Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gravitational Flux and Space Curvatures Under Gravitational Forces
Uploaded by
paharalalageOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gravitational Flux and Space Curvatures Under Gravitational Forces
Uploaded by
paharalalageCopyright:
Available Formats
1
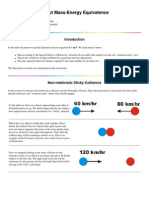
Gravitation & Space (26 November 2014)
Gravitational Flux and Space Curvatures under
Gravitational Forces
I.Eng. K.A.S.S. Kuruppuarachchi (MIIESL)
Ceylon Electricity Board,
Ethulkotte,
Sri Lanka
Our senses are limited. First of all we can consider about human senses limitations. Vision,
Hearing, Smiling, Taste and body sensation, all of these sensations of human are in limited
ranges. Another essential sense is mind. That is sixth sense of the human. In the absence of
those sensations, human life would depend on environmental situations and life time
boundaries.
Because of our limited senses, we can identify only limited range of the reality. How we can
detect which are beyond our sensation limits? Reality is relative to our senses, our points of
views, and individual attitudes.
For instance, take parallel universe concepts. We cant grasp it by our senses and only what
we can do is to consider identifying it by concentrating with relevant facts. Here, I wish to
explain it by gravitational flux space curves and gravitational field in my point of view.
Generally, a large asteroid and its gravitational force action can be predicted up to some
extend by using available limited senses.
In explaining above, first, I take the space curves and gravitational flux. Under gravitational
force effect of large asteroids, surrounding space is divided into layers with different flux
densities. Closer to asteroid, flux density is higher than that of distant end of the asteroid. Let
us consider light wave travelling under gravitational force of the large asteroid; closer to
asteroid, light wave travelling speed is lower than that of distant end of the asteroid.
It has been explained by considering light wave travelling through a prism as in figure (a).
Free Space
Free Space
Glass Prism
Figure (a)
In figure (a), we can see the deflection of the light wave. Same principles can be applied for
travelling light wave in the gravitational field.
Star (Actual Place)
Star (Visible Place)
Sun
Under the large asteroid gravitational force, space is divided to different layers and the layers
have different gravitational flux densities. In travelling light wave through each layer, light
wave velocity changes according to relevant layer flux densities. Gravitational flux should be
tiny and strongest of neutralized particle in the space.
We can apply the same phenomena to the surrounding space of large asteroid. That is
explained by figure (b).
Gravitational Field
Equal potential
layers of space
(space curves)
Asteroid
Figure (b)
Figure (b) shows deviation of the equal potential gravitational layers of space under
gravitational force. Closer to large asteroid gravitational flux density is high. When a mass is
travelling towards to asteroid with its increasing force, then it should be accelerated. This is
the phenomena of the gravitational acceleration.
According to Newtons gravitational force equation.
F = G M 1 M2
R2
F = Gravitational Force
G = Gravitational Constant
R = Distant Between Two Objects
M1 = Object 1 Mass
M2 = Object 2 Mass
Considering above facts, we can suggest that there should be gravitational flux in the space.
This flux is divided into layers under gravitational force. That flux acts as the medium of the
space. That phenomenon is explained by figure (b).
Gravitational flux density limits the light velocity place to place in the space. It means that
from layer to layer light wave velocity is deflecting. According to above facts, we can say
that gravitational flux density is the speed limiting factor of the space and also the friction for
the travelling object in space.
Considering following equations.
From Lorentz transformation,
LV = L0
When Objects Velocity is V, object Length = LV
Objects stationary Length = L0
C = Velocity of Light
From Einsteins Relativity Theory equation,
mV =
m0
m0 = Stationary mass of the object.
mV = Mass when travelling at velocity v of the object.
C = Velocity of Light.
According to above equations we can calculate relevant velocity of light (by solving equation
1) and relevant mass (by solving equation 2). We can observe that under high velocities,
length is reducing and mass is increasing.
Considering this phenomena we can describe that when velocity is increasing, space friction
also increases against to the travelling object. Hence we can say that there should be a space
friction against the travelling object in the space.
You might also like
- We Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseFrom EverandWe Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseNo ratings yet
- How Mass of The Universe Has Been Increasing?Document2 pagesHow Mass of The Universe Has Been Increasing?K.A.S.S. Kuruppuarachchi100% (2)
- Spacetime and EmptinessDocument2 pagesSpacetime and EmptinessK.A.S.S. Kuruppuarachchi100% (1)
- Gravitational Waves Provide Evidence for the Materiality of SpacetimeDocument5 pagesGravitational Waves Provide Evidence for the Materiality of SpacetimethemechanixNo ratings yet
- Einstein's Gravitational Waves DetectedDocument4 pagesEinstein's Gravitational Waves DetectedPrakash HiremathNo ratings yet
- Gravitational WavesDocument15 pagesGravitational WavesSourabh PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen AtomDocument8 pagesHydrogen AtomElyasse B.No ratings yet
- Stephan J.G. Gift - The Luminiferous Ether DetectedDocument6 pagesStephan J.G. Gift - The Luminiferous Ether DetectedOppekee0% (1)
- Lectures On Classical Mechanics1 PDFDocument3 pagesLectures On Classical Mechanics1 PDFehsanyari1100% (1)
- Intro SpecialDocument130 pagesIntro SpecialKit ChotNo ratings yet
- Phys 2o6 Sol Assign5Document13 pagesPhys 2o6 Sol Assign5a1malik420No ratings yet
- Stephan J.G. Gift - Einstein's Principle of Relativity and Stellar AberrationDocument4 pagesStephan J.G. Gift - Einstein's Principle of Relativity and Stellar AberrationJuiomSDFNo ratings yet
- Quantum Computation and Many-BodyDocument212 pagesQuantum Computation and Many-Bodyمهدي زمان مسعودNo ratings yet
- Lectures On Theoretical Mechanics - 7 (Rotating Coordinate System: Coriolis Force Etc.)Document6 pagesLectures On Theoretical Mechanics - 7 (Rotating Coordinate System: Coriolis Force Etc.)Abhijit Kar Gupta100% (1)
- Wave-Particle DualityDocument5 pagesWave-Particle Dualityapi-242480612No ratings yet
- A Semi-Classical Electron ModelDocument11 pagesA Semi-Classical Electron ModelnatejNo ratings yet
- Platonic Theory of SpacetimeDocument46 pagesPlatonic Theory of SpacetimeDimi ChakalovNo ratings yet
- General Theory of Relativity Explains Gravity Through Curved SpacetimeDocument1 pageGeneral Theory of Relativity Explains Gravity Through Curved SpacetimeCrazy watssapp videosNo ratings yet
- Understanding Time: Time Travel Is PossibleDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Time: Time Travel Is PossibleVeronika BannerjeeNo ratings yet
- Quantum 'Spooky Action at A Distance' Travels at Least 10,000 Times Faster Than LightDocument2 pagesQuantum 'Spooky Action at A Distance' Travels at Least 10,000 Times Faster Than LightquantumrealmNo ratings yet
- Photonic Topological Insulators A Beginners Introduction Electromagnetic PerspectivesDocument13 pagesPhotonic Topological Insulators A Beginners Introduction Electromagnetic PerspectivesabduNo ratings yet
- PhononDocument10 pagesPhononomiitgNo ratings yet
- Inducing A Magnetic Monopole With Topological Surface StatesDocument9 pagesInducing A Magnetic Monopole With Topological Surface StatesMike WestfallNo ratings yet
- Superluminals and The Speed of LightDocument5 pagesSuperluminals and The Speed of LightMia AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Further MechanicsDocument11 pagesFurther MechanicsBecky TenneyNo ratings yet
- Dragon Dreaming - Fact Sheet 1Document17 pagesDragon Dreaming - Fact Sheet 1ningstriNo ratings yet
- A superfluid Theory of Everything? Exploring Gravity as a Fluid Dynamic PhenomenonDocument38 pagesA superfluid Theory of Everything? Exploring Gravity as a Fluid Dynamic PhenomenonMilan PetrikNo ratings yet
- Quantum EntanglementDocument11 pagesQuantum EntanglementSanket ShahNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument14 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedRomesor ApolNo ratings yet
- SPH 202 Modern Physics: Dr. N. O.Hashim Department of Physics Kenyatta University January 13, 2015Document97 pagesSPH 202 Modern Physics: Dr. N. O.Hashim Department of Physics Kenyatta University January 13, 2015KeybateNo ratings yet
- Astral Matter ExplainedDocument14 pagesAstral Matter ExplainedMariaGrazia PirruccioNo ratings yet
- Berry Phase Patrick BrunoDocument33 pagesBerry Phase Patrick Brunodyegu1No ratings yet
- Mass EnergyDocument5 pagesMass EnergySzarastroNo ratings yet
- Stephen W. Hawking - Godel and the End of PhysicsDocument6 pagesStephen W. Hawking - Godel and the End of Physicsn0c0deNo ratings yet
- Measuring magnetic susceptibility via Quincke's methodDocument9 pagesMeasuring magnetic susceptibility via Quincke's methodMadhav MohanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Average Sky Glow by Digital CameraDocument6 pagesMeasurement of Average Sky Glow by Digital CameraAbhijit Kar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Black Holes and Holography Course NotesDocument71 pagesBlack Holes and Holography Course NotesLeonardoSanhuezaMardonesNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Math Concepts ExplainedDocument11 pagesFundamental Math Concepts ExplainedBace HickamNo ratings yet
- PHY 309 Quantum Physics IDocument130 pagesPHY 309 Quantum Physics Ioduola ademola100% (1)
- Michael Harney and Ioannis Iraklis Haranas - The Dark Energy ProblemDocument3 pagesMichael Harney and Ioannis Iraklis Haranas - The Dark Energy ProblemMuths999999No ratings yet
- Meditation and Quantum Physics in EnglishDocument8 pagesMeditation and Quantum Physics in EnglishadrirmNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning PhysicsDocument63 pagesQuantum Physics: Dan Hooper Fermilab Saturday Morning Physicsgracc mcdedeNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Hall EffectDocument44 pagesAnomalous Hall EffectImtiazAhmedNo ratings yet
- Relativity and Fundamental Physics: October 2016Document7 pagesRelativity and Fundamental Physics: October 2016Mgsi SofthouseNo ratings yet
- Origins of The UniverseDocument5 pagesOrigins of The Universecaarito_No ratings yet
- Wk2d2. Motion in One Dimension 1dDocument32 pagesWk2d2. Motion in One Dimension 1dAlex DeveldosNo ratings yet
- Harold E. Puthoff Et Al - Levi-Civita Effect in The Polarizable Vacuum (PV) Representation of General RelativityDocument7 pagesHarold E. Puthoff Et Al - Levi-Civita Effect in The Polarizable Vacuum (PV) Representation of General RelativityUtnyuNo ratings yet
- WudkaGR 7Document48 pagesWudkaGR 7Pranalistia Tiara PutriNo ratings yet
- Tesis Finalcorrections PDFDocument166 pagesTesis Finalcorrections PDFdaniej25No ratings yet
- Meh ENG2 PDFDocument37 pagesMeh ENG2 PDFInkeNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Lab Report Yasmeen6432Document7 pagesProjectile Motion Lab Report Yasmeen6432yesNo ratings yet
- Around The World in Eighty DaysDocument2 pagesAround The World in Eighty DaysFrederick David TombeNo ratings yet
- Labster Simulation Activity (Updated) - 1Document4 pagesLabster Simulation Activity (Updated) - 1PHILIP JOEL CEJASNo ratings yet
- Essays On The Intellectual Powers of Man: by Thomas Reid Preface and Preliminary EssayDocument295 pagesEssays On The Intellectual Powers of Man: by Thomas Reid Preface and Preliminary EssayolimojNo ratings yet
- David L. Bergman and Charles W. Lucas, Jr. - Physical Models of MatterDocument23 pagesDavid L. Bergman and Charles W. Lucas, Jr. - Physical Models of MatterJuiomSDF100% (1)
- HeisenbergDocument8 pagesHeisenbergJiveshkNo ratings yet
- A Short Treatise on the Space-Time ContinuumFrom EverandA Short Treatise on the Space-Time ContinuumRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Your Journey To The Basics of Quantum Realm Vol-I Edition 2: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #1From EverandYour Journey To The Basics of Quantum Realm Vol-I Edition 2: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Accenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Document28 pagesAccenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Ainia Putri Ayu KusumaNo ratings yet
- About Meat Eating in Sikh DharmDocument4 pagesAbout Meat Eating in Sikh Dharmvijay123inNo ratings yet
- An ISO 9001Document3 pagesAn ISO 9001Prasad IngoleNo ratings yet
- MT 06Document2 pagesMT 06Glen Rey BrunNo ratings yet
- ID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFDocument17 pagesID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFsabila azilaNo ratings yet
- Impact On Modern TechnologyDocument2 pagesImpact On Modern TechnologyNasrullah Khan AbidNo ratings yet
- ECO 201 Sample Midterm Exam (Paulo GuimaraesDocument14 pagesECO 201 Sample Midterm Exam (Paulo GuimaraesAhmed NegmNo ratings yet
- Tugas BHS InggrisDocument2 pagesTugas BHS InggrisJust NestNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week1 FinalDocument19 pagesGrade 12 - MIL - Q1 - Week1 FinalMa'am Regie Ricafort100% (2)
- Minimizing Dose Is DR PDFDocument4 pagesMinimizing Dose Is DR PDFYamuna GovindarajNo ratings yet
- ENG01P001S02U00Document14 pagesENG01P001S02U00arghasen2014100% (1)
- ARIMA Models in Python Chapter3Document52 pagesARIMA Models in Python Chapter3FgpeqwNo ratings yet
- Property Management Agreement TemplateDocument2 pagesProperty Management Agreement TemplatemarcelNo ratings yet
- Corruption PDFDocument11 pagesCorruption PDFkaleemullahNo ratings yet
- Disirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesDocument559 pagesDisirders of Synaptic Plasticity and Schizophrenia - J.smythiesBrett CromptonNo ratings yet
- The Oikos in Athenian LawDocument13 pagesThe Oikos in Athenian LawTúlio CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- SPELD SA A Trip To The Top End-DSDocument16 pagesSPELD SA A Trip To The Top End-DSThien Tho NguyenNo ratings yet
- The CIA Tavistock Institute and The GlobalDocument34 pagesThe CIA Tavistock Institute and The GlobalAnton Crellen100% (4)
- Sugar Cane White FlyDocument13 pagesSugar Cane White Flyvishnu0751No ratings yet
- Treasures Book 1 Unit 1Document33 pagesTreasures Book 1 Unit 1Janinne AbuegNo ratings yet
- Ebook Torrance (Dalam Stanberg) - 1-200 PDFDocument200 pagesEbook Torrance (Dalam Stanberg) - 1-200 PDFNisrina NurfajriantiNo ratings yet
- NOGALES Math Files for Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesNOGALES Math Files for Elementary SchoolMl Phil100% (6)
- EnHanced4 WB KeyDocument293 pagesEnHanced4 WB Keyezzeldin3khater100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Human Neuropsychology 7th Edition Kolb Test BankDanielYoungabrn100% (60)
- Cunningham S Book of Shadows PDFDocument258 pagesCunningham S Book of Shadows PDFAngela C. Allen100% (10)
- VV Siddipet Merit ListDocument81 pagesVV Siddipet Merit ListSubashNo ratings yet
- A Multivocal Literature Review of Decentralized Finance: Current Knowledge and Future Research AvenuesDocument37 pagesA Multivocal Literature Review of Decentralized Finance: Current Knowledge and Future Research Avenuesnofeh84660No ratings yet
- Rock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionDocument7 pagesRock and Roll and The American Dream: Essential QuestionChad HorsleyNo ratings yet
- Planning Worksheet For Access and QualityDocument3 pagesPlanning Worksheet For Access and QualityBar BetsNo ratings yet
- Description Text About Cathedral Church Jakarta Brian Evan X MIPA 2Document2 pagesDescription Text About Cathedral Church Jakarta Brian Evan X MIPA 2Brian KristantoNo ratings yet