Professional Documents
Culture Documents
R-A-A System, Heart Failure Drugs, Mechanisms of Action
Uploaded by
nizam_ghaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
R-A-A System, Heart Failure Drugs, Mechanisms of Action
Uploaded by
nizam_ghaniCopyright:
Available Formats
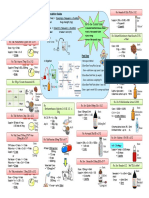
Pressure= Force/Area
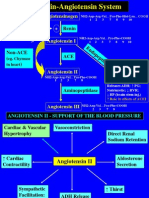
Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Aldosterone
VASOCONSTICTION
renin
ACE
R-A-A System
reduced
digoxin
dosage
Heart
Failure
Workload
myocardial
Contractility
Vasodilators
Fluid Retention
Nitroglicerine
Nitropruside/ Hydralazine
venous tone
Dilate coronary artery
Enhance blood O2 delivery to the heart
Relax arterioles
Diuretics(blood Vol)
ACE i
ARB
Aldosterone Antagonist
Aldosterone Antagonist
Beta blocker
B-type Natriuretic Peptide
Anticoagulants
MoA
slow the heart rate to improve myocardial perfusion by activating potassium
channels to relax the smooth muscle and dilate the arteries
A/E
Nightmare, tiredness
C/I
Asthma
decrease blood pressure by decreasing the cardiac output, also decreased
renin by affecting the JGAB1 receptor
increased TGs and decreases HDL (add a statin to reduce this effect)
Indication
hypertension
+ve Inotropic
Agent
Type
B1 selective
Alpha/Beta
Atenolol
Metoprolol
Carvedilol
Direct Vasodilator
Hydralzine
Sod Nitroprusside
Type
Loop Diuretic
Thiazide
Furosemide
Bumetanide
Hydrochlorothiazide
Metolazone
Spironolactone
Renin-Angiotensin
Sysytem blockers
ACE i
Mortality
Morbidity
Side effect
Skin rash
Persistent cough
Hyperkalemia
Angioedema possibly
Neotropenia
ARBs
eg
Fosinopril
Captopril
Enalapril
Lisinopril
Advice
Take in morning to prevent interrupted sleep
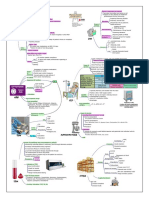
Cardiac
Glycosides
(Digitalis)
Digoxin
MoA
heart contractility, by blocking the sodium/potassium ATPase
channel, the sodium available which in turn the sodium/cal
cium exchange the calcium, it also the storage of calcium in
the cell. Ca2+ influx into myocardial cell an in
contractility of the muscle
Adverse Effect
Visual "yellow vision"
V tachiarrithmia
Hyper K+
Anti-digoxin antibody fragment
Nausea, Vomiting
C/I: myocarditis
Risk for
toxicity
Client at risk
elderly
with advanced heart disease
with severe dysrhythmias
with acute MI
Drug
Interaction
Quinidine
Verapamil
Amiodarone
Serum condition
digoxin > 2mcg/L
potassium < 3 mEq/L
low magnesium
Change in pulse rate / rhythm
Manifestation
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
bradycardia & junctional tachycardia
Confusion
Visual change
b1-agonist
Dobutamine
MoA
cAMP productionB1 receptor
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Amrinone
MoA
Block cAMP degredation in the heart
Advice
Renal failure's progression retarded
BP maybe by NSAIDs
eg.
Advice
Does not have cough & angioedema
Recommending for patients unable to tolerate ACEi
Cautious for renal insufficiency patients
Side effects:
Hyperkalemia
myalgia
dizziness
insomnia
Candersartan
Irbesartan
Losartan
Telmisartan
Valsartan
angina
myocardial infarct
arrhythmias
reduced
digoxin
dosage
Heart
Failure
Pressure= Force/Area
reduced
digoxin
dosage
You might also like
- MBBS Pharmacology PDFDocument20 pagesMBBS Pharmacology PDFAdeeb Aiman Rosli100% (6)
- Pharmacology of Inotropes and VasopressorsDocument51 pagesPharmacology of Inotropes and VasopressorsApen Silaban100% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cardiac MedicationsDocument26 pagesCardiac MedicationsAngie SaquingNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassDocument13 pagesDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Ch-13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument49 pagesCh-13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureShabrin SadikhNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Common Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument3 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Common Cardiovascular Medicationsmikaela_pascuaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NCLEX ReviewDocument128 pagesPharmacology NCLEX ReviewBritanny NelsonNo ratings yet
- C. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Document10 pagesC. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs.Nabeel AsifNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesPharmacology AbbreviationsChiisanaPlays LIFEAFTERNo ratings yet
- CHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart FailureDocument21 pagesCHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart Failuremohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs for Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDocument5 pagesCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocument53 pagesPharmacologyapi-3743565No ratings yet
- Pharma IndiaDocument58 pagesPharma IndiaSaravana Kumar50% (4)
- Merperidine (Demerol)Document1 pageMerperidine (Demerol)ENo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Renal DosingDocument5 pagesAntimicrobial Renal DosingdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- INCOMPATIBILITY CAUSESDocument40 pagesINCOMPATIBILITY CAUSESnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsDocument29 pagesLect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsRaneem ShiferNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in CCF: DR Mozna TalpurDocument14 pagesDrugs Used in CCF: DR Mozna TalpurShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNo ratings yet
- CVSDocument128 pagesCVSearldem1996No ratings yet
- Antiangina 2016Document40 pagesAntiangina 2016Indra Mahaputra100% (1)
- DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADocument36 pagesDRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADeling ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Lec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Document22 pagesLec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Abdul MananNo ratings yet
- Principles of Treatment of IhdDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Treatment of IhdArvinth Guna SegaranNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationDocument37 pagesHeart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationMaham AzmatNo ratings yet
- Anti Anginal DrugsDocument18 pagesAnti Anginal DrugsJuwairia tariqNo ratings yet
- Obat Gagal Jantung N Anti AnginaDocument42 pagesObat Gagal Jantung N Anti AnginaAyu Devi YantiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity Department Pharmacology FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaDocument30 pagesLab Activity Department Pharmacology FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaAnastasya Desy PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive DrugsDocument46 pagesAnti Hypertensive DrugsShabaka KashataNo ratings yet
- Drug Affecting Cardiovascular FunctionDocument21 pagesDrug Affecting Cardiovascular Functionnurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Drug Classes, Mechanisms, Uses and Side EffectsDocument3 pagesDrug Classes, Mechanisms, Uses and Side EffectsWahaj MujahidNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument48 pagesHeart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSanjay SathasevanNo ratings yet
- Obat Gagal Jantung FarmasiDocument25 pagesObat Gagal Jantung FarmasiChie ZhumieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 - Polypeptides - 16 Oct 2006Document63 pagesLecture 15 - Polypeptides - 16 Oct 2006api-3703352No ratings yet
- Hypertension TejaDocument64 pagesHypertension TejaAnushka MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Hypertension An OverviewDocument214 pagesHypertension An OverviewdkhandkeNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease Drug and MechanismsDocument1 pageHeart Disease Drug and MechanismscanuckiepenNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral ResistanceDocument52 pagesBlood Pressure Cardiac Output X Peripheral Resistancelourdes kusumadiNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Dr. Dr. Nicolaski Lumbuun, SPFK Clinical Pharmacologist Faculty of MedicineDocument67 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: Dr. Dr. Nicolaski Lumbuun, SPFK Clinical Pharmacologist Faculty of MedicineShally ChandraNo ratings yet
- RasystemDocument21 pagesRasystemSwathi VorugantiNo ratings yet
- Medications for Hypertension: Therapeutic Actions, Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesMedications for Hypertension: Therapeutic Actions, Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsJhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument54 pagesHypertensionBadri KarkiNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesAnti Hypertension: Dr. Putrya Hawa, M.BiomedputryaNo ratings yet
- The Renin-Angiotensin System: AngiotensinogenDocument7 pagesThe Renin-Angiotensin System: AngiotensinogenreewenNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsAiman TymerNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Kalaiselvan OtDocument46 pagesHeart Failure: Kalaiselvan Otplayme_nowNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument46 pagesHeart Failure: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentRamli HusenNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: DR - Liu LixinDocument46 pagesHeart Failure: DR - Liu LixinsanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Anti HypertensionDocument4 pagesAnti HypertensionMuhammad Zeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Glyceryltrinitrate: Cardiovascular PharmacologyDocument1 pageGlyceryltrinitrate: Cardiovascular PharmacologyChrissieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument6 pagesPharmacology NotesHarsh PawarNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: by J. Jayasutha Dept of Pharmacy PracticeDocument32 pagesHypertension: by J. Jayasutha Dept of Pharmacy PracticeRESHMA I MBANo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System: e CarbamatesDocument26 pagesCholinergic System: e CarbamatesAcai BoncaiNo ratings yet
- Antinanginal DrugsDocument43 pagesAntinanginal DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular-Pharmacology: Akeberegn G 1Document41 pagesCardiovascular-Pharmacology: Akeberegn G 1Nahi ManNo ratings yet
- Cardiotonics - Dr Anoosha BhandarkarDocument60 pagesCardiotonics - Dr Anoosha BhandarkaranooshabhandarkarNo ratings yet
- Drug Catagories For NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Catagories For NursingTabatha AustinMomNo ratings yet
- W3L1 Electrophysiology of The HeartDocument70 pagesW3L1 Electrophysiology of The HeartalfredNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Mohammad DiahDocument50 pagesHeart Failure: Mohammad DiahAdityaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05 - 306Document15 pagesLecture 05 - 306ShAkil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (O)Document26 pagesAngiotensin Receptor Blockers (O)farmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsFrom EverandPharmacotherapeutic Management of Cardiovascular Disease Complications: A Textbook for Medical StudentsNo ratings yet
- Soluble vs Insoluble: Understanding Solutions and SuspensionsDocument1 pageSoluble vs Insoluble: Understanding Solutions and Suspensionsnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Eyes ManagementDocument1 pageEyes Managementnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Calculation guide for stock levels and supplies of medicationsDocument2 pagesCalculation guide for stock levels and supplies of medicationsnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- CalculationDocument2 pagesCalculationnizam_ghani100% (1)
- Responding To SymptomsDocument29 pagesResponding To Symptomsnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy DepDocument1 pagePharmacy Depnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- 1a PA 52 PDFDocument1 page1a PA 52 PDFnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- "Poison" "Poison": Substances Listed in Poison List "Poison List"Document1 page"Poison" "Poison": Substances Listed in Poison List "Poison List"nizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- 1 Mole Cacl 147 G: 1 Mole 2 Eq 1 Mole 1 Eq 1 Mole 1 Eq 2 Eq 2 EqDocument1 page1 Mole Cacl 147 G: 1 Mole 2 Eq 1 Mole 1 Eq 1 Mole 1 Eq 2 Eq 2 Eqnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Calculation PPII Extra SmallDocument2 pagesCalculation PPII Extra Smallnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- PPCC6 pg1Document1 pagePPCC6 pg1nizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Sterile Compounding Chapter 15Document4 pagesQuiz 3 Sterile Compounding Chapter 15nizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Individual Drug For Anti ArrhythmicDocument1 pageIndividual Drug For Anti Arrhythmicnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Lipid Lowering Drugs: MoA, Effects, C/I of BARs, Niacin, Fibrates, Ezetimibe, StatinsDocument1 pageLipid Lowering Drugs: MoA, Effects, C/I of BARs, Niacin, Fibrates, Ezetimibe, Statinsnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmic Anti Arrhythmic: Class IDocument1 pageAnti Arrhythmic Anti Arrhythmic: Class Inizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- QAASSURANCEPHARMACEUTICALSDocument25 pagesQAASSURANCEPHARMACEUTICALSnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument22 pagesGrammarnizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Lirik Lagu Allahi Allah Kiya KaroDocument2 pagesLirik Lagu Allahi Allah Kiya Karonizam_ghaniNo ratings yet
- Laporan Stoc ObatDocument34 pagesLaporan Stoc ObatAyouItuYustirahayuNo ratings yet
- Spring Branch ISD - Spring Oaks School - 2008 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseDocument59 pagesSpring Branch ISD - Spring Oaks School - 2008 Texas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseTexas School Survey of Drug and Alcohol UseNo ratings yet
- NOVEL ORAL DRUG DELIVERY TECHNIQUESDocument11 pagesNOVEL ORAL DRUG DELIVERY TECHNIQUESckbhaiNo ratings yet
- Example of A Health Care Failure Mode and Effects Analysis For IV Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA)Document9 pagesExample of A Health Care Failure Mode and Effects Analysis For IV Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA)nopiNo ratings yet
- Medical Release FormDocument1 pageMedical Release FormNicole LeongNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - PDFDocument41 pagesPharmacology - PDFTanaka KobayashiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy How To Establishment in PakistanDocument7 pagesPharmacy How To Establishment in PakistansobiaNo ratings yet
- Joint Affidavit of UndertakingDocument1 pageJoint Affidavit of UndertakingKeyn TejadaNo ratings yet
- Dosis Ranitidin cw1Document5 pagesDosis Ranitidin cw1Cristine Indria Pieter IINo ratings yet
- Aurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Vancomycin Hydrochloride For Injection (Company Update)Document2 pagesAurobindo Pharma Receives USFDA Approval For Vancomycin Hydrochloride For Injection (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For InsomiaDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For InsomiaLord Pozak MillerNo ratings yet
- Kent R. Olson, MDDocument13 pagesKent R. Olson, MDIya GerzonNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy OTC medication use patternsDocument7 pagesPregnancy OTC medication use patternssyukkurNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument12 pagesCerebral PalsyEunice Lan ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Prescription ExamplesDocument2 pagesPrescription ExamplesJuttaSportNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument25 pagesWarfarinSHIVAM BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Role of Polymers As Gelling Agents in The Formulation of EmulgelsDocument8 pagesRole of Polymers As Gelling Agents in The Formulation of EmulgelsYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- Drug Regulation History Present FutureDocument13 pagesDrug Regulation History Present FutureceabymmbtNo ratings yet
- How To Lower Your TriglyceridesDocument4 pagesHow To Lower Your TriglyceridesNoli CanlasNo ratings yet
- Final CaseDocument45 pagesFinal Case_carido_No ratings yet
- Management of acute dystonic reactionsDocument2 pagesManagement of acute dystonic reactionstaqinosNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Medicine Prices PDFDocument71 pagesNigeria Medicine Prices PDFsumadhurainfoNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride - Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsDocument4 pagesPotassium Chloride - Uses, Dosage & Side EffectsKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocument7 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusNo ratings yet