Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rate of Reaction
Uploaded by
missririeyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rate of Reaction
Uploaded by
missririeyCopyright:
Available Formats
RATE OF REACTION
Definition
Speed at which reactants are converted into products in a chemical reaction.
Fast reaction;
time ta!en is short
So" the reactants is #uic!l$ converted to the products.
Thus" the rate of reaction is hi%h&hi%her.
Slow reaction;
time ta!en is lon%
So" the reactants is slowl$ converted to the products.
Thus" the rate of reaction is low&lower.
So'
(hat is the relation )etween rates of reaction with
time*
(hen the time ta!en is short" the rate of reaction is hi%her"
(hen the time ta!en is lon%er" the rate of reaction is lower,
Rate of reaction is directl$ proportional with +&time
Rate of reaction is inversel$ proportional with time
Exercise: pg 3 Learning Task 1.1 Classification
,easurin% the rate of reaction
Chan%es in selected #uantit$
Rate of reaction
-
........................................
Time ta!en
Suita)le chan%es'
volume of %as li)erated
precipitate formation
chan%e in mass durin% the reaction
colour chan%es
temperature chan%es
pressure chan%es
Other o)serva)le chan%es*
Avera%e rate of reaction /
The avera%e value of the rate of reaction within a
specified period of time.
Notes/
Reaction with hi%h rate of reaction"
completed in short time.
Reaction with low rate of reaction"
completed in lon%er time.
Rate of reaction at %iven&Instantaneous time /
The actual rate of reaction at that instant.
0a.!.a / Instantaneous rate of reaction1
Ta)le +.+ p% 2
Avera%e rate
of reaction
)alas
-
Changes in selected quantity
............................................
Tie taken
Instantaneous
rate of reaction
)alas
-
3radient of the curve at that instant
E4ample +.+ p% 2 05(note1
i. The avera%e rate of reaction in the first 67
seconds from %raph plotted*
Solutions/
The formula
8+.9 cm
8
67 s
7.82 cm
8
s
+
ii. The rate of reaction at 67 seconds*
0Instantaneous rate of reaction1
Solutions/ :lot a %raph
Draw a tan%ent
Find the %radient
The rate of reaction at 67 seconds
- %radient at 67 seconds
- ;en%th of DF
Avera%e rate
of reaction
)alas
-
Total !olue of gas li"erated
............................................
Tie taken
Instantaneous
rate of reaction
at 67 seconds
-
3radient of the curve at 67 seconds
-
-
;en%th of EF
- 7.+< cm8s+
#: $actors %ffecting The &ate of &eaction
(h$ these two %raph different*
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
a1
Total surface area of solid reactant
)1 Concentration of reactant
c1 Temperature of reactant
d1 =se of catal$st
e1 :ressure of %aseous reactant
Collision Theor$
Dear )o$s and %irls to )etter understand of
collision theor$ $ou must !now few thin%
related to the theor$ which is'
Collision
Effecti!e collision
%cti!ation energy
Collision frequency
Effecti!e collision frequency
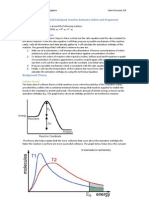
Energy profile diagra
> And also the chemical e#uation
'hat is the Collision Theory(
Durin% a reaction" the particles of the reactants must
collide with each other" for )ond )rea!in% and then )ond formation
to occur to produce product.
?ond )rea!in% : a"sor" heat energy
?ond formation : release heat energy
Those collisions which achieved a minimum activation ener%$
and with the correct orientation will result in a reaction.
These collisions are called effective collisions.
If the particles collide with less ener%$ than
activation ener%$ or with wron% orientation" it will
not result in reaction" is called ineffective collisions.
So what is i. effective collisions*
ii. activation ener%$*
Effective collisions
Those collisions )hich achie!ed a minimum activation
ener%$
and )ith the correct orientation, )ill result in a
reaction.
Activation Ener%$
Activation ener%$ is the energy "arrier that ust "e
o!ercoe "y the collidin% particles of the reactants in
order for reaction to occur
Ener%$ :rofile Dia%rams
i. E4othermic Reactions
Remem)er the process and dia%rams" we will stud$ more when we reach topic <.
ii. Endothermic Reactions
Energy
&eactants
*roducts
%cti!ation Energy
E4othermic Reaction
&eaction path
5eat chan%es
Activation ener%$ is the difference in ener%$ )etween the ener%$ in reactants and the ener%$ at the pea!
of curve
E4othermic Reaction
Reactants :roduct
Total 5eat Ener%$ 5i%her ;ower
5eat Ener%$ durin% reaction Ener%$ a)sor)s durin% )ond
)rea!in% is lower
Ener%$ releases durin% )ond
formation is hi%her
Thus'
5eat chan%es - 5eat Ener%$ in product @
5eat Ener%$ in reactant
- ve
Energy
&eactants
*roducts
%cti!ation Energy
Endothermic Reaction
&eaction path
Endothermic Reaction
Reactants :roduct
Total 5eat Ener%$ ;ower 5i%her
5eat Ener%$ durin% reaction Ener%$ a)sor)s durin% )ond
)rea!in% is hi%her
Ener%$ releases durin% )ond
formation is lower
Thus'
5eat chan%es - 5eat Ener%$ in product @
5eat Ener%$ in reactant
- A ve
The conclusion is'
The reaction occur when reactants collide'
a. achieved activation ener%$
). with correct orientation
An$ Buestion so far*
+ Effect of surface area&siCe
S,A;;ER siCe solid reactant"
?i%%er total surface area per volume
5i%her fre#uenc$ of effective collision
5i%her rate of reaction
?I33ER siCe solid reactant"
Smaller total surface area per volume
;ower fre#uenc$ of effective collision
;ower rate of reaction
S!etch %raph volume of %as a%ainst time
?ase from the %raph" please e4plain*
I / Small mar)le
II / ;ar%e mar)le
Dolume of
%as & cm
8
Time & min
I II
D
t
+
t
E
- 3raph I is more steeper than %raph II
- Thus" the %radient of %raph I is more than
%raph II
- Thus" the rate of reaction for the e4periment I
is hi%her than e4perimen II
Buestion/ (h$ the total volume of %as is
same*
%ns)er: the nu"er of mole of reactant
is sae
5(/ draw %raph fi%ure +.Fp%+7
Effect of SiCe
(hen the siCe of fi4ed mass of solid reactant
0name the reactant" CaCO
8
1 is smaller"
The total surface area per volume e4posed to collision with other
reactant 0name the reactant1 particles is )i%%er.
Thus" the num)er of collision amon% the
reactin% particles at the surface of the
solid reactants increases. Fre#uenc$ of collission is hi%her.
Thus" the num)er of collision achieved
the activation ener%$ to )ecome effective
collision is also increases.
This lead to an increase in the FREB=ENCG of EFFECTIDE
CO;;ISION.
5ence" a hi%her rate of reaction.
Effect of Concentration
(hen the concentration of the solution of a
reactant increases'
The num)er of particles per unit volume of the solution of the reactant also increases.
Thus" the num)er of collision amon% the
reactin% particles increases. Fre#uenc$ of collission is hi%her.
Thus" the num)er of collision achieved
the activation ener%$ to )ecome effective
collision is also increases.
This lead to an increase in the fre#uenc$ of
effective collision.
5ence" a hi%her rate of reaction.
5(/ draw %raph fi%ure +.9 p%++
5(/ draw %raph fi%ure +.6 p%+E
Effect of Temperature
(hen the temperature of a reactant increases'
The !inetic ener%$ of reactin% particles will increase" so the particles moves faster.
Thus" the num)er of collision amon% the
reactin% particles increases. Fre#uenc$ of collission is hi%her.
Thus" the num)er of collision achieved
the activation ener%$ to )ecome effective
collision is also increases.
This lead to an increase in the fre#uenc$ of
effective collision.
5ence" a hi%her rate of reaction.
5(/ draw %raph fi%ure +.+7 p%+8
draw %raph fi%ure +.++ p%+8
Effect of Catal$st
0:% +81
Catal$st/ a su)stance which alters the rate of
chemical reaction while it remains
chemicall$ unchan%ed at the end of
the reaction.
:roperties of catal$st'
(hen the catal$st is presence'
The catal$st allows the reactian to ta!e
place throu%h an alternative path which re#uires a
lower activation ener%$.
Ener%$
Reactant
E
a
:roduct
E
a
/ Activation ener%$
without catal$st
E
c
/ Activation Ener%$
with catal$st
E
c
Reaction with
catal$st
Reaction without
catal$st
Reaction path
Thus" more collision amon% the reactin%
particles are a)le to achive the lower
activation ener%$.
Thus" the num)er of collision achieved
the activation ener%$ to )ecome effective
collision is also increases.
This lead to an increase in the fre#uenc$ of
effective collision.
5ence" a hi%her rate of reaction.
Effect of :ressure
(hen the pressure of the %as of a reactant
increases'
The num)er of particles per unit volume of the %as of the reactant also increases.
Thus" the num)er of collision amon% the
reactin% particles increases. The fre#uenc$ of collision is increase.
Thus" the num)er of collision achieved
the activation ener%$ to )ecome effective
collision is also increases.
This lead to an increase in the fre#uenc$ of
effective collision.
5ence" a hi%her rate of reaction.
5(/ p%. E2 E:C no. +" E" <
S!etch %raph/
0i1 Concentration of solution a%ainst time
0ii1 Concentration of solution a%ainst +&time
Concentration of sodium thiosulfate
0Na
E
S
E
O
8
1 & mol dm
8
Time & s
So" what can $ou conclude from the %raph*
0iii1 Temperature a%ainst time
....
time
+
&s
+
Concentration of sodium thiosulfate
0Na
E
S
E
O
8
1 & mol dm
8
Temperature &
o
C
time &s
Teperature is directly proportional
to the rate of reaction
0iv1 Temperature a%ainst +&time
So" what can $ou conclude from the %raph*
Concentration is directly proportional
to the rate of reaction
Suhu &
o
C
+
time
.....
&s
+
5ow to anal$se the %raph*
First Situation/
All of these e4periments are usin% the same siCe
and mass of catal$st. The temperature of the
reactants remains the same.
(h$ are there differences in the rate of reaction
shown*
I and II
I and III I and ID HcomparisonI
:lease remem)er that the total volume of the %as
depends on the num)er of moles of the reactant.
Num)er of moles - ,olarit$ J Dolume
0solution1 +777
Can $ou anal$se the %raph )ased from the
volume and the concetration of the reactant*
Dolume of %as & cm
8
Time & min
I II
D
t
+
t
E
+++
+,
D&E
Second Situation/
All of these e4periments are usin% the same t$pe
of catal$st. The volume" concentration and
temperature of the reactants remains the same.
(h$ are there differences in the earl$ rate of reaction
shown*
The siCe of catal$st in e4p I is smaller compare to e4p II and III.
Or
The mass of catal$st in E4p I is more than e4p II and III.
Or
The siCe of reactant in e4p I is smaller than e4p II and III
2.E
E4ercise/
An e4periment is carried out )etween +7 %
of ma%nesium with E7 cm
8
h$drochloric acid
7.2 mol dm
8
. The reaction is completed in 9
minutes.
HRelatif atomic mass/ 5" +' Cl" 82 ' ,%" E<'
I II III
Dolume of the
%as & cm
8
D
t
+
t
E
Time & min
,olar volume of %as is E< dm
8
at room
conditionI
a1 (rite a )alanced chemical e#uation
for this reaction.
)1 Calculate the ma4imum volume of the
%as li)erated at room condition.
c1 Calculate the avera%e rate of reaction
within 9 minutes.
d1 Calculate the mass of the ma%nesium
used in the reaction.
e1 S!etch the %raph of volume a%ainst
time for these e4periment
The formula/
IF REACTANT IS SO;ID
Num)er of mole - . mass .
A
r
or ,
r
IF REACTANT IS SO;=TION
Num)er of moles - ,olarit$ J Dolume
+777
VOLUME OF THE GAS AT ROOM
CONDITION
Dolume of - Num)er of moles J E< dm
8
the %as
Solution/
a. ,% A E5Cl K ,%Cl
E
A 5
E
7.7+
). Num)er of moles of ,%
- mass ,%
A
r
- +7
E<
- 7.<E mol 0ELCESS
?ER;E?I5AN
Num)er of moles of h$drochloric acid
- Concentration J Dolume
+777
- ,D
+777
- 7.2 4 E7
+777
- 7.7+ mol
,% A E5Cl K ,%Cl
E
A 5
E
7.<E 07.7+1
F?CE'
E mol 5Cl produce + mol 5
E
7.7+ mol 5Cl produce M 4 7.7+ mol 5
E
Thus'
The no. of mole of 5
E
- 7.772 mol
0+ mol of %as - E< dm
8
in room condition1
Dolume of 5
E
- 7.772 L E< dm
8
5
E
- 7.+E dm
8
- +E7 cm
8
c. Avera%e reaction in 9 minute
- +E7 & 9 cm
8
min
+
- +2 cm
8
min
+
d.
F?CE'
E mol 5Cl reacts with + mol ,%
7.7+ mol 5Cl reacts with M 4 7.7+ mol ,%
Thus'
The no. of mole of ,% - 7.772 mol
0+ mol of ,% - E< %1
,ass of ,% - 7.772 L E< %
- 7.+E %
5(/ p%. E9E6 RB o)N.B no. +9 0cop$paste1
p%. E6 Su).B no. +
p%. 87 Ess.B no. E
E. An e4periment is carried out )etween E %
of ma%nesium car)onate with E7 cm
8
h$drochloric acid 7.E mol dm
8
.
0RA,/ 5" +' C" +E' O" +F' ,%" E<'
,olar volume of %as is EE.< dm
8
at s.t.p1
a1 (rite a )alanced chemical e#uation
for this reaction.
)1 Calculate the ma4imum volume of the
%as li)erated at s.t.p.
c1 Draw a la))eled apparatus for
e4perimet.
d1 5ow to test and confirm the %as
li)erated
Solution'
a1 ,%CO
8
A E5Cl ,%Cl
E
A CO
E
A 5
E
O
)1 No. mol of 5Cl - ,D&+777
- 7.E 4 E7 & +777
- 7.77< mol
F?CE'
5Cl CO
E
E mol +mol
7.77< mol 7.77E mol
No. of mol CO
E
- 7.77E mol
Dolume of CO
E
- 7.77E 4 EE.< dm
8
- 7.7<<9 dm
8
- 7.7<<9 4 +777 cm
8
- <<.9 cm
8
d1 Add E7 cm
8
lime water into a test tu)e" and
passed throu%h the %as into the test tu)e.
The lime water turns cloud$&chal!$.
You might also like
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 1Document37 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 1kslpeter87No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument40 pagesChemical KineticsHirdesh Sehgal100% (3)
- Topic 2.2 Kinetics Rates of Reaction Simple Collision Theory Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionDocument9 pagesTopic 2.2 Kinetics Rates of Reaction Simple Collision Theory Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionAngelLoveMusicNo ratings yet
- Short Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 1 Rate of ReactionDocument4 pagesShort Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 1 Rate of Reactionsalamah_sabri100% (1)
- Integral Rate Law, Half-LifeDocument10 pagesIntegral Rate Law, Half-LifeaminNo ratings yet
- Definition N FactorsDocument37 pagesDefinition N FactorsJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 1234 FinalDocument22 pagesChemical Kinetics 1234 FinalJayesh SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical Kineticspala100% (1)
- Topic 4.1 Kinetics Rate Equations Determining Orders of Reaction Explaining Orders of Reaction Effect of Changing Conditions On The Rate ConstantDocument9 pagesTopic 4.1 Kinetics Rate Equations Determining Orders of Reaction Explaining Orders of Reaction Effect of Changing Conditions On The Rate ConstantAsha D'saNo ratings yet
- Physical Change: Chemical ReactionsDocument9 pagesPhysical Change: Chemical ReactionsAishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Form 5 Chemistry 2015Document21 pagesChapter 1 Form 5 Chemistry 2015Alvieno Situl MintowNo ratings yet
- Colision TheoryDocument85 pagesColision Theoryactive learning educationNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument7 pagesRates of ReactionDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Entropy NotesDocument9 pagesEntropy NotescusgakungaNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Practice TestDocument3 pagesKinetics Practice Testlydia21111No ratings yet
- FactorDocument2 pagesFactorJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- One Stop For Colleges Education Career: Minglebox Engineering PrepDocument14 pagesOne Stop For Colleges Education Career: Minglebox Engineering PrepVigneshwar DhamodharanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsAyush singh PrinceNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument3 pagesRate of Reactionpancake89No ratings yet
- Collision Theory: Teori PerlanggaranDocument20 pagesCollision Theory: Teori Perlanggaranameermx0% (1)
- SS 2 Week 3Document71 pagesSS 2 Week 3Denzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium: Three Stooges in Chemical ReactionsDocument5 pagesEquilibrium: Three Stooges in Chemical ReactionsKhud SarNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry ResearchDocument7 pagesPhysical Chemistry ResearchBilal SattiNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate 2024Document47 pagesReaction Rate 2024Peter KiwanukaNo ratings yet
- This Is A Redox Equation. The Ion Permanganate (Purple) Is Reduced To Ion Manganese (II) Which Is ColourlessDocument3 pagesThis Is A Redox Equation. The Ion Permanganate (Purple) Is Reduced To Ion Manganese (II) Which Is ColourlessMelissa Ann VannanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument45 pagesChemical ReactionsSafwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument17 pagesEnzyme Kineticssherif87No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Rates of Reaction-1Document14 pagesModule 4 - Rates of Reaction-1Phí Nguyễn Thùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument6 pagesRates of ReactionesotericgraphicapparelNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Kinetics 6. 1 Rates of ReactionDocument7 pagesTopic 6: Kinetics 6. 1 Rates of Reactionnadia sykesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Rates of Reaction & Chemical CalculationsDocument2 pagesChemistry - Rates of Reaction & Chemical CalculationsMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- English WB IgcseDocument23 pagesEnglish WB Igcsetoleen playzNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter Reaction Kinetics Text Book ExerciseDocument14 pages11 Chapter Reaction Kinetics Text Book ExerciseSajid AzeemNo ratings yet
- 2 1 A) B) C) D) E) - 2 - 2 2 - 1 3 2 2 2 3Document2 pages2 1 A) B) C) D) E) - 2 - 2 2 - 1 3 2 2 2 3Abhishek MittalNo ratings yet
- Activation Energy: Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesActivation Energy: Key ConceptsChristopher BanolNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry For Systems Involving Recycles PDFDocument7 pagesStoichiometry For Systems Involving Recycles PDFGlory Usoro100% (1)
- Rates of Reaction NotesDocument13 pagesRates of Reaction NotesNia RamNo ratings yet
- SPM Form 5 Rate of ReactionsDocument2 pagesSPM Form 5 Rate of ReactionsAfida HamsaniNo ratings yet
- Definition N Factors 2Document27 pagesDefinition N Factors 2Thana SegarNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Collision Theory and Rates of ReactionsDocument4 pages6.1 Collision Theory and Rates of ReactionsSpic ArterNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesRate of ReactionRobin CabralNo ratings yet
- Chem f4 Chap7Document4 pagesChem f4 Chap7Alya QistinaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes: Chemical Kinetics: HomepageDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes: Chemical Kinetics: HomepageBHAVYA BNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument73 pagesKineticsshireen O. IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics 1Document114 pagesChemical Kinetics 1Ashish KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument48 pagesChemical KineticsTeahyvnqsNo ratings yet
- 1 Lab Handout PDFDocument5 pages1 Lab Handout PDFKhud SarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 RatesDocument23 pagesUnit 4 RatesSahanNivanthaNo ratings yet
- Rates & Energy NotesDocument11 pagesRates & Energy Notesdanielphilip68No ratings yet
- Lecture 4a. Chemical Kinetics 2020Document23 pagesLecture 4a. Chemical Kinetics 2020Montassar DridiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of The Acid Catalysed Reaction Between Iodine and Propanone Final LolDocument23 pagesKinetics of The Acid Catalysed Reaction Between Iodine and Propanone Final LolYann Perusset90% (10)
- Chemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 5 PDFDocument85 pagesChemistry Pre-U Chemistry Sem 1 Chap 5 PDFJIANHUI0160% (1)
- نظرية التصادمDocument6 pagesنظرية التصادمSrewaBenshebilNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Time Reversal: Application to EMC and Power SystemsFrom EverandElectromagnetic Time Reversal: Application to EMC and Power SystemsFarhad RachidiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemical Reaction EngineeringFrom EverandFundamentals of Chemical Reaction EngineeringRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Important Terms in SPM Chemistry For DefinitionDocument4 pagesImportant Terms in SPM Chemistry For DefinitionmissririeyNo ratings yet
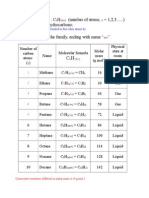
- General Formula: C H (Number of Atoms, 1,2,3...... ) 2. They Are Hydrocarbons 3. The Members of The Family, Ending With Name " "Document11 pagesGeneral Formula: C H (Number of Atoms, 1,2,3...... ) 2. They Are Hydrocarbons 3. The Members of The Family, Ending With Name " "missririeyNo ratings yet
- 4 Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesDocument3 pages4 Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesmissririeyNo ratings yet
- 4 Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesDocument3 pages4 Comparing Alkanes and AlkenesmissririeyNo ratings yet
- General Formula: C H (Number of Atoms, 1,2,3...... ) 2. They Are Hydrocarbons 3. The Members of The Family, Ending With Name " "Document11 pagesGeneral Formula: C H (Number of Atoms, 1,2,3...... ) 2. They Are Hydrocarbons 3. The Members of The Family, Ending With Name " "missririeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment ChemistryDocument2 pagesExperiment ChemistrymissririeyNo ratings yet
- 2 Heat of PrecipitationDocument20 pages2 Heat of PrecipitationmissririeyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFDocument118 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Workbook PDFSayan Dutta100% (1)
- Introductory Experiment: Calibration of Volumetric GlasswareDocument4 pagesIntroductory Experiment: Calibration of Volumetric GlasswareOcampo AmyNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Project - Snag List v1Document1 pageMicrosoft Office Project - Snag List v1Necdet KayıkcıNo ratings yet
- Motor SizesDocument10 pagesMotor SizesBruno KosNo ratings yet
- BCS ClassificationDocument13 pagesBCS ClassificationSandeep SainiNo ratings yet
- Guide To The Construction Installation Operation and Maintenance of Air ReceiversDocument34 pagesGuide To The Construction Installation Operation and Maintenance of Air Receiversjosh100% (1)
- Mal 4Document5 pagesMal 4Heri HidayatNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Dough and Bread As Affected by The Incorporation of Sweet Potato Paste in The FormulationDocument10 pagesCharacteristics of Dough and Bread As Affected by The Incorporation of Sweet Potato Paste in The FormulationDanaNo ratings yet
- IISER Pune Semester IIDocument12 pagesIISER Pune Semester IIAnmol SahuNo ratings yet
- Benzene Hydrogenation Over Ni/Al O Catalysts Prepared by Conventional and Sol-Gel TechniquesDocument9 pagesBenzene Hydrogenation Over Ni/Al O Catalysts Prepared by Conventional and Sol-Gel TechniquesHarun AydınNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument4 pagesSynopsisyashaahmadNo ratings yet
- Gantry CraneDocument20 pagesGantry Cranekushaljp8989No ratings yet
- B SC Analytical ChemDocument82 pagesB SC Analytical ChemEngineering PhysicistNo ratings yet
- I - 6 Batch 2022 Project ReportDocument72 pagesI - 6 Batch 2022 Project Reportvilla srisuryaNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Chemical Industry ProfileDocument7 pagesThe Philippine Chemical Industry ProfileEddie Resurreccion Jr.No ratings yet
- Understanding Underground Electric Transmission CablesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Underground Electric Transmission CablesSebastianCicognaNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Study of FoundriesDocument64 pagesWaste Management Study of FoundriesSumit GusainNo ratings yet
- Vessel Manways, Handholes Pose Special Sealing Challenges: Flanged PlatesDocument6 pagesVessel Manways, Handholes Pose Special Sealing Challenges: Flanged PlatesalokbdasNo ratings yet
- 01 - Properties of GasesDocument9 pages01 - Properties of GasesDede MulyamanNo ratings yet
- Problemas Geotecniafree1Document46 pagesProblemas Geotecniafree1Dickey Design100% (3)
- Fuelless GeneratorDocument20 pagesFuelless GeneratorazoubraNo ratings yet
- X-MET3000TX+ PMI BrochureDocument4 pagesX-MET3000TX+ PMI BrochureYulfikaenis MachroniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Power CircuitsDocument176 pagesFluid Power CircuitsMike Fredskilde97% (29)
- Juba Form Two ExamDocument8 pagesJuba Form Two ExamHossam Abdalla SalehNo ratings yet
- Flavor ChemistryDocument1 pageFlavor ChemistryMVNo ratings yet
- BenzilDocument5 pagesBenzildeviycNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Steam Turbine Training CourseDocument45 pagesSaudi Aramco Steam Turbine Training CourseDhananjay B K100% (2)
- Influence of Fly Ash On The Pore Structure and Shrinkage Characteristics of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Pastes and MortarsDocument10 pagesInfluence of Fly Ash On The Pore Structure and Shrinkage Characteristics of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Pastes and MortarsMuhammad Riaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Art of Candle and SoapDocument126 pagesThe Art of Candle and SoapMallory GuestNo ratings yet
- Pressure-Enthalpy Diagrams: Aturation Ubcooling AND UperheatDocument35 pagesPressure-Enthalpy Diagrams: Aturation Ubcooling AND UperheatAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet