Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonding 2
Uploaded by
yvg95Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Bonding 2
Uploaded by
yvg95Copyright:
Available Formats
AS-Level
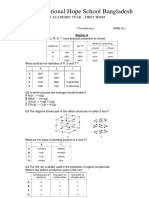
CHEMICAL BONDING
Section A
Q1 Three substances, R, S, T, have physical properties as shown.
What could be the identities of R, S and T ?
Q2 In which process are hydrogen bonds broken?
A H2(l) H2(g)
B NH3(l) NH3(g)
C 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g)
D CH4(g) C(g) + 4H(g)
Q3 The diagram shows part of the lattice structures of solids X and Y.
What are the types of bonding present in X and Y?
Q4 The CN ion is widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds.
What is the pattern of electron pairs in this ion?
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q5 Plastic bottles for fizzy drinks are made from a polymer with the following structure.
The ability of the polymer to prevent escape of carbon dioxide through the wall of the bottle
depends on the ability of the group X to form hydrogen bonds with the carbon dioxide in the
drink. Which group X best prevents loss of carbon dioxide?
D OH
A Cl
B CN
C CO2CH3
Q6 When barium metal burns in oxygen, the ionic compound barium peroxide, BaO2, is
formed. Which dot-and-cross diagram represents the electronic structure of the peroxide
anion in BaO2?
Q7 In this question, the methyl group, CH3, is represented by Me. Trimethylamine, Me3N,
reacts with boron trifluoride, BF3, to form a compound of formula Me3N.BF3. How may this
reaction be written in terms of the shapes of the reactants and products?
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q8 Which pair of elements have bonds of the same type between their atoms in the solid
state?
A aluminium and phosphorus
B chlorine and argon
C magnesium and silicon
D sulphur and chlorine
Q9 A crystal of iodine produces a purple vapour when gently heated.
Which pair of statements correctly describes this process?
Q10 Which diagram correctly shows the bonding in the ammonium ion, NH4+?
Q11 What is the most likely shape of a molecule of hydrazine, N2H4?
Q12 Which molecule has the largest overall dipole?
Q13 Which compound has a boiling point that is influenced by hydrogen bonding?
A CH3CHO
B CH3OCH3
C HCO2H
D HCO2CH3
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q14 Which diagram describes the formation of a bond from the overlap of its orbitals?
Q15 Magnesium oxide may be used for the lining of an electric furnace for making crockery.
Which properties of magnesium oxide help to explain this use?
Q16 Hydrogen bonding can occur between molecules of methanal, HCHO, and molecules of
liquid Y. What could liquid Y be?
A CH3OH
B CH3CHO
C CH3COCH3
D CH3CO2CH3
Q17 Lycra is a polyurethane fibre used in the fashion industry. It is a polymer made from two
monomers, one of which has the following formula.
O=C=N(CH2)n N=C=O
What is the OCN bond angle in this molecule?
A 90
B 109
C 120
D 180
Q18 What are the lattice structures of solid diamond, iodine and silicon(IV) oxide?
Q19 A substance commonly found in the house or garden has the following properties.
It is combustible.
It is an electrical insulator.
It melts over a range of temperature.
What could the substance be?
A brass
B paper
C poly(ethene)
D silicon(IV) oxide
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q20 The antidote molecule shown can help to prevent liver damage if someone takes too
many paracetamol tablets.
What is the order of decreasing size of the bond angles x, y and z?
Q21 Which molecule has the largest overall dipole?
Q22 The ability of an atom in a covalent bond to attract electrons to itself is called its
electronegativity. The greater the difference between the electronegativities of the two atoms
in the bond, the more polar is the bond.
Which pair will form the most polar covalent bond between the atoms?
A chlorine and bromine
B chlorine and iodine
C fluorine and chlorine
D fluorine and iodine
Q23 Which solid has a simple molecular lattice?
A calcium fluoride
B nickel
C silicon(IV) oxide
D sulfur
Q24 Which molecule or structure does not contain three atoms bonded at an angle between
109 and 110?
A ethanoic acid
B graphite
C propane
D silicon(IV) oxide
Q25 The presence of dipoles helps to explain why the element Br2 and the compound CHCl3
exist asliquids at room temperature. Which types of dipole are involved?
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q26 Three compounds have the physical properties shown in the table.
What might be the identities of P, Q and R?
Q27 Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, and boron trifluoride, BF3, are compounds of boron.
What are the shapes around boron in the borohydride ion and in boron trifluoride?
Q28 Some car paints contain small flakes of silica, SiO2.
In the structure of solid SiO2
each silicon atom is bonded to x oxygen atoms,
each oxygen atom is bonded to y silicon atoms,
each bond is a z type bond.
What is the correct combination of x, y and z in this statement?
Q29 In which pair do the molecules have the same shape as each other?
B H2O and SCl 2
C NH3 and BH3
D SCl 2 and BeCl 2
A H2O and CO2
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Section B
Q30 Which of the following molecules and ions have a regular trigonal planar shape?
+
2 CH 3
3 PH3
1 AlCl3
Q31 Which of the following solids contain more than one type of chemical bond?
1 brass (an alloy of copper and zinc)
2 graphite
3 ice
Q32 Which diagrams represent part of a giant molecular structure?
Q33 What is involved when a hydrogen bond is formed between two molecules?
1 a hydrogen atom bonded to an atom less electronegative than itself
2 a lone pair of electrons
3 an electrostatic attraction between opposite charges
Q34 Which molecules are planar?
1 BCl3
2 NH3
3 PH3
Q35 Boron is a non-metallic element which is placed above aluminium in Group III of the
PeriodicTable. It forms a compound with nitrogen known as boron nitride which has a
graphite structure. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this information?
1 The empirical formula of boron nitride is BN.
2 The boron and nitride atoms are likely to be arranged alternately in a hexagonal pattern.
3 Boron nitride has a layer structure with van der Waals forces between the layers.
Q36 Kevlar has the structure below.
Compared to a steel rope of similar dimensions, a Kevlar rope is both lighter and stronger.
Which properties of Kevlar help to explain these facts?
1 The fibres of Kevlar align due to hydrogen bonding.
2 The mass per unit length is less in a Kevlar rope than in a steel rope.
3 The Kevlar molecule has no permanent dipole.
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q37 Which physical properties are due to hydrogen bonding between water molecules?
1 Water has a higher boiling point than H2S.
2 Ice floats on water.
3 The HOH bond angle in water is approximately 104.
Q38 Which statements about covalent bonds are correct?
1 A triple bond consists of one bond and two bonds.
2 The electron density in a bond is highest along the axis between the two bonded atoms.
3 A bond restricts rotation about the bond axis.
Q39 Which statements about bond angles are correct?
1 The bond angle in SO2 is smaller than the bond angle in CO2.
2 The bond angle in H2O is smaller than the bond angle in CH4.
3 The bond angle in NH3 is smaller than the bond angle in BF3.
Q40 Which of these substances have a giant structure?
1 silicon(IV) oxide
2 baked clay found in crockery
3 phosphorus(V) oxide
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
C
B
B
C
D
D
C
D
C
C
D
B
C
B
A
A
D
A
C
C
B
D
D
B
C
B
D
C
B
B
C
B
C
D
A
B
B
C
A
B
0333-4200541
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q1 Ethyne C2H2 is a linear molecule with a triple bond between the two carbon atoms.
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram of an ethyne molecule.
(June 2006)
Q2 Ethene, C2H4, and hydrazine, N2H4, are hydrides of elements which are adjacent in
Periodic Table. Data about ethene and hydrazine are given in the table below.
C2H4
N2H4
melting
point/C
169
+2
boiling
point/C
104
+114
insoluble
high
solubility in
water
solubility in
high
high
ethanol
(a) Ethene and hydrazine have a similar arrangement of atoms but differently shaped
molecules.
(i)What is the H-C-H bond angle in ethene?
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii)Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for hydrazine.
(iii)What is the H-N-H bond angle in hydrazine?
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) The melting and boiling points of hydrazine are much higher than those of ethene.
Suggest reasons for these differences in terms of the intermolecular forces each
compound possesses.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
10
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
(c) Explain, with the aid of a diagram showing lone pairs of electrons and dipoles, why
hydrazine is very soluble in ethanol.
(June 2007)
Q3 The structural formulae of water, methanol and methoxymethane, CH3OCH3, are
given below.
(a)(i)How many lone pairs of electrons are there around the oxygen atom in
methoxymethane?
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Suggest the size of the COC bond angle in methoxymethane.
...................................................................................................................................................
Attractive forces between the molecules of compound differ in their strength and include the
following.
Ainteractions involving permanent dipoles
Binteractions involving temporary or induced dipoles
Chydrogen bonds
(b) By using the letters A, B, or C, state the strongest intermolecular force present in each
of the following compounds.
Ethanol
CH3CHO
..............
Ethanol
CH3CH2OH
..............
Methoxymethane
CH3OCH3
..............
2-Methylpropane
(CH3)2CHCH3
..............
(c) Methanol and water are completely soluble in each other.
(i)Which intermolecular force exists between methanol molecules and water molecules that
makes these two liquids soluble in each other?
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii)Draw a diagram that clearly shows this intermolecular force. Your diagram should show
any lone pairs or dipoles present on either molecule that you consider to be important.
(June 2008)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
11
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q4 At low temperatures, aluminium chloride vapour has the formula Al2Cl6.
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram to show the bonding in Al2Cl6.
Show outer electrons only.
(June 2009)
Q5 Elements and compounds which have small molecules usually exist as gases or liquids.
(a) Chlorine, Cl 2, is a gas at room temperature whereas bromine, Br 2, is a liquid under the
same conditions. Explain these observations.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) The gases nitrogen, N2, and carbon monoxide, CO, are isoelectronic, that is they have
the same number of electrons in their molecules.Suggest why N2 has a lower boiling point
than CO.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(c)A dot-and-cross diagram of a CO molecule is shown below. Only electrons from outer
shells are represented.
(June 2010 P21)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
12
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q6 Copper, proton number 29, and argon, proton number 18, are elements which have
different physical and chemical properties. In the solid state, each element has the same
face-centred cubic crystal structure which is shown below.
The particles present in such a crystal may be atoms, molecules, anions or cations. In the
diagram above, the particles present are represented by
.
(a) Which types of particle are present in the copper and argon crystals?
In each case, give their formula.
At room temperature, copper is a solid while argon is a gas.
(b) Explain these observations in terms of the forces present in each solid structure.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(June 2010 P22)
Q7 The boiling points of these two compounds are given below.
compound
BP / K
CH3CH3
184.5
CH3F
194.7
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
13
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Suggest explanations for the following.
(i) the close similarity of the boiling points of the two compounds
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) the slightly higher boiling point of CH3F
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(June 2011 P23)
Q8 Sulfur forms the compound S4N4 with nitrogen. The structure of S4N4 is shown
below.
Assume all bonds shown are single bonds.
(i) Determine the number of lone pairs of electrons around a nitrogen atom and a sulfur atom
in S4N4.
nitrogen atom .......................................... sulfur atom ..........................................
(ii) Which bond angle, a or b, in the S4N4 molecule will be smaller? Explain your answer.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(June 2012 P22)
Q9 Carbon disulphide, CS2, is a volatile, stinking liquid which is used to manufacture
viscose rayon and cellophane.
(a) The carbon atom is in the centre of the CS2 molecule. Draw a dot-and-cross diagram
of the carbon disulphide molecule. Show outer electrons only.
(b) Suggest the shape of the molecule and give its bond angle.
shape .........................................................
bond angle .................................................
(Nov 2005)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
14
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
Q10 Copper and iodine are both solids which have different physical and chemical
properties. Each element has the same face-centred crystal structure which is shown below.
The particles present in such a crystal may be atoms, molecules, anions or cations. In the
diagram above, the particles present are represented by a black circle.
(a) Which type of particles are present in the iodine crystal? Give their formula.
particle ..............................................
formula ..............................................
(b) When separate samples of copper or iodine are heated to 50 C, the copper remains as
a solid while the iodine turns into a vapour.
(i) Explain, in terms of the forces present in the solid structure, why copper remains a
solid at 50 C.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain, in terms of the forces present in the solid structure, why iodine turns into a
vapour when heated to 50C.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(Nov 2006)
Q11 This question is about the bonding of covalent compounds.
(a) On the axes below, sketch the shapes of a 1s, a 2s, and a 2px orbital.
(b) Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Covalent bonding
may also be described in terms of orbital overlap with the formation of sigmabonds.
(i) How are the two atoms in a covalent bond held together? In your answer, state which
particles are attracted to one another and the nature of the force of attraction.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
15
AS-Level
CHEMICAL BONDING
(ii) Draw sketches to show orbital overlap that produces the
HCl molecules.
bonding in the H2
and
(c) The bond in the HCl molecule is said to be polar.
(i) What is meant by the term bond polarity?
...................................................................................................................................................
(ii) Explain why the HCl molecule is polar.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(d) The bonding in ethene may be described as a mixture of
and
bonding.
Each carbon atom in ethene forms three
bonds as shown below.
On the diagram, sketch the
bond that is also present in ethene.
(Nov 2007)
Q12(a) Briefly explain, in terms of the chemical bonds and intermolecular forces present in
each compound, why CO2 is a gas and SiO2 is a solid at room temperature.
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
(b) Draw a simple diagram to show the structure of SiO2. Your diagram should contain at
least two silicon atoms and show clearly how many bonds each atom forms.
(Nov 2009 P22)
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
0333-4200541
16
You might also like
- Chap 4&5 WSDocument34 pagesChap 4&5 WSSaif AhmedNo ratings yet
- H1, MCQ, Oct 2022Document8 pagesH1, MCQ, Oct 2022school of schoolNo ratings yet
- Focus 3 Chemical BondingDocument10 pagesFocus 3 Chemical BondingHengLow100% (1)
- Gabriella Logue - Topic 4 Chemistry-Hodder (Practice Questions)Document2 pagesGabriella Logue - Topic 4 Chemistry-Hodder (Practice Questions)yesNo ratings yet
- Top Univ - Soal Latihan Kimia 01 PDFDocument7 pagesTop Univ - Soal Latihan Kimia 01 PDFDarma YogaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding-2Document7 pagesTopic 4 Bonding-2Murat KAYANo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision Questions 2014Document9 pagesBonding Revision Questions 2014Annie Ugf HoodNo ratings yet
- Cie QDocument17 pagesCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- I PUC Model QP AnswerDocument8 pagesI PUC Model QP AnswerSamanth PattarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Past Paper Ch2.2Document4 pagesChemistry Past Paper Ch2.2Raymond ChanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - Chem BondingDocument4 pages2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - Chem BondingxmxmxmxmxmNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding KRR PDFDocument40 pagesChemical Bonding KRR PDFggk201367% (3)
- 11th ChemistryDocument18 pages11th ChemistryGaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- Chem Hy1516 S4Document59 pagesChem Hy1516 S4Olivia LinNo ratings yet
- Bonding ..Q + MSDocument26 pagesBonding ..Q + MSSveta StepanovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MCQs AnswerDocument6 pagesChapter 9 MCQs AnswerJames WongNo ratings yet
- SL Score ! /30: Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: BondingDocument7 pagesSL Score ! /30: Practice Exam: Paper 1 Topic 4: Bondingraja_tanukuNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 14 MC PracticeDocument20 pagesTopic 4 14 MC PracticeDharmesh Ramnarayan YadavNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document32 pagesWa0010.Tanvi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2012 TrialDocument9 pages2012 TrialCin D NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Document4 pagesChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Section B AnsDocument7 pagesSection B AnsjimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument118 pagesChemistry Presentation: Multiple Choice QuestionsKhiZra ShahZadNo ratings yet
- Test Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesTest Topic: Atomic Structure, Formula Writing and Balancing Equation, Bonding and Structure, Redox, ElectrolysisArham Tamim100% (1)
- Part 1: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks)Document11 pagesPart 1: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks)kahguaNo ratings yet
- Class Xi Holiday Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesClass Xi Holiday Assignment PDF1234567No ratings yet
- Chem Topic 4 Questions + AnswersDocument25 pagesChem Topic 4 Questions + AnswersOscarHigson-Spence50% (2)
- Chemical Bonding and StructureDocument34 pagesChemical Bonding and StructureLaraStrbacNo ratings yet
- Practicetopic 4 Paper 1Document10 pagesPracticetopic 4 Paper 1api-312595005No ratings yet
- Ejercicios Estructura MolecularDocument4 pagesEjercicios Estructura MolecularDANNANo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 2Document68 pagesInorganic Chem 2yvg95100% (1)
- Chemistry: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class - XIDocument3 pagesChemistry: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class - XIAb CdNo ratings yet
- REVISION SEE Chemistry 2023Document10 pagesREVISION SEE Chemistry 2023Sahitya SumanNo ratings yet
- 2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Document16 pages2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P1Chow Kim WanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Document26 pagesLesson 110: Paper 1 Name: - Class: - Date: - A. Multiple Choice Questions. 1Siapa Al AhbashiNo ratings yet
- SAT Chem 02 BondingDocument2 pagesSAT Chem 02 Bondingebola123No ratings yet
- Sure-Shot Questions-Chemistry Class XII: 1markDocument5 pagesSure-Shot Questions-Chemistry Class XII: 1markudit pandyaNo ratings yet
- Combined OrganicDocument82 pagesCombined OrganicSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Examination, 2017-18: Chemistry Time: 3 Hrs. Class - XI M.M.: 70Document4 pagesHalf Yearly Examination, 2017-18: Chemistry Time: 3 Hrs. Class - XI M.M.: 70Prajin MuruganNo ratings yet
- Trial P1 2008Document14 pagesTrial P1 2008sherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Model Paper 6 SchemeDocument11 pagesModel Paper 6 SchemeKalyan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Prelim Sec4 p1 & p2Document30 pagesPrelim Sec4 p1 & p2dimpledblissNo ratings yet
- Chem Topic 4 QuestionsDocument19 pagesChem Topic 4 QuestionsOscarHigson-SpenceNo ratings yet
- IGCSE CHEMISTRY (Katryne)Document7 pagesIGCSE CHEMISTRY (Katryne)PriyantoBudiLaksonoNo ratings yet
- 1 in Which Option Do The Three Particles Each Have The Same Number of ElectronsDocument12 pages1 in Which Option Do The Three Particles Each Have The Same Number of Electronssololexzib100% (1)
- Carbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Magnesium Oxide MagnesiumDocument11 pagesCarbon Dioxide Carbon Monoxide Magnesium Oxide MagnesiumelizabethNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam - Class 11 - Chemistry Question PaperDocument4 pagesAnnual Exam - Class 11 - Chemistry Question PaperADITIYANo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MCQDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding MCQVinay Krishna Kodali50% (4)
- Cbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryDocument11 pagesCbse Sample Paper For Class 11 ChemistryAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Duplicate - 2007 Year End TestDocument11 pagesPaper 1 Duplicate - 2007 Year End Testsherry_christyNo ratings yet
- 2011 Chemistry Question PapersDocument4 pages2011 Chemistry Question Papersalex scottNo ratings yet
- One Mark Questions: Subject: Chemistry Chapter - 11: P-Block ElementDocument13 pagesOne Mark Questions: Subject: Chemistry Chapter - 11: P-Block ElementudaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Chemical BondingDocument2 pages11 Chemistry Chemical BondingHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Topical SaveMyExamDocument14 pagesTopical SaveMyExamzainkolachieduNo ratings yet
- Trial STPM Term2 2015Document8 pagesTrial STPM Term2 2015Earliany Mohd ShahriNo ratings yet
- CL-XI SC-Half Yearly-2021 (CHEM)Document5 pagesCL-XI SC-Half Yearly-2021 (CHEM)Rapelly NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandOrganometallic Chemistry: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Conference on Organometallic ChemistryF. G. A. StoneNo ratings yet
- Organosilicon Chemistry: 2: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Organosilicon ChemistryFrom EverandOrganosilicon Chemistry: 2: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Organosilicon ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 2Document68 pagesInorganic Chem 2yvg95100% (1)
- Moles 2Document15 pagesMoles 2yvg95No ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument11 pagesHydroxy Compoundsyvg95100% (1)
- Reaction Kinetics 2Document8 pagesReaction Kinetics 2yvg95No ratings yet
- Intro To Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntro To Organic Chemistryyvg95No ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument11 pagesHydroxy Compoundsyvg95100% (1)
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of Matternayeem_11No ratings yet
- As Important DefinationsDocument4 pagesAs Important DefinationsCleo PoulosNo ratings yet
- DDDocument21 pagesDDSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- 9701 s14 GTDocument2 pages9701 s14 GTyvg95No ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument14 pagesCarbonyl Compoundsyvg95100% (1)
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Needed For AS ChemistryDocument2 pagesSummary of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Needed For AS ChemistryTobeeraj PanchooNo ratings yet
- DDDocument21 pagesDDSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Mechanics M3Document28 pagesEdexcel GCE: Mechanics M3yvg95No ratings yet
- 9701 s13 GTDocument2 pages9701 s13 GTyvg95No ratings yet
- IonsDocument4 pagesIonsyvg95No ratings yet
- GCE Composite 1306 v2Document28 pagesGCE Composite 1306 v2Justin WrightNo ratings yet
- CH3Document51 pagesCH3yvg95No ratings yet
- GCE Composite 1306 v2Document28 pagesGCE Composite 1306 v2Justin WrightNo ratings yet
- 6EC01 June 2009 PaperDocument32 pages6EC01 June 2009 PaperMansi BhattNo ratings yet
- TcshyderDocument48 pagesTcshyderyvg95No ratings yet
- 4bio EdexcelDocument24 pages4bio EdexcelAsiff MohammedNo ratings yet
- CH4Document45 pagesCH4yvg95No ratings yet
- CH7Document159 pagesCH7yvg95No ratings yet
- Solutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsDocument1 pageSolutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematicsyvg95No ratings yet
- Core Maths 3 Chapter 2Document77 pagesCore Maths 3 Chapter 2samyoeNo ratings yet
- Solutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsDocument70 pagesSolutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematicsyvg95No ratings yet
- Solomon A MS - 2Document4 pagesSolomon A MS - 2Alex HadwehNo ratings yet
- Mxenes As 2D Inorganic Materials Layered StructureDocument7 pagesMxenes As 2D Inorganic Materials Layered StructureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Immiscible SolventsDocument8 pagesImmiscible SolventsAgeng Wahyu PatrianitaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Lab ReportDocument6 pagesAcid Base Lab ReportYEEHSHIN JILL GAYONo ratings yet
- Periodic Table - Study NotesDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dual Fuel EngineDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Dual Fuel EngineShrishant Patil100% (2)
- Demonstrating Job's Method With Colorimeter or SpectrophotometerDocument2 pagesDemonstrating Job's Method With Colorimeter or Spectrophotometeriabureid7460No ratings yet
- Astm A897 - A897m-22Document11 pagesAstm A897 - A897m-22anant11235No ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionDocument14 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionAusten Ammon AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Silver Nanoparticle Impact On Bacterial Growth: Effect of PH, Concentration, and Organic MatterDocument6 pagesSilver Nanoparticle Impact On Bacterial Growth: Effect of PH, Concentration, and Organic MatterGera CorralesNo ratings yet
- Drinking Water StandardsDocument2 pagesDrinking Water StandardsCharan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Standard Free Energy For The Following Reaction by Using Given DataDocument5 pagesCalculate The Standard Free Energy For The Following Reaction by Using Given DatamuraliMuNo ratings yet
- Am SteelDocument28 pagesAm Steelyogesh v100% (1)
- L Glutamine COADocument1 pageL Glutamine COAvbadsNo ratings yet
- Product Temperature: Specific GravityDocument8 pagesProduct Temperature: Specific GravityRyan BacalaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Paper 2Document2 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Paper 2Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Mass Balance of RR3 Grade of GreaseDocument116 pagesProject Report On Mass Balance of RR3 Grade of GreaseAkash Dhobale100% (2)
- MIL DTL 32495A Powders For Cold SprayDocument39 pagesMIL DTL 32495A Powders For Cold SprayDaniel VillaflorNo ratings yet
- En 10139Document2 pagesEn 10139Rajwinder Singh100% (3)
- Altiris - Infrared Reflecting Macro Titania For CoatingsDocument23 pagesAltiris - Infrared Reflecting Macro Titania For CoatingsMuhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Plate Heat Exchanger Chemical CleaningDocument23 pagesHeat Exchanger Plate Heat Exchanger Chemical Cleaningbtdoss72100% (2)
- 1-Atoms and Molecules - 2022Document50 pages1-Atoms and Molecules - 2022riva rizkianaNo ratings yet
- ch3 - MichalskiDocument48 pagesch3 - MichalskirquinesNo ratings yet
- ASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesDocument2 pagesASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesRafael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Self Healing Concrete SeminarDocument32 pagesSelf Healing Concrete SeminarAru GowdaNo ratings yet
- Bio GasDocument4 pagesBio GasRajko DakicNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesChemical BondingSenpai JenjenNo ratings yet
- 2064-2110 - Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles - Synthesis, Stabilization, VectorizationDocument47 pages2064-2110 - Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles - Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorizationehagar60No ratings yet
- Jo GradeDocument40 pagesJo GradeEvonne TanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Tankers: 3.1 Physical PropertiesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Gas Tankers: 3.1 Physical PropertiesŞansal DikmenerNo ratings yet
- Ceramic CoatingDocument16 pagesCeramic CoatingUsman PirzadaNo ratings yet