina densa. Blood vessels don't cross the dermal-epidermal junction to
reach the epidermis. Basement membrane contain both: 1)Lamina basale which include a.lamina
lucida and b.lamina densa( which contain collagene IV & other glycoproteins like laminins,fibronectin
etc.) 2)Lamina fibroreticularis contain collagen type III and anchoring fibrils (collagen type VII)
Q/Q(M)-481901 Report a Problem
5
In the epidermis, the cell most responsible for antigen detection and processing is the:
1
Keratinocytes
2
Merkel Cell
3
Melanocyte
4
Langerhans cell
5
CD4+ T cell
Q/Q(M)-474167 Report a Problem
In the epidermis, the cell most responsible for antigen detection and processing is the:
4
Langerhans cell
The Langerhans cell is a bone narrow-derived, antigen-presenting cell found in all layers of the
epidermis, oral mucosa, esophagus, and vagina. Langerhans cells ingest and process antigens, mature,
migrate to a local lymph node, and then present the antigen to a nave (or resting) T cell, activating
that T cell. The Langerhans cell is central to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, allergic
contact dermatitis, and certain infections, such as Leishmaniasis.
Q/Q(M)-474167 Report a Problem
What is the significance of the critical line of Auber?
1
It is the location of the insertion of the erector pili muscle
2
the bulk of the mitotic activity in the hair occurs above this line
3
the inner root sheath is formed above this line
4
It is the widest diameter of the hair bulb
5
It is where keratinization first occurs in the hair
Q/Q(M)-480112 Report a Problem
What is the significance of the critical line of Auber?
4
It is the widest diameter of the hair bulb
The critical line of Auber is at the widest diameter fo the hair bulb. Below this line, the bulk of mitotic
activity that gives rise to the hair and the inner root sheath occurs. The erector pili muscle inserts in the
isthmus region of the follicle. Keratinization first occurs above this line.
Q/Q(M)-480112 Report a Problem
The finding on DIF that reflects binding of the Ro and La antigens in subacute cutaneous lupus
erythematosus is:
1
Granular fluorescence throughout the cytoplasm and nucleus of basal keratinocytes
2
Cytoid bodies
3
Immune deposits along the DE junction
6
4
Granular deposits along the basement membrane
5
A "chicken-wire" pattern within the epidermis
Q/Q(M)-478136 Report a Problem
The finding on DIF that reflects binding of the Ro and La antigens in subacute cutaneous lupus
erythematosus is:
1
Granular fluorescence throughout the cytoplasm and nucleus of basal keratinocytes
Granular fluorescence throughout the cytoplasm and nucleus of basal keratinocytes reflect the binding
of Ro and La antigens and is unique to SCLE. Cytoid bodies and Immune deposits along dermal-
epidermal junction are seen in both DLE and SCLE. Granular deposits along the basement membrane
are seen in dermatitis herpetiformis and a chicken-wire pattern of staining is seen in pemphigus
vulgaris.
Q/Q(M)-478136 Report a Problem
Glomus cells are primarily found:
1
on hands/feet
2
on the trunk
3
on the lateral thighs
4
on the genital skin
5
on the face
Q/Q(M)-479250 Report a Problem
Glomus cells are primarily found:
1
on hands/feet
Glomus cells are derived from Susquet-Hoyer canals which function to shunt blood from the arterioles
to venules and are primarily found on hands and feet. There are two types of glomus tumors, solitary
and multiple. The solitary types tend to have paroxysmal pain which can be extreme. Multiple glomus
tumors can be a autosomally dominant trait with incomplete penetrance and are less likely to be
painful. Both have a predominance on the distal extremities, especially sub-ungual. Two tests are
helpful in diagnosing glomus tumors: Hildreth sign - disappearance of pain following application of a
tourniquet proximally. Love test - eliciting pain by applying pressure to a precise area with the tip of a
pencil.
Q/Q(M)-479250 Report a Problem
Desmosine and isodesmosine are typical amino acids found in:
1
Collagen fibers
2
Anchoring fibril
3
Elastic fibers
4
Heparan sulfate
7
5
Anchoring plaques
Q/Q(M)-478195 Report a Problem
Desmosine and isodesmosine are typical amino acids found in:
3
Elastic fibers
Desmosine and isodesmosine are typical amino acids found in elastic fibers. They crosslink fibrillin.
Anchoring fibrils are composed of collagen VII and collagen fibers and have the most typical amino
acids of proline and hydroxyproline. Heparan sulfate do not typically contain these amino acids.
Q/Q(M)-478195 Report a Problem
The most common type of pityriasis rubra pilaris in childhood is type:
1
I
2
II
3
III
4
IV
5
V
Q/Q(M)-482765 Report a Problem
The most common type of pityriasis rubra pilaris in childhood is type:
4
IV
Type IV, or circumscribed juvenile, accounts for 25% of total PRP cases. The most common type is
Type I, classical adult, which accounts for 55% of cases. Types II, III, and V account for less than
10% each.
Q/Q(M)-482765 Report a Problem
During embryogenesis, periderm cells of the fetus contain which of the following substances?
1
Ceramide
2
Glycogen
3
Free fatty acids
4
Porphyrins
5
Sebum
Q/Q(M)-476552 Report a Problem
During embryogenesis, periderm cells of the fetus contain which of the following substances?
2
Glycogen
In week 7 of embryogenesis the surface ectoderm produces two layers. The external layer is the
periderm which contains glycogen and gives rise to the stratum corneum by week 21. The other layer
is the stratum germinativum.
8
Q/Q(M)-476552 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the buccal mucosa and vermilion border of the lips?
1
Montgomery's tubercles
2
Tysons glands
3
Zeis glands
4
Meibomian glands
5
Fordyce's spots
Q/Q(M)-482657 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the buccal mucosa and vermilion border of the lips?
5
Fordyce's spots
Fordyce's spots are located on the buccal mucosa and vermilion border of the lips. Montgomery's
tubercles are present on the areola, Tyson's glands on the labia minora and glans, meibomina and
Zeis glands are present on the eyelids.
Q/Q(M)-482657 Report a Problem
Itch is most commonly transmitted by:
1
C-polymodal nociceptor class nerves
2
A-delta class nerves
3
A-beta class nerves
4
Parasympathetic postganglionic fibers
5
A-beta and A-delta fibers
Q/Q(M)-480147 Report a Problem
Itch is most commonly transmitted by:
1
C-polymodal nociceptor class nerves
Itch is transmitted primarily by C-polymodal nociceptor class nerves. These are small diameter
unmyelinated nerves that carry pain, thermal, mechanical and pruritic stimuli. A-delta fibers carry
pain, thermal, mechanical and in some cases pruritic stimuli. A-beta fibers carry light touch and
motion stimuli. Parasympathetic post-ganglionic fibers do not contribute to cutaneous pruritus
Q/Q(M)-480147 Report a Problem
Which of the following make up the major protein of the cornified cell envelope?
1
Loricrin
2
Involucrin
3
Envoplakin
9
4
Filaggrin
5
Laminin V
Q/Q(M)-478168 Report a Problem
Which of the following make up the major protein of the cornified cell envelope?
1
Loricrin
Loricrin is the major protein component of the cornified cell envelope (CE). Involucrin is cross-linked
by transglutaminase in the granular layer to form an insoluble cell boundary. Envoplakin may link the
CE to desmosomes and to keratin filaments. Filaggrin is thought to promote aggregation and disulfide
bonding of keratin filaments in CE. It is degraded into urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid.
Both of which hydrate the stratum corneum and block UV radiation. Laminin V is found in the
basement membrane and is not involved in the formation of the cornified cell envelope.
Q/Q(M)-478168 Report a Problem
In epidermolysis bullosa simplex, where on the blister does the signal localize on a salt split skin test?
1
Roof
2
Floor
3
Middle
4
Diffuse
5
No localization
Q/Q(M)-482782 Report a Problem
In epidermolysis bullosa simplex, where on the blister does the signal localize on a salt split skin test?
1
Roof
In dystrophic EB the signal localizes to the roof of the blister. In junctional EB, the roof has BPAG2
while the floor has type IV collagen.
Q/Q(M)-482782 Report a Problem
The major protein component of the cornified envelope is:
1
Envoplakin
2
Desmoplakin
3
Plectin
4
Loricrin
5
Transglutaminase
Q/Q(M)-474160 Report a Problem
The major protein component of the cornified envelope is:
4
Loricrin
10
Loricrin is the major component of the cornified envelope (CE). The proteins of the CE are
synthesized in the spinous and granular layers. The CE is primarily a protein/lipid polymer formed
within the differentiating layer of keratinocytes. The CE eventually exists outside of the cornified cells
after the granular cell undergoes a programmed destruction (apoptosis). Self-destructing granular cells
are called transition cells.
Q/Q(M)-474160 Report a Problem
All of the following are true regarding the formation of hair except:
1
The inner root sheath keratinizes by means of trichohyalin granules
2
Henles layer is outside of Huxleys layer
3
The outer root sheath is a downward extension of the epidermis
4
Huxleys layer contains melanin
5
The hair matrix becomes the hair and the inner root sheath
Q/Q(M)-477327 Report a Problem
All of the following are true regarding the formation of hair except:
4
Huxleys layer contains melanin
The inner root sheath is composed of three layers, which are the inner root sheath cuticle, Huxley
layer, Henle layer. None of these layers contain melanin. All three layer keratinize by trichohyaline
granules and disintegrate when they reach the isthmus of the hair follicle.
Q/Q(M)-477327 Report a Problem
Choose the correct answer regarding melanin and skin color:
1
In black and brown skin the melanosomes are smaller in diameter and length
2
Facultative skin color is the amount of cutaneous melanin pigment generated according to
cellular genetics
3
In white skin the melanosomes form groups within the secondary lysosomes
4
Eumelanin produces a yellow chromophore
5
The number of melanocytes increases with one exposure to UVA/visible light
Q/Q(M)-478573 Report a Problem
Choose the correct answer regarding melanin and skin color:
3
In white skin the melanosomes form groups within the secondary lysosomes
Melanocytes of dark skin synthesize melanosomes larger than those produced in light skin. The
number of melanocytes in the epidermis is the same, regardless of the person's race or color: it is the
number and size of the melanosomes or pigment granules, continuously synthesized by these
melanocytes, that determine differences in skin color. The size of th melanosome is the principle factor
in determining how the melanosomes will be distributed within the keratinocytes. The larger the
melanosomes of dark skin are individually dispersed within the cytoplasm of keratinocytes: smaller
melanosomes of light skin are packaged in membrane-bound complexes within keratinocytes.
11
Eumelanin is in dark oval melanosomes found in black hair
Q/Q(M)-478573 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands form a lipid-rich substance called sebum and are usually associated with a hair
follicle. They secrete sebum by what mechanism?
1
Vacuolar exocytosis
2
Passive diffusion
3
Decapitation secretion
4
Autocrine secretion
5
Holocrine secretion
Q/Q(M)-482426 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands form a lipid-rich substance called sebum and are usually associated with a hair
follicle. They secrete sebum by what mechanism?
5
Holocrine secretion
Sebaceous glands form a lipid-rich substance called sebum and are usually associated with a hair
follicle. They secrete sebum by means of holocrine secretion which means that they exude lipids by
disintegration of entire sebocytes. Sebum contains numerous lipids including cholesterol, cholesterol
esters, triglycerides, squalene, and wax esters. Sebaceous glands are regulated by androgens and the
activity can be regulated by retinoids.
Q/Q(M)-482426 Report a Problem
At what estimated gestational age are all layers of the keratinized epidermis identifiable?
1
8 weeks
2
12 weeks
3
16 weeks
4
20 weeks
5
24 weeks
Q/Q(M)-478444 Report a Problem
At what estimated gestational age are all layers of the keratinized epidermis identifiable?
5
24 weeks
At 24 weeks, all the layers of the mature epidermis can be identified, and the epidermis is keratinized.
Q/Q(M)-478444 Report a Problem
The embryonic periderm becomes part of the
1
vernix caseosa
12
2
stratum corneum
3
stratum basale
4
dermis
5
hair follicle
Q/Q(M)-482554 Report a Problem
The embryonic periderm becomes part of the
1
vernix caseosa
During the second trimester of fetal development, the periderm is sloughed from most of the skin
surface revealing the underlaying epidermis. The periderm becomes part of the protective coating,
vernix caseosa, together with the shed lanugo, sebum and other amniotic fluid materials. Bolognia
p.38
Q/Q(M)-482554 Report a Problem
The main collagen component of the basement membrane is:
1
Collagen IV
2
Collagen III
3
Collagen I
4
Tenascin-X
5
Collagen VII
Q/Q(M)-479177 Report a Problem
The main collagen component of the basement membrane is:
1
Collagen IV
Collagen IV is the main collagen component of basement membranes. Collagen I is the main collagen
of mature dermis, bone and tendon. Collagen III is found in fetal skin, blood vessels and intestines.
Tenascin-X is mutated in some forms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and is not associated with the
basement membrane. Collagen VII makes up anchoring fibrils and amnion.
Q/Q(M)-479177 Report a Problem
Mast cells are derived from bone marrow ____+ cells?
1
CD3
2
CD6
3
CD20
4
CD34
5
CD68
Q/Q(M)-479248 Report a Problem
13
Mast cells are derived from bone marrow ____+ cells?
4
CD34
CD34+ cells in the bone marrow are the precursors of mast cells. CD3 and CD20 are T and B cell
markers respectively. CD6 is found on mononuclear phagocytic cells in the dermis, CD68 is a
macrophage marker.
Q/Q(M)-479248 Report a Problem
When do melanocytes begin to synthesize melanin?
1
2nd month of gestation
2
3rd month of gestation
3
4th month of gestation
4
5th month of gestation
5
6th month of gestation
Q/Q(M)-478591 Report a Problem
When do melanocytes begin to synthesize melanin?
2
3rd month of gestation
Melanocytes begin to synthesize melanin in the 3rd month of gestation.
Q/Q(M)-478591 Report a Problem
Which of the following cytokines are secreted from keratinocytes?
1
IL-2
2
IL-3
3
IL-17
4
IL-22
5
IL-23
Q/Q(M)-482402 Report a Problem
Which of the following cytokines are secreted from keratinocytes?
5
IL-23
IL-2 is a cytokine that primarily produced by T lymphocytes and acts on other T lymphocytes as a
growth factor for both survival and differentiation. IL-3 is also produced by T lymphocytes and acts as
a growth factor for cells of the myeloid lineage. IL-17 is an effector cytokine that is implicated in the
pathogenesis of psoriasis and produced by Th17 cells. IL-22 is also an effector cytokine produced by T
lymphocytes that contributes to epidermal acanthosis in psoriasis. All of these cytokines are not
secreted from epidermal keratinocytes. IL-23, which promotes Th17 effector function, is secreted by
epidermal keratinocytes and upregulated in psoriasis. The p40 subunit of IL-23 is the target of drug
14
ustekinimab used to treat psoriasis.
Q/Q(M)-482402 Report a Problem
Numerous neuromediators are involved in cutaneous neurobiology and many play a role in the
development of inflammation in the skin. One such mediator can be induced by application of
capsaicin to the skin. Which of the following is the correct neuromediator?
1
Noradernaline
2
Substance P
3
Neurokinin A
4
Acetylcholine
5
Pro-opiomelanocortin
Q/Q(M)-482432 Report a Problem
Numerous neuromediators are involved in cutaneous neurobiology and many play a role in the
development of inflammation in the skin. One such mediator can be induced by application of
capsaicin to the skin. Which of the following is the correct neuromediator?
2
Substance P
Substance P is a neuromediator that binds the tachykinin receptor. It is released upon stimulation of
sensory nerve fibers. It has numerous cutaneous functions, including development of skin edema,
erythema, and pruritus, upregulation of adhesion molecule expression, release of proinflammatory
mediators, etc. Capsaicin causes release of substance P. This has been utilized pharmacologically in
conditions such as zoster, in which consistent application of capsaicin leads to depletion of substance
P, which in turn can help to reduce/eliminate post-herpetic neuralgia. The other answer choices are
also neuromediators that are involved in cutaneous inflammation, but their release is not induced by
capsaicin.
Q/Q(M)-482432 Report a Problem
Tissue contraction begins:
1
At 3rd day of wound healing
2
During the 2nd week of wound healing
3
After the first month of wound healing
4
After the 3rd month of wound healing
5
After the 9th month of wound healing
Q/Q(M)-474176 Report a Problem
Tissue contraction begins:
2
During the 2nd week of wound healing
Wound healing tends to be a predictable process that begins initially with the inflammatory stage.
During this stage, clot formation occurs. This is the initial step in wound healing. Platelets, neutrophils
and macrophages all migrate to the wound and secrete many mediators of wound healing.
15
Epithelialization then begins hours after injury. This is followed by granulation tissue formation (four
days after injury) and angiogenesis (first week of repair). Wound contraction ensues during the second
week of healing.
Q/Q(M)-474176 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes have been shown to secrete all of the following cytokines except:
1
IL-1
2
IL-6
3
IL-8
4
TNF-alpha
5
IL-2
Q/Q(M)-478144 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes have been shown to secrete all of the following cytokines except:
5
IL-2
Keratinocytes have been shown to secrete all of the above cytokines, except IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-
gamma.
Q/Q(M)-478144 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not a specialized type of sebaceous gland?
1
Moll's gland
2
Meibomian gland
3
Gland of Zeis
4
Montgomery's tubercle
5
Fordyce spot
Q/Q(M)-476520 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not a specialized type of sebaceous gland?
1
Moll's gland
There are several types of specialized sebaceous glands that are not associated with a hair follicle.
They include Montgomery's areolar tubercle, Fordyce spots of the lip, Glands of Zeis of the cutaneous
eyelid, and Meibomian glands of the eyelid. Moll's gland of the eyelid are a modified apocrine gland.
Q/Q(M)-476520 Report a Problem
Which part of the nose is not innervated by V2 branch of Cranial nerve V?
1
nasal columella
16
2
nasal ala
3
nasal tip
4
nasal dorsum
5
all sensory of the nose is innervated by V2
Q/Q(M)-482911 Report a Problem
Which part of the nose is not innervated by V2 branch of Cranial nerve V?
3
nasal tip
This is innervated by the anterior ethmoidal branch of V1. The infraorbital nerve of V2 innervates the
nasal ala. The nasopalantine branch of V2 innervates the columella.
Q/Q(M)-482911 Report a Problem
Meibomian glands are:
1
Modified sebaceous glands
2
Found everywhere except on the palms and soles
3
Sebaceous lobules that feed into a lactiferous duct
4
Modified ceruminous glands
5
Modified apocrine glands
Q/Q(M)-480543 Report a Problem
Meibomian glands are:
1
Modified sebaceous glands
Meibomian glands of the eyelids are modified sebaceous glands. Sebaceous glands are found
everywhere on the skin except the palms and soles. Montgomery's areolar tubercles consist of several
sebaceous lobules feeding into a lactiferous duct. Ceruminous glands are apocrine glands of the
external ear canal. Apocrine glands in the eyelids are Moll's glands.
Q/Q(M)-480543 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum via:
1
Holocrine mechanism
2
Exocrine mechanism
3
Endocrine mechanism
4
Exostosis
5
Mecrocrine mechanism
Q/Q(M)-478594 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum via:
17
1
Holocrine mechanism
The sebaceous lobules have basal germinative cells and central sebocytes, which gradually become
more distended with lipid vacuoles until they are shed into the lumen (holocrine secretion).
Q/Q(M)-478594 Report a Problem
Asboe-Hansen Sign refers to:
1
When an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface
2
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla
3
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin
4
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed along its margins
5
Disappearance of color when the lesion is pressed
Q/Q(M)-482672 Report a Problem
Asboe-Hansen Sign refers to:
2
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla is referred to as Asboe-Hansen sign,
commonly seen with pemphigus vulgaris. Nikolsky sign can be seen when an intact epidermis shears
away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface (seen in pemphigus vulgaris, staphylococcus
scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), and toxic epidermal necrosis). Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking
the skin is referred to Dariers sign and can be seen in systemic mastocytosis or urticaria
pigmentosa. Central depression within a lesion when squeezed is referred to as the dimpling sign and
is seen in dermatofibromas. Disappearance of color or blanching when the lesion is pressed is
commonly found on vascular lesions
Q/Q(M)-482672 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the eyelids in association with eyelashes?
1
Montgomery's tubercles
2
Tysons glands
3
Zeis glands
4
Meibomian glands
5
Fordyce's spots
Q/Q(M)-482660 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the eyelids in association with eyelashes?
3
Zeis glands
Zeis glands are sebaceous glands associated with eyelashes. Montgomery's tubercles are present on the
areola, Tyson's glands on the labia minora and glans, and Fordyce's spots are located on the buccal
mucosa.
Q/Q(M)-482660 Report a Problem
18
During a salt split skin test, if the location of the deposition if found on the roof (lamina lucida),
which of the following could be a diagnosis?
1
Bullous pemphigoid
2
Anti-epiligrin cicatricial pemphigoid
3
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
4
Bullous eruption of lupus erythematosus
5
Bullous eruption of tinea
Q/Q(M)-482670 Report a Problem
During a salt split skin test, if the location of the deposition if found on the roof (lamina lucida),
which of the following could be a diagnosis?
1
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid is one of the many bullous diseases that may be found on the roof of the
blister, the others include pemphigoid gestationis, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, cicatricial
pemphigoid. The other answer (except for bullous tinea, in which a salt split would not be performed)
are those found on the floor of the blister (lamina densa).
Q/Q(M)-482670 Report a Problem
Which of the following markers are specific and reliable for Merkel cells?
1
CD20
2
HMB-45
3
CD34
4
CD3
5
CK20
Q/Q(M)-478192 Report a Problem
Which of the following markers are specific and reliable for Merkel cells?
5
CK20
Cytokeratin (CK) 20 is a reliable marker for Merkel cells. CD20 is a marker for B-cells and CD3 is a
T-cell marker. HMB-45 is used in staining for immature melanosomes and is reactive in melanoma.
CD34 is used to stain dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.
Q/Q(M)-478192 Report a Problem
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa results from mutations in:
1
Collagen type I
2
Collagen type II
3
Collagen type III
19
4
Collagen type V
5
Collagen type VII
Q/Q(M)-474179 Report a Problem
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa results from mutations in:
5
Collagen type VII
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa results from mutations in Type 7 collagen. Type I collagen
mutations are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta. Antibodies to Type II collagen are associated
with relapsing polychondritis. Mutations in type V collagen result in the classic form of Ehlers Danlos
while mutations in type III collagen result in the vascular form of Ehlers Danlos.
Q/Q(M)-474179 Report a Problem
Regarding the stratum germinativum (basale):
1
Intermediate filaments in basal cells insert into only hemidesmosomes
2
Keratins 1 and 10 are expressed
3
Not all basal cells have the potential to divide
4
Microfilaments assist in downward movement of cells
5
Plectins regulate adhesion and initiation of differentiation.
Q/Q(M)-478164 Report a Problem
Regarding the stratum germinativum (basale):
3
Not all basal cells have the potential to divide
Not all basal cells have the potential to divide. Stem cells give rise to transient amplifying cells which
give rise to the epidermal keratinocytes. Intermediate filaments in basal cells insert into desmosomes
and hemidesmosomes. Keratins 5/14 are predominantly expressed. Microfilaments assist in upward
movement of cells. Integrins regulate adhesion and initiation of differentiation.
Q/Q(M)-478164 Report a Problem
Merkel cells are mechanoreceptors found in areas of high-tactile sensitivity. This
immunohistochemical marker is restricted to Merkel cells in the skin and is thus a reliable marker for
these cells:
1
Keratin 7
2
Keratin 20
3
S-100
4
Factor XIIIa
5
LYVE-1
Q/Q(M)-482407 Report a Problem
20
Merkel cells are mechanoreceptors found in areas of high-tactile sensitivity. This
immunohistochemical marker is restricted to Merkel cells in the skin and is thus a reliable marker for
these cells:
2
Keratin 20
Keratin 20 is reliable immunohistochemical markers for Merkel cells as it is restricted to these cells in
the skin. Keratin 7 can be used as a marker for Paget's Disease. S-100 is frequently used to stain neural
cells and melanocytes. Factor XIIIa can be used to differentiate a dermatofibroma from
dermatofibroma sarcoma pertuberans (positive in DF; negative in DFSP). LYVE-1 is a marker for
lymphatics.
Q/Q(M)-482407 Report a Problem
A child presents with a 1 cm yellow-red nodule on the face. Pathology shows Touton giant cells. What
is the most frequent site of extracutaneous involvement in this disease?
1
Eye
2
Lung
3
Bone
4
CNS
5
Visceral
Q/Q(M)-482772 Report a Problem
A child presents with a 1 cm yellow-red nodule on the face. Pathology shows Touton giant cells. What
is the most frequent site of extracutaneous involvement in this disease?
1
Eye
The eye is the most frequent site of extracutaneous juvenile xamthogranuloma. The second most
common site of extracutaneous disease is the lungs. Ocular involvement is typically unilateral.
Q/Q(M)-482772 Report a Problem
Acral melanomas are particularly concerning because they:
1
Are diagnosed at a later stage
2
Invade perineurally
3
Cannot be resected
4
Metastasize frequently even at shallow Breslow depth
5
Do not respond to ipilimumab
Q/Q(M)-482761 Report a Problem
Acral melanomas are particularly concerning because they:
1
Are diagnosed at a later stage
Acral melanoma is problematic because it is diagnosed at a later stage. It accounts for 5-10% of all
21
melanomas.
Q/Q(M)-482761 Report a Problem
What does a western blot identify?
1
Protein
2
RNA
3
DNA
4
Genes
5
Cell membranes
Q/Q(M)-482774 Report a Problem
What does a western blot identify?
1
Protein
A northern blot identifies RNA and a southern blot identifies DNA.
Q/Q(M)-482774 Report a Problem
Which of the following groups of adhesion proteins are found in both the hemidesomsome-anchoring
filament complexes and lamina densa?
1
Plectin
2
Heparin sulfate proteoglycan
3
Laminin 5
4
Nidogen
5
Type VII collagen
Q/Q(M)-482666 Report a Problem
Which of the following groups of adhesion proteins are found in both the hemidesomsome-anchoring
filament complexes and lamina densa?
3
Laminin 5
Laminin 5 is found both in the hemidesomsome-anchoring filament complexes and lamina densa.
Plectin is found in the hemidesomsome-anchoring filament complexes. Heparin sulfate proteoglycan is
found only in the lamina densa, collagen VII in the sublamina densa, and nidogen in the lamina densa.
Q/Q(M)-482666 Report a Problem
Retinoids upregulate transcription of which types of collagen?
1
1 and 3
2
1 and 4
3
1 and 7
22
4
3 and 7
5
4 and 7
Q/Q(M)-477496 Report a Problem
Retinoids upregulate transcription of which types of collagen?
3
1 and 7
Retinoids upregulate the transcription of collagens one and seven thereby strengthening the dermis.
Q/Q(M)-477496 Report a Problem
As you move upward through the epidermis toward the stratum corneum, which of the following is
true?
1
calcium increases, phospholipids decrease, sphingolipids decrease
2
calcium increases, phospholipids increase sphingolipids increase
3
calcium increases, phospholipids decrease, sphingolipids increase
4
calcium decreases, phospholipids decrease, sphingolipids decrease
5
calcium decreases, phospholipids increase sphingolipids decrease
Q/Q(M)-482922 Report a Problem
As you move upward through the epidermis toward the stratum corneum, which of the following is
true?
3
calcium increases, phospholipids decrease, sphingolipids increase
Calcium increases, phospholipids decrease, sphingolipids increase. Calcium is needed for desmosome
formation and enzyme activation. Phospholipid content of epidermis decreases with differentiation but
neutral lipids and sphingolipids (ceramide) increase with differentiation.
Q/Q(M)-482922 Report a Problem
Nikolsky sign can be seen when:
1
When an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface
2
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla
3
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin
4
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed along its margins
5
Disappearance of color when the lesion is pressed
Q/Q(M)-482671 Report a Problem
Nikolsky sign can be seen when:
1
When an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface
Nikolsky sign can be seen when an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a
moist surface (seen in pemphigus vulgaris, staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), and toxic
23
epidermal necrosis). Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla is referred to as
Asboe-Hansen sign, commonly seen with pemphigus vulgaris. Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking
the skin is referred to Dariers sign and can be seen in systemic mastocytosis or urticaria
pigmentosa. Central depression within a lesion when squeezed is referred to as the dimpling sign and
is seen in dermatofibromas. Disappearance of color or blanching when the lesion is pressed is
commonly found on vascular lesions
Q/Q(M)-482671 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements is true about eccrine glands?
1
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers with acetylcholine as the principal neurotransmitter
2
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers with norepinephrine as the principal neurotransmitter
3
Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers with acetylcholine as the principal neurotransmitter
4
Postganglionic parasympathetic fibers with norepinephrine as the principal neurotransmitter
5
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers with both norepinephrine and acetylcholine as the principal
neurotransmitters
Q/Q(M)-478148 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements is true about eccrine glands?
1
Postganglionic sympathetic fibers with acetylcholine as the principal neurotransmitter
Eccrine glands are innervated by postganglionic sympathetic fibers with acetylcholine as the principal
neurotransmitter. This explains why medications associated with anticholinergic side effects may be
associated with hypohidrosis.
Q/Q(M)-478148 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes are derived from which of the following:
1
Endoderm
2
Mesoderm
3
Ectoderm
4
Neural Crest
5
Bone marrow precursors
Q/Q(M)-478205 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes are derived from which of the following:
3
Ectoderm
As implied by the root 'ecto', a prefix meaning "outer", the keratinocytes of the epidermis are derived
from the ectoderm. The other layers do contribute cell populations that are present in the skin.
Q/Q(M)-478205 Report a Problem
What is the most abundant collagen found on fetal skin?
24
1
Type I Collagen
2
Type II Collagen
3
Type III Collagen
4
Type IV Collagen
5
Type VII Collagen
Q/Q(M)-476514 Report a Problem
What is the most abundant collagen found on fetal skin?
3
Type III Collagen
Type III collagen is found in the fetal skin. It is also present in the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels,
and the basement membrane. A defect in this collagen results in the Ehlers-Danlos, vascular type.
Q/Q(M)-476514 Report a Problem
Which of the following diseases has decreased or absent lamellar granules?
1
Flegel's
2
Psoriasis
3
Lamellar ichthyosis
4
Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis
5
Pemphigus vulgaris
Q/Q(M)-480136 Report a Problem
Which of the following diseases has decreased or absent lamellar granules?
1
Flegel's
Flegel's disease has decreased or absent lamellar granules. AKA hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans,
this is a rare, possibly AD disorder with multiple disc-like keratotic papules predominenty on the distal
extremities and feet of older individuals (Bolognia, p 1714).
Q/Q(M)-480136 Report a Problem
Which of the following dermal cells always express CD11c and CD6?
1
Mononuclear phagocytic cells
2
Fibroblasts
3
Mast cells
4
Erythrocytes
5
Glomus cells
Q/Q(M)-478201 Report a Problem
25
Which of the following dermal cells always express CD11c and CD6?
1
Mononuclear phagocytic cells
The mononuclear phagocytic cell includes monocytes, macrophages and dermal dendrocytes. All
phagocytic skin macrophages express CD11c and CD6. Fibroblasts do not produce a CD marker. Mast
cells are derived from bone marrow-residing CD34+ stem cells. They do not produce CD11c or CD6.
Q/Q(M)-478201 Report a Problem
Direct immunofluorescence staining of intercellular spaces and the basement membrane zone, in
combination, is seen in:
1
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
2
Anti-epiligrin pemphigoid
3
Pemphigus vegetans
4
Pemphigus foliaceous
5
IgA pemphigus
Q/Q(M)-480545 Report a Problem
Direct immunofluorescence staining of intercellular spaces and the basement membrane zone, in
combination, is seen in:
1
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Paraneoplastic pemphigus and drug-induced pemphigus demonstrate direct immunofluorescence
staining of the intercellular space and the BMZ, in combination. Anti-epiligrin pemphigoid
demonstrates BMZ staining (dermal staining on salt-split skin). Pemphigus vegetans, pemphigus
foliaceous, and IgA pemphigus all show intercellular space deposition without staining of the BMZ.
Q/Q(M)-480545 Report a Problem
Where are glomus cells derived from?
1
Mesenchyme
2
Bone marrow
3
Susquet-Hoyer canal
4
Skeletal muscle
5
Dermis
Q/Q(M)-482279 Report a Problem
Where are glomus cells derived from?
3
Susquet-Hoyer canal
Glomus cells are vascular smooth muscle cells derived from the arterial portion of the glomus body, or
the Sucquet-Hoyer canal, which is an arteriovenous shunt in the dermis that contributes to temperature
regulation. Glomus are found primarily on the palms and soles and function to allow the rapid
shunting of blood from the arteioles to venules. Disease processes involving glomus cells include
26
glomus tumor and glomangioma.
Q/Q(M)-482279 Report a Problem
The antibody target in ocular cicatricial pemphigoid is also mutated in:
1
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa, Herlitz type
2
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
3
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with myotonic dystrophy
4
Dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
5
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia
Q/Q(M)-482337 Report a Problem
The antibody target in ocular cicatricial pemphigoid is also mutated in:
5
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia
JEB with pyloric atresia and ocular cicatricial pemphigoid both have mutations in Beta4integrin.
Herlitz type JEB is due to laminin 5. Recessive and dominant dystrophic EB is due to COL17A1 (type
VII collagen). JEB with myotonic dystrophy is due to plectin.
Q/Q(M)-482337 Report a Problem
Type VII collagen in found in anchoring fibrils and also in:
1
Fetal skin
2
Bone
3
Amnion
4
Aorta
5
Blood vessels
Q/Q(M)-480537 Report a Problem
Type VII collagen in found in anchoring fibrils and also in:
3
Amnion
Type VII collagen is present in anchoring fibrils and amnion. Fetal skin and blood vessels contain type
III collagen. The aorta contains type VI collagen. Bone contains type I collagen.
Q/Q(M)-480537 Report a Problem
1 melanocyte has contact with:
1
6 keratinocytes
2
12 keratinocytes
3
18 keratinocytes
4
30 keratinocytes
27
5
36 keratinocytes
Q/Q(M)-479181 Report a Problem
1 melanocyte has contact with:
5
36 keratinocytes
One melanocyte and 36 keratinocytes make up one epidermal melanin unit. This melanocytes transfers
pigment to these keratinocytes.
Q/Q(M)-479181 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true regarding BPAg1?
1
It is pathogenic in cicatricial pemphigoid
2
It is a member of the plakin family
3
It is pathogenic in pemphigoid gestationis
4
It is not pathogenic in paraneoplastic pemphigus
5
It coprecipitates with plakoglobin
Q/Q(M)-480540 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true regarding BPAg1?
2
It is a member of the plakin family
BPAg1 is a member of the plakin family, which includes envoplakin, periplakin, desmoplakin, plectin,
and BPAg1. BPAg2 is pathogenic in cicatricial pemphigoid and pemphigoid gestationis. BPAg1 is
pathogenic in paraneoplastic pemphigus. Desmoglein 3 is pathogenic in pemphigus vulgaris and
coprecipitates with plakoglobin.
Q/Q(M)-480540 Report a Problem
Surgery, Parturition, Fever, Kwashiokor and Hypervitaminosis A are all causes of:
1
Telogen effluvium
2
Anagen effluvium
3
Alopecia areata
4
Androgenetic alopecia
5
Both telogen and anagen effluvium
Q/Q(M)-478017 Report a Problem
Surgery, Parturition, Fever, Kwashiokor and Hypervitaminosis A are all causes of:
1
Telogen effluvium
All of the listed stressors can induce telogen effluvium. Other causes include traction and some drug
exposures. Usually will only involve up to 50% of scalp hairs and will resolve within 2-3 months.
Q/Q(M)-478017 Report a Problem
28
What component is the major barrier in the stratum corneum?
1
Sebum
2
Squalene
3
Collagen
4
Ceramide
5
Triglycerides
Q/Q(M)-476553 Report a Problem
What component is the major barrier in the stratum corneum?
4
Ceramide
The major component of lamellar granules of the keratinocytes is ceramide. These play a major role in
the barrier function of the skin.
Q/Q(M)-476553 Report a Problem
Regarding the stratum spinosum, which of the following is correct?
1
No keratin 1/10 is present
2
New synthesis of K5/14 occurs in this layer
3
The "spines" seen on pathology are due to desmosomal connections between keratinocytes
4
This layer contains melanocytes
5
This layer contains the cornified cell membrane
Q/Q(M)-478166 Report a Problem
Regarding the stratum spinosum, which of the following is correct?
3
The "spines" seen on pathology are due to desmosomal connections between keratinocytes
The "spines" seen on pathology are due to desmosomal connections between keratinocytes, NOT
hemidesmosomes. The hemidesmosomes are present in the cells at the base of the basal layer and are
part of the connection between the epidermis and basement membrane. Keratin expression continues
in the spinous layer. Keratins 1/10 are synthesized, not keratins 5/14. Keratin 5/14, however, is still
present. Keratohyaline granules are typically seen in the granular layer.
Q/Q(M)-478166 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands:
1
Demonstrate holocrine secretion
2
Demonstrate decapitation secretion
3
Are fully functional at birth
4
Are diffusely distributed on the body
29
5
Are thermoregulatory
Q/Q(M)-474182 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands:
2
Demonstrate decapitation secretion
Apocrine glands show decapitation secretion. Like eccrine glands, apocrine glands are composed of
three segments, the intraepidermal duct, the intradermal duct, and the secretory portion. The duct of
the apocrine gland usually leads to a pilosebaceous follicle above the entrance of the sebaceous duct.
Apocrine glands are found in the axillae, anogenital region, external ear canal (ceruminous glands), in
the eyelids (Molls glands), and in the breast (mammary glands). Apocrine glans are functional only
at puberty. Their initial secretion is odorless. Hidradenitis suppuritiva is a disease involving apocrine
glands.
Q/Q(M)-474182 Report a Problem
On electron microscopy, which cell demonstrates cytoplasmic projections and secretory granules?
1
Langerhans cell
2
Keratinocyte
3
Mast cell
4
Melanocyte
5
Macrophage
Q/Q(M)-475867 Report a Problem
On electron microscopy, which cell demonstrates cytoplasmic projections and secretory granules?
3
Mast cell
Electron microscopy of mast cells demonstrates large long villi at the periphery and round or oval
secretory granules. Langerhans cells show a folded nucleus and rarely phagocytized melanosomes on
electron microscopy. Their characteristic feature is the presence of Birbeck granules whose disk shape
with one or two vesicles at either end represents a tennis raquet. Examination of melanocytes shows an
absence of tonofilaments or desmosomes with characteristic melanosomes in various stages of
formation. Macrophages often contain phagocytized material within phagosomes.
Q/Q(M)-475867 Report a Problem
Jessners solution includes:
1
Lactic acid, alcohol, glycolic acid, resorcinol
2
Lactic acid, alcohol, glycolic acid, TCA
3
Lactic acid, alcohol, salicylic acid, glycolic acid
4
Lactic acid, resorcinol, salicylic acid, glycolic acid
5
Lactic acid, alcohol, salicylic acid, resorcinol
Q/Q(M)-482764 Report a Problem
30
Jessners solution includes:
5
Lactic acid, alcohol, salicylic acid, resorcinol
Jessners is a superficial peeling agent, which may be used to treat dyschromia and texture
abnormalities. TCA and glycolic acid are not ingredients in this formulation.
Q/Q(M)-482764 Report a Problem
Which eponym describes vestigial lines of pigmentary demarcation?
1
Fuchter lines
2
Wallace's lines
3
Langer's lines
4
Lines of Blaschko
5
Dermatome
Q/Q(M)-476758 Report a Problem
Which eponym describes vestigial lines of pigmentary demarcation?
1
Fuchter lines
Fuchter lines are vestigial lines in which the dorsal surface has more melanocytes than ventral surface.
Wallace's lines are the well-demarcated lines around the margin of the foot and hand.
Q/Q(M)-476758 Report a Problem
Which element is necessary for function of matrix metalloproteinases?
1
Iron
2
Nitrogen
3
Manganese
4
Magnesium
5
Zinc
Q/Q(M)-476759 Report a Problem
Which element is necessary for function of matrix metalloproteinases?
5
Zinc
Matrix metalloproteinases are required for normal tissue architecture and normal turnover of the
extracellular matric. All of them have zinc at the active site and require octahedral binding of calcium
ions to maintain structural integrity.
Q/Q(M)-476759 Report a Problem
Anchoring filaments originate at the hemidesmosomes and insert into the:
31
1
Desmosome
2
Sub basal dense plate
3
Lamina lucida
4
BPAG 180
5
Lamina densa
Q/Q(M)-478577 Report a Problem
Anchoring filaments originate at the hemidesmosomes and insert into the:
5
Lamina densa
Anchoring filaments (smaller than anchoring fibrils) stretch from the plasma membrane through the
subbasal dense plaque and the lamina lucida to the lamina densa.
Q/Q(M)-478577 Report a Problem
What percentage of the dry weight of skin in elastin?
1
2
2
4
3
6
4
8
5
10
Q/Q(M)-479243 Report a Problem
What percentage of the dry weight of skin in elastin?
2
4
Elastin fibers make up 4% of dry weight of the skin, forming a complex meshwork extending from
lamina densa of the dermoepidermal junction through the dermis and into the hypodermis. Elastins
help return the skin to the normal configuration after being stretched. Elastic fibers are 90% elastin
wrapped by fibrillin microfibrils. Fibrillin is mutated in Marfan syndrome. The typical amino acids
found in elastic fibers are desmosine and isodesmosine. Elastic fibers turn over slowly in the skin and
are damaged by ultraviolet radiation.
Q/Q(M)-479243 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about glomus cells is correct?
1
Tumors of glomus cells are most commonly found on the tongue
2
Are of neural origin
3
Allow rapid shunting of blood from the arterioles to venules, bypassing capillaries
4
Tumors composed of glomus cells are asymptomatic
5
Tumors composed of glomus cells are often malignant
Q/Q(M)-478202 Report a Problem
32
Which of the following statements about glomus cells is correct?
3
Allow rapid shunting of blood from the arterioles to venules, bypassing capillaries
Tumors composed of glomus cells are usually PAINFUL, not asymptomatic. The are derived from
Suquet-Hoyer canals and allow rapid shunting of blood from the arterioles to venules. Glomus cells
are part of glomus tumors which are most often solitary, purple dermal nodules on the extremities.
Most often, they are seen on the fingers and toes. They are usually painful and rarely malignant. As
opposed to a glomus tumor, glomangiomas are usually painless. They also most often occur on
extremities, but can also occur on the trunk.
Q/Q(M)-478202 Report a Problem
Human sebum is distinguished from lipids of internal organs by the presence of:
1
Cholestrol
2
Cholestrol esters
3
Squalene
4
Wax esters
5
Glycerides
Q/Q(M)-476956 Report a Problem
Human sebum is distinguished from lipids of internal organs by the presence of:
4
Wax esters
As human sebum exits the sebaceous gland, its major constituents are squalene, cholesterol,
cholesterol esters, triglycerides, and wax esters. With passage through the hair follicle, triyglycerides
in the sebum become hydrolyzed by bacterial enzymes, so that by the time the sebum reaches the skin
surface, it contains free fatty acids, mono- and diglycerides in addition to the original components.
Human sebum is distinguished by the presence of wax esters and squalene. The lipids of human
internal organs contain no wax esters and little squalene. The squalene that is produced in internal
organs is quickly converted to lanosterol and then to cholesterol, so it does not remain in its original
form. Human sebaceous glands do not convert squalene to sterols.
Q/Q(M)-476956 Report a Problem
Which protein is the largest component of the cornified cell envelope?
1
Keratin
2
Involucrin
3
Profilaggrin
4
Loricrin
5
Ceramide
Q/Q(M)-477196 Report a Problem
Which protein is the largest component of the cornified cell envelope?
33
4
Loricrin
The cornified cell envelope is a durable, protein-lipid polymer that eventually acts as a mechanical and
chemical barrier on the exterior of cornified cells. In the upper spinous layer, keratohyaline granules
release profilagrin and loricrin. Profilaggrin is cleaved to filaggrin and subsequently aggregates keratin
filaments. Loricrin is the major protein component of the cornified cell envelope and is bound to the
cell membrane by transglutaminases (in addition to other structural proteins like involucrin, keratins,
elafin, cystatin A and desmosomal peptides). This forms the highly insoluble proteinaceous
component of the cornified cell envelope.
Q/Q(M)-477196 Report a Problem
The desmosomal connections of the epidermis are dependent on which of the following ions?
1
Iron
2
Zinc
3
Selenium
4
Calcium
5
Sodium
Q/Q(M)-478167 Report a Problem
The desmosomal connections of the epidermis are dependent on which of the following ions?
4
Calcium
The desmosomal connections in the epidermis are calcium dependent. The other options are not
required for these connections.
Q/Q(M)-478167 Report a Problem
Each of the following is true about the basement membrane zone except:
1
Anchoring filaments attach the basal cell membrane to the lamin lucida
2
Can be visualized on light microscopy with PAS staining
3
Lamina densa is composed of type IV collagen
4
Contains laminin 1 and laminin 5
5
Anchoring fibrils are composed of type VII collagen
Q/Q(M)-477220 Report a Problem
Each of the following is true about the basement membrane zone except:
1
Anchoring filaments attach the basal cell membrane to the lamin lucida
The basement membrane zone is seen on staining with PAS stain. It appears as a homogenous band
approximately 1 micron thick at the dermo-epidermal junction. The hemidesmosomal complex and
basement membrane zone play an integral role in maintaining cellular adhesion. Anchoring filaments
(primarily composed of laminin 5 and BPAG2) attach the basal cell membrane to the lamina densa
NOT lamina lucida.
Q/Q(M)-477220 Report a Problem
34
Which of the following medications is concentrated in the eccrine glands?
1
Cyclophosphamide
2
Cytarabine
3
Ciprofloxacin
4
Cephalexin
5
All of the answers are correct
Q/Q(M)-478149 Report a Problem
Which of the following medications is concentrated in the eccrine glands?
5
All of the answers are correct
The above listed drugs, as well as beta-lactam antibiotics, antifungals such as ketoconazole and
griseofulvin, are known to be secreted into eccrine sweat ducts. This feature may explain the
development of neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis and eccrine squamous syringometaplasia in the
context of chemotherapy.
Q/Q(M)-478149 Report a Problem
Which PPK is associated with a right-sided cardiomyopathy?
1
Haim-Munk
2
Papillon-Lefevre
3
Naxos
4
Olmstead
5
Huriez
Q/Q(M)-482769 Report a Problem
Which PPK is associated with a right-sided cardiomyopathy?
3
Naxos
Naxos is associated with right sided cardiomyopathy. It is an AR, non epidermolytic PPK in which
patients have congenital wooly hair and fragile desmosomes. These patients are at risk for heart failure
and death.
Q/Q(M)-482769 Report a Problem
What is the most important cell for wound healing?
1
Fibroblasts
2
Neutrophils
3
Macrophages
35
4
Lymphocytes
5
Mast cells
Q/Q(M)-482387 Report a Problem
What is the most important cell for wound healing?
3
Macrophages
Macrophages are the most important cell for wound healing. They secrete TFGs, cytokinas, IL-1,
TNF, and PDGF. Neutropenic or lymphopenic patients do not have impaired wound healing, whereas
macrophage-deficient (quantity or function) patients heal poorly. Neutrophils however are the first cell
type to flood the wound during phage I of inflammation (within first 6-8 hours); this movement is
facilitated by TGF-beta. Fibroblasts migrate into the wound by stage II (granulation) where they
produced glycosaminoglycans and fibronectin.
Q/Q(M)-482387 Report a Problem
What structure delineates the anatomic region between the nail bed and the distal groove, where the
nail plate detaches of the distal portion of the digit?
1
Nail matrix
2
Proximal nail fold
3
Lunula
4
Eponychium
5
Hyponychium
Q/Q(M)-482431 Report a Problem
What structure delineates the anatomic region between the nail bed and the distal groove, where the
nail plate detaches of the distal portion of the digit?
5
Hyponychium
The hyponychium is the structure that delineates the anatomic region between the nail bed and the
distal groove, where the nail plate detaches of the distal portion of the digit. The corneal layer of the
hyponychium accumulates in part under the free margin of the nail plate. In most cases, the
hyponychium is covered by the distal nail plate, however, it may become visible in the case of nail
biters.
Q/Q(M)-482431 Report a Problem
The formation of granulation tissue depends on the presence of:
1
Neutrophils
2
Fibronectin
3
Collagen type I
4
Platelets
5
Collagen type IV
36
Q/Q(M)-474177 Report a Problem
The formation of granulation tissue depends on the presence of:
2
Fibronectin
Granulation tissue forms approximately four days after injury. It is composed of new capillaries,
macrophages, fibroblasts, and blood vessels. The formation is dependent on the presence of
fibronectin. There tends to be an ordered sequence of matrix deposition. Fibronectin is deposited first
followed by collagen 3 and then collagen 1. Granulation tissue primarily contains type 3 collagen.
Q/Q(M)-474177 Report a Problem
Acid keratins (K10-20) are expressed on which of the following chromosomes?
1
17
2
18
3
19
4
10
5
12
Q/Q(M)-478165 Report a Problem
Acid keratins (K10-20) are expressed on which of the following chromosomes?
1
17
Acid keratins are expressed on chromosome 17 and basic keratins on chromosome 12. The other listed
options do not have active keratin functions.
Q/Q(M)-478165 Report a Problem
All mononuclear phagocytic cells in the dermis express:
1
CD3
2
CD6
3
CD34
4
CD68
5
CD20
Q/Q(M)-479246 Report a Problem
All mononuclear phagocytic cells in the dermis express:
2
CD6
CD6 and CD11c are expressed on all mononuclear phagocytic cells in the dermis. CD3 is a T-cell
marker and CD20 is a B-cell marker. CD34 is expressed on mast cells and CD68 on macrophages.
Q/Q(M)-479246 Report a Problem
37
The microflora of pilosebaceous unit consist of which of the following:
1
Pityrosporum ovale
2
Staphylococcus aureus
3
Escherichia coli
4
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
5
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Q/Q(M)-478151 Report a Problem
The microflora of pilosebaceous unit consist of which of the following:
1
Pityrosporum ovale
All the above bacteria and fungi are found within sebaceous glands; the Malasssezia spp. and P. ovale
are found within the acroinfundibulum, S. epidermidis is found within the midinfundibulum, and
Propionibacterium spp. deep within the follicle.
Q/Q(M)-478151 Report a Problem
Homocystinuria has abnormal crosslinking of collagen because of a mutation in:
1
Cystathione synthase
2
Type I collagen N-peptidase gene
3
Lysyl hydroxylase
4
Tenascin X
5
Lysyl oxidase
Q/Q(M)-478194 Report a Problem
Homocystinuria has abnormal crosslinking of collagen because of a mutation in:
1
Cystathione synthase
Homocystinuria is caused by a mutation in cystathione synthase. The main skin findings are a malar
flush, livedo reticularis and leg ulcerations. A characteristic eye finding is the downward displacement
of the lens. The other options are involved in abnormalities associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Lysyl hydroxylase is deficient in Kyphoscoliosis type of EDS. Tenascin X is involves in ~3% of
Classical type EDS cases. Dermatosparaxis type EDS has recessive mutations in the type I collagen N-
peptidase gene.
Q/Q(M)-478194 Report a Problem
A specific marker of Merkel cells is:
1
Cytokeratin 10
2
Cytokeratin 15
3
Cytokeratin 20
38
4
Loricrin
5
Envoplakin
Q/Q(M)-474166 Report a Problem
A specific marker of Merkel cells is:
3
Cytokeratin 20
Cytokeratin 20 is a specific marker for the Merkel cell. Merkel cells are mechanoreceptors located at
body sites requiring high tactile sensitivity. Keratinocyte deformation results in a secretion of
chemokines by Merkel cells, which make synaptic connection with neurons.
Q/Q(M)-474166 Report a Problem
How soon does epithelialization begin after a skin wound occurs?
1
Minutes
2
Hours
3
2 days
4
4 days
5
6 days
Q/Q(M)-479408 Report a Problem
How soon does epithelialization begin after a skin wound occurs?
2
Hours
Re-epithelialization begins hours after an injury occurs. Keratinocytes from residual epithelial
structures leapfrog each other. One to two days after injury, cells at the wound margin proliferate and
begin to migrate into the wound.
Q/Q(M)-479408 Report a Problem
Which of the following enzymes does not require copper for functioning?
1
Lysyl oxidase
2
ATP7a
3
Tyrosinase
4
Cystathione beta-synthase
5
Ferrochelatase
Q/Q(M)-478198 Report a Problem
Which of the following enzymes does not require copper for functioning?
5
Ferrochelatase
All of the listed enzymes are copper containing or dependent except ferrochelatase. Lysyl oxidase
39
facilitates crosslinking of fibrillin in elastic fibers. ATP7a is deficient in Menkes Kinky Hair
Syndrome. Cystathione beta-synthase is defective in homocystinuria. Tyrosinase catalyzes the first 2
steps, and at least 1 subsequent step, in the conversion of tyrosine to melanin. Ferrochelatase mutation
leads to excess protoporphyrin production and photosensitivity.
Q/Q(M)-478198 Report a Problem
Direct immunofluorescence is of no value in the diagnosis of:
1
Neonatal LE
2
Lichen planus
3
Mixed connective tissue disease
4
SLE
5
Erythema multiforme
Q/Q(M)-480546 Report a Problem
Direct immunofluorescence is of no value in the diagnosis of:
1
Neonatal LE
DIF is of no value in the diagnosis of scleroderma, morphea, and neonatal LE. DIF of lichen planus is
positive in the vast majority, with granular DEJ deposition and IgM and fibrinogen staining within
cytoid bodies in the superficial dermis. In MCTD DIF shows IgG deposits within epidermal cell
nuclei, and rarely along the DEJ. In SLE, while serology is more reliable, DIF can show DEJ
deposition in the lupus band test. DIF of erythema multiforme shows immunoglobulin within
superficial vessel walls, DEJ, and cytoid bodies.
Q/Q(M)-480546 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains would you expect to be positive in a normal eccrine unit?
1
S-100
2
Prussian blue
3
Giemsa
4
Verhoeff von Gieson
5
Steiner
Q/Q(M)-480145 Report a Problem
Which of the following stains would you expect to be positive in a normal eccrine unit?
1
S-100
Eccrine glands stain S-100 and CEA positive. The remaining stains would not be expected to stain
normal eccrine sweat glands. Prussian blue (Perls) is an iron stain which stains iron or hemosiderin
bright blue. Giemsa stains mast cell granules purple (heparin in the granules) and can also be useful in
staining in Leishmaniasis. Verhoeff von Gieson is a stain for elastic tissue that stains blue-black.
Steiner stain is a silver stin for spirochetes similar to a Warthin Starry or Dieterle stain.
40
Q/Q(M)-480145 Report a Problem
Which is a major criterion for the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 1?
1
One plexiform neurofibroma
2
Scoliosis
3
Pheochromocytoma
4
Hypertension
5
Two caf au lait macules
Q/Q(M)-482783 Report a Problem
Which is a major criterion for the diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 1?
1
One plexiform neurofibroma
The major diagnostic criteria are: 6 or more caf au lait macules >5mm in prepubertal individuals and
>15mm in post pubertal individuals, 2 or more neurofibromas of any type or one plexiform
neurofibroma, axillary or inguinal freckling, 2 or more lisch nodules, sphenoid wing dysplasia or
thinning of long bone cortex with or without pseudoarthosis, first degree relative with NF1.
Q/Q(M)-482783 Report a Problem
Which of the following polypeptides is found in the lamina lucida?
1
plakoglobin
2
desmoplakin
3
keratocalmin
4
demoyokin
5
laminin 5
Q/Q(M)-479077 Report a Problem
Which of the following polypeptides is found in the lamina lucida?
5
laminin 5
Laminin-5 is a basement membrane extracellular matrix protein that mediates attachment substrate for
both adhesion and migration in a wide variety of cell types, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts,
neurons and leukocytes and is a preferred adhesion substrate for epithelial cells (Koshikawa et al.,
2001). The remaining listed items are part of the desmosomal plaque in the epidermis.
Q/Q(M)-479077 Report a Problem
Sneddon Wilkinson disease is caused by a defect in what antigen?
1
Desmocollin 1
2
Desmoglein 1
3
Desmogelin 3
41
4
BPAg1
5
BPAg2
Q/Q(M)-482280 Report a Problem
Sneddon Wilkinson disease is caused by a defect in what antigen?
1
Desmocollin 1
Sneddon- Wilkinson disease, also known as sub-corneal pustular dermatosis is due to a defect in
desmocollin 1. Desmoglein 1 defect is seen in pemphigus foliaceous and staph scalded skin syndrome.
Desmoglein 3 defect is seen in pemphigus vulgaris and intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis.
BPAg1 is seen in paraneoplastic pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. BPAg2 is seen in bullous
pemphigoid, cicatricial mucous membrane pemphigoid and linear IgA disease.
Q/Q(M)-482280 Report a Problem
Type 1 collagen is the most prevalent collagen in skin, accounting for 80% or more of the total
collagen in the adult dermis. The next most predominant collagen in adult human dermis is:
1
Type II collagen
2
Type III collagen
3
Type IV collagen
4
Type VII collagen
5
Type XVII collagen
Q/Q(M)-482412 Report a Problem
Type 1 collagen is the most prevalent collagen in skin, accounting for 80% or more of the total
collagen in the adult dermis. The next most predominant collagen in adult human dermis is:
2
Type III collagen
Type 1 collagen is the most prevalent collagen in skin, accounting for 80% or more of the total
collagen in the adult dermis. Type III collagen is the next most predominant collagen in human
dermis, accounting for approximately 10%. Type IV collagen is found in basement membranes. Type
VII collagen is found in human dermis as anchoring fibrils. Type XVII collagen, also known as
BPAG2, is an important transmembrane protein in the basement membrane zone.
Q/Q(M)-482412 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands:
1
Respond to chemical stimuli such as hormones
2
Respond to cholinergic neural activity, exclusively
3
Respond to adrenergic neural activity, exclusively
4
Respond to both adrenergic and cholinergic stimuli
5
Respond to the local release of cytokines from inflammatory cells
Q/Q(M)-474175 Report a Problem
42
Sebaceous glands:
1
Respond to chemical stimuli such as hormones
Sebaceous glands are androgen-responsive holocrine glands that enlarge at puberty. Meibomian glands
of the eyelids are modified sebaceous glands. Sebaceous glands are found everywhere on the skin
except the palms and soles. Fordyces condition involves free sebaceous glands on the vermillion
border of the lips and on the buccal mucosa. Eccrine glands are thermoregulatory structures that
respond to cholinergic stimulation.
Q/Q(M)-474175 Report a Problem
Which epidermal layer do pilar cysts generally not have a:
1
Stratum corneum
2
Stratum granulosum
3
Stratum spinosum
4
Stratum basale
5
Stratum lucidum
Q/Q(M)-482652 Report a Problem
Which epidermal layer do pilar cysts generally not have a:
2
Stratum granulosum
Pilar cysts do not have a granular layer, they do have all the other layers.
Q/Q(M)-482652 Report a Problem
At any one time, the approximate proportion of hair follicles in anagen is:
1
40%
2
60%
3
85%
4
95%
5
15%
Q/Q(M)-474172 Report a Problem
At any one time, the approximate proportion of hair follicles in anagen is:
3
85%
Most hair follicles are in anagen, and thus most hair follicles involve growing hair. The longer a hair
follicle is anagen, the longer the hair can grow in length. Hairs of the scalp grow approximately 0.4
mm per day, and thus the date of your next hair cut can be accurately calculated.
Q/Q(M)-474172 Report a Problem
43
Which of the following statements about elastic fibers is true?
1
Elastic fibers form 35% of the dry weight of the skin
2
Elastic fibers are 90% elastin wrapped in fibrillin
3
Collagen 1 is mutated in Marfan syndrome
4
Oxytalan fibers run parallel within the superficial papillary dermis
5
Elaunin fibers run perpendicular in thin bands within the reticular dermis
Q/Q(M)-478199 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about elastic fibers is true?
2
Elastic fibers are 90% elastin wrapped in fibrillin
Elastic fibers are responsible for much of the elasticity of the dermis. They are essentially 90% elastin
wrapped in fibrillin. They form 4% of the dry weight of the skin. Fibrillin 1 is mutated in Marfan
syndrome. Oxytalan fibers run PERPENDICULAR from the DEJ within the superficial papillary
dermis. Elaunin fibers run parallell in thin bands within the reticular dermis.
Q/Q(M)-478199 Report a Problem
Pick the correctly paired keratin with its structure:
1
K1/K10 - basal cells
2
K3/K12 - esophagus
3
K4/K13 - cornea
4
K5/K14 - suprabasal cells
5
K16/K6 - palms and soles
Q/Q(M)-478576 Report a Problem
Pick the correctly paired keratin with its structure:
5
K16/K6 - palms and soles
Keratin 1 and 10 are found in the stratum spinosum. K5 and K14 are found in the basal layer. K3 and
K12 are found in the suprabasilar cells of the cornea. K4 and K13 are found in the non-cornifying cells
of stratified mucosa. K16 and K6 are found in the palms and soles.
Q/Q(M)-478576 Report a Problem
Necobiosis is characteristic of which two entities below?
1
Sarcoid and granuloma annulare
2
Sarcoid and necrobiosis lipoidica
3
Sarcoid and annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
4
Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica
5
Granuloma annulare and cutaneous Crohns disease
Q/Q(M)-482778 Report a Problem
44
Necobiosis is characteristic of which two entities below?
4
Granuloma annulare and necrobiosis lipoidica
Necrobiosis is seen in GA and NLD as well as rheumatoid nodules, interstitial granulomatous
dermatitis and palisading neutrophilic and granulomatous dermatitis. Mucin is also present in GA.
NLD shows giant cells, extracellular lipid, and vascular changes.
Q/Q(M)-482778 Report a Problem
Which of the following keratins would most likely be expressed in the nail bed?
1
K6a/16
2
K6b/17
3
K1/9
4
K2e/10
5
K4/13
Q/Q(M)-478552 Report a Problem
Which of the following keratins would most likely be expressed in the nail bed?
2
K6b/17
Keratins 6b & 17 are expressed in the nail bed. K6a/16 is expressed in the outer root sheath and in
hyperproliferative keratinocytes, 1/9 in palmoplantar suprabasalar keratinocytes, 2e/10 in the upper
spinous and granular cell layers, and 4/13 are expressed in mucosal epithelium.
Q/Q(M)-478552 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum through which of the following secretory mechanisms?
1
Holocrine
2
Merocrine
3
Apocrine
4
Holocrine and Merocrine
5
Holocrine and Apocrine
Q/Q(M)-478152 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands secrete sebum through which of the following secretory mechanisms?
1
Holocrine
Sebaceous glands exhibit holocrine secretion, whereby the sebocytes disintegrate in transit to the gland
center, releasing their sebum contents. Merocrine secretion refers to the formation of intracellular
secretory vesicles that translocate to the apical cell surface for secretion. Apocrine secretion refers to
the process whereby secretory contents are packaged using the apical cell membrane, and 'pinched off'
to achieve secretion.
Q/Q(M)-478152 Report a Problem
45
Which hair condition is associated with abnormal regulation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor- (PPAR):
1
Alopecia areata
2
lichen planopilaris
3
telogen effluvium
4
seborrheic dermatitis
5
androgenic alopecia
Q/Q(M)-482526 Report a Problem
Which hair condition is associated with abnormal regulation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor- (PPAR):
2
lichen planopilaris
Lichen planopilaris is a chronic, scarring condition that results in permanent loss of hair and
destruction of the hair follicles. Defect in lipid metabolism and peroxisome biogenesis may contribute
to LPP pathogenesis. Medications that act as PPAR agonists, such as pioglitazone, may have a role in
controlling the progression of this disease. (Karnik P, et al. (2009) Hair follicle stem cell-specific
PPAR deletion causes scarring alopecia. J Invest Dermatol 129:124357)
Q/Q(M)-482526 Report a Problem
Defects in what kind of structural protein lead to pyloric atresia associated with junctional
epidermolysis bullosa:
1
Collagen
2
Elastin
3
Loricrin
4
Integrin
5
Plectin
Q/Q(M)-474161 Report a Problem
Defects in what kind of structural protein lead to pyloric atresia associated with junctional
epidermolysis bullosa:
4
Integrin
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia involves a defect in the b4 subunit of the a6b4
integrin. The expression of this protein is limited to the basal layer of the epidermis. This integrin is a
transmembrane protein that coordinates a link between the intermediate filaments (keratins) and the
extracellular matrix of the basement membrane. The b4 domain mediates an interaction with both
plectin and BP180; its absence prevents hemidesmosomal assembly.
Q/Q(M)-474161 Report a Problem
46
Which of the following options is characteristic of integrins?
1
Defects in the alpha-6 domain of integrin result in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular
dystrophy
2
Alpha-6-Beta-4 integrin is found at sites where desmogleins attach
3
Expression is seen in all layers of the epidermis
4
The extracellular alpha6 domain binds collagen 7
5
These proteins coordinate linkage between intermediate filaments and extracellular matrix of
the basement membrane
Q/Q(M)-478170 Report a Problem
Which of the following options is characteristic of integrins?
5
These proteins coordinate linkage between intermediate filaments and extracellular matrix of
the basement membrane
Defects in the BETA-4 (not alpha-6) domain of integrin result in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with
pyloric atresia. Its expression is seen in the basal cell layer and binds to laminins.
Q/Q(M)-478170 Report a Problem
What is the location of the unbound corticosteroid receptor?
1
Cytoplasm
2
Nucleus
3
Mitochondria
4
Plasma membrane
5
golgi apparatus
Q/Q(M)-476530 Report a Problem
What is the location of the unbound corticosteroid receptor?
1
Cytoplasm
Both androgen and corticosteroid receptors localize to the cytoplasm. Estrogen receptors are found in
the nucleus. Progesterone receptors are distributed in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Q/Q(M)-476530 Report a Problem
The main permeability barrier in the lamina densa is:
1
heparan sulfate proteoglycan
2
collagen IV
3
laminin 5
4
nidogen
5
alpha-6-beta-4 integrin
Q/Q(M)-479178 Report a Problem
47
The main permeability barrier in the lamina densa is:
1
heparan sulfate proteoglycan
All of the listed proteins are present in the lamina densa except alpha-6-beta-4 integrin, which
connects the hemidesmosome to laminin 5 in the lamina lucida. The heparin sulfate proteoglycans
(perlecan) are negatively charged, thus serve as a permeability barrier. The other listed proteins do not
serve this function in the lamina densa. Collagen IV is the main basic basement membrane scaffold.
Defects in Collagen IV have been linked to Alports and Goodpastures syndrome. Nidogen has a
dumbbell shape and binds both laminins and collagen IV in the lamina densa.
Q/Q(M)-479178 Report a Problem
Spontaneous mutations causing tuberous sclerosis are more likely to occur in which gene?
1
TSC2
2
TSC1
3
TSC 3
4
TSC 4
5
TSC 5
Q/Q(M)-482784 Report a Problem
Spontaneous mutations causing tuberous sclerosis are more likely to occur in which gene?
1
TSC2
Spontaneous mutations are four times more likely to occur in TSC2. In familial TS half mutations are
in TSC1 and half in TSC2.
Q/Q(M)-482784 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands are found in all of the following areas of the body except:
1
Axillae
2
Breasts
3
Eyelid
4
Palms
5
Perineum
Q/Q(M)-477312 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands are found in all of the following areas of the body except:
4
Palms
Apocrine glands operate by decapitation secretion and are activated by epinephrine and
norepinephrine. They are located in a few distinct areas of the body, which include axillae, anogenital
region, Molls glands of the eyelids, mammary glands of the breast and the ceruminous glands of the
external auditory canal.
48
Q/Q(M)-477312 Report a Problem
Elastic fibers contain the specific amino acids:
1
Lysine and proline
2
Leucine and isoleucine
3
Alanine and phenylalanine
4
Desmosine and isodesmosine
5
Glycine and proline
Q/Q(M)-474168 Report a Problem
Elastic fibers contain the specific amino acids:
4
Desmosine and isodesmosine
Desmosine and isodesmosine are the typical amino acids of elastic fibers. Elastic fibers are comprised
of elastin that is wrapped by fibrillin microfibrils. Elastic fibers form a complex meshwork extending
from the lamina densa of the dermo-epidermo junction through the dermis. Elastic fibers return the
skin to a normal shape after being stretched.
Q/Q(M)-474168 Report a Problem
Which component of hair is positive for citrulline?
1
Outer root sheath
2
Inner root sheath
3
Cortex
4
Glassy vitreous layer
5
Medulla
Q/Q(M)-482303 Report a Problem
Which component of hair is positive for citrulline?
2
Inner root sheath
The inner root sheath stains red because it contains citrulline. The cortex and medulla along with the
cuticle make up the hair shaft. The outer root sheath is the most peripheral cellular structure. The
glassy vitreous layer is the basement zone equivalent of hair and is the outermost layer.
Q/Q(M)-482303 Report a Problem
The epidermis is comprised of what type of cells?
1
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Merkel cells, Langerhan cells
2
Keratinocytes, Endothelial cells, Merkel cells, Langerhan cells
3
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Neutrophils, Langerhan cells
49
4
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Merkel cells, Goblet cells
5
Keratinocytes, Endothelial cells, Merkel cells, Goblet cells
Q/Q(M)-478587 Report a Problem
The epidermis is comprised of what type of cells?
1
Keratinocytes, Melanocytes, Merkel cells, Langerhan cells
The adult epidermis is composed of three basic cell types: Keratinocytes, melanocytes, and
Langerhans cells. An additional cell, the Merkel cell, can be found in the basal layer of the palms and
soles, the oral and genital mucosa, the nail bed, and the follicular infundibula.
Q/Q(M)-478587 Report a Problem
What type of skin cancer is associated with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa?
1
Squamous cell carcinoma
2
Basal cell carcinoma
3
Merkel cell carcinoma
4
Melanoma
5
Actinic keratosis
Q/Q(M)-482781 Report a Problem
What type of skin cancer is associated with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa?
1
Squamous cell carcinoma
Patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa havea high risk of aggressive SCC in the
areas of chronic erosion and must be screened thoroughly and frequently. Actinic keratosis is not skin
cancer.
Q/Q(M)-482781 Report a Problem
Keratin filaments in basal cells insert into:
1
Desmosomes
2
Adherens junctions
3
Connexins
4
Lamellar granules
5
Odland bodies
Q/Q(M)-479075 Report a Problem
Keratin filaments in basal cells insert into:
1
Desmosomes
Keratin filaments insert into desmosomes and hemidesmosomes in the basal cell layer and into
desmosomes in the layers above. Connexins do not bind keratin filaments. Odland bodies and lamellar
50
granules are synonyms. These are a "membrane bounded organelle, specialized for the storage and
secretion various substances (surfactant phospholipids, glycoproteins and acid phosphates) which are
arranged in the form of tightly packed, concentric, membrane sheets or lamellae. Has some similar
properties to, but is distinct from, a lysosome."
Q/Q(M)-479075 Report a Problem
A 78 year-old man is diagnosed with cicatricial pemphigoid. Which of the following antigens being
implicated in his disease should trigger a work-up for malignancy?
1
BPAg2
2
Laminin 5
3
Laminin 6
4
Beta-4 integrin
5
Type VII collagen
Q/Q(M)-479404 Report a Problem
A 78 year-old man is diagnosed with cicatricial pemphigoid. Which of the following antigens being
implicated in his disease should trigger a work-up for malignancy?
2
Laminin 5
Involvement of Laminin 5 would raise the suspicion for malignancy when found. ~30-40% of cases
may have associated malignancy. Patients with antiepiligrin (laminin 5) CP indicated an increased risk
of malignancy that approximates that for adults with dermatomyositis. The risk is particularly high in
the first year of disease (E-medicine, www.emedicine.com/derm/topic79.htm). Reports of both lung
and gastric carcinomas are seen in the literature with some feeling that gastric malignancy is most
common.
Q/Q(M)-479404 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true about melanosomes?
1
Spheroid melanosomes have concentric lamellae
2
Spheroid melanosomes synthesize brown-black eumelanin
3
Elliptical melanosomes have microvesicular structure
4
Elliptical melanosomes synthesize yellow or red pheomelanin.
5
The melanosomes are positioned after the Golgi apparatus in the secretory pathway.
Q/Q(M)-482528 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true about melanosomes?
5
The melanosomes are positioned after the Golgi apparatus in the secretory pathway.
Melanosomes are organelles related to lysosomes and are positioned after the Golgi apparatus in the
secretory pathway. Elliptical melanosomes have concentric lamellae and synthesize brown-black
eumelanin. Spheroid melanosomes have microvesicular structure and synthesize yellow or red
pheomelanin.
51
Q/Q(M)-482528 Report a Problem
Which signaling molecule mediates the transition of hair cycling from telogen to anagen phase?
1
Foxn1
2
Fgf5
3
Sonic hedgehog
4
Dihydotestosterone
5
5a-reductase
Q/Q(M)-478590 Report a Problem
Which signaling molecule mediates the transition of hair cycling from telogen to anagen phase?
3
Sonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog (Shh), a signaling molecule secreted by ectodermal cells of the developing hair
follicle, appears to be critical in mediating the transition from telogen to anagen during postnatal hair
cycling
Q/Q(M)-478590 Report a Problem
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy is due to which defective molecule
1
Plectin
2
Keratin 5 and 14
3
Laminin 5
4
Collagen VII
5
Integrin alpha 6 or beta 4
Q/Q(M)-482785 Report a Problem
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy is due to which defective molecule
1
Plectin
EBS with muscular dystrophy is due to a mutation in plectin, plectin is also found in skeletal muscle.
Keratin 5 and 14 are defective in EBS, EBS herpetiformis, EBS weber cockayne, EBS koebner.
Laminin 5 is defective in Herlitz Junctional EB. Collagen VII is mutated in dominant dystrophic EB,
Barts syndrome and EB acquisita. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 is mutated in junctional epidermolysis
bullosa with pyloric atresia.
Q/Q(M)-482785 Report a Problem
For the treatment of drug induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis, after stopping offensive medication,
what other treatments may be used?
1
Interferon alpha
2
Interferon gamma
52
3
Psoralen plus UVA
4
Interleukin 2
5
Dapsone
Q/Q(M)-482648 Report a Problem
For the treatment of drug induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis, after stopping offensive medication,
what other treatments may be used?
5
Dapsone
Dapsone may be used to treat patients with drug induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis which persist
after the offending medication has been discontinued. The other medications listed are rare causes of
drug induced linear IgA bullous dermatosis and so should not be used for treatment.
Q/Q(M)-482648 Report a Problem
Tyrosinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of tyrosine to DOPA and DOPA to
DOPAquinone. The enzyme contains which of the following ions?
1
Zinc
2
Copper
3
Selenium
4
Iron
5
Magnesium
Q/Q(M)-478191 Report a Problem
Tyrosinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of tyrosine to DOPA and DOPA to
DOPAquinone. The enzyme contains which of the following ions?
2
Copper
Tyrosinase is a copper containing enzyme that is responsible for the conversion fo tyrosine to DOPA
and DOPA to DOPAquinone.
Q/Q(M)-478191 Report a Problem
Apocrine chromhidrosis results from which of the following contents of apocrine sweat?
1
Lipofuschin
2
Squalene
3
Cholesterol
4
Fatty acids
5
Ammonia
Q/Q(M)-478150 Report a Problem
Apocrine chromhidrosis results from which of the following contents of apocrine sweat?
53
1
Lipofuschin
Chromhidrosis refers to the secretion of pigmented sweat, most commonly yellow, green or black. It
reflects the rich lipofuschin content of apocrine sweat. Extrinsic apocrine chromhidrosis results from
staining of sweat and garments by chromogenic bacteria, such as Corynebacterium spp.
Q/Q(M)-478150 Report a Problem
Which of the following is the most common genetic alteration seen in mucosal melanomas?
1
GNAQ
2
Cyclin Dependant Kinase 4/6
3
BRAF
4
KIT
5
HDM2
Q/Q(M)-482228 Report a Problem
Which of the following is the most common genetic alteration seen in mucosal melanomas?
4
KIT
Mucosal melanomas tend to have an activating mutation in KIT. GNAQ mutations are seen in both
uveal melanomas and blue nevi. Cyclin dependant kinase 4/6 binds cyclin D and together
phosphorylate Retinoblastoma. HDM2 targets p53 for ubiquitination.
Q/Q(M)-482228 Report a Problem
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), Weber Cockayne type, is caused by what defect?
1
Collagen VII
2
Alpha-6-beta-4 integrin
3
Keratins 1 & 10
4
Keratins 5
5
Plectin
Q/Q(M)-482278 Report a Problem
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), Weber Cockayne type, is caused by what defect?
4
Keratins 5
All subtypes of EBS are caused by a defect in keratins 5 & 14 except EBS with muscular dystrophy
which is caused by a defect in plectin. An alpha-6-beta-4 integrin defect is seen in junctional
epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) with pyloric atresia. Collagen VII defect is seen in EB aquisita (EBA),
Bart's syndrome and dominant EB (DEB). Keratin 1 & 10 defects are not seen in any of the EB
subtypes.
Q/Q(M)-482278 Report a Problem
54
Elastophagocytosis is characteristic of which condition?
1
Sarcoidosis
2
Granuloma annulare
3
Necrobiosis lipoidica
4
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
5
Palisading neutrophilic and granulomatous dermatitis
Q/Q(M)-482777 Report a Problem
Elastophagocytosis is characteristic of which condition?
4
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is characterized by asymptomatic annular plaques on sun
exposed surfaces. Elastic fibers are absent in the center of lesions. The disease is seen primarily in
middle aged women.
Q/Q(M)-482777 Report a Problem
Meibomian glands are:
1
Eccrine glands localized to the vermillion border of the lips
2
Sebaceous glands found on the areola of the breast
3
Sebaceous glands found on the eyelids
4
Apocrine glands found in the anogenital regions
5
Apocrine glands found on the eylelids
Q/Q(M)-474174 Report a Problem
Meibomian glands are:
3
Sebaceous glands found on the eyelids
Sebaceous glands enlarge at puberty in response to increased levels of androgens. They are holocrine
glands. Meibomian glands are modified sebaceous glands found in the eyelids. Free sebaceous glands
not associated with hairs are found in the nipple and areola and are called Montgomerys tubercles.
Fordyces condition involves free sebaceous glands on the vermillion border of the lips and on the
buccal mucosa. Sebaceous glands are found everywhere on the skin except the palms and soles.
Q/Q(M)-474174 Report a Problem
Melanocytes are derived from:
1
Bone marrow
2
Neural crest
3
Mesodermal precursors
55
4
Endodermal precursors
5
Yolk sac derived
Q/Q(M)-479180 Report a Problem
Melanocytes are derived from:
2
Neural crest
Melanocytes are derived from neural crest precursors and migrate to the epidermis, hair matrix, retinal
pigment epithelium, ear (stria vascularis), leptomeninges, and mucous membranes. The other options
listed are incorrect and are not involved with melanocytes.
Q/Q(M)-479180 Report a Problem
Moving from internally to externally choose the correct description of the hair follicle:
1
Inner root sheath cuticle - Huxley's layer - Henle's layer - medulla - cortex - hair shaft cuticle
2
Hair shaft cuticle - cortex - medulla - Henle's layer - Huxley's layer _ inner root sheath cuticle
3
Henle's layer - Huxley's layer - inner root sheath cuticle - hair shaft cuticle - cortex - medulla
4
Medulla _ cortex _ hair shaft cuticle _ inner root sheath cuticle _ Huxley's layer _ Henle's layer
5
Inner root sheath cuticle _ outer root sheath cuticle _ hair shaft cuticle _ cortex _ Huxley's layer
_ Henle's layer
Q/Q(M)-474170 Report a Problem
Moving from internally to externally choose the correct description of the hair follicle:
4
Medulla _ cortex _ hair shaft cuticle _ inner root sheath cuticle _ Huxley's layer _ Henle's layer
(As described in correct choice)
Q/Q(M)-474170 Report a Problem
The first primordial hair follicles form on the eyebrows, upper lip and chin at which gestational age?
1
7 weeks
2
9 weeks
3
12 weeks
4
16 weeks
5
20 weeks
Q/Q(M)-479410 Report a Problem
The first primordial hair follicles form on the eyebrows, upper lip and chin at which gestational age?
2
9 weeks
The first primordial hair follicles form at 9 weeks gestation on the eyebrows, upper lip and chin. The
remaining follicles develop at 4-5 months in a cephalad to caudal direction. New follicles cannot
develop in adult skin.
56
Q/Q(M)-479410 Report a Problem
Which keratins are upregulated in hyperproliferative disease such as psoriasis?
1
Keratins 1 and 10
2
Keratins 2e and 10
3
Keratins 5 and 14
4
Keratins 6 and 16
5
Keratins 8 and 18
Q/Q(M)-476518 Report a Problem
Which keratins are upregulated in hyperproliferative disease such as psoriasis?
4
Keratins 6 and 16
Keratins 6 and 16 are upregulated in hyperproliferative keratinocytes, outer root sheath, and oral
epithelium. A defect in these keratins may result in pachyonychia congenita.
Q/Q(M)-476518 Report a Problem
Krause end bulbs are:
1
Adapting mechanoreceptors found on weight-bearing sites that respond to vibrational stimul
2
Found on the vermillion border of the lips
3
Located in the dermal papillae of digital skin
4
Located in the deep dermis and within the subcutis in weight-bearing sites of the body
5
Found at the orifice of the hair follicle and particularly sensitive to cold
Q/Q(M)-480544 Report a Problem
Krause end bulbs are:
2
Found on the vermillion border of the lips
Krause end bulbs are mucocutaneous receptors found on the glans penis, clitoris, labia minora,
perianal area, and vermillion border of the lips. Papillary nerve endings are free nerve endings found at
the orifice of the hair follicle and particularly sensitive to cold. Meissner's corpuscles are ovoid,
elongated mechanoreceptors located in the dermal papillae of digital skin that detect touch and light
pressure. Pacinian (Vater-Pacini) corpuscles exist in the deep dermis and within the subcutis in
weight-bearing sites and function as adapting mechanoreceptors that respond to vibrational stimuli.
Q/Q(M)-480544 Report a Problem
Anchoring fibrils are primarily composed of:
1
Type I collagen
57
2
Type III collagen
3
Type IV collagen
4
Type VII collagen
5
Type II collagen
Q/Q(M)-474164 Report a Problem
Anchoring fibrils are primarily composed of:
4
Type VII collagen
Anchoring fibrils are found in the sublamina densa and are made up of collagen type VII. This
collagen type is mutated in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, and targeted in epidermolysis bullosa
acquisita and bullous lupus erythematosus.
Q/Q(M)-474164 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the areola?
1
Montgomery's tubercles
2
Tysons glands
3
Zeis glands
4
Meibomian glands
5
Fordyce's spots
Q/Q(M)-482658 Report a Problem
Which sebaceous gland is located on the areola?
1
Montgomery's tubercles
Montgomery's tubercles are sebaceous glands not associated with hair follicles present on the
areola. Tyson's glands on the labia minora and glans, meibomina and Zeis glands are present on
the eyelids , and Fordyce's spots are located on the buccal mucosa.
Q/Q(M)-482658 Report a Problem
Hair follicle development in the human embryo begins during:
1
1st trimester
2
2nd trimester
3
3rd trimester
4
At the blastocoele stage
5
Within 2 weeks of fertiization
Q/Q(M)-478595 Report a Problem
Hair follicle development in the human embryo begins during:
58
1
1st trimester
Hair follicles begin in the third month of fetal life as a downgrowth of cells from the epidermis (3rd
month=12th week=1st trimester).
Q/Q(M)-478595 Report a Problem
What is the average duration of the telogen cycle in terminal scalp hair?
1
2-6 years
2
2-3 weeks
3
3 months
4
6 months
5
9 months
Q/Q(M)-478173 Report a Problem
What is the average duration of the telogen cycle in terminal scalp hair?
3
3 months
The average duration of the telogen phase of the hair cycle is 3 months; this feature explains why
telogen effluvium is typically observed 3 months following a traumatic event or serious illness. The
average duration of the anagen phase of the hair cycle is 2-6 years, whereas that of the catagen cycle is
2-3 weeks.
Q/Q(M)-478173 Report a Problem
Which type of collagen in mutated in osteogenesis imperfecta?
1
Collagen I
2
Collagen II
3
Collagen III
4
Collagen IV
5
Collagen VII
Q/Q(M)-479241 Report a Problem
Which type of collagen in mutated in osteogenesis imperfecta?
1
Collagen I
Collagen type I is mutated in osteogenesis imperfecta. The COL1A2 gene is located on 7q22 and the
COL1A1 is on 17q22. The other listed collagens are not involved in osteogenesis imperfecta. Collagen
II is in cartilage and vitreous, Collagen III is in fetal skin, blood vessels and intestines, Collagen IV is
in basement membranes and Collagen VII in anchoring fibrils and amnion.
Q/Q(M)-479241 Report a Problem
Dermal dendrocytes:
59
1
Are responsible for immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions.
2
Actively synthesize and release IgG.
3
Present antigen to nave T cells in the lymph node.
4
Are the primary cell found in a glomangioma.
5
Are the primary cell found in an angiosarcoma.
Q/Q(M)-474169 Report a Problem
Dermal dendrocytes:
3
Present antigen to nave T cells in the lymph node.
A dermal dendrocyte is a mononuclear phagocytic cell that is a type of antigen presenting cell. It is
derived from the bone marrow and found both in the papillary and upper reticular dermis. This cell is
highly phagocytic and synonymous with the melanophage that has ingested pigment. Dermal
dendrocytes are likely very important to the afferent limb of the immune response.
Q/Q(M)-474169 Report a Problem
Which cytokeratin would you expect to be preferentially expressed in the keratinocytes of a psoriatic
plaque:
1
K1
2
K5
3
K12
4
K15
5
K16
Q/Q(M)-478570 Report a Problem
Which cytokeratin would you expect to be preferentially expressed in the keratinocytes of a psoriatic
plaque:
5
K16
K16 and K6 act as markers for hyperproliferative keratinocytes. They are found in skin disease such as
psoriasis, warts, actinic keratoses, and SCC's.
Q/Q(M)-478570 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a member of the armadillo family of linking proteins?
1
E-cadherin
2
Periplakin
3
Envoplakin
4
Desmocollin
5
Plakoglobin
60
Q/Q(M)-478265 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a member of the armadillo family of linking proteins?
5
Plakoglobin
Plakoglobin is an example of an armadillo protein, which links the cytoskeleton associated linking
proteins (such as plakins in the case of intermediate filaments and alpha-catenin in the case of actin) to
the transmembrane adhesion molecules, termed cadherins. E-cadherin and desmocollin are examples
of cadherins. Periplakin and envoplakin are examples of plakin linking proteins.
Q/Q(M)-478265 Report a Problem
The hair follicle is the site of production or conversion of which of the following hormones?
1
All the options are correct
2
dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
3
prolactin
4
adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
5
alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH)
Q/Q(M)-477731 Report a Problem
The hair follicle is the site of production or conversion of which of the following hormones?
1
All the options are correct
The hair follicle converts gonadal or aderenal testosterone to dihydrotestosterone locally via 5-alpha
reductase. It also cleaves proopiomelanocortin to ACTH, alpha-MSH, and B-endorphin via
prohormone convertase. It also secretes corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) as well as prolactin.
Q/Q(M)-477731 Report a Problem
What is the major function of urocanic acid?
1
Bacteriocidal acid produced by stratum corneum
2
Primarily a UVB filter
3
Primarily a UVA filter
4
Helps degrade free fatty acids
5
Aids in protecting the skin from dermatophytes
Q/Q(M)-477500 Report a Problem
What is the major function of urocanic acid?
3
Primarily a UVA filter
Urocanic acid a by product of filaggrin degradation and has a peak absorbtion of 345 nm. It serves as a
major UVA filter.
Q/Q(M)-477500 Report a Problem
61
People with darker skin show:
1
Smaller, more concentrated melanosomes
2
A more rapid degradation of melanosomes
3
A lessened production of melanosomes within melanocytes
4
A higher degree of dispersion of melanosomes in keratinocytes
5
A grouping of melanosomes with a low degree of melanization
Q/Q(M)-474165 Report a Problem
People with darker skin show:
4
A higher degree of dispersion of melanosomes in keratinocytes
More darkly pigmented races show a greater production of melanosomes in the melanocyte,
melanosomes with a higher degree of melanization, larger melanosomes, a higher degree of dispersion
of melanosomes in the keratinocytes, and a slower rate of melanosome degradation.
Q/Q(M)-474165 Report a Problem
LEMD3 is mutated in which of the following syndromes?
1
Buschke Ollendorf
2
Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy
3
Goltz
4
McCune-Albright
5
Menkes
Q/Q(M)-480132 Report a Problem
LEMD3 is mutated in which of the following syndromes?
1
Buschke Ollendorf
LEMD3 or MAN1 is mutated in Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome. Common skin findings include
dermatofibrofibrosis lenticularis disseminata. The radiographic finding commonly seen is
osteopoikilosis. The gene defect was recently described as MAN1/LEMD3, a gene encoding for a
nuclear membrane protein. Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy is caused by inactivation of GNAS1,
Goltz is an x-linked dominant condition with unknown pathogenesis, McCune-Albright syndrome is
caused by an activation of GNAS1. Menke's Syndrome is caused by a defect in ATP7A/MKN on
Xq13.
Q/Q(M)-480132 Report a Problem
The classical types of Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (Type 1 and 2) lead to varying degrees of
hyperextensible skin, easy bruising, wide, atrophic scars, and hypermobile joints. The underlying
defect in this disorder is a mutation in:
1
Elastin
62
2
Fibrillin 1
3
ABCC6
4
Collagen V
5
Cystathionine beta-synthase
Q/Q(M)-482413 Report a Problem
The classical types of Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (Type 1 and 2) lead to varying degrees of
hyperextensible skin, easy bruising, wide, atrophic scars, and hypermobile joints. The underlying
defect in this disorder is a mutation in:
4
Collagen V
Classical types of Ehrlers-Danlos are manifested by varying degrees of hyperextensible skin, easy
bruising, wide, atrophic scars, and hypermobile joints. The genetic defect is in Collagen V. Elastin is
mutated in Cutis Laxa. ABCC6 is defective in Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Cystathionine beta-
synthase is mutated in homocystinuria.
Q/Q(M)-482413 Report a Problem
Which of the following amino acids are typically found in elastic fibers?
1
Desmosine
2
Isoleucine
3
Proline
4
Hydroxyproline
5
Glycine
Q/Q(M)-479244 Report a Problem
Which of the following amino acids are typically found in elastic fibers?
1
Desmosine
Desmosine and isodesmosine are typical amino acids found in elastic fibers. Glycine, proline and
hydroxyproline are found as components of collagen. Isoleucine is not specific for elastin fibers.
Q/Q(M)-479244 Report a Problem
The cutaneous immunofluorescence pattern in patients with Senear-Usher syndrome is:
1
Intercellular IgG and C3
2
Linear IgG and C3 along the basement membrane zone
3
Intercellular IgG on guinea pig esophagus
4
Intercellular IgG and C3 and linear IgG and C3 along the basement membrane zone
5
Linear IgG and C3 along the basement membrane zone and intercellular IgG on guinea pig
esophagus
Q/Q(M)-478147 Report a Problem
63
The cutaneous immunofluorescence pattern in patients with Senear-Usher syndrome is:
4
Intercellular IgG and C3 and linear IgG and C3 along the basement membrane zone
Senear-Usher syndrome, or pemphigus erythematosus, is a variant of pemphigus foliaceus
characterized by crusted papules and plaques with a seborrheic distribution (malar region, scalp, upper
chest and back). They demonstrate in-vivo IgG and C3 deposition on keratinocyte cell membranes and
the basement membrane zone, in addition to circulating anti-nuclear antibodies.
Q/Q(M)-478147 Report a Problem
Keratohyalin granules contain:
1
Desmoplakin
2
Envoplakin and Keratin 6
3
Profilaggrin and loricrin
4
Numerous Golgi apparati
5
Involucrin
Q/Q(M)-474158 Report a Problem
Keratohyalin granules contain:
3
Profilaggrin and loricrin
Keratohyalin granules are found in the stratum granulosum (the granular layer), and contain the
proteins profilaggrin and loricrin. Profilaggrin is converted to filaggrin during the transformation of
the granular layer to the cornified layer. This is a calcium-dependent process. Loricrin comprises 75%
of the cornified envelopes mass.
Q/Q(M)-474158 Report a Problem
S100 staining would be negative in?
1
langerhans cells
2
eccrine cells
3
schwann cells
4
adipocytes
5
keratinocytes
Q/Q(M)-482211 Report a Problem
S100 staining would be negative in?
5
keratinocytes
S100 is sensitive for melanocytes and melanoma, but not specific as it also stains langerhans cells,
eccrine cells, schwann cell, adipocytes, and chondrocytes. It is negative in keratinocytes and can help
discriminate melanoma from pagetoid bowens or spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma.
64
Q/Q(M)-482211 Report a Problem
The triple helix of the collagen molecule is largely maintained due to its amino acid composition. The
polypeptide chains of collagen are repeating triplets of Glycine-X-Y. The X and Y positions can be
occupied by multiple amino acids, but are most often:
1
Alanine and asparagine
2
Tyrosine and threonine
3
Histidine and ornithine
4
Leucine and isoleucine
5
Proline and hydroxyproline
Q/Q(M)-482411 Report a Problem
The triple helix of the collagen molecule is largely maintained due to its amino acid composition. The
polypeptide chains of collagen are repeating triplets of Glycine-X-Y. The X and Y positions can be
occupied by multiple amino acids, but are most often:
5
Proline and hydroxyproline
Collagen fibers provide tensile strength to the skin and allow it to serve as a protective organ against
the external environment. Collagen makes up 80% of the dry weight of the dermis. The structure of
collagen is comprised of three alpha chains arranged into a triple helix. The repeating amino acid
triplets of the triple helix of collagen are most often Glycine-Proline-Hydroxyproline.
Q/Q(M)-482411 Report a Problem
Telogen effluvium:
1
Involves a diffuse alopecia affecting more than 50% of the scalp
2
Often results from antimetabolites used during cancer chemotherapy
3
Is an inflammatory alopecia devoid of scarring
4
Is a patchy alopecia affecting less than 50% of the scalp
5
Results from sudden illness or surgery
Q/Q(M)-474180 Report a Problem
Telogen effluvium:
5
Results from sudden illness or surgery
Telogen effluvium is an excessive loss of club hairs from the normal resting follicles of the scalp. The
follicle is pushed from anagen to catagen to telogen. There is no inflammatory process involved.
Causes of telogen effluvium are illness, surgery, parturition, fever, drugs, traction, starvation, and
hypervitaminosis A. Usually, the hair loss only involves less than 50% of the scalp. There is no
specific therapy, and most cases are self-resolving within months.
Q/Q(M)-474180 Report a Problem
65
Which of the following statements about darkly pigmented races versus lighter pigmented races is
correct?
1
The number of melanosomes in melanocytes are the same
2
The individual melanosomes have the same degree of melanization
3
The melanosomes are equal in size melanosomes
4
There are equal numbers of melanocytes
5
There is a faster rate of melanosome degradation
Q/Q(M)-478193 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about darkly pigmented races versus lighter pigmented races is
correct?
4
There are equal numbers of melanocytes
Individuals with darker pigmentation have an equal ratio of melanoyctes to keratinocytes. Darker
pigmentation is related to an increased number of melanosomes, increased melanization, greater size
of melanosomes, and slower degradation.
Q/Q(M)-478193 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands are located in each of the following locations except:
1
Nipple
2
Labia minora
3
Palms
4
Eyelids
5
Buccal mucosa
Q/Q(M)-477356 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands are located in each of the following locations except:
3
Palms
Sebaceous glands secrete their contents in a holocrine fashion and are primarily under the influence of
androgens. They secrete triglycerides, phospholipids, esterified cholesterol, waxes but not free
cholesterol. They may be found in association with hair follicles or in some areas of modified skin
such as the nipple/areola, labia minora, prepuce, vermilion border, and eyelids.
Q/Q(M)-477356 Report a Problem
Acid keratins are expressed on which of the following chromosomes?
1
12
2
17
3
9
66
4
16
5
3
Q/Q(M)-479074 Report a Problem
Acid keratins are expressed on which of the following chromosomes?
2
17
Acidic keratins (K10-20) are expressed from chromosome 17. Basic keratins (K1-9) are on
chromosome 12. The other listed chromosomes are not involved in keratins.
Q/Q(M)-479074 Report a Problem
Dimple sign refers to:
1
When an intact epidermis shears away from the underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface
2
Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an intact bulla
3
Swollen, itchy and or red after stroking the skin
4
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed along its margins
5
Disappearance of color when the lesion is pressed
Q/Q(M)-482674 Report a Problem
Dimple sign refers to:
4
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed along its margins
Central depression within a lesion when squeezed is referred to as the dimpling sign and is seen in
dermatofibromas. Nikolsky sign can be seen when an intact epidermis shears away from the
underlying dermis, leaving a moist surface (seen in pemphigus vulgaris, staphylococcus scalded skin
syndrome (SSSS), and toxic epidermal necrosis). Spreading bulla phenomenon with pressure on an
intact bulla is referred to as Asboe-Hansen sign, commonly seen with pemphigus vulgaris. Swollen,
itchy and or red after stroking the skin is referred to Dariers sign and can be seen in systemic
mastocytosis or urticaria pigmentosa. Disappearance of color or blanching when the lesion is pressed
is commonly found on vascular lesions
Q/Q(M)-482674 Report a Problem
Sebaceous carcinoma stains positive for:
1
EMA
2
CEA
3
S100
4
cKIT
5
CD1a
Q/Q(M)-482662 Report a Problem
Sebaceous carcinoma stains positive for:
67
1
EMA
Sebaceous carcinomas stain positive for EMA. The other answer choices are incorrect as they do not
stain positive in sebaceous carcinoma.
Q/Q(M)-482662 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about plectin is correct?
1
Links fillagrin to the plasma membrane
2
Crosslinks proteins in adherens junction
3
Mutations result in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia
4
Plectin is a member of the plakin family
5
Plectin is a constituent protein of the desmosomal plaque
Q/Q(M)-478169 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about plectin is correct?
4
Plectin is a member of the plakin family
Plectin is a hemidesmosomal protein and is not present in the desmosome. It links intermediate
filaments to the plasma membrane, crosslinks hemidesmosomal proteins, mutations result in
epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy and is a member of the plakin family.
Q/Q(M)-478169 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true regarding the development of hair follicles?
1
The first primordial hair follicles form at 15 weeks gestation
2
The first hair follicles form on the scalp and eyelashes
3
Follicles develop in a cephalad to caudal direction
4
New follicles develop during the first 3 months postpartum
5
The eyebrows develop late in gestation
Q/Q(M)-480542 Report a Problem
Which of the following is true regarding the development of hair follicles?
3
Follicles develop in a cephalad to caudal direction
The first primordial hair follicles form at 9 weeks gestation on the eyebrows, upper lip, and chin. The
remaining follicles develop at 4-5 months in a cephalad to caudal direction. New follicles cannot
develop in adult skin.
Q/Q(M)-480542 Report a Problem
In which of the following locations would you be least likely to identify melanocytes?
1
Stria vascularis of the ear
68
2
Iris
3
Leptomeninges
4
Retina
5
Pericardium
Q/Q(M)-479179 Report a Problem
In which of the following locations would you be least likely to identify melanocytes?
5
Pericardium
Melanocytes are found in the stria vascularis of the ear, iris, leptomeninges and retina. There are no
normal populations of melanocytes found in the pericardium.
Q/Q(M)-479179 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis attach to the basement membrane zone at
hemidesmosomes via what intermediate filament molecules?
1
Keratins 1 and 10
2
Keratins 5 and 14
3
Desmogleins 1 and 3
4
Desmoplakin and Desmoglobin
5
BPAG1 and BPAG2
Q/Q(M)-482405 Report a Problem
Keratinocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis attach to the basement membrane zone at
hemidesmosomes via what intermediate filament molecules?
2
Keratins 5 and 14
Keratins 5 and 14 are intermediate filaments found in the basal layer of the epidermis that play a role
in attaching basal layer keratinocytes to the basement membrane zone. Keratins 1 and 10 are found in
more superficial layers of the epidermis. Desmogleins, desmoplakin, and desmoglobin are all
components of desmosomes which attach keratinocytes to other surrounding keratinocytes. BPAG1
and BPAG2 are basement membrane proteins.
Q/Q(M)-482405 Report a Problem
Granulation tissue primarily contains:
1
Collagen I
2
Collagen III
3
Collagen IV
4
Fibrin
5
Collagen VII
69
Q/Q(M)-479409 Report a Problem
Granulation tissue primarily contains:
2
Collagen III
Granulation tissue begins to form four days after injury and is composed of new capillaries,
macrophages, fibroblasts, blood vessels and primarily collagen type III. Formulation of granulation
tissue is dependent on the presence of fibronectin and progresses through an orderly sequence of
matrix deposition: fibronectin to collagen III then finally collagen I.
Q/Q(M)-479409 Report a Problem
The strength of a scar:
1
Is 5% at 1 week
2
Is 20% at 3 weeks
3
Is 70% at 1 year
4
All of these options are correct
5
None of these options are correct
Q/Q(M)-478015 Report a Problem
The strength of a scar:
4
All of these options are correct
A scar has 5% strength at 1 week, 20% at 3 weeks and 70% at 1 year. It will never recover strength to
the level of pre-injury.
Q/Q(M)-478015 Report a Problem
Which of the following elements is necessary for melanin production?
1
Copper
2
Selenium
3
Iron
4
Zinc
5
Calcium
Q/Q(M)-479182 Report a Problem
Which of the following elements is necessary for melanin production?
1
Copper
Melanin is synthesized from tyrosine vis the action of the enzyme tyrosinase (tyrosine to DOPA to
DOPAquinone to melanin). Tyrosinase is a copper containing enzyme. The other elements are not
specifically required for melanin synthesis.
Q/Q(M)-479182 Report a Problem
70
Anagen effluvium is
1
Rarely seen following administration of cancer chemotherapeutic agents
2
Stimulus induces the abrupt cessation of miotic activity in the rapidly dividing hair matrix cells
3
Occurs within 24 to 48 hours of exposure
4
Entirely inreversible
5
Patients being treated with nitrosurea agents are usually spared
Q/Q(M)-478016 Report a Problem
Anagen effluvium is
2
Stimulus induces the abrupt cessation of miotic activity in the rapidly dividing hair matrix
cells
It is frequently seen following administration of cancer chemotherapeutic agents. Stimulus induces the
abrupt cessation of mitotic activity in the rapidly dividing hair matrix cells. Occurs within days to
weeks following exposure to the inciting agent and is entirely reversible. Frequent causes include
antimetabolites, alkylating agents, mitotic inhibitors, thallium, boron. Frequent causes include
doxorubicin, nitrosureas and cyclophosphamide.
Q/Q(M)-478016 Report a Problem
Elaunin fibers:
1
Run parallel in bands within the superficial papillary dermis
2
Run perpendicular from the dermo-epidermal junction within the superficial papillary dermis
3
Run parallel in bands within the reticular dermis
4
Run perpendicular in bands within the deep dermis
5
Run perpendicular in bands within the reticular dermis
Q/Q(M)-474181 Report a Problem
Elaunin fibers:
3
Run parallel in bands within the reticular dermis
Elaunin fibers are elastic fibers that have less elastin and more fibrillin and run parallel in thin bands
within the reticular dermis. Oxytalin fibers contain no elastin and run perpendicular from the dermo-
epidermal junction within the superficial papillary dermis. Elastic fibers turn over slowly in the skin,
and are damaged by ultraviolet radiation.
Q/Q(M)-474181 Report a Problem
Which of the following cells are required for wound healing?
1
Neutrophil
2
Macrophage
71
3
Eosinophil
4
Langerhans cell
5
Lymphocyte
Q/Q(M)-478014 Report a Problem
Which of the following cells are required for wound healing?
2
Macrophage
The macrophage is required for wound healing. The macrophages debride tissue, secrete collagenase
and stimulate expression of FGF, IL-1, TGF-beta, PDGF and TGF-alpha thus facilitating transition
from inflammation to repair.
Q/Q(M)-478014 Report a Problem
A patient presents with painless firm nodules. Pathology reveals no epidermal involvement. The
patient is ultimately diagnosed with sarcoid. What is this type of involvement called?
1
Darier-Roussy disease
2
Lofgrens syndrome
3
Heerfordts syndrome
4
Lupus Pernio
5
Kveim-Siltzbach disease
Q/Q(M)-482776 Report a Problem
A patient presents with painless firm nodules. Pathology reveals no epidermal involvement. The
patient is ultimately diagnosed with sarcoid. What is this type of involvement called?
1
Darier-Roussy disease
Darier Roussy disease refers to subcutaneous sarcoid. Lofgrens syndrome is sarcoid presenting as
erythema nodosum, hilar lymphadenopathy, fever, migrating polyarthritis, and acute iritis. Heerfordts
is parotid gland enlargement, uveitis, fever and cranial nerve palsies. Kveim-Siltzbach antigen is used
rarely in the US but can aid in the diagnosis of sarcoid.
Q/Q(M)-482776 Report a Problem
Cutaneous warts in renal transplant recipients show increased expression of which keratin?
1
K2
2
K5
3
K9
4
K13
5
K16
Q/Q(M)-475858 Report a Problem
72
Cutaneous warts in renal transplant recipients show increased expression of which keratin?
4
K13
Keratins are divided into acidic (type I) and basic (type II) subtypes. Keratin 13 is a type I keratin
which is expressed suprabasally in adult epithelia and is associated with terminal differentiation. Renal
transplant recipients have an increased risk of developing skin cancers and multiple warts. Factors
contributing to this increased risk include human papillomavirus infection, immunosuppressive
therapy, and exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Increased expression of K13 has been demonstrated in
high-risk papillomas in this patient population.
Q/Q(M)-475858 Report a Problem
Fragmentation and/or loss of elastic fibers in not seen in:
1
Cutis laxa
2
Marfan's syndrome
3
Anetoderma
4
Psuedoxanthoma elasticum
5
Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome
Q/Q(M)-480538 Report a Problem
Fragmentation and/or loss of elastic fibers in not seen in:
5
Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome
Cutis laxa results from decreased desmosine and lysyl oxidase and demonstrates fragmentation and
loss of elastic fibers. Marfan's sydnrome results from decreased fibrillin I and demonstrates
fragmentation of elastic fibers. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum demonstrates increased
glycosaminoglycans on elastic fibers and the accumulation of fragmented and calcified elastic fibers.
Anetoderma has decreased desmosine and demonstrates loss and fragmentation of elastic fibers.
Buschke-Ollendorf syndrome exhibits increased desmosine and an increased amount of thickened
elastic fibers.
Q/Q(M)-480538 Report a Problem
Regarding sebaceous glands:
1
These glands are present at birth at their adult size
2
Size of the gland is proportional to the size of the associated hair follicle
3
Are always associated with a hair follicle
4
Are found everywhere on the skin except palms and soles
5
Are unilobular glands
Q/Q(M)-480144 Report a Problem
Regarding sebaceous glands:
73
4
Are found everywhere on the skin except palms and soles
Sebaceous glands are found everywhere on the skin except on the palms and soles. They are
multilobular, emptying into the sebaceous duct. Most sebaceous glands are associated with hair
follicles, but free glands exist, especially on the lip (Fordyce spots), on the nipple/areola
(Montgomerys tubercles), Meibomian glands of the eyelids and Tysons glands on the genitalia.
The size of the sebaceous glands are not related to the size of the associated follicle. The sebaceous
gland enlarges at puberty in response to increased androgens.
Q/Q(M)-480144 Report a Problem
The mechanism of action of ipilimumab can be described as
1
Inhibitor of CTLA-4
2
Antibody to CD27
3
Fusion protein binding B7
4
Antibody to CD 8 T cell
5
Inhibitor of CD27
Q/Q(M)-482622 Report a Problem
The mechanism of action of ipilimumab can be described as
1
Inhibitor of CTLA-4
Ipilimumab is an antibody to CTLA-4, this interaction causes inhibition of CTLA-4 which normally
inhibits T cell co-activation by binding to B7 (which normally binds to CD28).
Q/Q(M)-482622 Report a Problem
Once a keratinocyte leaves the basal cell layer, the normal transit time to stratum corneum is at least:
1
7 days
2
14 days
3
21 days
4
28 days
5
35 days
Q/Q(M)-479076 Report a Problem
Once a keratinocyte leaves the basal cell layer, the normal transit time to stratum corneum is at least:
2
14 days
Once a basal cell leaves the basal layer in humans, normal transit time to stratum corneum is at least
14 days. Transit time through the stratum corneum to desquamation requires 14 more days.
Q/Q(M)-479076 Report a Problem
BP230 is a member of of which of the following families?
74
1
Plakin
2
Integrin
3
Laminin
4
Collagen
5
Elastin
Q/Q(M)-479173 Report a Problem
BP230 is a member of of which of the following families?
1
Plakin
BP230 is a member of the plakin family and is homologous to desmoplakin and is intracellular. It
attaches intermediate filaments to hemidesmosomal plaque. The remaining options are not part of the
plakin family.
Q/Q(M)-479173 Report a Problem
The first cell type to migrate into a new wound in great numbers is the:
1
Neutrophil
2
Monocyte
3
Macrophage
4
Lymphocyte
5
Mast cell
Q/Q(M)-479406 Report a Problem
The first cell type to migrate into a new wound in great numbers is the:
1
Neutrophil
Neutrophils migrate with monocytes concurrently, but arrive first in great numbers because of their
abundance in circulation. Chemoattractants for the PMNs are fibrinogen, fibrin split products, C5a and
leukotrienes. If wound contamination is controlled, PMN migration ceases within a few days and they
become entrapped within the wound clot, undergo apoptosis or are phagocytosed by macrophages.
Q/Q(M)-479406 Report a Problem
A 21 year old college student returning back to school from a spring break trip presents with 12 days
of headache, fever, and a skin lesion with annular erythema on her upper back measuring 15 cm in
diameter. This multi-system disease is most likely caused by?
1
Treponema pallidum
2
Borrelia burgdorferi
3
Staphylococcus aureus
4
Francisella tularensis
5
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
75
Q/Q(M)-482786 Report a Problem
A 21 year old college student returning back to school from a spring break trip presents with 12 days
of headache, fever, and a skin lesion with annular erythema on her upper back measuring 15 cm in
diameter. This multi-system disease is most likely caused by?
2
Borrelia burgdorferi
Lyme disease is a multisystem disease caused by Borrelia burgdorferi that is transmitted to humans by
ticks of the genus Ixodes. Patients present with variable constitutional symptoms including HA, fever,
malaise, and arthralgias. 75% of patients develop erythema chronicum migrans that begin as an
erythematous papule that can progress to an annular erythema reaching 20 cm or more in size.
Q/Q(M)-482786 Report a Problem
Which cell type is required for wound healing?
1
Macrophage
2
Lymphocyte
3
Mast cell
4
Dermal dendrocyte
5
Neutrophil
Q/Q(M)-479407 Report a Problem
Which cell type is required for wound healing?
1
Macrophage
The macrophage is required for wound healing. Without macrophages, there is no healing.
Macrophages debride tissue through phagocytosis and digestion of organisms, tissue debris and effete
PMN's. They secrete collagenase and secrete growth factors that facilitate transition from
inflammation to repair.
Q/Q(M)-479407 Report a Problem
Embryologically, epidermal stratification occurs at approximately what estimated gestational age?
1
4 weeks
2
8 weeks
3
12 weeks
4
16 weeks
5
20 weeks
Q/Q(M)-478117 Report a Problem
Embryologically, epidermal stratification occurs at approximately what estimated gestational age?
2
8 weeks
Epidermal stratification begins at about 8 weeks estimated gestational age and is completed by the 2nd
76
trimester. Epideral stratification occurs when an 'intermediate layer' develops between the epidermal
basal cells and the overlying layer of periderm cells. The periderm is an embryonic structure that
covers the primitive epidermis until keratinization begins, at which point the periderm sloughs off and
contributes to the protective covering of the newborn, the vernix caseosa. This intermediate layer is
highly proliferative, such that by 24-25 weeks estimated gestaional age, the epidermis consists of 4 or
5 layers, in addition to the degenerating periderm.
Q/Q(M)-478117 Report a Problem
Mutations in which of the following proteins results in epidermolysis bullosa simplex associated with
muscular dystrophy:
1
Uncein
2
Plectin
3
a6b4 integrin
4
Laminin 5
5
Collagen type IV
Q/Q(M)-474163 Report a Problem
Mutations in which of the following proteins results in epidermolysis bullosa simplex associated with
muscular dystrophy:
2
Plectin
Anchoring filaments exist within the lamina lucida. They are primarily comprised of laminin 5 and
BP180. Laminin 5 is a cross-shaped assembly of 3 classes of polypeptides, a, b, g. The anchoring
filaments function as a structural network to which other proteins attach, and they function as
signaling molecules that transmit morphogenetic information to transmembrane proteins of the basal
cell layer (such as the integrins). Laminin 5 is also called epiligrin and binds to the a6b4 integrin at the
hemidesmosome.
Q/Q(M)-474163 Report a Problem
Which hormone is homologous to alpha-MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone)?
1
Insulin
2
Human growth factor
3
Prolactin
4
Thyroid stimulating hormone
5
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Q/Q(M)-476528 Report a Problem
Which hormone is homologous to alpha-MSH (melanocyte stimulating hormone)?
5
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Both alpha-MSH and ACTH are cleavage products of proopiomelanocortin (POMC).
Q/Q(M)-476528 Report a Problem
77
Fibrofolliculomas are associated with:
1
Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome
2
Cowdens
3
Cutis Laxa
4
Marfans
5
Brook Spiegler
Q/Q(M)-482655 Report a Problem
Fibrofolliculomas are associated with:
1
Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome
Fibrofolliculomas are associated with Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome and not in the other answer choices.
Q/Q(M)-482655 Report a Problem
When evaluating a foreign body, which substance would be PAS negative and have no bifringence on
polarizing microscopy?
1
Silica
2
Talc
3
Zinc
4
Aluminium
5
Wood splinters
Q/Q(M)-482780 Report a Problem
When evaluating a foreign body, which substance would be PAS negative and have no bifringence on
polarizing microscopy?
4
Aluminium
Starch, cactus spines, and wood splinters are PAS positive. Silica, talc, zinc, and wood splinters are
positive for bifringence on microscopy.
Q/Q(M)-482780 Report a Problem
Which cadherin is responsible for adhesion of Langerhan cells to the epidermis?
1
E-cadherin
2
P-cadherin
3
N-cadherin
4
Desmoglein
5
Desmocollin
78
Q/Q(M)-476515 Report a Problem
Which cadherin is responsible for adhesion of Langerhan cells to the epidermis?
1
E-cadherin
E-cadherin is responsible for the adhesion of Langerhan cells to the epidermis. There are two major
subclasses of cadherins which mediate cell adhesion and play a fundamental role in normal
development, classic (E-,P-,N-cadherin) and desmosomal (desmoglein and desmocollin). They depend
on calcium for their function.
Q/Q(M)-476515 Report a Problem
The function of glycosaminoglycans/proteoglycans in the dermis is:
1
Regulate water-binding capacity
2
Interact with dermal dendrocytes
3
Facilitate COLVII binding to the anchoring plaques
4
Facilitate mast cell degranulation
5
Regulate lymphocyte trafficking
Q/Q(M)-479245 Report a Problem
The function of glycosaminoglycans/proteoglycans in the dermis is:
1
Regulate water-binding capacity
The function of glycosaminoglycans/proteoglycans in the dermis is to regulate water-binding capacity.
The other listed options are not functions of glycosaminoglycans / proteoglycans.
Q/Q(M)-479245 Report a Problem
A mitten deformity is most characteristic of what inherited disease?
1
Hallopeau Siemens dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
2
Non-hallopeau Siemens dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
3
Herlitz type junctional epidermolysis bullosa
4
Non-herlitz type junctional epidermolysis bullosa
5
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
Q/Q(M)-482775 Report a Problem
A mitten deformity is most characteristic of what inherited disease?
1
Hallopeau Siemens dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
Hallopeau Siemens dystrophic EB is characterized by pseudosyndactyly, mitten deformities of the
hands and feet. Non Hallopeau Siemens is much less severe. Not present in junctional epidermolysis
bullosa or epidermolyisis bullosa simplex.
Q/Q(M)-482775 Report a Problem
79
Sebaceous glands use what type of secretion?
1
Exocrine
2
Endocrine
3
Apocrine
4
Holocrine
5
Merocrine
Q/Q(M)-482656 Report a Problem
Sebaceous glands use what type of secretion?
4
Holocrine
Sebaceous glands are associated with holocrine type secretion (release by rupture of the plasma
membrane). Apocrine is used to describe decapitation secretion for the cell (as seen in apocrine
glands). Merocrine secretions are characterized by exocytosis (salivary glands as well as some eccrine
and apocrine glands). Exocrine and Endocrine describe glands that secrete directly into the
extracellular environment and directly into the blood stream respectively.
Q/Q(M)-482656 Report a Problem
Aprocrine glands are adnexal glands that are quiescent until puberty. Once active, they secrete their
contents by what mechanism?
1
Vacuolar exocytosis
2
Passive diffusion
3
Decapitation secretion
4
Autocrine secretion
5
Holocrine secretion
Q/Q(M)-482427 Report a Problem
Aprocrine glands are adnexal glands that are quiescent until puberty. Once active, they secrete their
contents by what mechanism?
3
Decapitation secretion
Apocrine glands are adnexal glands that are quiescent until puberty. They are found in the axillae, the
anogenital region, mammary glands, Moll's gland of the eyelid, and ceruminous glands of the external
auditory meatus. They develop from the upper bulge of the hair follicle during embryology. Once
active, apocrine glands secrete their contents by means of decapitation secretion. During this process
the apical portion of the gland pinches off and enters the lumen of the gland.
Q/Q(M)-482427 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about the direct immunofluorescence pattern in lichen planus is
correct?
80
1
The DIF is negative in the vast majority of cases
2
Deposition of IgG is within cytoid bodies in the superficial dermis
3
The DEJ deposition is granular
4
Deposition of fibrinogen is within cytoid bodies in the deep dermis
5
There is prominent deposition of IgM within the spinous layer of the epidermis.
Q/Q(M)-478203 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about the direct immunofluorescence pattern in lichen planus is
correct?
3
The DEJ deposition is granular
The DEJ deposition is granular. The DIF is positive in the vast majority of cases. Deposition of IgM
and fibrinogen is within cytoid bodies in the superficial dermis. There is no deposition of IgM within
the spinous layer of the epidermis.
Q/Q(M)-478203 Report a Problem
Which mechanoreceptor found in hair bearing areas sense deep touch and vibration?
1
Merkel cell
2
Meissner corpuscle
3
Vater-Pacini corpuscle
4
Krase end-bulb
5
Free nerve ending
Q/Q(M)-476513 Report a Problem
Which mechanoreceptor found in hair bearing areas sense deep touch and vibration?
3
Vater-Pacini corpuscle
Vater-Pacini corpuscles sense deep touch and vibration. Merkel cells are slow adapting type I
mechanoreceptors found among basal keratinocytes. Meissner corpuscles are found in the dermal
papilla, especially in the palms and soles. Krase end-bulbs are mucocutaneous end-organs found on
the glans penis, prepuce, clitoris, labia minora, and vermillion border of the lip.
Q/Q(M)-476513 Report a Problem
Which of the following cytokines is secreted by adipocytes?
1
IL-2
2
Il-4
3
IL-6
4
IL-10
5
IL-12
Q/Q(M)-482532 Report a Problem
81
Which of the following cytokines is secreted by adipocytes?
3
IL-6
Adipocytes secrete tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-6 (IL-6), leptin, adiponectin,
angiotensinogen, and resistin. Specifically it has been shown that IL-6 mRNA levels in human
subjects are significantly greater in adipose tissue than in other tissues known to express IL-6. It is
thought that circulating IL-6 levels may be higher in obese patients, contributing to the development
and progression of vascular disease in this patient population.
Q/Q(M)-482532 Report a Problem
Regarding the Langerhans cell histiocytoses, which of the following statements is true:
1
Letterer-Siwe primarily affects children ages 2-4 years
2
Hand-Schller-Christian represents the triad of diabetes mellitus, bone lesions, and
exophthalmos
3
Hashimoto-Pritzker is characterized by a solitary, self-resolving papule or nodule
4
Approximately 50% of cells will have Birbeck granules.
5
Langerhans cell histiocytoses stain positively for CD1a, S100, HAM56, and CD68.
Q/Q(M)-482771 Report a Problem
Regarding the Langerhans cell histiocytoses, which of the following statements is true:
4
Approximately 50% of cells will have Birbeck granules.
Letterer-Siwe primarily affects children under age 2. Hand-Schller-Christian represents the triad of
diabetes insipidus, bone lesions, and exophthalmos. Hashimoto-Pritzker is characterized by a self-
resolving widespread eruption. Langerhans cell histiocytoses stain positively for CD1a and S100 but
not for HAM56 and CD68.
Q/Q(M)-482771 Report a Problem
Elastic fibers are present in the dermis and are responsible for providing tissue resiliency. They are
comprised of elastin as well as microfibrillar proteins including:
1
Fibrillins and fibulins
2
Hyaluronic acid
3
Collagen II
4
Laminin 5 and BPAG2
5
Desmoplakin and plakoglobin
Q/Q(M)-482414 Report a Problem
Elastic fibers are present in the dermis and are responsible for providing tissue resiliency. They are
comprised of elastin as well as microfibrillar proteins including:
82
1
Fibrillins and fibulins
Elastic fibers are comprised of elastin as well as microfibrillar proteins including fibrillins and
fibulins. Hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan found in the extracellular matrix of the dermis.
Collagen II is the predominant collagen found in cartilage. Laminin 5 and BPAG2 are important
anchoring filaments in the basement membrane zone. Desmoplakin and plakoblobin are proteins found
in the anchoring plaques of desmosomes in the epidermis.
Q/Q(M)-482414 Report a Problem
Which of the following protein plays a major role in wound healing?
1
Uncein
2
Fibronectin
3
Nidogen
4
Entactin
5
Band-6 protein
Q/Q(M)-479176 Report a Problem
Which of the following protein plays a major role in wound healing?
2
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a key player in wound healing, initially secreted by myofibroblasts. The bed/matrix of
fibronectin provides an adherent base for migration into the wound, provides scaffolding for collagen
fibrils and mediates wound contraction. Band-6 protein is a constituent of the desmosomes
intracellular plaque. Entactin and nidogen are synonyms and are found in the dermal-epidermal
junction, binding to laminin 1s alpha chain. Uncein is associated with anchoring filaments.
Q/Q(M)-479176 Report a Problem
Glomus cells are:
1
Modified fibroblasts
2
Modified skeletal muscle cells
3
Vascular smooth muscle cells
4
Monocytes
5
Neuronal cells
Q/Q(M)-474178 Report a Problem
Glomus cells are:
3
Vascular smooth muscle cells
Glomus cells are derived from Suquet-Hoyer canals. They are vascular smooth muscle cells that allow
the rapid shunting of blood from the arterioral to venular system, bypassing the capillaries. This
process occurs primarily on the palms and soles.
Q/Q(M)-474178 Report a Problem
83
Which one of the following is responsible for maintaining a barrier to water loss in the stratum
corneum?
1
Involucrin
2
Filaggrin
3
Loricrin
4
Transglutaminase
5
Odland bodies
Q/Q(M)-475853 Report a Problem
Which one of the following is responsible for maintaining a barrier to water loss in the stratum
corneum?
5
Odland bodies
Odland bodies, also known as lamellar granules, keratinosomes, and membrane-coating granules, are
small organelles that are discharged from granular cells into the intracellular space of the granular
layer of the epidermis. These bodies have two known functions: they mediate stratum corneum cell
cohesion and they form a barrier to water loss. Odland bodies are round to oval, measure
approximately 300 to 500 nm in diameter, and possess a trilaminar membrane and a laminated interior.
They contain neutral sugars linked to lipids and/or proteins, hydrolytic enzymes, and free sterols.
Filaggrin is a breakdown product of filaggrin precursor, a component of keratohyaline granules, which
aggregates with keratin filaments and acts as a "glue" for keratin filaments. Involucrin is a cysteine-
rich protein synthesized in the cytoplasm of spinous cells. The enzyme, transglutaminase, cross-links
involucrin in the granular layer forming an insoluble cell boundary that is resistant to denaturing and
reducing chemicals. Loricrin, is a highly insoluble sulfur- and glycine/serine-rich protein, which is the
major protein comprising the cornified cell envelope.
Q/Q(M)-475853 Report a Problem
The greatest density of mast cells is found in the:
1
Stratum spinosum
2
Stratum basale
3
Papillary dermis
4
Reticular dermis
5
Subcutaneous fat
Q/Q(M)-479247 Report a Problem
The greatest density of mast cells is found in the:
3
Papillary dermis
Mast cells are found in the greatest density in the papillary dermis, in sheaths of the appendages, and
around blood vessels and nerves of the subpapillary plexus. These cells are derived from CD34+ stem
cells residing in the bone marrow. They produce and store in secretory granules many inflammatory
mediators such as histamine, heparin, tryptase, chymase, carboxypeptidase, neutrophil chemotactic
84
factor and eosinophilic chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. They also release, without storing, growth
factors, cytokines and leukotrienes. Giemsa or Leder stains are used to identify mast cells in biopsy
specimens. Giemsa stains mast cell granules purple. Leder stains granules red.
Q/Q(M)-479247 Report a Problem
Which keratins are expressed in the stratum germinativum and are present but not made de novo in the
stratum spinosum?
1
K4, 13
2
K1,10
3
K2e, 10
4
K3,12
5
K5,14
Q/Q(M)-480536 Report a Problem
Which keratins are expressed in the stratum germinativum and are present but not made de novo in the
stratum spinosum?
5
K5,14
K5 and K14 are expressed in the stratum germinativum (basal layer) and are defective in
epidermolysis bullosa simplex. They are still present in the stratum spinosum but are not made de
novo in this layer. K4 and 13 are found in mucosal epithelium. K1 and 10 are expressed in suprabasal
keratinocytes, K2e and 10 in the upper spinous and granular layers, and K3 and K12 in the cornea.
Q/Q(M)-480536 Report a Problem
Each of the following is true about melanosomes except:
1
Most characteristic organelle of the melanocyte
2
Tyrosinase activity decreases as melanosomoes mature
3
Are transferred to keratinocytes via phagocytosis
4
Are singly dispersed in the basal layer in white skin
5
Are larger in size in black skin compared to white skin
Q/Q(M)-477192 Report a Problem
Each of the following is true about melanosomes except:
4
Are singly dispersed in the basal layer in white skin
Several differences exist that may explain the heterogeneity of skin color. The number of melanocytes
are the same; however, there are several differences in the melanosomes. Differences in skin color can
be attributed to five factors. In racially heavily pigmented skin, (1) there is greater production of
melanosomes in melanocytes, (2) individual melanosomes show a higher degree of melanization, (3)
melanosomes are larger, (4) the melanosomes are dispersed to a greater degree in the keratinocytes,
and (5) there is a slower rate of degradation.
Q/Q(M)-477192 Report a Problem
85
Upon presentation of an antigen in the skin surface, a hapten forms. The first cell to take up the hapten
is:
1
B cells
2
Langerhans cells
3
keratinocytes
4
T cells
5
Mast cell
Q/Q(M)-478578 Report a Problem
Upon presentation of an antigen in the skin surface, a hapten forms. The first cell to take up the hapten
is:
2
Langerhans cells
Most of the contact allergens are low-molecular weight chemicals, which after penetrating into the
skin, have to couple with host proteins to be able to act as full antigens. These are called haptens.
Upon epicutaneous application to a naive host, Langerhans cells take up the hapten, process it and
migrate towards the regional lymph nodes, where the anitgen is presented to the naive T cells.
Q/Q(M)-478578 Report a Problem
Mutations in which of the following genes will produce red hair?
1
MC1-R
2
Agouti
3
Hairless
4
c-kit
5
Tyrosinase
Q/Q(M)-480131 Report a Problem
Mutations in which of the following genes will produce red hair?
1
MC1-R
MC1-R is the receptor that binds alpha-MSH, and ACTH>alpha-MSH. Defects in this receptor will
produce a phenotype including red hair. Agouti is not involved in this process. Agouti describes the
banding of hairs seen in some mammals such as dogs, foxes, and mice, which is due to alternating
production of eumelanin and pheomelanin occurs. This has not been described in humans (Bolognia,
p942). The hairless gene is associated with alopecia totalis. C-kit mutations are associated with
piebaldism and urticaria pigmentosa. Tyrosinase defects are associated with Type I Oculocutaneous
albinism.
Q/Q(M)-480131 Report a Problem
Hair grows at:
86
1
0.004 mm/day
2
0.04 mm/day
3
0.4 mm/day
4
4 mm/day
5
10 mm/day
Q/Q(M)-478018 Report a Problem
Hair grows at:
3
0.4 mm/day
Hair grows at an average of 0.4 mm/day. The other options are incorrect.
Q/Q(M)-478018 Report a Problem
Anagen effluvium is best described as:
1
An abrubt transition from anagen to catagen in rapidly dividing hair matrix cells
2
A cessation of mitotic activity in rapidly dividing hair matrix cells
3
An abrupt transition of telogen to anagen in resting hair matrix cells
4
A cessation of mitotic activity in resting hair matrix cells
5
A scarring alopecia affecting only anagen stage follicles
Q/Q(M)-474171 Report a Problem
Anagen effluvium is best described as:
2
A cessation of mitotic activity in rapidly dividing hair matrix cells
Anagen effluvium results from an outside stimulus most often an antimetabolite, chemotherapeutic
drug inducing an abrupt cessation of hair matrix cell mitotic activity. This process occurs within
days to weeks of the stimulus, and is reversible with cessation of the drug therapy.
Q/Q(M)-474171 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands:
1
Are coiled glands
2
Have a two segment ducts that empties onto the skin
3
Are present everywhere on the skin except on the palms and soles
4
Function from birth
5
Secretions are initially odorless
Q/Q(M)-480146 Report a Problem
Apocrine glands:
87
5
Secretions are initially odorless
Apocrine glands are tubular glands that demonstrate decapitation secretion. Like eccrine glands, the
ducts are composed of three segments: intraepidermal duct, intradermal duct and secrectory portion.
The duct usually leads to a pilosebaceous follicle above the entrance of the sebaceous duct. They are
found in the axillae, anogenital region, external ear canal (ceruminous glands), in the eyelids
(Molls glands) and in the breast (mammary glands). These glands are functional starting at
puberty. The initial secretions are odorless with the odor being derived from C6 C11 acids. The
most abundant being 3-methyl-2-hexenoic acid.
Q/Q(M)-480146 Report a Problem
Which of the following skin conditions involves elastin?
1
Rothmund-Thompson
2
Epidermolytic Hyperkeratosis
3
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
4
Progeria
5
Classic type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Q/Q(M)-478200 Report a Problem
Which of the following skin conditions involves elastin?
3
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum
There are many genodermatoses that involve elastin. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum shows increased
glycosaminoglycans on elastic fibers, calcium deposition and accumulation of fragmented and
calcified elastic fibers. Cutis laxa shows decreased desmosine and lysyl oxidase. In Marfan sydrome
there is decreased fibrillin I and fragmentation of elastic fibers. Buschke-Ollendorf syndroms shows
increased desmosine and increased amount of thickend elastic fibers. Other elastin disease are
congenital contractural arachnodactyly from a mutation in fibrillin II and anetoderma which shows
decreased desmosine and loss/fragmentation of elastic fibers. Classic type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is
caused by a defect in collagen V and not in elastin. Progeria is caused by a defect in lamin A. EHK is
caused by a defect in keratin 1/10. Rothmund Thompson is caused by a defect in RecQL4, a helicase
gene.
Q/Q(M)-478200 Report a Problem
Eccrine glands are found in all the following areas of the body except:
1
Axillae
2
Palms
3
Labia minora
4
Scalp
5
Cutaneous lip
Q/Q(M)-477163 Report a Problem
Eccrine glands are found in all the following areas of the body except:
88
3
Labia minora
Eccrine glands are sweat glands enervated by cholinergic sympathetic nerves mediated by
acetylcholine. They absent on modified skin which lacks appendages like the vermillion border, nail
beds, glans penis, inner aspect of the prepuce and the labia minora.
Q/Q(M)-477163 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about Laminins is correct?
1
Laminins span from the plasma membrane of basal keratinocytes to the lamina lucida
2
Laminins provide little structural support in the basement membrane
3
Laminins provide signaling molecules that interact with other proteins to transmit
morphogenetic information to the cell's interior
4
Laminin 5 is also called plectin
5
Laminin 5 is the only laminin found in the basement membrane
Q/Q(M)-478190 Report a Problem
Which of the following statements about Laminins is correct?
3
Laminins provide signaling molecules that interact with other proteins to transmit
morphogenetic information to the cell's interior
Laminins do transmit signals to the cell's interior. They span from the plasma membrane of basal
keratinocytes to the lamina DENSA, not lucida. Laminin 5 (also known as epiligrin) is part of a
structural network in the basement membrane that also includes laminin 6.
Q/Q(M)-478190 Report a Problem
Platelets release which of the following factors to promote new tissue growth?
1
Neutrophil chemotactic factor
2
IL-1
3
ADP
4
TGF-alpha
5
FGF
Q/Q(M)-479405 Report a Problem
Platelets release which of the following factors to promote new tissue growth?
4
TGF-alpha
Platelets release PDGF, TGF-alpha and TGF-beta which promote new tissue growth. FGF and IL-1
are released from monocytes as growth factors (monocytes also release PDGF, TGF-alpha and TGF-
beta). ADP is released from platelets, but is not functioning as a growth factor. Neutrophil chemotactic
factor is released from mast cells and is an inflammatory mediator.
Q/Q(M)-479405 Report a Problem
89
Which of the following abnormalities would be present in a patient with Harlequin ichthyosis?
1
lamellar granules are uniformly absent
2
keratohyaline granules are normal in all types of harlequin fetus
3
demoyokin mutation
4
band 6 protein is absent
5
plakoglobin is abnormal
Q/Q(M)-479175 Report a Problem
Which of the following abnormalities would be present in a patient with Harlequin ichthyosis?
1
lamellar granules are uniformly absent
In Harlequin ichthyosis, the lamellar granules are uniformly abnormal or absent. On electron
microscopy, there is no evidence of the lipid lamellae which form due to lamellar granule discharge
into the region between the granular and cornified cells (Fitz v6, p493). This is suggestive of a primary
defect in lipid synthesis and protein dephosphorylation resulting in faulty lamellar body formation and
secretion (Bolognia, ch. 57). Harlequin fetus/ichthyosis can be divided into three types based on the
microscopic appearance of the keratohyaline granules. Type I - normal, Type II - too small to be seen
by light microscopy, Type III - absent keratohyaline granules. Demoyokin, band-6 protein (a plaque
component) and plakoglobin are desmosomal proteins and not involved in Harlequin ichthyosis.
Recently, the gene defect was localized a defect in the ABCA12 protein.
Q/Q(M)-479175 Report a Problem
A 55 year-old male presents with a indurated yellow-brown plaque near the eye. Work-up reveals:
1
IgG monoclonal gammopathy
2
IgG polyclonal gammopathy
3
IgA monoclonal gammopathy
4
IgA polyclonal gammopathy
5
no paraproteinemia seen in 50% of cases
Q/Q(M)-482773 Report a Problem
A 55 year-old male presents with a indurated yellow-brown plaque near the eye. Work-up reveals:
1
IgG monoclonal gammopathy
IgG monoclonal gammopathy is seen in over 80% of cases of necrobiotic xanthogranuloma. Pathology
reveals palisading granulomas with necrobiosis and cholesterol clefts. Recurrence rates as high as 42%
have been reported after surgical excision.
Q/Q(M)-482773 Report a Problem
Homocystinuria is an autosomal recessive condition with findings including a marfanoid habitus,
downward dislocation of the lens, cardiovascular disease and mental retardation. It is caused by a
mutation in cystathionine beta-synthetase. What does this mutation in cystathionine beta-synthetase
cause other than an accumulation of homocystine?
90
1
Abnormal crosslinking of collagen
2
Abnormal development of elastin fibers
3
Melanocyte death
4
Pigmentation of cartilage
5
Black urine
Q/Q(M)-479242 Report a Problem
Homocystinuria is an autosomal recessive condition with findings including a marfanoid habitus,
downward dislocation of the lens, cardiovascular disease and mental retardation. It is caused by a
mutation in cystathionine beta-synthetase. What does this mutation in cystathionine beta-synthetase
cause other than an accumulation of homocystine?
1
Abnormal crosslinking of collagen
Excess homocystine leads to abnormal crosslinking of collagen, with only ~1/3 of crosslinking activity
compared to normal controls (OMIM 236200). The other listed findings are not features of
homocystinuria, though hypopigmentation can be a feature.
Q/Q(M)-479242 Report a Problem
Odland bodies:
1
Contain keratins
2
Are found intercellularly in the basal cell layer
3
Are exclusively intracellular
4
Crosslink with keratins 5 and 14
5
Are secretory granules with features of lysosomes
Q/Q(M)-478163 Report a Problem
Odland bodies:
5
Are secretory granules with features of lysosomes
Odland bodies (AKA lamellar granules) are lamellated bodies containing ceramide, are found
intercellularly in upper level keratinocytes; they discharge contents into the extracellular space at the
junction of the granular and horny layers, establish a barrier to water loss, and with filaggrin mediate
stratum corneum adhesion. Recent studies suggest that they are a type of secretory granule with
features of lysosomes. (They contain lamellar-body-derived enzymes that are important in
desquamation.)
Q/Q(M)-478163 Report a Problem
Which of the following domains is targeted by the autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid?
1
NC16A of BP180
2
Laminin 5
3
Plectin
4
alpha-6 integrin
91
5
NC16A of BP230
Q/Q(M)-478171 Report a Problem
Which of the following domains is targeted by the autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid?
1
NC16A of BP180
The NC16A domain of BP180 is the target of autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid. It interacts with
alpha-6 integrin extracellularly.
Q/Q(M)-478171 Report a Problem
The proteins that make up the cornified cell envelope are synthesized in the:
1
Stratum corneum
2
Stratum basale
3
Melanocytes
4
Stratum granulosum
5
Langerhans cells
Q/Q(M)-479172 Report a Problem
The proteins that make up the cornified cell envelope are synthesized in the:
4
Stratum granulosum
The proteins that make up the cornified cell envelope are synthesized in the spinous and granular cell
layer. The stratum basale is not involved in production of these proteins and there is no protein
synthesis in the stratum corneum. Melanocytes and Langerhans cells are components of the epidermis
but are not involved in this process.
Q/Q(M)-479172 Report a Problem
All of the following pertain to Odland bodies EXCEPT:
1
Contain squalene
2
Are found intracellularly in upper level keratinocytes
3
Discharge their contents into the extracellular space at the junction of the granular and cornified
layers
4
Establish a barrier to water loss
5
Mediate stratum corneum adhesion in conjunction with filaggrin.
Q/Q(M)-479078 Report a Problem
All of the following pertain to Odland bodies EXCEPT:
1
Contain squalene
Odland bodies mediate stratum corneum adhesion in conjunction with FILAGGRIN. They discharge
their contents into the extracellular space at the junction of the granular and horny layers establish a
92
barrier to water loss. They are first found intracellularly in upper level keratinocytes and contain
ceramides not squalene.
Q/Q(M)-479078 Report a Problem
You might also like
- Photodermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocument152 pagesGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Vesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDocument59 pagesVesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Immunedermatology MCQsDocument73 pagesImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDocument58 pagesCutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- General Dermatology MCQsDocument197 pagesGeneral Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed95% (19)
- Pediatric Dermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPediatric Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed89% (18)
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 pagesETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 pagesSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Hair and Nail Disorders MCQsDocument67 pagesHair and Nail Disorders MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Dermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDocument77 pagesDermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDr.Tawheed100% (3)
- Histopathology ETASDocument89 pagesHistopathology ETASDr.Tawheed75% (4)
- Mycology MCQsDocument48 pagesMycology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (11)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 pagesQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- Red and green skin answers keyDocument9 pagesRed and green skin answers keyNiwashiny CnyNo ratings yet
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Document67 pagesMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDocument111 pagesAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument2 pagesMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- Dermatology QuizDocument7 pagesDermatology QuizFaddy OrahaNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument17 pagesDermatologyEbn Seena75% (4)
- Dermatopathology Q - ADocument55 pagesDermatopathology Q - AKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (7)
- Dermatology QuestionsDocument3 pagesDermatology QuestionsMuziki Wa KiafrikaNo ratings yet
- MCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)Document17 pagesMCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)R Ratheesh100% (9)
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- MCQ in Dermatology NMT 10Document18 pagesMCQ in Dermatology NMT 10R Ratheesh100% (2)
- Dermatology MCQ With AnswersDocument27 pagesDermatology MCQ With Answershesham0% (1)
- 11Document3 pages11faresaltaii100% (2)
- Derma MCQ Ch01Document20 pagesDerma MCQ Ch01Rasha Dabbagh75% (4)
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzDocument27 pagesMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Document31 pagesMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument121 pagesDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument42 pagesMCQ Dermatologydraik71100% (5)
- Dermatology QuizDocument10 pagesDermatology QuizSyed Ali Haider0% (1)
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pages101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- PSORIASIS STUDY GUIDEDocument5 pagesPSORIASIS STUDY GUIDEhesham100% (4)
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 pagesDerma CD McqsheshamNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MCQ FRCPDocument101 pagesDermatology MCQ FRCPhesham89% (19)
- Dermatology MCQ With ExplinationsDocument46 pagesDermatology MCQ With ExplinationsheshamNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument3 pagesDermatologyDrkhslid890% (1)
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionDocument207 pagesPrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (1)
- Dermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2Document56 pagesDermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2hesham50% (2)
- Photo QuizDocument21 pagesPhoto Quizabas_maytham1021100% (3)
- End Round of Dermatology, MCQsDocument20 pagesEnd Round of Dermatology, MCQsMuhdZaeed100% (2)
- Dermatology Written Exam 2007Document6 pagesDermatology Written Exam 2007Abdullah Matar BadranNo ratings yet
- Dermatology RecertificatDocument8 pagesDermatology RecertificatKhalifa AL-WishahiNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyDocument7 pagesMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemNo ratings yet
- Dermatology EMQDocument4 pagesDermatology EMQislamawniNo ratings yet
- Dermatoven MCQDocument30 pagesDermatoven MCQS2 GIZI FKUI 2020No ratings yet
- Rubin Skin Review Q's&a'sDocument7 pagesRubin Skin Review Q's&a'sJUSASBNo ratings yet
- Genodermatoses and Vascular MalformationsDocument60 pagesGenodermatoses and Vascular Malformationsalh bashar100% (1)
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationDocument41 pages1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007No ratings yet
- Hair MCQsDocument35 pagesHair MCQsHybat Elsheikh100% (1)
- 1310 Anti-Aging Effects of Retinoid HydroxypinacolDocument2 pages1310 Anti-Aging Effects of Retinoid HydroxypinacolTrâm NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DERMATOLOGY Notes From Uworld, DR-KYDocument22 pagesDERMATOLOGY Notes From Uworld, DR-KYLayan Mohammad100% (1)
- Vitiligo MetaloproteinasesDocument7 pagesVitiligo MetaloproteinasesJose Rodrigues JuniorNo ratings yet
- Dermis Is A Specialized EpidermisDocument4 pagesDermis Is A Specialized EpidermisfaisNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Keperluan PentingDocument4 pagesJurnal Keperluan PentingmhdtaufikkNo ratings yet
- National CollageDocument7 pagesNational CollageSolve App IssuesNo ratings yet
- Dermatologica Sinica: Ai-Young LeeDocument7 pagesDermatologica Sinica: Ai-Young LeeNatta ApucaranaNo ratings yet
- Procapil TechnEngDocument52 pagesProcapil TechnEngbbi bbiNo ratings yet
- General Dermatology MCQsDocument197 pagesGeneral Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed95% (19)
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument88 pagesPharmacology MCQsDr.Tawheed86% (7)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 pagesSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Dermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDocument77 pagesDermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDr.Tawheed100% (3)
- Hair and Nail Disorders MCQsDocument67 pagesHair and Nail Disorders MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Plant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsDocument50 pagesPlant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (2)
- Pediatric Dermatology MCQsDocument53 pagesPediatric Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed89% (18)
- Mycology MCQsDocument48 pagesMycology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (11)
- Histopathology ETASDocument89 pagesHistopathology ETASDr.Tawheed75% (4)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDocument111 pagesAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 pagesQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument2 pagesMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- Regulate Body Temperature with AntiperspirantsDocument6 pagesRegulate Body Temperature with Antiperspirantsanakren296No ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes - PPTX 2020-2021Document103 pagesSkin and Body Membranes - PPTX 2020-2021Faatoots FatsNo ratings yet
- Waiver Guide 2010Document887 pagesWaiver Guide 2010Linette Sabatini ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Tissue Types and FunctionsDocument7 pagesTissue Types and FunctionsJi JiNo ratings yet
- Andrews - Chapter 1 - Skin Basic Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesAndrews - Chapter 1 - Skin Basic Structure and FunctionAngeli Ramos-EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Midterm ExamBulajyo Pangngay JolinaNo ratings yet
- C Handbook. Varna - RevDocument133 pagesC Handbook. Varna - RevAastha SethNo ratings yet
- 11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpDocument26 pages11 Properties of The Hair and ScalpsofiaNo ratings yet
- MOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Document41 pagesMOYA, John Zeus A. (HUMANA Classwork #3 Prelim)Suez AyomNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument61 pagesIntegumentary SystemNicole EncinaresNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chapter 7 PDFDocument41 pages11 - Chapter 7 PDFRakesh RakiNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 Questions A&P 1Document14 pagesQuiz #1 Questions A&P 1trick49No ratings yet
- Integumentary System Terminology WorksheetDocument2 pagesIntegumentary System Terminology WorksheetfernandaNo ratings yet
- ABT Dermaclarine BrochureDocument4 pagesABT Dermaclarine BrochurePatris EliadisNo ratings yet
- HB LSHBB WLDTRBT DHT LLQDocument62 pagesHB LSHBB WLDTRBT DHT LLQtricia isabellaNo ratings yet
- CatioLift Technical InformationDocument9 pagesCatioLift Technical InformationNazihCosmetics0% (1)
- The Complete Book of Hairstyling - NodrmDocument63 pagesThe Complete Book of Hairstyling - Nodrmrvf1No ratings yet
- Hair Shampoos and ColourantsDocument5 pagesHair Shampoos and ColourantsALESANDRA DAWN PAYOTNo ratings yet
- Microneedling in All Skin Types A ReviewDocument9 pagesMicroneedling in All Skin Types A Reviewangela TavaresNo ratings yet
- Dr. Derm CatalogDocument20 pagesDr. Derm CatalogCosmetics Bulgaria100% (1)
- Skincare guide covering external preparationsDocument20 pagesSkincare guide covering external preparationsShailendra SkNo ratings yet
- USMLE World: Revision QuestionsDocument65 pagesUSMLE World: Revision QuestionsDustin91% (22)
- The 3 Layers of Skin: Epidermis, Dermis and Subcutaneous FatDocument11 pagesThe 3 Layers of Skin: Epidermis, Dermis and Subcutaneous FatPanggih Sekar Palupi IINo ratings yet
- Introducing The Epidermis.: ReallyDocument47 pagesIntroducing The Epidermis.: ReallyNaila JinNo ratings yet
- Modul Kulit SsDocument22 pagesModul Kulit Ssshafiraa29No ratings yet
- Integumentary System Diseases ExplainedDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System Diseases Explained리아No ratings yet
- Grow Hair Fast - 7 Steps To A New Head of Hair in 90 DaysDocument145 pagesGrow Hair Fast - 7 Steps To A New Head of Hair in 90 DaysReshma SakpalNo ratings yet
- Cosmetology Learning Module 8 12 Skin Diseases and DisordersDocument15 pagesCosmetology Learning Module 8 12 Skin Diseases and DisorderssofiaNo ratings yet
- Hair Loss EbookDocument252 pagesHair Loss EbookManuelNo ratings yet
- Skin, Hair, and NailsDocument9 pagesSkin, Hair, and NailsJustine JimenezNo ratings yet