Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate - AMR - Codec V8.20 20091230 PDF
Uploaded by
abojablOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate - AMR - Codec V8.20 20091230 PDF
Uploaded by
abojablCopyright:
Available Formats
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive MultiRate (AMR) Codec
Feature Description
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Version
Date
Author
Approved By
Remarks
V8.11
2009-02-26
Not open to the Third Party
V8.12
2009-08-16
Not open to the Third Party
V8.20
2009-12-30
Not open to the Third Party
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE CONFIDENTIAL: This document contains proprietary information of ZTE and is not to be
disclosed or used without the prior written permission of ZTE.
Due to update and improvement of ZTE products and technologies, information of the document is
subjected to change without notice.
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Feature Attributey ...................................................................................................... 1
2
2.1
2.2
Overview ..................................................................................................................... 1
Feature Introduction..................................................................................................... 1
Corelation with Other Features .................................................................................... 4
3
3.1
3.2
3.3
3.3.1
3.3.2
3.3.3
3.3.4
3.4
Technical Description ................................................................................................ 4
AMR Procedure ........................................................................................................... 4
Description of AMR Functions ..................................................................................... 7
Description of AMR Parameters .................................................................................. 8
ACS.............................................................................................................................. 8
Threshold and Hysteresis ............................................................................................ 9
ICM ............................................................................................................................ 10
Others ........................................................................................................................ 11
AMR with TrFO .......................................................................................................... 11
4
4.1
4.2
Parameters and Configurations.............................................................................. 13
Parameter List ........................................................................................................... 13
Parameter Configurations .......................................................................................... 16
5
5.1
5.2
Related Counters and Alarms ................................................................................. 20
Related Counters ....................................................................................................... 20
Related Alarms .......................................................................................................... 23
6
6.1
6.2
6.3
Engineering Guide ................................................................................................... 23
Application Scenario .................................................................................................. 23
Configuration Description .......................................................................................... 23
Network Impact .......................................................................................................... 23
Abbreviation ............................................................................................................. 24
Reference Document ............................................................................................... 24
FIGURES
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
Figure 9
Figure 10
Figure 11
Figure 12
AMR coding modes ....................................................................................................... 3
AMR speech quality ....................................................................................................... 4
Message procedure of AMR on major system interfaces .............................................. 5
Speech Version Establishment Flow ............................................................................. 7
Definition of threshold and hysteresis during code mode adaptation ............................ 9
Out-of-band codec negotiation procedure ................................................................... 12
Windows for AMR Configuration-1 .............................................................................. 17
Windows for AMR FR Configuration ............................................................................ 18
Windows for AMR HR Configuration ........................................................................... 18
Windows for AMR Configuration-2 .............................................................................. 19
19
Windows for AMR Configuration-3 .............................................................................. 19
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 13
Windows for AMR Configuration-4 .............................................................................. 20
TABLES
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3
Table 4
Table 5
List of coding rate modes in ACS .................................................................................. 9
Counter List for CS Basic Measurement ..................................................................... 20
Counter List of Radio Resource Availability Measurement ......................................... 21
Counter List of TCH/F Measurement ........................................................................... 21
Counter List of TCH/H Measurement .......................................................................... 22
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Feature Attributey
iBSC Version: [ZXG10 iBSC V6.20].
BTS Version: [Independent of BTS software and hardware platforms]
Property: [Optional function]
Related Network Element:
NE Name
Involved Or Not
MS
BTS
BSC
MSC
MGW
SGSN
GGSN
HLR
Special Requirement
Dependent Function: [None].
Exclusive Function: [None].
Note: [None].
Overview
2.1
Feature Introduction
As a second generation digital cellular communication system, Global System for Mobile
Communications has been widely used around the world. At present, voice services are
the major services in GSM. The development of voice services and coding technologies
is fuelled up by users' demand for high-quality voice communication services and
operators demand for capacity increase to reduce investment. Therefore, the Adaptive
Multi-Rate Codec (AMR) technology was introduced into ETSI standards in 1999.
Compared with the original GSM voice codec that adopts constant coding rate, AMR
uses link adaptation to select the optimal channel mode (Full Rate (FR) or Half Rate
(HR)) and source coding mode (differentiated by bit rate) for speech transmission based
on radio channel and transmission conditions, so as to offer the best trade-off between
speech quality and system capacity.
AMR contains the following two adaptive technologies:
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Adaptive channel rate mode.
The channel rate mode only changes when a call is set up or MS enters a new cell.
MSC allocates constant channel rate mode (FR/HR) for both communication parties
based on channel quality and utilization (for example, frequency and frequency
band utilization. When fewer frequency band is available, MSC will allocate lower
rate mode for new calls to balance the network capacity and service quality.). The
channel rate mode, once established, will not change during conversation.
Adaptive source coding mode and channel coding mode
AMR performs adaptive change of source coding and channel coding modes during
conversion based on estimated channel quality, that is, adjust source coding and
channel coding rates while keeping total channel transmission rate unchanged.
AMR adjusts channel coding rate (by providing extra bits) to ensure conversation
quality by reducing source coding rate when channel conditions are bad and
redundant bits in channel codes are insufficient to correct transmission error.
Contrarily, it increases source coding rate to enhance speech quality when channel
conditions are good.
The algorithm adopted by AMR is Multi-Rate Algebraic Code Excited Linear Prediction
(MR-ACELP). As a hybrid algorithm of CELP, MR-ACELP not only inherits general
technical features of CELP (for example, hybrid parameter analysis and excitation
generation, and ABS), but also combines advantages of multiple speech-related hybrid
coding algorithms in digital mobile communication to adapt to speech coding
requirements of different mobile networks.
AMR speech coding frames are 20 ms long. One frame contains 4 sub-frames, with
sampling frequency of 8kHz (160 samples for 20 ms frames). AMR algorithm
implements coding/decoding (respectively relative to the downlink/uplink processing of
speech links) of consecutive 20 ms speech frames based on different rate modes.
As a part of coding data, the coding mode and speech coding data are both involved in
channel coding and are referred to as in-band information. According to the protocol,
there are a total of 14 modes of the AMR codec, 8 are available in a full rate channel
(FR) and 6 on a half rate channel (HR), as shown in Figure 1. In practice, a maximum of
4 modes can be adopted whether in FR or HR. These four modes or less constitute the
Active Codec Set (ACS).
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 1
AMR coding modes
AMR contains three core parameters:
ACS: refers to the Active Codec Set of AMR.
Threshold: refers to the threshold value for code change.
Hysteresis: refers to code change Hysteresis.
The latter two parameters are used to determine which rate mode is adopted.
AMR is of variable rate compared with other speech coding modes. It adjusts speech
coding rate based on equivalent Carrier-to-Interference Ratio (C/I) value to ensure the
best possible speech quality under different C/I values, as shown in Figure 2. AMR is
enabled based on user requirements when channel conditions are bad.
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 2
2.2
AMR speech quality
Correlation with Other Features
This feature is functionally related to the following features:
ZGO-04-02-007 AMR Radio Link Timers
ZGO-03-02-006 Independent Threshold for Dynamic AMR HR-FR Conversion
ZGO-04-02-008 AMR Power Control
The specific descriptions are as follows:
Relation with AMR Radio Link Timers, Independent Threshold for Dynamic AMR HRFR Conversion and AMR Power Control: These three features can only be
implemented when AMR is adopted.
Technical Description
3.1
AMR Procedure
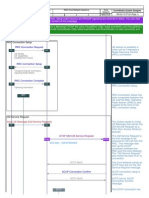
Figure 3 shows the message procedure of AMR on major system interfaces.
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 3
Message procedure of AMR on major system interfaces
As shown in Figure 3, speech data frame is associated with Codec Mode Indication
(CMI) in both uplink and downlink directions. The CMI is used at the receiving end to
select correct channel and source decoders, and it is also sent to TC to select correct
source decoding on mobile network.
BTS must estimate uplink channel quality for uplink coding adaptation, select optimal
coding for current propagation environment and send the information to MS over air
interface through a message.
MS must estimate downlink channel quality for downlink coding adaptation, and send a
message containing quality information to BTS. The quality information is mapped to a
coding mode.
The coding mode is theoretically variable in each speech frame, but in practice, coding
adaptation is performed at low rate due to transmission delay and necessary filtering
during adaptation. Each link may adopt different coding modes, but the same channel
type (FR or HR) must be adopted for uplink/downlink.
Channel type is selected during call setup or upon handover through radio resource
management function and can be changed based on channel conditions during
conversation.
The calling procedures involved in AMR include: assignment, incoming inter-BSC
handover, outgoing inter-BSC handover, and intra-BSC handover.
Assignment procedure is as follows:
MSC judges whether MS is AMR-capable based on MS support capability, call
service type, speech version allowed by MSC and No. of circuit pool of A interface
circuit.
MSC determines speech version set allowed in this call and send it to BSC through
an Assignment Request message.
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
BSC obtains the available speech versions by taking the intersection of speech
version set carried in the Assignment Request message and that supported by the
cell.
BSC selects a speech version of highest level from the available speech versions
as the final speech version based on allocated channel type.
If AMR speech codec is selected, BSC sends AMR service parameters to BTS
through channel activation command or mode modification command, and to MS
through assignment command or mode modification command. Upon receiving the
assignment command or mode modification command, MS returns an Assignment
Complete message to MSC. AMR call assignment procedure ends.
Incoming inter-BSC handover procedure is as follows:
MSC judges whether MS is AMR-capable based on MS support capability, call
service type, speech version allowed by MSC and No. of circuit pool of A interface
circuit.
MSC determines speech version set allowed in this call and send it to BSC through
an Assignment Request message.
BSC obtains the available speech versions by taking the intersection of speech
version set carried in the Assignment Request message from MSC and that
supported by the cell.
BSC selects a speech version of highest level from the available speech versions
as the final speech version based on allocated channel type.
If AMR speech codec is selected, BSC sends AMR service parameters to BTS
through channel activation command. Upon receiving channel activation response
from BTS, BSC returns a handover request response message to MSC and sends
AMR service parameters to MS through handover command.
Outgoing inter-BSC handover procedure is as follows:
BSC handover decision algorithm initiates outgoing inter-BSC handover procedure, and
sends a HO RQD message to MSC, containing the speech version used in current call.
Intra-BSC handover procedure is as follows:
BSC handover decision algorithm initiates intra-BSC handover, and obtains the final
speech version in the same way described in assignment procedure.
If AMR speech codec is selected, BSC sends AMR service parameters to BTS
through channel activation command and to MS through handover command.
Figure 4 shows speech version establishment flow.
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 4
3.2
Speech Version Establishment Flow
Description of AMR Functions
AMR supports the following functions:
Support AMR-FR speech codec function, including 8 types of speech rates:
12.2kbit/s (GSM EFR)
10.2kbit/s
7.95kbit/s
7.40kbit/s (IS-641)
6.70kbit/s
5.90kbit/s
5.15kbit/s
4.75kbit/s
Support AMR-FR coding rate adjustment in ACS based on C/I values.
Support AMR-HR speech codec function, including 6 types of speech rates:
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
7.95kbit/s
7.40kbit/s(IS-641)
6.70kbit/s
5.90kbit/s
5.15kbit/s
4.75kbit/s
Support AMR-HR coding rate adjustment in ACS based on C/I values.
Note:
The coding rate 7.95kbit/s is supported only when IP transmission mode instead of
TDM is adopted on A interface.
Support cell-level enabling and disabling of AMR.
Support cell-level settings of different ACSs, coding rate adjustment threshold
values and hysteresis values and initial coding rates.
Support dynamic configuration of AMR enabling/disabling, ACS, coding rate
adjustment threshold, hysteresis and initial coding rate.
Support different radio link timers for AMR and non-AMR calls. For details, see
ZGO-04-02-007 AMR Radio Link Timers.
Support different threshold values for AMR HR-FR conversion and non-AMR HRFR conversion.
Support different power control strategies for AMR and non-AMR calls. For details,
see ZGO-04-02-008 AMR Power Control.
Support TFO and TrFO.
Support ACS change during handover rather than during channel hold.
3.3
Description of AMR Parameters
3.3.1
ACS
The ACS used in BSS and MS is defined through L3 signaling during call setup or
handover, and set through the parameters AMR-FR coding rate mode set (AmrFullAcs)
or AMR-HR coding rate mode set (AmrHalfAcs). ACS contains a maximum of 4 coding
modes, as listed in Table 1.
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Table 1
3.3.2
List of coding rate modes in ACS
Identifier
Description
CODEC_MODE_1
It indicates the lowest coding mode (lowest bit rate) in
ACS.
CODEC_MODE_2
It indicates next lowest mode if ACS contains more than
one mode.
CODEC_MODE_3
It indicates the third lowest mode if ACS contains more
than two modes.
CODEC_MODE_4
It indicates the highest mode if ACS contains four
modes.
Threshold and Hysteresis
AMR coding mode is selected from ACS (generally containing one to four coding modes)
based on one to three threshold values (parameter AmrThresholds) and hysteresis
(parameter AmrHysteresis) during call setup. ACS, threshold and hysteresis are all
defined during call initiation.
Channel quality measurement and estimate are based on equivalent C/I. Both MS and
BSS constantly adjust QI based on C/I norm, and CMR and CMC are judged based on
quantized values of QI. Hysteresis is used to prevent frequency switching of CMR and
CMC among different modes. The previously sent CMC (CMR) is used as the status of
current adaptation logic, and upper and lower thresholds are defined for each status: For
CMC, lower threshold: THR_MC_Dn and upper threshold: THR_MC_Up; for CMR, lower
threshold: THR_MR_Dn and upper threshold: THR_MR_Up. If the measurement value
falls below the lower threshold, next CMC/CMR will request a lower coding rate. If the
measurement value rises above the upper threshold, next CMC/CMR will request a
higher coding rate. If the measurement value falls between upper and lower thresholds,
CMC/CMR will retain current coding rate, as shown in Figure 5.
To avoid channel error and bit error, CMC, CMR and CMI must control the rate mode to
change stepwise (instead of mode skip) between adjacent modes unless because of
handover or TFO.
C/I
CODEC_MODE_4
THR_3 + HYST_3 = THR_MX_Up(3)
THR_3
= THR_MX_Dn(4)
CODEC_MODE_3
THR_2 + HYST_2 = THR_MX_Up(2)
CODEC_MODE_2
THR_2
= THR_MX_Dn(3)
THR_1 + HYST_1 = THR_MX_Up(1)
CODEC_MODE_1
Figure 5
THR_1
= THR_MX_Dn(2)
Definition of threshold and hysteresis during code mode adaptation
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
The switch thresholds shall be given by network in consecutive order.
THR _1 THR _ 2 THR _ 3
THR _1 + HYST _1 THR _ 2 + HYST _ 2 THR _ 3 + HYST _ 3
Parameter
Description
Scope
Number
of bits
THR_1/2/3
Lowest threshold for switching from j to j-1.
0-63
HYST_1/2/3
Hysteresis to obtain higher threshold from j to j+1.
0-15
Threshold (THR) is given in a step length of absolute value 0.5 dB. The threshold
between 0 and 63 must be mapped to normalized C/I:
When threshold and hysteresis parameters defined through L3 signaling are used,
HYST_1/2/3 must be coded in a step length of 0.5dB:
3.3.3
ICM
The Initial Codec Mode (ICM) adopted during call setup and handover can be indicated
through L3 signaling. The value of ICM is judged through the parameters AMR codec
mode (IsAmrICM) and AMR start codec mode (AmrStartMod). The clearly indicated
ICM must have higher priority than default ICM. The default value of ICM is defined as
follows:
If ACS contains:
One codec mode, then ICM is the initial codec mode.
Two or three codec modes, then ICM is the most robust (lowest bit rate) mode in the set.
Four codec modes, then ICM is the next most robust (next lowest bit rate) mode in the
set. If the ACS changes during calling, then the default ICM will be used all the time until
another clearly indicated ICM is received.
10
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
For example,
Assume ACS contains four bit rates of 12.2 kbit/s, 7.95 kbit/s, 6.70 kbit/s and 4.75 kbit/s:
Condition 1: IsAmrICM= Startmode, and AmrStartMode=1,
Then ICM=4.75 kbit/s.
Condition 2: IsAmrICM= Startmode, and AmrStartMode=2,
Then ICM = 6.70 kbit/s.
Condition 3: IsAmrICM=6.70 kbit/s,
Then AmrStartMode is invalid and ICM=6.70 kbit/s.
3.3.4
Others
The parameter AMR Noise Suppression (IsAmrNscb) is used to judge whether AMR
noise suppression is allowed.
3.4
AMR with TrFO
Transcoder Free Operation (TrFO), also known as Out-of-Band Transcoder Control
(OoBTC), is a technology used to negotiate speech codec modes through out-of-band
call control signaling during call setup. After negotiation, MSs can make calls with one
another without using codec, and hence speech quality is improved. The out-of-band
negotiation mechanism makes TC resources dispensable for TrFO, and thus saves
precious TC resources and reduces power consumption arising thereof. In addition,
using TrFO in group carrier can save bandwidth because speech can be transmitted in
core networks at the rate of AMR 12.2 kbps.
In A-interface over TDM mode, TRAU is located on BSS side. For voice services, it
implements codec conversion from 2G coding/decoding to TDM PCM, and for data
services, it implements 64k for rate matching. MGW receives the PCM mode, and
coding/decoding algorithm is G.711. TC is not required when MGW accesses A interface
terminal, and a TrFO call cannot be established in the call process.
In A interface over IP (AoIP) mode, TRAU is built in the MGW. Therefore, the voice
packets from BSS may include several types such as GSM HR, GSM FR, GSM EFR, FR
AMR, and HR AMR.
For calls adopting GSM HR, GSM FR, and GSM EFR codec modes, TrFO calls are
judged based on the following conditions:
All streams of terminals at the stream layer are voice services.
The codec types of all streams of terminals at the stream layer are consistent.
For calls adopting HR AMR, FR AMR, UMTS AMR and UMTS AMR2 codec modes,
TrFO calls are judged based on the following conditions:
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
11
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
All streams of terminals at the stream layer are voice services.
The codec types of all streams of terminals at the stream layer are consistent.
The UP Version of streams of UP-capable terminals at the stream layer supports 2.
The ACSs of all streams of terminals at the stream layer are consistent.
Generally, TrFO negotiation is implemented by MGW. At first, BSC performs channel
allocation based on the ACS specified in the ASSIGNMENT REQUEST (Asssignment)
or HANDOVER REQUEST (outgoing inter-BSC handover) message. The sequence of
channel types and speech version represents the result of TrFO negotiation
implemented by MSC.
Then, BSC will make the final decision for channel allocation in terms of different
strategy like requirement from MSC, BSS channel allocation strategy and busy status of
traffic, etc. Afterwards, BSC will send the selected channel type and speech version to
the MSC through the ASSIGNMENT COMPLETE and HANDOVER REQUEST
ACKNOWLEDGE messages based on the final decision. At this time, TrFO
implementation requirements may be met or may not be met. If its failed to meet the
requirement on establishing TrFO call, then MSC will make MGW insert a pair of TCs to
do the voice transcoding
Finally, BSC inserts TC unit in MGW.
O-MSC
T-MSC
Transit
Transit
MGW
O-MGW
T-MGW
Codec List (v, w, x, y, z)
Codec List (v, w, x, z)
Selected Codec = v
Selected Codec = v, Available List (v, x, z, )
Selected Codec = v, Available
List (v, x, z, )
Selected Codec = v
Selected Codec = v
Bearer Established
Figure 6
Bearer Established
Out-of-band codec negotiation procedure
The TrFO negotiation procedure in MGW is illustrated in Figure 6, with details listed as
follows:
12
A calling MS sends a SETUP message carrying a codec list supported by the
calling UE to a calling MSC Server. At this moment, the out-of-band codec
negotiation procedure for TrFo call setup starts. Upon obtaining the codec list, the
calling MSC Server takes an intersection of ACSs supported by RNC and MGW,
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
and then sends an IAM message containing the supported codec list to the called
MSC Server. The codec list in the example is (v, w, x, y, z).
The intermediate switch can delete the codec types not supported by itself, for
example, y is deleted from the instance.
Upon obtaining the codec list (v, w, x, z) supported by the calling side, the called
switch calculates the codec list supported by RNC and MGW in connection with the
called MS, and that supported by the called UE, to acquire the available codec list
(ACL). In the above example, the ACL is (v, x, z), where, the first codec v
represents SC, that is, selecting codec v as the current codec type.
The called MSC Server sends the negotiated SC and ACL to the caller's network to
inform MGW, and sets up a user-plane bearer by using codec V. Upon receiving the
SC and ACL, the calling MSC Server If there is a codec is available in ACL, the call
will be set up with inserting TC and then MSC could modify the codec type during
the call to rebuild the TrFO call.
Parameters and Configurations
4.1
Parameter List
Full Name
AMR Full Active Codec Set
Abbreviation
AmrFullAcs
The code has 8 bits. The code has 8 bits. Bit 8:12.2 kbps;
Bit 7: 10.2 kbps; Bit 6: 7.95 kbps; Bit 5: 6.70 kbps
Bit 2: 5.15 kbps; Bit 1: 4.75 kbps.
Yes represents 1 and No represents 0.
Default code is 10101010 (that is 170)
Description
Value Range
From 4.75 kbit/s, 5.15 kbit/s, 5.90 kbit/s, 6.70 kbit/s, 7.40
kbit/s, 7.95 kbit/s, 10.2 kbit/s to 12.2 kbit/s, value range is
Yes/No.
Unit
None
Default
Default is [No, Yes, No, Yes, No, Yes, No, Yes] in order.
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
Threshold of AMR
Abbreviation
AmrThresholds
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
13
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
The threshold of changing AMR mode includes seven
factors: AmrThresholds1, AmrThresholds2,
AmrThresholds3, AmrThresholds4, AmrThresholds5,
AmrThresholds6, AmrThresholds7. Also,the following
restricted conditions shall be met:
AmrThresholds1AmrThresholds2AmrThresholds3
AmrThresholds4AmrThresholds5AmrThresholds6AmrThresholds7 AmrThresholds1
AmrHysteresis1AmrThresholds2 AmrHysteresis2
AmrThresholds3 AmrHysteresis3AmrThresholds4 AmrHysteresis4AmrThresholds5
AmrHysteresis5AmrThresholds6 AmrHysteresis6
AmrThresholds7 AmrHysteresis7
Description
Including mode 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. Value range is
0~63.
Value Range
0: 0.0 dB;
1: 0.5 dB;
2: 1.0 dB
63: 31.5 dB
Unit
None
Default
691318243139
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
Hysteresis of AMR
Abbreviation
AmrHysteresis
The hysteresis of changing AMR mode includes seven
factors: AmrHysteresis1, AmrHysteresis2,
AmrHysteresis3, AmrHysteresis4, AmrHysteresis5,
AmrHysteresis6, AmrHysteresis7. Also, the
following restricted conditions shall be met:
AmrThresholds1AmrHysteresis1AmrThresholds2
AmrHysteresis2AmrThresholds3 AmrHysteresis3
AmrThresholds4 AmrHysteresis4AmrThresholds5 AmrHysteresis5AmrThresholds6
AmrHysteresis6AmrThresholds7AmrHysteresis7
Description
Including mode 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. Value range is
0~15.
Value Range
0: 0.0 dB;
1: 0.5 dB;
2: 1.0 dB
Unit
14
15: 7.5 dB
None
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Default
3435556
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
Initial codec mode
Abbreviation
IsAmrICM
Description
Use the coding mode specified by Startmode
Value Range
Startmode codec, Initial codec mode
Unit
None
Default
Startmode codec
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
Start mode
Abbreviation
AmrStartMode
Description
Startmode codec mode
Value Range
When four values are configured as "No" within 8
elements in "AMR full Active Codec Set (AmrFullAcs)"
interface, value range is 1~4;
When five values are configured as "No" within 8
elements in "AMR full Active Codec Set (AmrFullAcs)"
interface, value range is 1~3;
When six values are configured as "No" within 8
elements in "AMR full Active Codec Set (AmrFullAcs)"
interface, value range is 1~2;
When seven values are configured as "No" within 8
elements in "AMR full Active Codec Set (AmrFullAcs)"
interface, value range is 1;
When all values are configured as "No" for 8 elements
in "AMR full Active Codec Set (AmrFullAcs)" interface,
value range is null;
The values are as follows:
1: Select the coding mode with lowest bit rate as the
initial coding mode.
2: Select the coding mode with the second lowest bit
rate, if there is more than one coding mode.
3: Select the coding mode with the third lowest bit
rate, if there is more than two coding modes.
4: Select the coding mode with the fourth lowest bit
rate, if there are more than three coding modes.
Unit
None
Default
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
15
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Management
Object
BSC
Full Name
Enable noise control
IsAmrNscb
Abbreviation
Description
This parameter defines whether AMR noise control is
enabled, that is, to suppress background noise and keep
original voice quality.
No: Enable noise suppression;
Yes: Disable noise suppression;
Value Range
Yes/No
Unit
None
Default
No
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
AMR Half Active Codec Set
AmrHalfAcs
Abbreviation
4.2
Description
The code has 8 bits. Bit 6~ Bit 8: reserved; Bit 5: 7.40
kbps; Bit 4: 6.70 kbps
Bit 2: 5.15kbps; Bit 1: 4.75 kbps.
Yes represents 1 and No
represents 0.
Four coding modes could be set at the most. Default code
is 00011110 (that is 30).
Value Range
From 4.75 kbit/s, 5.15 kbit/s, 5.90 kbit/s, 6.70 kbit/s to 7.40
kbit/s, value range is Yes/No.
Unit
None
Default
Default is [No, Yes, Yes, Yes, Yes] in order.
Management
Object
Cell
Full Name
IP A AMR Start Mode
Abbreviation
IPAAmrStartMode
Description
AMR Start Mode when IP A configured
Value Range
Default rate, start rate will be the largest rate of ACS
Unit
None
Default
Default rate
Management
Object
Cell
Parameter Configurations
In the configuration resource tree window, select [OMC GERAN Subnetwork BSC
16
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Managed Element Config Set BSC Function BTS Config BTS ID Cell ID],
as shown in the following figure;
Figure 7
Windows for AMR Configuration-1
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
17
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Figure 8
Windows for AMR FR Configuration
Figure 9
Windows for AMR HR Configuration
In the configuration resource tree window, select [OMC GERAN Subnetwork
BSC Managed Element Config Set BSC Function BTS Config BTS ID
18
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Cell ID], in the tag on the left side, to configure the AMR functions, as shown in
the following figure;
Figure 10 Windows for AMR Configuration-2
In the tag for [AMR half method params], set the following parameters,
AMR Half Active Codec Set
Threshold of AMR
Hysteresis of AMR
Figure 11 Windows for AMR Configuration-3
In the tag for [AMR Full method params], set the following parameters,
AMR Full Active Codec Set
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
19
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Threshold of AMR
Hysteresis of AMR
Figure 12 Windows for AMR Configuration-4
Related Counters and Alarms
5.1
Related Counters
Table 2
20
Counter List of CS Basic Measurement
Counters
What it counts
C900060026
Number of TCH/F allocation success for assignment (speech
version3)
C900060027
Number of TCH/F allocation failure for assignment (speech
version3)
C900060145
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to BTS connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060146
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to BIU connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060147
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to TCU connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060164
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to channel activation
failure for handover(speech version3)
C900060165
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to BTS connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Counters
What it counts
C900060166
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to BIU connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
C900060167
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to TCU connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
C900060191
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to channel activation
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060192
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to BTS connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060193
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to BIU connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060194
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to TCU connection
failure for assignment (speech version3)
C900060195
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to channel activation
failure for handover (speech version3)
C900060196
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to BTS connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
C900060197
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to BIU connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
C900060198
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to TCU connection
failure for handover (speech version3)
Table 3
Counter List of Radio Resource Availability Measurement
Counter
What It Counts
C901080017
TCH/H busy time(SpeechVer3)
C901080018
TCH/H congestion time
Table 4
Counter List of TCH/F Measurement
Counter
What It Counts
C901260050
Number of TCH/F allocation attempts by BSC for assignment
(speech version 3)
C901260056
Number of TCH/F allocation attempts by BSC for handover
(speech version 3)
C901260057
Number of TCH/F allocation success by BSC for handover
(speech version 3)
C901260102
Number of data TCH/F allocation failure for assignment due to
TIPB connection failure (Speech version 3)
C901260103
Number of data TCH/F allocation failure for assignment due to
Resource request to iTC failure (Speech version 3)
C901260104
Number of data TCH/F allocation failure for handover due to
TIPB connection failure (Speech version 3)
C901260105
Number of data TCH/F allocation failure for handover due to
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
21
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Counter
What It Counts
Resource request to iTC failure (Speech version 3)
C901260118
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to request AIPB
resource failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901260119
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to request UDP port
failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901260120
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to AIPB connection
failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901260121
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to request AIPB
resource failure for handover (speech version 3)
C901260122
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to request UDP port
failure for handover (speech version 3)
C901260123
Number of TCH/F allocation failure due to AIPB connection
failure for handover (speech version 3)
Table 5
22
Counter List of TCH/H Measurement
Counter
What It Counts
C901270050
Number of TCH/H allocation attempts for assignment (speech
version 3)
C901270051
Number of TCH/H allocation success for assignment (speech
version 3)
C901270056
Number of TCH/H allocation attempts by BSC for handover
(speech version 3)
C901270057
Number of TCH/H allocation success for handover (speech
version 3)
C901270094
Number of TCH/H allocation failure for assignment due to TIPB
connection failure (Speech version 1)
C901270095
Number of TCH/H allocation failure for assignment due to
Resource request to iTC failure (Speech version 1)
C901270096
Number of TCH/H allocation failure for handover due to TIPB
connection failure (Speech version 1)
C901270097
Number of TCH/H allocation failure for handover due to
Resource request to iTC failure (Speech version 1)
C901270118
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to request AIPB
resource failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901270119
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to request UDP port
failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901270120
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to AIPB connection
failure for assignment (speech version 3)
C901270121
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to request AIPB
resource failure for handover (speech version 3)
C901270122
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to request UDP port
failure for handover (speech version 3)
C901270123
Number of TCH/H allocation failure due to AIPB connection
failure for handover (speech version 3)
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
5.2
Related Alarms
There are no relevant alarms for this function.
Engineering Guide
6.1
Application Scenario
This feature can be applied in important business areas, special areas with higher
requirements for speech quality, and areas with poor radio environments. The following
s the typical application scenarios of AMR:
1. AMR can be used in BSS system with TDM stream and IP data.
2. If the core network (CN) connects two/more BSS systems which are original from
different films, AMR also has an effect on this kind of system (CN with different BSS
systems).
3. When 3G RAN and 2G RAN want to have a conversation, they can use AMR.
AMR speech coding can improve the speech codec transmission rate, ease the conflict
between speech quality and system capacity, thus enhancing the speech conception.
6.2
Configuration Description
This feature does not involve the adjustment of iBSC or BTS hardware configuration.
6.3
Network Impact
1
Impacts on network
AMR speech codec features a stronger anti-interference capability than common
speech codec, so it can deliver better speech quality. In terms of speech quality,
AMR HR-FR lies between HR and FR, and only the network performance indexes
of uplink/downlink RQ and MOS values are affected. The uplink/downlink RQ and
MOS values of AMR HR-FR also lie between HR and FR.
Furthermore, the activation of AMR enables uplink and downlink channels to adopt
the coding schemes that are more applicable to the actual radio environment, thus
reducing the call drop rate during service initiation.
Impacts on NEs
This feature has no impact on the capacity of iBSC and BTS.
ZTE Confidential Proprietary
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
23
ZGO-01-01-003 Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) Codec
Abbreviation
Abbreviations
Full Characteristics
ACS
Active Codec Set
AMR
Adaptive Multi-Rate Codec
AoIP
A-interface over IP
BSC
Base Station Controller
BTS
Base Transceiver Station
CELP
Code-Excited Linear Predictive
C/I
Carrier/Interference
CMC
Code Mode Command
CMI
Codec Mode Indication
CMR
Code Mode Request
FR
Full Rate
HR
Half Rate
MOS
Mean Opinion Score
MS
Mobile Station
MSC
Mobile services Switching Centre
QI
Quality Indicator
RQ
Receive Quality
Reference Document
[[None]
24
2010 ZTE Corporation. All rights reserved.
ZTE ConfidentialProprietary
You might also like
- PDP Context Activation GuideDocument124 pagesPDP Context Activation GuideUmar Abbas BabarNo ratings yet
- Excel FunctionsDocument206 pagesExcel FunctionstiwaribcetNo ratings yet
- Huawei CS Fallback (CSFB) Solution Vtraining PDFDocument41 pagesHuawei CS Fallback (CSFB) Solution Vtraining PDFFreddy Segales80% (5)
- GSM - Radio Network PlanningDocument20 pagesGSM - Radio Network PlanningpalakqNo ratings yet
- Fast WCDMA Reselection at 2G CS Call Release Feature Delivery GuideDocument17 pagesFast WCDMA Reselection at 2G CS Call Release Feature Delivery GuideabojablNo ratings yet
- BBU3900 Description 01 - 20120730 PDFDocument22 pagesBBU3900 Description 01 - 20120730 PDFDerrick WhiteNo ratings yet
- Huawei Traffic Balance ApproachDocument2 pagesHuawei Traffic Balance ApproachJitendra Kumar100% (5)
- OWA324020 WCDMA HSUPA RAN12 Principles ISSUE1.10 PDFDocument59 pagesOWA324020 WCDMA HSUPA RAN12 Principles ISSUE1.10 PDFabojablNo ratings yet
- Impact of HSUPA A On Umts CapacityDocument121 pagesImpact of HSUPA A On Umts Capacityleonidg54No ratings yet
- Access Failures Troubleshooting WorkshopDocument30 pagesAccess Failures Troubleshooting Workshopsyedusama100% (2)
- 01B-QoS in Telecommunications Networks Module 1Document59 pages01B-QoS in Telecommunications Networks Module 1abojablNo ratings yet
- State Transition Huawei DescriptionDocument35 pagesState Transition Huawei Descriptionrodrigo_gonzalez_6650% (2)
- 3GPP RabDocument13 pages3GPP RababojablNo ratings yet
- Huawei KPI ManagementDocument65 pagesHuawei KPI ManagementSabea100% (1)
- 3g Umts Originating CallDocument6 pages3g Umts Originating Callk.naveedNo ratings yet
- ZTE UMTS Admission Control Feature Guide U9.2 PDFDocument85 pagesZTE UMTS Admission Control Feature Guide U9.2 PDFabojabl100% (1)
- Case Study UMTS EventDocument2 pagesCase Study UMTS EventabojablNo ratings yet
- W (Level1) UMTS UTRAN Signaling Procedures 20050614 A 1 (1) .0Document48 pagesW (Level1) UMTS UTRAN Signaling Procedures 20050614 A 1 (1) .0Chidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Drive Testing Benchmarking v4bDocument16 pagesDrive Testing Benchmarking v4bAhmed MoniemNo ratings yet
- A2 General Description of 3GDocument51 pagesA2 General Description of 3GabojablNo ratings yet
- RF CalcDocument2 pagesRF CalcabojablNo ratings yet
- Network PlanningDocument20 pagesNetwork PlanningFarrukhNo ratings yet
- 18 Optimization of UMTS Radio Network Parameters Cases - PPT-62Document62 pages18 Optimization of UMTS Radio Network Parameters Cases - PPT-62abojablNo ratings yet
- Introduction - WCDMA Radio Network PlanningDocument7 pagesIntroduction - WCDMA Radio Network PlanningWsuece05100% (1)
- Hierarchical Wireless Network Architecture For Distributed ApplicationsDocument6 pagesHierarchical Wireless Network Architecture For Distributed ApplicationsabojablNo ratings yet
- 27 OMC Radio Parameters 104 OkDocument104 pages27 OMC Radio Parameters 104 OkabojablNo ratings yet
- Fast Dormancy (RAN13.0 02)Document30 pagesFast Dormancy (RAN13.0 02)Mikhail SolovievNo ratings yet
- ZGO-01-01-001 Half Rate V8.20 20091230 PDFDocument26 pagesZGO-01-01-001 Half Rate V8.20 20091230 PDFabojablNo ratings yet
- W RF Optimization Guide 20060608 A 3 1Document65 pagesW RF Optimization Guide 20060608 A 3 1Matthew JejeloyeNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 1993 Eurocopter AS-365-N2 6446 LN-OCMDocument2 pages1993 Eurocopter AS-365-N2 6446 LN-OCMWilliam RiosNo ratings yet
- Usa Hip-Hop MusicDocument14 pagesUsa Hip-Hop MusicRebeca AvatavuluiNo ratings yet
- Huawei ELTE3.3 DBS3900 Product DescriptionDocument36 pagesHuawei ELTE3.3 DBS3900 Product DescriptionLuis Terry TorresNo ratings yet
- Wave Speed WorksheetDocument3 pagesWave Speed WorksheetYassin HafezNo ratings yet
- Owner's Manual: Precautions Pages 4, 5Document36 pagesOwner's Manual: Precautions Pages 4, 5alejo_ucj9217No ratings yet
- Cortinas GL r63fDocument3 pagesCortinas GL r63fviernes06No ratings yet
- EmptinessDocument6 pagesEmptinesssavej92No ratings yet
- RHCP Can't StopDocument4 pagesRHCP Can't StopRed Raphael SanzioNo ratings yet
- Blues For Ben: Stanton Moore Funk Luca FreericksenDocument7 pagesBlues For Ben: Stanton Moore Funk Luca Freericksenmisaeldutra34100% (1)
- Sweetest Feeling:Build Me Up Buttercup - Jackie Wilson:The Foundations CTCDocument4 pagesSweetest Feeling:Build Me Up Buttercup - Jackie Wilson:The Foundations CTCCariss CrosbieNo ratings yet
- 【20170226】NB-IoT Commercialization Starts Sailing-V2.8Document79 pages【20170226】NB-IoT Commercialization Starts Sailing-V2.8Ejaz Ahmad100% (2)
- Performance Analysis of Massive MIMODocument12 pagesPerformance Analysis of Massive MIMOXiangyu LiuNo ratings yet
- Bull and Back, Intro To Auditory Culture ReaderDocument10 pagesBull and Back, Intro To Auditory Culture ReaderBo AnNo ratings yet
- HALO CHORDS (Ver 2) by Beyoncé @Document5 pagesHALO CHORDS (Ver 2) by Beyoncé @Miss_AccountantNo ratings yet
- Performance Directions: Grade 3 Music TheoryDocument13 pagesPerformance Directions: Grade 3 Music TheoryBelinda LohNo ratings yet
- Kpop EssayDocument6 pagesKpop EssayRazaw HamdiNo ratings yet
- Privacy-Preserving and Truthful Detection of Packet Dropping Attacks in WirelessAd Hoc Networks PDFDocument16 pagesPrivacy-Preserving and Truthful Detection of Packet Dropping Attacks in WirelessAd Hoc Networks PDFNavya Sri AddagarlaNo ratings yet
- Atheros 6 G Mini-Pci Adapter Emp-8602 Plus-S: 2.4 / 5.0 GHZ 802.11A/B/G 54 MbpsDocument2 pagesAtheros 6 G Mini-Pci Adapter Emp-8602 Plus-S: 2.4 / 5.0 GHZ 802.11A/B/G 54 MbpsAudiofilo84No ratings yet
- Jazz Reviews: ConsecrationBill Evans Trio - by Harvey Siders - Jazz Articles PDFDocument5 pagesJazz Reviews: ConsecrationBill Evans Trio - by Harvey Siders - Jazz Articles PDFa3677824No ratings yet
- Film Dan SportDocument8 pagesFilm Dan SportBally AndroNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Circuits: 2.1 Experiments in Rectifiers 2.1.1 Aim of The ExperimentDocument12 pagesRectifier Circuits: 2.1 Experiments in Rectifiers 2.1.1 Aim of The ExperimentrajNo ratings yet
- Written CommunicationDocument18 pagesWritten Communicationdimas108No ratings yet
- Digital Sound For Digital VideoDocument11 pagesDigital Sound For Digital VideoMark BehmNo ratings yet
- Lecture On The Songs of DuhallowDocument10 pagesLecture On The Songs of Duhallowapi-283296173No ratings yet
- Tossounian Figuring Modernity and National IdentityDocument37 pagesTossounian Figuring Modernity and National IdentityalejokhNo ratings yet
- Annabel Lee (Bilingüe)Document1 pageAnnabel Lee (Bilingüe)Cipriano Alonso100% (1)
- Atlas of Human Anatomy On MRI Spine Extremities Joints PDFDocument139 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy On MRI Spine Extremities Joints PDFAnca Mehedintu100% (1)
- Symbolism PDFDocument11 pagesSymbolism PDF畏100% (1)
- Dcrules of KDMCDocument262 pagesDcrules of KDMCankurshetye304288% (17)
- Panasonic TX-l32u2e TX-l42g20e Es TX-lf42g20s Chassis Glp25 SMDocument86 pagesPanasonic TX-l32u2e TX-l42g20e Es TX-lf42g20s Chassis Glp25 SMToni Martin SebéNo ratings yet