Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BSC 250 Chapter 3 Blank Notes
Uploaded by
sarahreyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BSC 250 Chapter 3 Blank Notes
Uploaded by
sarahreyCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Cell Biology and Genetics
Read 3.1 3.9 and 3.11; Note: we will discuss plasma
membrane last
1. Describe the characteristic functions of the cell.
2. Define cytoplasm.
3. What are the general functions of the cytoskeleton?
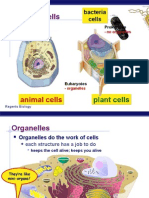
4. Define organelle.
5. Describe the function of each of the following: nucleus,
nucleolus, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi
apparatus, secretory vesicles, lysosome, peroxisome,
mitochondrion, centrioles, cilia, flagella, and microvilli.
6. What is mitosis?
7. Describe the structure of the plasma membrane.
8. List and describe the different types of membrane
proteins.
9. List four ways that substances move across the plasma
membrane.
10.
Define diffusion.
11.
What is osmosis? Distinguish between isotonic,
hypotonic, and hypertonic.
12.
What is mediated transport?
13.
Contrast facilitated diffusion and active transport.
14.
Define endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and
exocytosis.
Notes:
A typical somatic cell is surrounded by a watery medium known as
extracellular fluid (ECF) or interstitial fluid.
Components of a cell (See table 3.1)
Plasma membrane cell membrane
Cytoplasm cytosol and organelles
Nucleus control center of the cell
Components of the Cytoplasm:
Cytosol
Organelles
Inclusions
Organelles:
1. Cytoskeleton:
Internal scaffolding of cell
protein filaments common in all cells
o Microfilaments
o Microtubules
2. Nucleus
Determines the characteristics of cell
Most cells have one nucleus, but there are exceptions
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pores
Nucleolus
Genetic material: DNA
3. Ribosome
Composed of proteins and RNA
Workbench of protein synthesis
Types of ribosomes: free v. attached
4. Endoplasmic Reticulum
Network of membranes
Involved in protein, lipid and carbohydrate synthesis
Stores material
Neutralizes toxins
Two types: Rough ER v. Smooth ER
5. Golgi Apparatus
Flattened membranous discs stacked together
Communicates with the ER and plasma membrane
Modifies and packages secretions
Renews and modifies the plasma membrane
Packages material that remain in the cell
6. Lysosome
Vesicle filled with digestive enzymes
7. Peroxisome
Vesicle filled with enzymes that detoxify
8. Mitochondrion
Power house of the cell
Site of ATP production
Double membrane with two internal compartments:
intermembrane space and matrix
9. Centriole
Composed of microtubules
Direct movement of genetic material during cell division
10.
Cilia
Hair-like, motile extensions
Moves secretions or fluids across the surface of cells
11.
Flagellum
Similar to cilia but longer
12.
Microvilli
short extensions of cell
increase surface area for absorption
Cell Cycle:
Interphase: non-dividing phase; cell growth and DNA replication
Mitosis: cell divides. Identify the events of prophase, metaphase,
anaphase, and telophase
Types of cell division:
Mitosis: one diploid cell divides to produce two diploid cells
Meiosis: one diploid cell divides to produce multiple haploid cells
The Plasma Membrane
Functions:
Physical isolation
Regulation of exchange
Sensitivity
Structural support
The plasma membrane is a bilayer of phospholipids with associated
proteins and carbohydrates.
Membrane Lipid
Phospholipids: most of the surface of the membrane
Cholesterol: stabilize the position of the phospholipids
Membrane Proteins (See table 3.2)
Integral proteins
Peripheral proteins
Marker
Attachment
Channel
Carrier
ATP-powered pumps
Receptors
Enzymes
Membrane Permeability
Determines what enters or leaves the cell
Selectively permeable
Movement across the membrane is either
Passive: cell does not expend any energy
Active: cell expends energy
Categories of transport (See table 3.3)
Diffusion
Mediated transport
Vesicular
Diffusion: Movement of a substance from an area of high concentration
to an area of lower concentration; passive process
Osmosis: diffusion of water
Tonicity: describes the concentration of a solution relative to the
cytoplasm (see figure 3.17)
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
Mediate transport: substance moves across the membrane through
interactions with membrane proteins
Facilitated diffusion
Active transport
Vesicular Transport: bulk transport across the membrane by the
formation or release of vesicles
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
o Pinocytosis
o Phagocytosis
o Receptor-mediated endocytosis
13.
You might also like
- Mccance: Pathophysiology, 6Th Edition: Chapter 01: Cellular Biology Key Points - Print Summary ReviewDocument5 pagesMccance: Pathophysiology, 6Th Edition: Chapter 01: Cellular Biology Key Points - Print Summary ReviewAbiah IsraelNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2Document3 pagesLab Exercise 2Patricia Andrea Alexei FernandezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Document55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 3Yasin Putra EsbeyeNo ratings yet
- CELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesCELL THE UNIT OF LIFE Important QuestionsAli WarisNo ratings yet
- Cell StrucutreDocument40 pagesCell StrucutreJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Anatomy)Document86 pagesChapter 3 (Anatomy)Phan SokkheangNo ratings yet
- Assignment Research: CELLS Second PeriodDocument7 pagesAssignment Research: CELLS Second PeriodMaria FabianNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF MaterialDocument8 pagesUnit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF Materialsimhaenator7109No ratings yet
- CH 6 BiologyDocument4 pagesCH 6 BiologysophieowensNo ratings yet
- Grade 12-General Biology (Cells)Document11 pagesGrade 12-General Biology (Cells)angeliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Reviewer Seeley'sDocument2 pagesCell Reviewer Seeley'smarielle castroNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Lifevivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Official Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesOfficial Chapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-528700386No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-530699294No ratings yet
- A. Parts of The Cell 1. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document3 pagesA. Parts of The Cell 1. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)akosidanielaNo ratings yet
- CH - 03 The CellDocument29 pagesCH - 03 The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Cellular Components 2.3.1 Membrane, Cell Wall, and Cytoplasm Davson-Danielli Model of The MembraneDocument16 pages2.3 Cellular Components 2.3.1 Membrane, Cell Wall, and Cytoplasm Davson-Danielli Model of The Membranedavid ngNo ratings yet
- Cellular Worlds: MDSC 1001 PBL Problem 1 Tutor: DR S. ChaseDocument27 pagesCellular Worlds: MDSC 1001 PBL Problem 1 Tutor: DR S. Chasebrennan12345No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Structure and Function Worksheetcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument68 pagesCell Biologyleanavill100% (2)
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument5 pagesCell Structures and Functions9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument15 pagesCellsMaria Stephanie LabutapNo ratings yet
- Genetics 101Document4 pagesGenetics 101Jhon Ric BajeNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMDocument40 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-26 at 8.50.46 PMnomysalihNo ratings yet
- Bio Midterm ReviewDocument49 pagesBio Midterm ReviewLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document6 pagesBio Assignment 1ditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 2 Cell NotesS PaulNo ratings yet
- 8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsDocument13 pages8 & 9: Cell Structure and Function: CellsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument37 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGYAliyu Aisha100% (1)
- Cell AnalogyDocument17 pagesCell AnalogyJianne CabildoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Functions & DefinitionsDocument4 pagesCell Organelle Functions & DefinitionsFarah Jaye Verde CayayanNo ratings yet
- CH 2: The Cell: GoalsDocument38 pagesCH 2: The Cell: GoalsHitansh KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cell, Cell Theory, and Cell TypesDocument34 pagesLesson 1 Cell, Cell Theory, and Cell TypesAbubakar DucaysaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyDocument31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyAzher MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellvjaNo ratings yet
- DEFINITIONS FOR THE PROJECTDocument2 pagesDEFINITIONS FOR THE PROJECTzoe.pizarrofNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Typical Cell and Their Functions: Maintains Cell Shape Selectively PermeableDocument2 pagesParts of A Typical Cell and Their Functions: Maintains Cell Shape Selectively PermeableMaria Sahara FregilNo ratings yet
- Cells Chapter 2 OverviewDocument107 pagesCells Chapter 2 Overviewida hadiNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument6 pagesCell Theory: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeRiy KimNo ratings yet
- Cells Questions and VocabDocument12 pagesCells Questions and VocabFanna Sharma100% (1)
- AS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellDocument11 pagesAS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Edible Cell Model: Make Plant or Animal CellDocument9 pagesEdible Cell Model: Make Plant or Animal CellSheena Mar dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and OrganizationDocument7 pagesPlant Cell and OrganizationMatthew Reyes RemegiaNo ratings yet
- 01-The CellDocument25 pages01-The Cellfordgt989No ratings yet
- Class NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Document28 pagesClass NOTES - Cell Structures and Their Function.Cyril Josh MaisogNo ratings yet
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (14)
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell E-BookDocument21 pagesPlant Cell E-BookSammy ShnayderNo ratings yet
- Cell Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCell Cheat SheetAJ Coots100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Student Copy ZoologyDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Student Copy Zoologyapi-523871804No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsFrancis PhimphivongNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life Question AnswerDocument8 pagesCell Unit of Life Question Answershafiahmad2014.15No ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Document10 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Justin RajanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function 1Document4 pagesCell Structure and Function 1Dianne LarozaNo ratings yet
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarDocument61 pagesSeminar On Cell: Sri Guru Ram Das Instituite of Dental Sciences and Research Sri AmritsarKomal MittalNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class IX Biology Fundament Unit of Life Chapter NotesDremaraanNo ratings yet
- Baldwin's Glimpse at Racial Injustice in AmericaDocument5 pagesBaldwin's Glimpse at Racial Injustice in AmericasarahreyNo ratings yet
- James Baldwin FINAL DRAFTDocument5 pagesJames Baldwin FINAL DRAFTsarahreyNo ratings yet
- James Baldwin FINAL DRAFTDocument5 pagesJames Baldwin FINAL DRAFTsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Letter To LitteDocument1 pageLetter To LittesarahreyNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument5 pagesSpeechsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Sarah Reyner: 118 College Drive Hattiesburg, MS 39406 Cell: 251-406-2222 Sarah - Reyner@eagles - Usm.eduDocument2 pagesSarah Reyner: 118 College Drive Hattiesburg, MS 39406 Cell: 251-406-2222 Sarah - Reyner@eagles - Usm.edusarahreyNo ratings yet
- HIS Exam 1 NotesDocument23 pagesHIS Exam 1 NotessarahreyNo ratings yet
- His 102 Paper 2Document5 pagesHis 102 Paper 2sarahreyNo ratings yet
- Response To Kristens CritiqueDocument2 pagesResponse To Kristens CritiquesarahreyNo ratings yet
- Synthesis AssignmentDocument1 pageSynthesis AssignmentsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Final Draft of Rick Santorum CritiqueDocument5 pagesFinal Draft of Rick Santorum CritiquesarahreyNo ratings yet
- His 102 Paper 2Document5 pagesHis 102 Paper 2sarahreyNo ratings yet
- ENG 102-Research Paper ProposalDocument3 pagesENG 102-Research Paper ProposalsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Americans' Inherent Suspicion of AuthorityDocument4 pagesAmericans' Inherent Suspicion of AuthoritysarahreyNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument5 pagesSpeechsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Notes To SavannahDocument22 pagesNotes To SavannahsarahreyNo ratings yet
- ENG Rough DraftDocument3 pagesENG Rough DraftsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Final DraftDocument9 pagesSynthesis Final DraftsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Cms Persuasive SpeechDocument6 pagesCms Persuasive SpeechsarahreyNo ratings yet
- His 102 Exam II NotesDocument30 pagesHis 102 Exam II NotessarahreyNo ratings yet
- ENG 102-Research Paper BibliographyDocument5 pagesENG 102-Research Paper BibliographysarahreyNo ratings yet
- Americans' Ingrained Skepticism of AuthorityDocument9 pagesAmericans' Ingrained Skepticism of AuthoritysarahreyNo ratings yet
- Research RRRDDocument7 pagesResearch RRRDsarahreyNo ratings yet
- CMS P Speech (Ref. Page)Document1 pageCMS P Speech (Ref. Page)sarahreyNo ratings yet
- Persuasive SpeechDocument5 pagesPersuasive Speechsarahrey100% (2)
- Port JBDocument5 pagesPort JBsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Research RRD2Document7 pagesResearch RRD2sarahreyNo ratings yet
- PORT CoverDocument2 pagesPORT CoversarahreyNo ratings yet
- Obesity Paradox: How Poverty Leads to Excess WeightDocument13 pagesObesity Paradox: How Poverty Leads to Excess WeightsarahreyNo ratings yet
- PORT ResearchDocument13 pagesPORT ResearchsarahreyNo ratings yet
- Ibo (The International Biology Olympiad)Document6 pagesIbo (The International Biology Olympiad)RadpandjiNo ratings yet
- Precision Nutrition Certification Level 1 - Chapter 1Document76 pagesPrecision Nutrition Certification Level 1 - Chapter 1trungchinh8xxx100% (2)
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Aubrianna Labonte-Postell - CellStructure GizmoDocument5 pagesKami Export - Aubrianna Labonte-Postell - CellStructure Gizmoaubrianna.postellNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A ReviewDocument15 pagesRecent Advances in Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: A ReviewMayang AprilianiNo ratings yet
- Protein TargettingDocument11 pagesProtein TargettingPMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- Lipid Map of The Mammalian CellDocument4 pagesLipid Map of The Mammalian Celljuan joseNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Anatomy and FunctionsDocument11 pagesEukaryotic Cell Anatomy and FunctionskleeNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport and Vesicle MovementDocument4 pagesMembrane Transport and Vesicle MovementNiharika GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structure & Functions-1 PDFSTEM 8 PRODUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Airway Mucus Secretion PDFDocument16 pagesPhysiology of Airway Mucus Secretion PDFPaoly PalmaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd EdDocument8 pagesCytoplasm: Color Textbook of Histology, 3rd EdJanet GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13th Edition Tortora Test Bankpithlessriverp4d6100% (31)
- Levels of Organization in Animal ComplexibilityDocument93 pagesLevels of Organization in Animal ComplexibilityRion BaiganNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument24 pagesCell Structureapi-298438014No ratings yet
- Highly-Purified Exosomes and Shed Microvesicles Isolated From The Human Colon Cancer Cell Line LIM1863 by Sequential Centrifugal Ultrafiltration Are Biochemically and Functionally DistinctDocument15 pagesHighly-Purified Exosomes and Shed Microvesicles Isolated From The Human Colon Cancer Cell Line LIM1863 by Sequential Centrifugal Ultrafiltration Are Biochemically and Functionally DistinctLidia RLNo ratings yet
- Modern Proteomics Sample Preparation Analysis and Practical ApplicationsDocument525 pagesModern Proteomics Sample Preparation Analysis and Practical ApplicationsDesiree De la Cruz100% (2)
- Histology Uestions From LecturioDocument80 pagesHistology Uestions From LecturioChinyere OkoraforNo ratings yet
- Vedicinals Spike Protein Detox and Long Covid - Joachim Gerlach-CompressedDocument162 pagesVedicinals Spike Protein Detox and Long Covid - Joachim Gerlach-CompressedvaikyumiNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Membrane TransportDocument30 pages1.4 Membrane TransportDana PorterNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life LESSONDocument104 pagesCell - The Fundamental Unit of Life LESSONGrade 4 B TeacherNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 BioenergeticsDocument15 pagesLesson 2 BioenergeticsJboy MnlNo ratings yet
- 1 Exam Style Answers 1 Asal Biology CBDocument4 pages1 Exam Style Answers 1 Asal Biology CBvadixa6007100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Subcellular Fractionation and Isolation of OrganellesDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Subcellular Fractionation and Isolation of OrganellesrajaNo ratings yet
- TRANSFERSOMES AS NOVEL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMcDocument5 pagesTRANSFERSOMES AS NOVEL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMcIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Elements of Human BiologyDocument182 pagesElements of Human BiologyGayathriNo ratings yet
- A-Level H2 Biology Topical 2004-2013 AnswersDocument82 pagesA-Level H2 Biology Topical 2004-2013 AnswersMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Liposomes For Use in Gene DeliveryDocument13 pagesReview Article: Liposomes For Use in Gene DeliveryParagRoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Exam 1Document29 pagesCell Bio Exam 1Marisabel CorreaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without NotesDocument86 pagesLecture Outline: See Separate Powerpoint Slides For All Figures and Tables Pre-Inserted Into Powerpoint Without Notesellie marcusNo ratings yet