Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Asthma - Nhlbi, Nih
Uploaded by
reenaarumugamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Asthma - Nhlbi, Nih
Uploaded by
reenaarumugamCopyright:
Available Formats
11/7/2014
What Is Asthma? - NHLBI, NIH
What Is Asthma?
Asthma (AZ-ma) is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that
inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes
recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you
breathe), chest tightness, shortness of breath, and
coughing. The coughing often occurs at night or early in
the morning.
Asthma affects people of all ages, but it most often starts
during childhood. In the United States, more than 25
million people are known to have asthma. About 7 million
of these people are children.
Overview
To understand asthma, it helps to know how the airways
work. The airways are tubes that carry air into and out of
your lungs. People who have asthma have inflamed
airways. The inflammation makes the airways swollen and
very sensitive. The airways tend to react strongly to certain
inhaled substances.
When the airways react, the muscles around them tighten.
This narrows the airways, causing less air to flow into the
lungs. The swelling also can worsen, making the airways
even narrower. Cells in the airways might make more
mucus than usual. Mucus is a sticky, thick liquid that can
further narrow the airways.
This chain reaction can result in asthma symptoms.
Symptoms can happen each time the airways are inflamed.
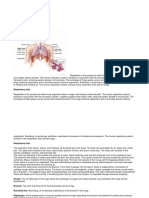
Asthma
Figure A shows the location of the lungs and airways in
the body. Figure B shows a cross-section of a normal
airway. Figure C shows a cross-section of an airway
during asthma symptoms.
Sometimes asthma symptoms are mild and go away on
their own or after minimal treatment with asthma
medicine. Other times, symptoms continue to get worse.
When symptoms get more intense and/or more symptoms
occur, you're having an asthma attack. Asthma attacks also
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/asthma/
1/3
11/7/2014
What Is Asthma? - NHLBI, NIH
are called flareups or exacerbations (eg-zas-er-BA-shuns).
Treating symptoms when you first notice them is
important. This will help prevent the symptoms from
worsening and causing a severe asthma attack. Severe
asthma attacks may require emergency care, and they can
be fatal.
Outlook
Asthma has no cure. Even when you feel fine, you still have
the disease and it can flare up at any time.
However, with today's knowledge and treatments, most
people who have asthma are able to manage the disease.
They have few, if any, symptoms. They can live normal,
active lives and sleep through the night without
interruption from asthma.
If you have asthma, you can take an active role in
managing the disease. For successful, thorough, and
ongoing treatment, build strong partnerships with your
doctor and other health care providers.
Rate This Content:
Featured Video
Hard to breathe: NHLBI researchers seek treatments for
severe asthma
Hard to
breathe:
NHLBI
researchers
seek
treatments
for severe
asthma
05/29/2014
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/asthma/
Asthma
Awareness
Google+
Hangout
On Air
06/04/2013
Respirar es
vida
(Breath of
life)
05/09/2013
2/3
11/7/2014
What Is Asthma? - NHLBI, NIH
SEARCH | SITE INDEX | ACCESSIBILITY | PRIVACY STATEMENT | FOIA | OIG | CONTACT US
National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services USA.gov
August 04, 2014
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/asthma/
3/3
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Suctioning Techniques ExplainedDocument17 pagesSuctioning Techniques ExplainedKandi Issaya100% (1)
- Growing Thriving TrachDocument138 pagesGrowing Thriving TrachShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InsuffiencyDocument21 pagesOxygen InsuffiencyAntony Raj Culandai Swamy100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- One Lung Ventilation: Llalando L. Austin Ii, MHSC, Aa-C, RRT Nova Southeastern UniversityDocument47 pagesOne Lung Ventilation: Llalando L. Austin Ii, MHSC, Aa-C, RRT Nova Southeastern UniversityZulkarnainBustamam100% (1)
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramDocument6 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramRick Frea100% (5)
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanDocument11 pagesTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanYk TayNo ratings yet
- Suggested Experiments f4 and F 5 (6b)Document2 pagesSuggested Experiments f4 and F 5 (6b)reenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- How o Write A Biology Peka ReportDocument3 pagesHow o Write A Biology Peka ReportpinkylollyNo ratings yet
- Kontrak Latihan Biologi Murid t5Document2 pagesKontrak Latihan Biologi Murid t5reenaarumugam100% (1)
- ElninoDocument3 pagesElninoreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- FluteDocument3 pagesFlutereenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Hots BioDocument3 pagesHots BioreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- HOTS CLASS XII REPRODUCTIONDocument21 pagesHOTS CLASS XII REPRODUCTIONreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Colonisation and Succession in Mangrove Swamps and PondsDocument2 pagesColonisation and Succession in Mangrove Swamps and PondsreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- 01 Kbat Lembaga PeperiksaanDocument77 pages01 Kbat Lembaga PeperiksaanSharif Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Borang Book ReviewDocument1 pageBorang Book ReviewreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument1 pageDigestionreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument1 pageAnaerobic RespirationreenaarumugamNo ratings yet
- Breathing Control: Pistol@tenrings - Co.ukDocument1 pageBreathing Control: Pistol@tenrings - Co.ukmanfromgladNo ratings yet
- Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus GuideDocument6 pagesSelf-Contained Breathing Apparatus Guideomar benounaNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System Based On Law of ThermodynamicsDocument9 pagesHuman Respiratory System Based On Law of ThermodynamicsfatimahNo ratings yet
- Short Course (Tevaki Cohort 4C)Document19 pagesShort Course (Tevaki Cohort 4C)Tevaki MathavanNo ratings yet
- Cell 3dDocument8 pagesCell 3dStefania DavidNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1Document24 pagesScience 9 Module 1etheyl fangonNo ratings yet
- Relaxation ResponseDocument3 pagesRelaxation ResponseANNA MAE PANONo ratings yet
- Activity ZoneDocument2 pagesActivity Zonetech timeNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Values Case Study InterpretationDocument3 pagesArterial Blood Gas Values Case Study InterpretationjulissaNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document26 pagesCH 9nfnf otupyooorefnNo ratings yet
- Retdem OxygenationDocument3 pagesRetdem OxygenationCharlize PareNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemBritany ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for COPD PatientDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for COPD PatientKelly BaumannNo ratings yet
- Analysis of COD, BOD and DO Levels in Wastewater TreatmentDocument10 pagesAnalysis of COD, BOD and DO Levels in Wastewater TreatmentSeptifa DiteNo ratings yet
- Lower Airways ConditionsDocument6 pagesLower Airways ConditionsMabesNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Facilitation Techniques: Dr. Hina Vaish (PT) Assistant Professor, CSJMUDocument24 pagesVentilation Facilitation Techniques: Dr. Hina Vaish (PT) Assistant Professor, CSJMUAnandhu GNo ratings yet
- AX800 - Specification V 1.2 2020.2.1Document6 pagesAX800 - Specification V 1.2 2020.2.1AndresNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics NotesDocument14 pagesBioenergetics NotesMarcela Stevie HadinataNo ratings yet
- Science 9: Quarter 1 Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesScience 9: Quarter 1 Respiratory Systemjelly marie flores0% (1)
- Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesCellular RespirationConcepcion, Jemaelah P.No ratings yet
- Inventory List at in Emergei (Cy: PrsentDocument1 pageInventory List at in Emergei (Cy: PrsentVirginia BennettNo ratings yet
- Diafragmatic Breathing 1Document8 pagesDiafragmatic Breathing 1Veven FeryatamaNo ratings yet
- Ventilatory Support For Chronic Respiratory FailureDocument642 pagesVentilatory Support For Chronic Respiratory FailureNuno DuarteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologymalindaNo ratings yet