Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spotlight On Cardiac Drugs
Uploaded by
pauerish100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
904 views2 pagesBrief summary of cardiac drugs
Original Title
Spotlight on Cardiac Drugs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBrief summary of cardiac drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
904 views2 pagesSpotlight On Cardiac Drugs
Uploaded by
pauerishBrief summary of cardiac drugs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
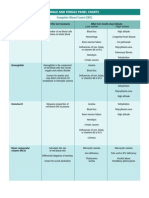
Spotlight on Cardiac Drugs Spotlight on Cardiac Drugs
Drug Class Effect Nursing Considerations
Platelet Inhibitors
Aspirin
Ticlopidine (Ticlid)
Clopidogrel (Plavix)
Glycoprotein IIb/IIa inhibitors
(abciximab, tirofiban, eptifibatide)
nfractionated heparin
!o"#molec$lar#"eight heparin
(enoxaparin %!ovenox&)
Inhibit factors necessary
for platelets to aggregate
on r$pt$red arterial
pla'$e
Ticlodipine can ca$se thrombocytopenia and agran$locytosis, so
fre'$ently monitor platelet co$nts
nfractionated heparin has limited and changeable bioavailability,
so the patient needs fre'$ent activated partial thromboplastin
times to monitor for therape$tic levels
!o" molec$lar heparin has greater bioavailability and more
predictable effects, so it doesn(t re'$ire coag$lation assays
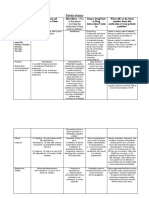
Beta-blockers
Cardioselective types (metoprolol
%Toprol, !opressor&) ) bloc* beta +
receptors in the heart
Noncardioselective types
(propanolol %Inderal&, labetalol
% ,ormodyne, Trandate,&,
Carvedilol %Coreg&) ) bloc* both
the beta + receptors in the heart
and beta - receptors in the l$ngs
and blood vessels
.ed$ce heart rate,
contractility, and speed of
imp$lse cond$ction
thro$gh the A/ node
0eta#bloc*ers are $sed to treat hypertension, angina, cardiac
arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, hyperthyroidism, migraines,
stage fright, and gla$coma1
,oncardioselective beta#bloc*ers aren(t appropriate for someone
"ith a history of constrictive air"ay disease beca$se they can
ca$se bronchoconstriction1 They can also mas* signs of
hypoglycemia1
Carvedilol may be $sed "ith AC2 inhibitors, digitalis, and di$retics
to manage heart fail$re, b$t the combination can slo" A/
cond$ction, so closely monitor the patient for cardiac rhythm
dist$rbances
Peripheral alpha 1-adrenergic blockers
Pra3osin (4inipress)
Tera3osin (5ytrin)
6oxa3osin (Card$ra)
6ilate blood vessels and
decrease blood press$re
The first dose can ca$se severe orthostatic hypotension, ca$sing
the patient to feel light#headed or to faint1
7ho$ld not be $sed alone to treat hypertension beca$se
monotherapy increases the ris* of heart fail$re, stro*e, and chest
pain1
Central alpha 2- agonists
Clonidine (Catapres)
4ethyldopa (Aldomet)
7tim$late receptors in
the brain to decrease 5.
and C8, dilate 0/ and
decrease 0P
Clonidine and methyldopa are approved for hypertension
Clonidine is also being investigated as treatment for menopa$sal
fl$shing,, migraines, and "ithdra"al from opioids, alcohol and
tobacco1
ACE Inhibitors
!osartan (Co3aar)
/alsartan (6iovan)
Irbesartan (Avapro)
Candesartan (Atacand)
Telmisartan (4icardis)
6ecrease p$lmonary
congestion and
peripheral edema9
promote sodi$m and
"ater excretion, and
dilate 0/9 decrease
ventric$lar remodeling
related to 4I or 5:1
4onitor for first dose hypotension
The most common reason to d/c is a dry, irritating co$gh
4onitor the patient for hyper*alemia and avoid potassi$m#sparing
di$retics and potassi$m s$pplements1
6iscontin$e immediately if angioedema develops1
Ta*ing ,7AI6s may increase 0P
Calcium Channel Blockers
Affecting peripheral blood vessels
,ifedipine (Adalat, Procardia)
Amlodipine (,orvasc)
:elodipine (Plendil)
Isradipine (6ynaCirc)
,icardipine (Cardene)
Affecting the heart
/erapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
6iltia3em (Cardi3em, 6ilacor)
4anage coronary
vasospasm and decrease
the heart(s "or*load by
dilating blood vessels
(nondihydropyridines also
decrease contractions)
After 4I, $se only if beta bloc*ers are contraindicated or the
patient can(t tolerate them,
sef$l in patients "ith diabetes, asthma, or migraines
Positie Inotropic Agent
6igoxin Increases force of
ventric$lar contraction9
decreases a$tomaticity of
7A node to maintain an
acceptable heart rhythm
Tell the patient to report irreg$lar heartbeat, vis$al dist$rbances
(bl$rred vision, yello" halo aro$nd ob;ects), fatig$e, anorexia,
na$sea and vomiting1
!asodilators
,itroglycerin (,itrostat)
Isosorbide (Isordil)
6ilate blood vessels to
decrease ventric$lar
filling, preload, and
myocardial oxygen
demand
If the patient develops a tolerance to nitroglycerin, the physician
may prescribe a <nitro#free= period each day (s$ch as removing
the dr$g patch at bedtime)
Diuretics
!oop di$retic (:$rosemide)
Thia3ide di$retic (5CT>)
8smotic di$retic (4annitol)
?#7paring di$retic (7pironolactone)
0loc* reabsorption of
sodi$m and chloride to
decrease intravasc$lar
vol$me
4onitor for dehydration, hypo*alemia ($nless the patient is ta*ing
a potassi$m#sparing di$retic), and hypotension
Teach the patient to ta*e the di$retic in the morning beca$se it "ill
increase the need to $rinate for @ to A ho$rs1 Tell her to "eigh
herself daily and to report any "eight gain of more than B po$nds
(+1C *g) to her health care provider1
Teach her the signs of orthostatic hypotension1 Tell her to get $p
slo"ly and to sit or lie do"n if she feels di33y or faint1
Lifted from: How Cardiac Drugs Do What They Do by Anne Marie Palatnik !" C#C M#" "ursing $%%& '&:( ()*+%
You might also like
- Cardiac MedicationsDocument9 pagesCardiac Medicationsnovikane100% (1)
- Lab ValuesDocument3 pagesLab Valuessurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias ChartDocument6 pagesDysrhythmias Chartjkrix100% (1)
- ECG StripsDocument5 pagesECG Stripssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocument1 pageCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocument7 pagesCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation GuideDocument3 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretation Guideis_aradanas0% (1)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4Document3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med-Surg NUR4ktfosterfd2096% (96)
- Cardiac Medications and Treatments GuideDocument10 pagesCardiac Medications and Treatments GuideNursePoor98% (47)
- Pulmonary Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pagePulmonary Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes123475% (4)
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasNo ratings yet
- MAP, CO, and SV+HRDocument11 pagesMAP, CO, and SV+HRjenwiley318096% (73)
- Critical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableDocument7 pagesCritical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableVictoria Romero100% (2)
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Commonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1Document9 pagesCommonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1annatw100% (10)
- Diabetes and Endocrine ChartsDocument3 pagesDiabetes and Endocrine ChartsAja Blue86% (7)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument10 pagesCardiac Drugssurviving nursing school100% (3)
- Shock Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesShock Comparison Chartlinnaete88% (8)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Adult III Cardiac Study GuideDocument15 pagesAdult III Cardiac Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (6)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- BUN Test Overview and Normal RangesDocument3 pagesBUN Test Overview and Normal Rangesashdmb217100% (49)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Matt McGlothlin85% (13)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument5 pagesCardiac Drugseric100% (17)
- Cardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseDocument19 pagesCardiac Drugs Study Guide CourseAmanda Brittain100% (6)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasKatherine Santiago92% (62)
- Cardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsJessica100% (1)
- Ir-026 Fluid and Electrolytes - 1Document4 pagesIr-026 Fluid and Electrolytes - 1Muhammad ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Drug CardsDocument32 pagesNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)
- Inherent Rates: Cardiovascular System Alterations Module BDocument7 pagesInherent Rates: Cardiovascular System Alterations Module Bmp_329No ratings yet
- Ekg Guidelines PDFDocument7 pagesEkg Guidelines PDFd.ramadhan100% (1)
- ACLS EKG Rhythms and InterpretationDocument10 pagesACLS EKG Rhythms and Interpretationdonheyzz_02No ratings yet
- Basic Drug CardsDocument13 pagesBasic Drug Cardsnene lewis100% (2)
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Drugslhayes123488% (16)
- Basic Arrhythmia RulesDocument3 pagesBasic Arrhythmia Rulesgreenflames0997% (30)
- Cardiac DrugsDocument8 pagesCardiac Drugsdawggj100% (2)
- Fluid & Electrolytes Cheat Sheet v3Document1 pageFluid & Electrolytes Cheat Sheet v3faten100% (1)
- Drug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut HereDocument60 pagesDrug Receptor Types: Cut Here Cut Heredlneisha61100% (13)
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDocument5 pagesCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Sinus BradycardiaPascal St Peter NwaorguNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- Dysrhythmia Interpretation Modules 1-6 June 2012Document126 pagesDysrhythmia Interpretation Modules 1-6 June 2012Jess Varose100% (3)
- Cardiac DisordersDocument15 pagesCardiac Disordersgold_enriquez100% (3)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Document9 pagesLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- Acetazolamide drug profileDocument33 pagesAcetazolamide drug profileAshley Topp100% (1)
- EKG Crash Course NuRsing 390 SMC - 4Document57 pagesEKG Crash Course NuRsing 390 SMC - 4m1k0e100% (2)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Treatment For Cardiac Failure: ACE InhibitorsDocument36 pagesPharmacologic Treatment For Cardiac Failure: ACE InhibitorsGleden UmayamNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants: Commonly Prescribed IncludeDocument8 pagesAnticoagulants: Commonly Prescribed IncludeRusmir GadzoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PharmacotherapyDocument32 pagesCardiovascular PharmacotherapyFarahEzzlynnNo ratings yet
- What Are The Toxicities of Amiodarone?: CardiologyDocument33 pagesWhat Are The Toxicities of Amiodarone?: Cardiologylakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive 20191211Document35 pagesAnti Hypertensive 20191211helloitsmenadNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Rev 1Document38 pagesHypertension Rev 1endah ayunengrumNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction Medication GuideDocument11 pagesMyocardial Infarction Medication GuideAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Treating Heart Failure: Current Guidelines for Pharmacological ManagementDocument11 pagesTreating Heart Failure: Current Guidelines for Pharmacological ManagementKareem SaeedNo ratings yet
- Kee: Pharmacology, 8th EditionDocument5 pagesKee: Pharmacology, 8th EditionLondera BainNo ratings yet
- Case 1 & 2Document4 pagesCase 1 & 2Adeel ShahidNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MedsDocument4 pagesCardiac MedsJohan Barrios100% (1)
- Red Velvet CakeDocument1 pageRed Velvet CakepauerishNo ratings yet
- Oh My Back!: Low Back Pain and Its ManagementDocument36 pagesOh My Back!: Low Back Pain and Its ManagementpauerishNo ratings yet
- Ace InhibitorsDocument1 pageAce InhibitorspauerishNo ratings yet
- Chest Movement Intercostal Retractions Xiphoid Retraction Nares Dilatation Expiratory GruntDocument1 pageChest Movement Intercostal Retractions Xiphoid Retraction Nares Dilatation Expiratory GruntpauerishNo ratings yet
- A To Zed, A To Zee - A Guide To The Differences Between British and American EnglishDocument128 pagesA To Zed, A To Zee - A Guide To The Differences Between British and American Englishapi-384097894% (16)
- Pain MedsDocument1 pagePain MedspauerishNo ratings yet
- Lans Tour ItineraryDocument24 pagesLans Tour ItinerarypauerishNo ratings yet
- 2005 Aha Bls and Acls SummaryDocument3 pages2005 Aha Bls and Acls SummarypauerishNo ratings yet
- 2005 Aha Bls and Acls SummaryDocument3 pages2005 Aha Bls and Acls SummarypauerishNo ratings yet
- Anti Diabetic DrugDocument45 pagesAnti Diabetic DrugRahul LokhandeNo ratings yet
- ArdsDocument16 pagesArdsCryptococcus NeoformansNo ratings yet
- Ramucirumab PaclitaxelDocument2 pagesRamucirumab Paclitaxelapi-567600964No ratings yet
- Ketorolac DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesKetorolac DRUG STUDYA.No ratings yet
- GHSB2024 Superficial Structures of The Neck and Posterior TriangleDocument5 pagesGHSB2024 Superficial Structures of The Neck and Posterior Trianglekang seulgi can set me on fire with her gaze aloneNo ratings yet
- +1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Document38 pages+1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Ameena BegumNo ratings yet
- 4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalDocument29 pages4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalLuqmanul Hakim Junaidden100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaNo ratings yet
- Value of Epicardial Adipose Tissue Assessment by Cardiac Computerized Tomography in Heart Failure Patients With Preserved Ejection FractionDocument6 pagesValue of Epicardial Adipose Tissue Assessment by Cardiac Computerized Tomography in Heart Failure Patients With Preserved Ejection FractionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Gallstone Disease: Tad Kim, M.D. Connie Lee, M.DDocument35 pagesGallstone Disease: Tad Kim, M.D. Connie Lee, M.DWorapat ChNo ratings yet
- Basics of Microvascular SurgeryDocument33 pagesBasics of Microvascular SurgeryPratikshya KothiaNo ratings yet
- Livia Sagita Ruslim Cardio StemiDocument34 pagesLivia Sagita Ruslim Cardio StemiAnthony ChandraNo ratings yet
- Propofol Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPropofol Drug Studygersalia.christiennikkiNo ratings yet
- NCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingDocument3 pagesNCP-Difficulty of Breathing Related To Presence of Phlegm and Always CoughingCedie BarcaNo ratings yet
- Role of MPV in Complication of Diabetes Mellitus 2Document7 pagesRole of MPV in Complication of Diabetes Mellitus 2IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Medications For ObDocument9 pagesMedications For ObMaria Cecilia Pereyra SulzerNo ratings yet
- ECG Characteristics and Management of Cardiac RhythmsDocument6 pagesECG Characteristics and Management of Cardiac RhythmsJeffrey Viernes100% (1)
- ECG Fast and Easy chp12 PDFDocument40 pagesECG Fast and Easy chp12 PDFkikyfauziaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Variability of Hemoglobin Value On Type and Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy in Adult Type II Diabetes Mellitus PatientsDocument11 pagesEffect of Variability of Hemoglobin Value On Type and Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy in Adult Type II Diabetes Mellitus PatientsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia in First Degree Atrioventricular Block: 37, Pages 1190-1 194Document5 pagesAnaesthesia in First Degree Atrioventricular Block: 37, Pages 1190-1 194achmad mustikaNo ratings yet
- Hipofisis 3Document23 pagesHipofisis 3RafaelPetitNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain DDDocument79 pagesChest Pain DDkashmala afzalNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument41 pagesBlood TransfusionajNo ratings yet
- Generic Brand Classification Action IndicationDocument23 pagesGeneric Brand Classification Action IndicationMerro KellyNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument12 pagesFetal CirculationRiya Joy83% (6)
- Urinary System-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesUrinary System-WPS OfficeClara ZirimNo ratings yet
- Mallet AnatomyDocument277 pagesMallet AnatomyJethro Rola SiguaNo ratings yet
- National Clinical Guideline For Stroke 2023Document239 pagesNational Clinical Guideline For Stroke 2023uci coronaria100% (1)
- PUBlic Challenges An Extended Stay ASSIGN 1Document7 pagesPUBlic Challenges An Extended Stay ASSIGN 1Areesha KaleemNo ratings yet
- Rossi SvO2 Monitoring After CHSDocument61 pagesRossi SvO2 Monitoring After CHSAnthony RossiNo ratings yet