Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 PDF
Uploaded by
AnthonyUniqueOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9 PDF
Uploaded by
AnthonyUniqueCopyright:
Available Formats
THE PRODUCT Page 1 of 2
A product is successful, only when it satisfies the customers wants & needs.
A. Goods: Tangible products
Services: Intangible products
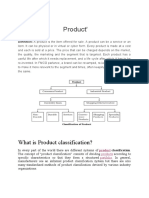
B. Layers of the product concept: There are three layers of the product:
1. Core product: The basic benefits provided in the exchange
2. Actual product: The physical goods or delivered services
3. Augmented product: The actual product + supporting features
A. Types of customer products:
1. Product classes defined by how long a product lasts:
(a.) Durable
(b.) Non-durable
2. Product classes defined by how consumers buy the product:
(a.) Convenience Product: Low priced, widely available, purchased frequently, and a min
comparison.
(b.) Shopping Product: Consumers will spend considerable time & effort gathering
information.
(c.) Specialty Product: It has unique characteristics & buyer will devote significant
effort.
(d.) Unsought Product: The consumer has little awareness or interest.
B. Types of Business-to-Business Products:
MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operating) Equipments, etc.
Innovation (In marketing) Innovation = New product (Goods, Services, Ideas)
A. The Importance of Innovations
B. What is a New Product? Anything that customers perceive as new
C. Types of Innovation
1. On a Symbolic Level: (communicates a new social meaning) e.g. a new hair style
2. On a Technological Level: (involves some functional changes) e.g. car airbags
(a.) Continuous Innovation: A modification of an existing product to set one brand apart
from its competitors
(b.) Dynamically Continuous Innovation: A pronounced change in an existing product
(c.) Discontinuous Innovation: A totally new product
D. Adoption & Diffusion Processes
1. Product Adoption: the process by which an individual begins to use a good, service or an
idea
2. Diffusion of Innovations: the process by which the use of an innovation spreads through a
society or a population
THE PRODUCT Page 2 of 2
E. Stages in a Customers Adoption of a New Product
1. Awareness
2. Interest
3. Evaluation
4. Trial
5. Adoption
6. Confirmation
F. Innovators and Adopter Categories:
1. Innovators (2.5 %)
2. Early Adopters (13.5 %)
3. Early Majority (34 %)
4. Late majority (34 %)
5. Laggards (16%)
G. Product Factors Affecting the Rate of Adoption:
1. Relative advantage
2. Compatibility
3. Complexity
4. Trialability
5. Observability (Tangibility)
H. Organizational Differences Affect Adoption:
Different readiness & willingness
A. Introduction Stage
B. Growth Stage
C. Maturity Stage
D. Decline Stage
E. Variations in the Product Life Cycle (PLC):
1. The Dreamer Curve: Product sales never achieve a growth stage in the PLC
2. The Contagion Curve: Product quickly & completely diffuse into the market place
3. The Fad Curve: Products rapidly become popular and then lose their appeal quickly
4. The Redevelopment Curve: Revived Sales of a product that come from product changes or
repositioning
You might also like
- Debit Card Replacement Kiosk Locations v2Document3 pagesDebit Card Replacement Kiosk Locations v2aiaiyaya33% (3)
- MM MCQ2Document32 pagesMM MCQ2nirudimpy3382No ratings yet
- PrinciplesofMarketing Ch10 TBDocument8 pagesPrinciplesofMarketing Ch10 TBowais saleemNo ratings yet
- Advertising 2Document9 pagesAdvertising 2Jellivie ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Product Development: A Structured Approach to Consumer Product Development, Design, and ManufactureFrom EverandProduct Development: A Structured Approach to Consumer Product Development, Design, and ManufactureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Blue Umbrella: VALUABLE CODE FOR HUMAN GOODNESS AND KINDNESSDocument6 pagesBlue Umbrella: VALUABLE CODE FOR HUMAN GOODNESS AND KINDNESSAvinash Kumar100% (1)
- Tow Truck Law SuitDocument4 pagesTow Truck Law SuitAnthony TalcottNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management 2Nd Edition Marshall Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesMarketing Management 2Nd Edition Marshall Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFfarleyphedral0p100% (11)
- Opertion Management Module 3 Product and Service Design 23 24 SSDocument7 pagesOpertion Management Module 3 Product and Service Design 23 24 SSEric GuapinNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Innovation SELF STUDYDocument16 pagesStrategy and Innovation SELF STUDYChandan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing q2 m1Document10 pagesPrinciples of Marketing q2 m1Angel DarucaNo ratings yet
- KAHOOT - Group 3 No AnswerDocument12 pagesKAHOOT - Group 3 No AnswerPhúc LợiNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument24 pagesUnit IISaurav KakkarNo ratings yet
- Product Design & DevelopmentDocument50 pagesProduct Design & DevelopmentAshok Dargar100% (1)
- Product PDFDocument15 pagesProduct PDFVIDHI KAMATH 2122084No ratings yet
- PM Full Notes LatestDocument29 pagesPM Full Notes LatestSuchitraRainaNo ratings yet
- Quiz QuestionsDocument7 pagesQuiz QuestionsJolly Sushma0% (2)
- 3 Product Strategy NotesDocument10 pages3 Product Strategy NotesSujeet KumarNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL MARKETING SYSTEM - Lesson 4 Product StrategyDocument16 pagesINDUSTRIAL MARKETING SYSTEM - Lesson 4 Product StrategyJhomhel RealesNo ratings yet
- OM Unit IIDocument16 pagesOM Unit IIJagadish MaturuNo ratings yet
- Unit - VDocument25 pagesUnit - VBhuvana GanesanNo ratings yet
- Product DesignDocument6 pagesProduct DesignHadeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- My Imp Quiz NotesDocument22 pagesMy Imp Quiz NotesBaraaNo ratings yet
- Products Development and MarketingDocument21 pagesProducts Development and MarketingTitus ClementNo ratings yet
- Product Design and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesProduct Design and DevelopmentAvni Dodia RathodNo ratings yet
- Marketing Real People Real Choices 8th Edition Solomon Test BankDocument38 pagesMarketing Real People Real Choices 8th Edition Solomon Test Bankjethrohacokkbns100% (33)
- Developing Products and ServicesDocument18 pagesDeveloping Products and ServicesVincent WilsonNo ratings yet
- Mdi Murshidabad: Dr. Vibhas AmawateDocument37 pagesMdi Murshidabad: Dr. Vibhas AmawateTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument9 pagesMarketing MixSaksham SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PRODUCT AND BRAND MANAGEMENT-ShortDocument19 pagesPRODUCT AND BRAND MANAGEMENT-ShortVineeth S PanickerNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Managing ProductsDocument43 pagesChapter Three Managing ProductsBoru jarsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter ObjectivesDocument28 pagesChapter ObjectivesakmohideenNo ratings yet
- CH - 5.1 ProductDocument43 pagesCH - 5.1 ProductArayaselasie TechaluNo ratings yet
- BST SeminarDocument41 pagesBST SeminarAkshaya Bijuraj NairNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision-Making Diffusion and Adoption of InnovationsDocument27 pagesConsumer Decision-Making Diffusion and Adoption of InnovationsroshniNo ratings yet
- Framework For Marketing Management Global 6th Edition Kotler Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesFramework For Marketing Management Global 6th Edition Kotler Solutions Manualomicronelegiac8k6st100% (27)
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6Yus LindaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Definition: Development or Production StageDocument4 pagesProduct Life Cycle Definition: Development or Production StageMujahid AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 SDocument44 pagesLecture6 Saqukinnouo100% (1)
- Product - 1Document33 pagesProduct - 1AkkamaNo ratings yet
- MKTG6Document12 pagesMKTG6Himanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- FinalpdndDocument32 pagesFinalpdndPulkit Garg100% (1)
- Module-2 Product Mix: Features of The ProductDocument9 pagesModule-2 Product Mix: Features of The Productmurshidaman3No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Product StrategyDocument22 pagesUnit 5 Product StrategyantenehNo ratings yet
- Product StrategyDocument17 pagesProduct StrategyVANDANKUMAR MINTUBHAI PATELNo ratings yet
- Carpentry: Environment and Market (Em)Document14 pagesCarpentry: Environment and Market (Em)LaurenceFabialaNo ratings yet
- Entrep Product-is-Nature-and-SustainabilityDocument20 pagesEntrep Product-is-Nature-and-SustainabilityCandyAnonymous100% (1)
- Bond With Pidilite Case Study 2Document3 pagesBond With Pidilite Case Study 2CAT 2020No ratings yet
- Caca&Caillo - Developing Products For The Foreign Market Entry StrategiesDocument18 pagesCaca&Caillo - Developing Products For The Foreign Market Entry StrategiesDulce Amor Margallo ValdescoNo ratings yet
- 12 Products and Services For ConsumersDocument10 pages12 Products and Services For ConsumersViễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- MarketingDocument37 pagesMarketingSyed Hammad Ul Rahman SheraziNo ratings yet
- Product: Under Guidance of Prof A.A.PatilDocument17 pagesProduct: Under Guidance of Prof A.A.PatilManjunath KinagiNo ratings yet
- Basic of Management: Marketing AssignmentDocument9 pagesBasic of Management: Marketing AssignmentGãurãv SãndhãlNo ratings yet
- International Product DecisionDocument24 pagesInternational Product DecisionSidharth SingheeNo ratings yet
- MKTDocument15 pagesMKTtrustme77No ratings yet
- Buying Decision For A New Product - Adoption and DiffusionDocument8 pagesBuying Decision For A New Product - Adoption and DiffusionWhitney ChaoNo ratings yet
- ProductDocument10 pagesProductKhushi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Product DecisionsDocument48 pagesUnit 6 Product DecisionsAnjana RamjaliNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Product Planning and Development: Submitted By: Orca, Chris Paul Y. 09-1453 BSBM 41C (PM)Document28 pagesAssignment in Product Planning and Development: Submitted By: Orca, Chris Paul Y. 09-1453 BSBM 41C (PM)Jhona Labe ÜNo ratings yet
- 6: Product Strategy: By: Mtra. Mariana SierraDocument36 pages6: Product Strategy: By: Mtra. Mariana SierraEugenio A. G.No ratings yet
- BizTech - Product Life CycleDocument2 pagesBizTech - Product Life CycleAayushi KoriNo ratings yet
- BM-B - Group 10Document7 pagesBM-B - Group 10UTKARSH PABALENo ratings yet
- English Quiz #16Document1 pageEnglish Quiz #16AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- Learning Task Global Warming, Global ConcernDocument4 pagesLearning Task Global Warming, Global ConcernAnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- English Quiz #14Document1 pageEnglish Quiz #14AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- Grammar 1396.11.28Document8 pagesGrammar 1396.11.28AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- English 1400-1401 Grammar 11Document4 pagesEnglish 1400-1401 Grammar 11AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- English Quiz 16Document1 pageEnglish Quiz 16AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- English 1400-1401 Vocabulary 11Document2 pagesEnglish 1400-1401 Vocabulary 11AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- English Quiz 14Document1 pageEnglish Quiz 14AnthonyUniqueNo ratings yet
- Iron Maiden - Can I Play With MadnessDocument9 pagesIron Maiden - Can I Play With MadnessJuliano Mendes de Oliveira NetoNo ratings yet
- Gundarks Fantastic Technology Personal Gear WEG40158 PDFDocument114 pagesGundarks Fantastic Technology Personal Gear WEG40158 PDFPed_exing100% (3)
- A Brief History & Development of Banking in India and Its FutureDocument12 pagesA Brief History & Development of Banking in India and Its FutureMani KrishNo ratings yet
- Who Am I NowDocument7 pagesWho Am I Nowapi-300966994No ratings yet
- Capability' Brown & The Landscapes of Middle EnglandDocument17 pagesCapability' Brown & The Landscapes of Middle EnglandRogério PêgoNo ratings yet
- 35 Childrens BooksDocument4 pages35 Childrens Booksapi-710628938No ratings yet
- Grandparents 2Document13 pagesGrandparents 2api-288503311No ratings yet
- JioMart Invoice 16776503530129742ADocument1 pageJioMart Invoice 16776503530129742ARatikant SutarNo ratings yet
- CrackJPSC Mains Paper III Module A HistoryDocument172 pagesCrackJPSC Mains Paper III Module A HistoryL S KalundiaNo ratings yet
- Catalogu PDFDocument24 pagesCatalogu PDFFer GuNo ratings yet
- Workplace Wellness Survey Report - FinalDocument43 pagesWorkplace Wellness Survey Report - FinalMeeraNo ratings yet
- Lea3 Final ExamDocument4 pagesLea3 Final ExamTfig Fo EcaepNo ratings yet
- Oracle IRecruitment Setup V 1.1Document14 pagesOracle IRecruitment Setup V 1.1Irfan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ch13 (Man)Document44 pagesCh13 (Man)kevin echiverriNo ratings yet
- Basic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDocument17 pagesBasic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDenisa PriftiNo ratings yet
- Forn VännenDocument14 pagesForn VännenDana KoopNo ratings yet
- 006 2014 Hans TjioDocument17 pages006 2014 Hans TjioarshadtabassumNo ratings yet
- Climate Resilience FrameworkDocument1 pageClimate Resilience FrameworkJezzica BalmesNo ratings yet
- 50CDocument65 pages50Cvvikram7566No ratings yet
- Configuring Srewquid Proxy ServerDocument4 pagesConfiguring Srewquid Proxy ServerPendekar BlankNo ratings yet
- Time ClockDocument21 pagesTime ClockMarvin BrunoNo ratings yet
- Case Exercise On Layer Unit (2000 Birds)Document2 pagesCase Exercise On Layer Unit (2000 Birds)Priya KalraNo ratings yet
- S 1 SdresourceswalkthroughDocument57 pagesS 1 SdresourceswalkthroughJanine Marcos75% (4)
- ASSIGNMENT MGT 657 myNEWSDocument35 pagesASSIGNMENT MGT 657 myNEWSazrin aziziNo ratings yet
- Zmaja Od Bosne BB, UN Common House, 71000 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Tel: +387 33 293 400 Fax: +387 33 293 726 E-Mail: Missionsarajevo@iom - Int - InternetDocument5 pagesZmaja Od Bosne BB, UN Common House, 71000 Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Tel: +387 33 293 400 Fax: +387 33 293 726 E-Mail: Missionsarajevo@iom - Int - InternetavatarpetrovicNo ratings yet
- Determinate and GenericDocument5 pagesDeterminate and GenericKlara Alcaraz100% (5)
- Reading 53 Pricing and Valuation of Futures ContractsDocument3 pagesReading 53 Pricing and Valuation of Futures ContractsNeerajNo ratings yet