Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C ARTAALIRANs EBATIANKARBONBIaddon 2008
Uploaded by
Wong1234567890Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C ARTAALIRANs EBATIANKARBONBIaddon 2008
Uploaded by
Wong1234567890Copyright:
Available Formats
FLOW CHART OF REACTIONS BETWEEN ALKANE, ALKENE, ALCOHOL, CARBOXYLIC ACID AND ESTER
PETROLEUM
ALKANE
CnH2n + 2
Substitution
reaction
Name of carbon
compounds
C2H6 + Cl2 C2H5Cl + HCl
position of alkyl parent
position of
suffix of
alkyl group group chain functional group homologous series
To differentiate alkane and alkene:
1. Neutralisation reaction salt and water
Method
Observation
CH
COOH
+
NaOH
CH
COONa
+
H
O
3
3
2
Hot
Add
bromine
Alkene
Sunlight /uv
2. With active metals (Mg, Zn, Al) salt + H2 gas
Alumina
water, Br2
decolourise
Yeast
2
CH
COOH
+
Mg
(CH
COO)
Mg
+
H
3
3
2
2
C2H4 + HCl C2H5Cl
C2H4 + H2 C2H6
Cracking
the brown
Fermentation
3. With metallic carbonate salt + CO2 + H2O
Hydrogenation
Reaction
colour of
HCl gas
H2
C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2 CO2
2 CH3COOH + CaCO3
reaction
bromine water.
r.t.p
Nickel / platinum
(CH3COO)2Ca + CO2 + H2O
Alkane no
200oC
ALCOHOL
Hydration
visible change.
C2H4 + H2O C2H5OH
C2H4 + H2O + [O] CH2OHCH2OH
CnH2n + 1
reaction
Oxidation
Add
acidified
Alkene
Steam, Phosphoric acid, H3PO4
reaction
o
potassium
decolourise
Acidified
C2H5OH + 2[O] CH3COOH + H2O
Ethane-1,2-diol
300
C
/
60
atm
ETHENE
ETHANOL
manganate(VII),
the purple
CH2OHCH2OH
KMnO4
C2H4
C2H5OH
i) Acidified potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7 Ethanoic acid
KMnO4
colour of
i) Aluminium oxide/hot porcelain
CH3COOH
KMnO4.
ii) Acidified potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4
ALKENE
o
ii) Concentrated H2SO4, 180 C
Alkane no
CnH2n
o
Dehydration
iii) Concentrated H3PO4, 80 C
visible change.
Concentrated
C2H4 + Cl2 CH2ClCH2Cl
reaction
Esterification
C2H5OH C2H4 + H2O
H
SO
Br2 in
2
4
reaction
reflux C2H5OH + CH3COOH CH3COOC2H5+ H2O
Halogenation
tetrachloromethane
o
Addition
200 C,
reaction
1500 atm polymerisatio
All carbon compound combust in excess
Ethyl ethanoate
oxygen to CO2 and H2O
CH3COOC2H5
1, 2-dibromoethane
poly(ethene)
Alkene burns with more sooty flame
Addition
CH2BrCH2Br
( CH2CH2 )n
than corresponding alkane due to higher
ESTER
reaction
% of carbon by mass.
CnH2n + 1COOCmH2m + 1
n C2H4 (CH2CH2)n
Definition
1. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain the elements
Naming of Carbon compound (Prefix)
Number of Isomer
carbon and hydrogen only.
No. of
Prefix
Example
Formula
Isomers have different physical properties because they have different
2.
Saturated hydrocarbon is hydrocarbon that have only single
carbon
molecular structural. However, isomers have the same chemical properties
covalent bonds between all the carbon atoms in the molecules.
1C
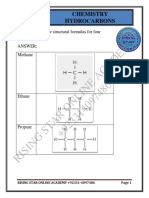
Meth
Methane
CH4
because they belong to the same homologous series.
3. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is hydrocarbon that have at least one
2C
Eth
Ethanol
C2H5OH
Homologo
No. of
No. of
Structural formula
carbon-carbon multiple bond in the molecule.
3C
Prop
Propene
C3H6
us Series
carbon
isomer
4. The molecular formula is a chemical formula that shows the
4C
But
Butanoic acid
C3H7COOH
4
2
actual numbers of atoms of each element present in one
C-C-C-C ; C-C-C
5C
Pent
Pentane
C5H12
Alkane
Butane
C
molecule of the substance.
6C
Hex
Hexene
C6H12
5.
The structural formula of an organic compound is the chemical
5
3
C
7C
Hept
Heptanol
C7H15OH
formula that shows the arrangement of atoms and covalent
Pentane
C-C-C-C-C ; C-C-C-C ; C-C-C
8C
Oct
Octanoic acid
C7H15COOH
C
bonds between atoms in a molecule of the compound.
C
9C
Non
Nonane
C9H20
6. A homologous is a family of organic compounds with the same
4
3
C=C-C-C ; C-C=C-C ; C=C-C
10C
Dec
Decene
C10H20
functional group and with similar chemical properties.
Alkene
Butene
C
7.
A functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that
6 characteristics of Homologous series
5
5
C=C-C-C-C ;C=C-C-C ;C=C-C-C
determines the characteristic properties of an organic compound.
(1) Members can be represented by a same general formula.
Pentene
C-C=C-C-C
C
C
8. Isomerism is the existence of two or more compounds that have
(2) Members can be prepared using similar methods.
3
2
; C-C-C
C-C-C
the same molecular formula but different structural formulae.
(3) Members show a gradual change in their physical properties.
Alcohol
Propanol
OH
OH
(4) Members have similar chemical properties.
9.
Isomers are compounds which have the same molecular formula
4
4
C-C-C-C C-C-C-C
;
; C
; C
(5) Members have same functional group.
but different structural formulae. Each isomer has a different
C-C-C
C-C-C
OH
OH
Butanol
(6) Successive member differ by CH2 group and RMM of 14.
arrangement of atoms in space.
OH
OH
ETHANE
C2H6
Cl2
Chloroethane
CH3CH2Cl + HCl
Starch/glucose
Created with novaPDF Printer (www.novaPDF.com). Please register to remove this message.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Reactions P-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Derivatives and Their Methyl Ethers With Molecular Chlorine'Document6 pagesReactions P-Hydroxybenzyl Alcohol Derivatives and Their Methyl Ethers With Molecular Chlorine'Sandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- Argumentative EssayDocument1 pageArgumentative EssayZhymeah Nicoline Kate BacarroNo ratings yet
- "Senggol Basah" Poisson: Sales PriceDocument1 page"Senggol Basah" Poisson: Sales PriceRasyaputra AndyNo ratings yet
- Municipal Ordinance No. 11 Series of 2018Document2 pagesMunicipal Ordinance No. 11 Series of 2018sports.sanpablocityNo ratings yet
- An Advanced Laboratory Manual of Organic ChemistryDocument103 pagesAn Advanced Laboratory Manual of Organic Chemistryalkem7100% (1)
- 2 Year Chemistry Chapter # 11Document1 page2 Year Chemistry Chapter # 11Shahid Ali Saim AttariNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire For BiraDocument7 pagesQuestionnaire For BiraDEBADIPTO DASNo ratings yet
- Ch18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFDocument43 pagesCh18.pdf Aldehyde and Ketone PDFShakesha HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Brand Detail MRPDocument32 pagesBrand Detail MRPLalita Bisht0% (1)
- ProhibitionDocument21 pagesProhibitionjonasdossantos06No ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetMariel TagazaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument91 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryfilchibuffNo ratings yet
- KursmitschriftenDocument1 pageKursmitschriftenNóbik BalázsNo ratings yet
- Important Reactions For Conversions Class 12 Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesImportant Reactions For Conversions Class 12 Organic Chemistryyoyo2669679% (115)
- Experiment 8 Analysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesExperiment 8 Analysis of Oxygen-Bearing Organic CompoundsE100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundsSreejit0% (1)
- AldehydesDocument21 pagesAldehydesNoor Farrah Wahida MuradNo ratings yet
- Alcohol BeveragesDocument3 pagesAlcohol BeveragesBarnabas UdehNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,598,377 B2Document8 pagesUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,598,377 B2Vaibhav MoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Book Chapter 1 - 7Document171 pagesChemistry Book Chapter 1 - 7SamNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveDocument7 pagesAlkanes Alkenes Alkynes ObjectiveVishal_93No ratings yet
- Gaskets PDFDocument58 pagesGaskets PDFAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- BeerDocument3 pagesBeerlee seyeongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BeverageDocument48 pagesChapter 4 BeverageDarlene Mae HumbeNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument477 pagesBansal Classes Organic Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEAditya Kavuluri40% (5)
- Chemraz: Superior Chemical ResistanceDocument33 pagesChemraz: Superior Chemical ResistanceDario BitettiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Report 4Document11 pagesChemistry Lab Report 4THASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document28 pagesCH 14ffffffff dfdfdfNo ratings yet
- THRISSURDocument17 pagesTHRISSURlovely singhNo ratings yet
- Ncert Chemistry 12Document3 pagesNcert Chemistry 12Simranjit SinghNo ratings yet