Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment3forming Solutions
Uploaded by
Fu DinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment3forming Solutions
Uploaded by
Fu DinCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSIENMENT [2]
METAL FORMING
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1- What are the differences between bulk deformation processes and sheet metal processes? Answer. In bulk
deformation, the shape changes are significant, and the work parts have a low area-to-volume ratio. In sheet
metal processes, the area-to-volume ratio is high.
2- Etrusion is a fundamental shaping process. !escribe it.
Answer. Etrusion is a compression process in which the work material is forced to flow through a die
orifice, thereb" forcing its cross section to assume the profile of the orifice.
#- Wh" is the term press working often used for sheet metal processes?
Answer. $he term press working is used because most sheet metal operations are performed on presses.
%- What is the difference between deep drawing and bar drawing?
Answer. !eep drawing is a sheet metal forming process used to fabricate cup-shaped parts& bar drawing
is a bulk deformation process used to reduce the diameter of a c"lindrical work part.
'- Indicate the mathematical e(uation for the flow curve.
Answer. $he flow curve is defined in E(. )1*.1+ as Y
f
, K-
n
.
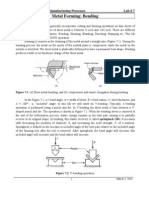
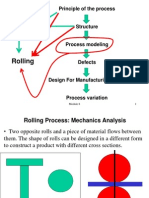
.- /ist some of the products produced on a rolling mill. Answer. 0olled products include flat sheet and plate
stock, round bar and rod stock, rails, structural shapes such as I-beams and channels.
1- What is draft in a rolling operation?
Answer. !raft is the difference between the starting thickness and the final thickness as the workpiece
passes between the two opposing rolls.
*- What is sticking in a hot rolling operation?
Answer. 2ticking is a condition in hot rolling in which the surface of the workpiece adheres to the rolls
as the piece passes between the rolls, causing severe deformation of the metal below the surface in order
to allow passage through the roll gap.
3- Identif" some of the wa"s in which force in flat rolling can be reduced.
Answer. Wa"s to reduce force in flat rolling include )1+ use hot rolling, )2+ reduce draft in each pass, and
)#+ use smaller diameter rolls.
13.13 !istinguish between direct and indirect etrusion. Answer. In direct etrusion, also known as
forward etrusion, a metal billet is loaded into a container, and a ram compresses the material, forcing it
to flow through a die opening at the opposite end of the container. In indirect etrusion, also known as
backward etrusion, the die is incorporated into the ram, and as the ram compresses into the metal billet,
the metal is forced to flow through the die opening in a direction that is opposite )backwards+ of the ram
motion.
14- 5ame some products that are produced b" etrusion.
Answer. 6roducts produced b" continuous etrusion include structural shapes )window frames, shower
stalls, channels+, tubes and pipes, and rods of various cross sections. 6roducts made b" discrete etrusion
include toothpaste tubes, aluminium beverage cans, and batter" cases.
11- In blanking of a circular sheet metal part, is the clearance applied to the punch diameter or the die diameter?
Answer. $he die diameter e(uals the blank diameter, and the punch diameter is smaller b" twice the
clearance.
Multiple C!i"e QUESTIONS
1- Which of the following is t"pical of the starting work geometr" in sheet metal processes7 )a+ high
volume-to-area ratio or )b+ low volume-to-area ratio?
Answer. )b+.
2- $he flow curve epresses the behaviour of a metal in which of the following regions of the stress-strain curve7
)a+ elastic region or )b+ plastic region?
Answer. )b+.
#- $he average flow stress is the flow stress multiplied b" which of the following factors7 )a+ n, )b+ )18n+, )c+
19n, or )d+ 19)18n+, where n is the strain hardening eponent?
Answer. )d+.
%- :ot working of metals refers to which one of the following temperature regions relative to the melting point
of the given metal on an absolute temperature scale7 )a+ room temperature, )b+ 4.2T
m
, )c+ 4.%T
m
, or )d+
4..T
m
?
Answer. )d+.
'- $he starting workpiece in steel hot rolling of plate and sheet stock is which of the following )one best
answer+7 )a+ bar stock, )b+ billet, )c+ bloom, )d+ slab, or )e+ wire stock?
Answer. )d+.
.- $he maimum possible draft in a rolling operation depends on which of the following parameters )two correct
answers+7 )a+ coefficient of friction between roll and work, )b+ roll diameter, )c+ roll velocit", )d+ stock
thickness, )e+ strain, and )f+ strength coefficient of the work metal?
Answer. )a+ and )b+.
1- Which of the following are alternative names for indirect etrusion )two correct answers+7 )a+ backward
etrusion, )b+ direct etrusion, )c+ forward etrusion, )d+ impact etrusion, and )e+ reverse etrusion?
Answer. )a+ and )e+.
*- $he production of tubing is possible in indirect etrusion but not in direct etrusion7 )a+ true or )b+ false?
Answer. )b+. $ube and pipe cross sections can be produced b" either direct or indirect etrusion.
3- Which of the following stress or strength parameters is used in the computation of the force in an etrusion
operation )one best answer+7 )a+ average flow stress, )b+ compression strength, )c+ final flow stress, )d+
tensile strength, )e+ "ield strength?
Answer. )a+.
14- In which of the following etrusion operation is friction a factor in determining the etrusion force )one best
answer+7 )a+ direct etrusion or )b+ indirect etrusion?
Answer. )a+.
11- ; circular sheet metal slug produced in a hole punching operation will have the same diameter as which of
the following7 )a+ the die opening or )b+ the punch?
Answer. )a+.
12- $he cutting force in a sheet metal blanking operation depends on which mechanical propert" of the metal
)one correct answer+7 )a+ compressive strength, )b+ modulus of elasticit", )c+ shear strength, )d+ strain rate, )e+
tensile strength, or )f+ "ield strength?
Answer. )c+.
1#- $he holding force in drawing is most likel" to be )a+ greater than, )b+ e(ual to, or )c+ less than the maimum
drawing force?
Answer. )c+.
#RO$LEMS
1- $he strength coefficient , ''4 <6a and strain-hardening eponent , 4.22 for a certain metal. !uring a
forming operation, the final true strain that the metal eperiences , 4.*'. !etermine the flow stress at this strain
and the average flow stress that the metal eperienced during the operation.
S!luti!n7 =low stress Y
f
, ''4)4.*'+
4.22
, %&' M#()
;verage flow stress fY, ''4)4.*'+
4.22
91.22 , *&% M#()
2- ; metal has a flow curve with parameters7 strength coefficient , *'4 <6a and strain-hardening eponent ,
4.#4. ; tensile specimen of the metal with gage length , 144 mm is stretched to a length , 1'1 mm. !etermine
the flow stress at the new length and the average flow stress that the metal has been sub>ected to during the
deformation.
S!luti!n7 - , ln )1'19144+ , ln 1.'1 , 4.%'1
=low stress Y
f
, *'4)4.%'1+
4.#4
, ++,)* M#()
;verage flow stress fY, *'4)4.%'1+
4.#4
91.#4 , %'*), M#()
&- =or a certain metal, the strength coefficient , 144 <6a and strain-hardening eponent , 4.21.
!etermine the average flow stress that the metal eperiences if it is sub>ected to a stress that is e(ual to its
strength coefficient K.
S!luti!n7 Y
f
, K , 144 , K-
n
, 144-
.21
- must be e(ual to 1.4.
fY, 144)1.4+
.21
91.21 , 14491.21 , %%')2 M#(
%- !etermine the value of the strain-hardening eponent for a metal that will cause the average flow stress to be
#9% of the final flow stress after deformation.
S!luti!n7 fY, 4.1' Y
f
K-
n
9)18n+ , 4.1' K-
n
19)18n+ , 4.1'
1 , 4.1')18n+ , 4.1' 8 4.1'n
4.2' , 4.1'n n . /)&&&
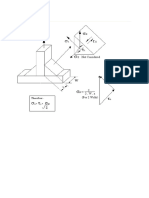
'- ; 2.4 in thick slab is 14.4 in wide and 12.4 ft long. $hickness is to be reduced in three steps in a hot rolling
operation. Each step will reduce the slab to 1'? of its previous thickness. It is epected that for this metal and
reduction, the slab will widen b" #? in each step. If the entr" speed of the slab in the first step is %4 ft9min, and
roll speed is the same for the three steps, determine7 )a+ length and )b+ eit velocit" of the slab after the final
reduction.
S!luti!n0 )a+ ;fter three passes, t
f
, )4.1'+)4.1'+)4.1'+)2.4+ , 4.*%% in
w
f
, )1.4#+)1.4#+)1.4#+)14.4+ , 14.321 in
t
o
w
o
L
o
, t
f
w
f
L
f
)2.4+)14.4+)12 12+ , )4.*%%+)14.321+L
f
L
f
, )2.4+)14.4+)12 12+9)4.*%%+)14.321+ , #12.# in , 2+)/2% 1t
)b+ @iven that roll speed is the same at all three stands and that t
o
w
o
v
o
, t
f
w
f
v
f
,
.- !etermine the blanking force re(uired in 6roblem 24.2, if the steel has shear strength , #2' <6a and the
tensile strength is %'4 <6a.
S!luti!n7 F , StL
t , 2.4 mm from 6roblem 24.2.
L , AD , 1'A , 2#'..' mm
F , #2')2.4+)2#'..'+ , '%&22// N
1- !etermine the tonnage re(uirement for the blanking operation in 6roblem 24.%, given that the stainless steel
has a shear strength , .44 <6a.
S!luti!n7 F , StL
t , % mm from 6roblem 24.%.
L , *' 8 '4 8 2' 8 2' 8 #' 8 2' 8 2' 8 '4 , #24 mm
F , .44)%.4+)#24+ , 3+42/// N) $his is about 4+)& t!ns
You might also like
- Metal Forming Processes GuideDocument4 pagesMetal Forming Processes GuideRenaldi Khaesar KumaraNo ratings yet
- Welding - Group G - Welding-02Document27 pagesWelding - Group G - Welding-02christofer kevinNo ratings yet
- Burnishing Is A Process by Which A Smooth Hard Tool (UsingDocument9 pagesBurnishing Is A Process by Which A Smooth Hard Tool (UsingΒασίλης ΜπουντιούκοςNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Crack Propagation in Stiffened Panels - Poe OCRDocument19 pagesFatigue Crack Propagation in Stiffened Panels - Poe OCRRaniero FalzonNo ratings yet
- 7.metal Forming Bending-1Document4 pages7.metal Forming Bending-1Victor NalinNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3 - Procesos de Conformado MasivoDocument3 pagesTarea 3 - Procesos de Conformado MasivoYuliana Montserrat SanchezNo ratings yet
- IES Civil Engineering 2009Document52 pagesIES Civil Engineering 2009mathivanans2007No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Twist Springback Prediction After An Ahss Forming ProcessDocument12 pagesEvaluation of Twist Springback Prediction After An Ahss Forming ProcessDVP EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Working Processes GuideDocument50 pagesMechanical Working Processes GuideAlvin Garcia Palanca100% (1)
- 4 Failure CriteriaDocument43 pages4 Failure Criteriaali381No ratings yet
- N0174147G Manufacturing ProcessesDocument10 pagesN0174147G Manufacturing Processesphillip chirongweNo ratings yet
- 6 Spring Back in Bending of Sheets and PlatesDocument5 pages6 Spring Back in Bending of Sheets and Platespkumar_824016No ratings yet
- A Study On The Fatigue Behaviour of Damaged Welded Joints Repaired by Hammer PeeningDocument8 pagesA Study On The Fatigue Behaviour of Damaged Welded Joints Repaired by Hammer PeeningAnonymous ZC1ld1CLmNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Operations: ExperimentDocument9 pagesExtrusion Operations: Experimentzainikamal1975No ratings yet
- METALWORKINGDocument23 pagesMETALWORKINGDr Rajamani R - PSGCTNo ratings yet
- Imperfection, Residual Stress and Yield Slenderness Limit of Very High Strength (VHS) Circular Steel Tubes, 2003 (H Jiao, X.-L Zhao)Document17 pagesImperfection, Residual Stress and Yield Slenderness Limit of Very High Strength (VHS) Circular Steel Tubes, 2003 (H Jiao, X.-L Zhao)Phan Đào Hoàng HiệpNo ratings yet
- Warner R.F. - Simplified Analysis of Creep in Prestressed Concrete BeamsDocument9 pagesWarner R.F. - Simplified Analysis of Creep in Prestressed Concrete BeamsCristóbal BerríosNo ratings yet
- Production GATE/ESE METAL FORMING & SHEET METAL OPERATIONDocument60 pagesProduction GATE/ESE METAL FORMING & SHEET METAL OPERATIONDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Strain Based Evaluation of Dents in Pressurized PipesDocument6 pagesStrain Based Evaluation of Dents in Pressurized Pipesmaziar60No ratings yet
- Connections in Steel Structures PDFDocument54 pagesConnections in Steel Structures PDFsmmsajediNo ratings yet
- Review Questions - 2 Group of Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesReview Questions - 2 Group of Review QuestionsVenkata DineshNo ratings yet
- 1Document14 pages1bk100% (2)
- Strain Nonuniformity in the Upsetting ProcessDocument11 pagesStrain Nonuniformity in the Upsetting Processmarc53042No ratings yet
- Mechanical PapersDocument23 pagesMechanical PapersSachin AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Forming Assessment Questions - SanfoundryDocument5 pagesForming Assessment Questions - SanfoundryrahmaNo ratings yet
- Zhao-2002-Strength and Ductility of Concrete FDocument15 pagesZhao-2002-Strength and Ductility of Concrete FIhsanNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes - Mechanical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processes - Mechanical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and AnswersrahmaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Punch Radius in Dieless Incremental FormingDocument6 pagesThe Effect of The Punch Radius in Dieless Incremental FormingCarlos ArenasNo ratings yet
- T Fillet WeldsDocument26 pagesT Fillet WeldssereNo ratings yet
- Effect of Die Surface Roughness on Cavitation in Superplastic Alloy FormingDocument6 pagesEffect of Die Surface Roughness on Cavitation in Superplastic Alloy FormingAlagu EswaranNo ratings yet
- 18 Fundamentals of Metal Forming Review Questions and Multiple Choice QuizDocument2 pages18 Fundamentals of Metal Forming Review Questions and Multiple Choice Quizhzeem50% (2)
- PCMT 4304-Mechanical Working and Testing of MaterialsDocument126 pagesPCMT 4304-Mechanical Working and Testing of MaterialsSubhasishNathNo ratings yet
- Stress Intensifiyer in Tanks 01Document22 pagesStress Intensifiyer in Tanks 01gechaves1No ratings yet
- Extrusion Lab ReportDocument20 pagesExtrusion Lab Reportex4182100% (1)
- MP1 Quiz 4Document3 pagesMP1 Quiz 4Veerakumar SNo ratings yet
- بحث الميتالDocument7 pagesبحث الميتالAhmed fahmyNo ratings yet
- MCQ-Metal Forming ProcessDocument16 pagesMCQ-Metal Forming ProcessKunal Wagh67% (9)
- Proses Manufaktur-5 - MhsDocument47 pagesProses Manufaktur-5 - MhsBintang NurimanNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Soal Uas Teknik PembentukanDocument25 pagesKumpulan Soal Uas Teknik PembentukanNur'aini Virani PutriNo ratings yet
- Tensile Strength of Good Quality BricksDocument21 pagesTensile Strength of Good Quality BricksFiaz Gujjar100% (1)
- Testing and Analysis of Steel-Concrete-Steel Sandwich BeamsDocument23 pagesTesting and Analysis of Steel-Concrete-Steel Sandwich Beamsgy279571025No ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements: Piri Reis University Maritime Faculty Marine Engineering DepartmentDocument33 pagesDesign of Machine Elements: Piri Reis University Maritime Faculty Marine Engineering DepartmentCemre berk TUNANo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength of Cold-Formed Steel C-Shape Columns With Slotted Web HolesDocument15 pagesCompressive Strength of Cold-Formed Steel C-Shape Columns With Slotted Web HolesDinesh lakshmananNo ratings yet
- StressinCurvedCircularThinWallTubes PDFDocument2 pagesStressinCurvedCircularThinWallTubes PDFskyerfreeNo ratings yet
- Ass 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsDocument2 pagesAss 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsVarinder ThandiNo ratings yet
- Main Exam Paper Nov08, Smt211tDocument6 pagesMain Exam Paper Nov08, Smt211tPortia ShilengeNo ratings yet
- ISF Aachen Welding Technology Part II PDFDocument140 pagesISF Aachen Welding Technology Part II PDFscott2355No ratings yet
- Impact Failure Analysis of Re-Circulating Mechanism in Ball ScrewDocument13 pagesImpact Failure Analysis of Re-Circulating Mechanism in Ball ScrewJigar M. UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- APSC 278 Midterm Feb 13 2013 SolutionsDocument9 pagesAPSC 278 Midterm Feb 13 2013 SolutionsykfungNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel and Composite Beams With Web OpeningsDocument19 pagesDesign of Steel and Composite Beams With Web OpeningsAngelica Gamiz ArciniegaNo ratings yet
- Hapter: MetalsDocument55 pagesHapter: Metalsbedo39No ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Solid MechanicsDocument8 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Solid MechanicsSaikat DattaNo ratings yet
- MECH2300 TEST 1 - Paper B AnswersDocument8 pagesMECH2300 TEST 1 - Paper B Answersbgrin7No ratings yet
- MCQDocument43 pagesMCQBansal RajNeesh67% (6)
- ADMET Sheet Metal Testing Guide July 2013Document9 pagesADMET Sheet Metal Testing Guide July 2013Elaine JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Yin DKK (2014)Document10 pagesYin DKK (2014)Fu DinNo ratings yet
- Konversi - MudahDocument10 pagesKonversi - MudahFu DinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering OverviewDocument29 pagesMechanical Engineering OverviewFu DinNo ratings yet
- 16-cylinder gas engine volume analysisDocument2 pages16-cylinder gas engine volume analysisFu DinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering OverviewDocument29 pagesMechanical Engineering OverviewFu DinNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: My Name My Position, Contact Information or Project DescriptionDocument4 pagesPresentation Title: My Name My Position, Contact Information or Project DescriptionFu DinNo ratings yet
- TugasDocument6 pagesTugasFu DinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Avinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Geometri EngineDocument2 pagesGeometri EngineFu DinNo ratings yet
- TemaDocument2 pagesTemaFu DinNo ratings yet
- TUGAS 4 MekfluDocument5 pagesTUGAS 4 MekfluFu DinNo ratings yet
- TemaDocument2 pagesTemaFu DinNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4Document2 pagesTugas 4Fu DinNo ratings yet
- Water Jet MachiningDocument10 pagesWater Jet MachiningSyarif MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Dan Jawaban Transformasi LaplaceDocument3 pagesContoh Soal Dan Jawaban Transformasi LaplaceMiftah Farid100% (8)
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace Tablecabeza2750% (2)
- Handout 8b Metal RollingDocument14 pagesHandout 8b Metal RollingFu DinNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument20 pagesSteam Tablesajitsamal456No ratings yet
- Kurikulum Program Sarjana1Document2 pagesKurikulum Program Sarjana1Gilank GunawanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Fatigue 16.0 L01 PDFDocument70 pagesMechanical Fatigue 16.0 L01 PDFAlexander NarváezNo ratings yet
- OEE Primer Understanding OverDocument483 pagesOEE Primer Understanding OverJorge Cuadros Blas100% (1)
- Summer Training Report On Delta Electronics, GurugramDocument12 pagesSummer Training Report On Delta Electronics, Gurugramred viperNo ratings yet
- AcronymsDocument65 pagesAcronymsSaid TouhamiNo ratings yet
- Test Case Report TemplateDocument2 pagesTest Case Report TemplateArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Construction Workers Fall Accidents from ScaffoldingDocument5 pagesConstruction Workers Fall Accidents from ScaffoldingNikola LopacaninNo ratings yet
- Projected cash flow and accomplishments for construction contractDocument6 pagesProjected cash flow and accomplishments for construction contractswazNo ratings yet
- Simplified Assessment of Bending Moment Capacity For RCDocument11 pagesSimplified Assessment of Bending Moment Capacity For RCAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- TS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFDocument303 pagesTS00E v1.2 Student Noteset PDFpatrick morris100% (1)
- WideFlange All PDFDocument19 pagesWideFlange All PDFDede HerdiantoNo ratings yet
- Resume - Mark Edison D Fellone - 2014Document2 pagesResume - Mark Edison D Fellone - 2014api-262936729No ratings yet
- Opening and Closing Rank IIT CSE GENDocument1 pageOpening and Closing Rank IIT CSE GENramchanderNo ratings yet
- Commissioning ChartDocument21 pagesCommissioning ChartSarif IslamNo ratings yet
- BbsDocument72 pagesBbsAkd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Research Scientist - Engineer Job - Ingenia Polymers - Brantford, ON - Indeed - CaDocument2 pagesResearch Scientist - Engineer Job - Ingenia Polymers - Brantford, ON - Indeed - Caming_zhu10No ratings yet
- B.C.A. (Received On 30.05.2023)Document198 pagesB.C.A. (Received On 30.05.2023)JohnsonNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument2 pagesResearchSalman AliNo ratings yet
- Simplify drive solutions up to 2,400 kWDocument12 pagesSimplify drive solutions up to 2,400 kWcatalinccNo ratings yet
- ProblemSheet - Unit 1Document1 pageProblemSheet - Unit 1Vishal VaziraniNo ratings yet
- Extended DIA - Ne XT - AccessDocument2 pagesExtended DIA - Ne XT - Accesslaiquz zaman33% (3)
- Koseki-4paper Seismic Stability of Reinforced Soil Walls PDFDocument28 pagesKoseki-4paper Seismic Stability of Reinforced Soil Walls PDFpabulumzengNo ratings yet
- Electrical/Lighting Design Engineer-CVDocument3 pagesElectrical/Lighting Design Engineer-CVMohamed67% (6)
- PLC Automation ProjectsDocument3 pagesPLC Automation Projectswhanumant100% (1)
- Jntua r13 Eee SyllabusDocument116 pagesJntua r13 Eee SyllabusRayapati Devi PrasadNo ratings yet
- LUMP SUM PRICE BREAKDOWN FOR SITE CONSTRUCTIONDocument117 pagesLUMP SUM PRICE BREAKDOWN FOR SITE CONSTRUCTIONgunturlp100% (2)
- Unit 17 Computer Aided Manufacture CamDocument11 pagesUnit 17 Computer Aided Manufacture CamManiDeepNo ratings yet
- Yield Stress Sa 240 304Document1 pageYield Stress Sa 240 304faizalNo ratings yet
- Factor of SafetyDocument12 pagesFactor of SafetyRavi TarunNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument1 pageAnalysis and Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamLouise DiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of A BuildingDocument13 pagesBasic Components of A Buildingkhim zukami100% (1)