Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Guidelines For First-Line Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in Adults
Uploaded by
Anonymous s4yarxOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Guidelines For First-Line Empirical Antibiotic Therapy in Adults
Uploaded by
Anonymous s4yarxCopyright:
Available Formats
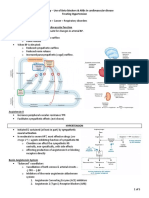
Guidelines for first-line empirical antibiotic therapy in adults
INFECTION SYNDROME / INDICATION
Community Acquired Pneumonia
Pneumonia is typically an acute febrile illness with cough, breathlessness, often
productive of sputum and pleurisy in a patient with or without existing chest
disease and new shadowing on CXR.
CURB 65 0-1
CURB 65 2
CURB 65 3-5
Assess severity using CURB 65 score: new Confusion, Urea >7mmol, Respiratory
rate >30 / min, BP <90 systolic or 60 diastolic, Age 65 (Each criterion scores 0
or 1. Therefore, max score = 5).
Community Acquired Aspiration Pneumonia
When patients aspirate gastric contents, they develop aspiration pneumonitis for which antimicrobial chemotherapy is NOT
required. Pneumonitis does not require treatment in first 48 hours unless there is a change in sputum quality to purulent /
mucopurulent, fever and new CXR changes which usually occur after 48hrs.
Bronchitis (Chronic) OR Infective Exacerbation of COPD
No pneumonic changes on CXR. For infective exacerbations of COPD, only prescribe for patients with two of the following:
increased SOB, increased sputum volume, increased sputum purulence.
Hospital Acquired Pneumonia including Hospital Acquired Aspiration
Pneumonia
HAP is over diagnosed clinically. HAP diagnosis requires radiological evidence of
new pulmonary infiltrates. Alternative diagnoses should be actively excluded.
< 4 days post admission
or > 4 days and non-severe
4 days post admission if severe
Uncomplicated (Lower) UTI
ASYMPTOMATIC BACTERIURIA; do not treat unless pregnant or urology procedures planned, even if catheter present.
Complicated (Upper) UTI
Risks for complicated UTI include: structural abnormality of the renal tract, male sex, recent urinary tract instrumentation,
symptoms> 7days at presentation, diabetes, immunosuppression.
Catheter associated UTI
Patients with urinary catheter invariably develop bacteriuria after a few days. However, treatment with an antibiotic is required only
if there are signs & symptoms of systemic infection.
Neutropenic sepsis
Neutrophil count of 1.0 x 109/l + Temp > 38C.
Sepsis of unknown origin
SEPSIS Criteria: Clinical impression of infection + 2 of; Temp >38C or < 36C ,
pulse > 90bpm, resp rate > 20/min, WCC >12 or <4 x 109/l.
SEVERE SEPSIS: Sepsis + organ dysfunction or hypoperfusion or hypotension.
Intra-abdominal sepsis (including biliary tract infections)
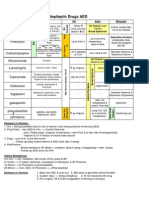
PREFERRED REGIMEN
Review antibiotic therapy once culture results known
ALTERNATIVE REGIMEN
including patients with serious penicillin allergy
SUGGESTED
DURATION
Amoxicillin 500mg 1g 8 hourly PO
Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO
5 7days
Levofloxacin 500 mg 12 hourly IV + Clarithromycin 500mg 12 hourly IV
Consider referral to ICU: If paO2 < 8kPa despite high FiO2; Progressive Hypercapnia; pH <
7.26; hypotension; GCS falling
7 10 days
Send blood cultures, Legionella and
Pneumococcal urinary antigen tests and sputum
culture.
5 7 days
Only treat if clinical / CXR evidence of pneumonia.
5 7 days
A cough of less than 2 weeks duration in healthy
adults with no co-morbidities or systemic illness
does not require antibiotics. Consider antibiotic
use in >60 years or if underlying chest disease.
Pseudomonas or staphylococcal pneumonia may
require a longer duration of therapy.
Amoxicillin 1g 8 hourly IV / PO + Clarithromycin 500mg 12 hourly PO
Co-amoxiclav 1.2g 6 hourly IV + Clarithromycin 500mg 12 hourly IV.
Consider referral to ICU: If paO2 < 8kPa despite high FiO2; Progressive Hypercapnia; pH <
7.26; hypotension; GCS falling
Amoxicillin 1g 8 hourly IV + metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly IV
Patient with no recent exposure to amoxicillin: amoxicillin 1g 8 hourly PO
Previous recent amoxicillin: Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO OR
Clarithromycin 500mg 12 hourly PO / IV
This should be guided by previous sputum / endotracheal culture results
Co-amoxiclav 625mg 8 hourly PO or 1.2g 8 hourly IV
Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g 8 hourly IV Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV (if severe)
Nitrofurantoin 100mg 6 hourly PO with food
Antibiotic therapy should be guided by previous urine culture results
Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
OR
Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g 8 hourly IV if gentamicin inappropriate
Antibiotic therapy should be guided by previous urine culture results
Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g 6 hourly IV + gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g 8 hourly IV + gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
PLUS:
If patient has risk factors for MRSA then add: Teicoplanin 10mg / kg 12 hourly IV x 3
doses then 10mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Community acquired non-severe:
Co-amoxiclav 1.2g 8 hourly IV
Bacterial meningitis
Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhoea
Mild / moderate Disease: WCC < 15, CRP < 150 Normal Abdominal XR.
Severe disease: WCC > 15, CRP > 150, Abnormal Abdominal XR, Distended Abdomen.
Clarithromycin 500mg 12 hourly IV
+ Metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly IV
Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO
Vancomycin 1g 12 hourly IV (see therapeutic drug monitoring)
+ Ciprofloxacin 400mg 12 hourly IV + metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly IV
NB - This should be guided by previous sputum / endotracheal culture results
Trimethoprim 200mg 12 hourly po
Antibiotic therapy should be guided by previous urine culture results
Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
OR
Ciprofloxacin 400mg 12 hourly IV only if gentamicin inappropriate
If Gentamicin therapy is inappropriate:
Ciprofloxacin 400mg 12 hourly IV or
Ciprofloxacin 500mg 12 hourly PO
Ciprofloxacin 600mg 12 hourly IV
+ Teicoplanin 10mg / kg 12 hourly IV x 3 doses then 10mg / kg 24 hourly IV
+ Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Ciprofloxacin 600mg 12 hourly IV
+ Teicoplanin 10mg / kg 12 hourly IV x 3 doses then 10mg / kg 24 hourly IV
+ Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Mild: Flucloxacillin 750 mg-1g 6 hourly PO
Community acquired non-severe:
Vancomycin 1g 12 hourly IV (see therapeutic drug monitoring) +
Metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly IV + Aztreonam 2g 8-hourly IV
Hospital acquired / Severe:
Vancomycin 1g 12 hourly IV (see therapeutic drug monitoring) +
Metronidazole 500mg 8 hourly IV + Ciprofloxacin 400mg 12 hourly IV
Mild: Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO
Severe eg. necrotising fasciitis- Urgent Micro / ID and Surgery advice
Severe e.g. necrotising fasciitis- Urgent Micro / ID and Surgery advice
Hospital acquired / Severe:
Piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5g 8 hourly IV Gentamicin 5mg / kg 24 hourly IV
Cellulitis / soft tissue infections: No MRSA
Note: If symptoms bilateral, cellulitis unlikely
Mild: no signs of systemic toxicity, have no uncontrolled co- morbidity.
Moderate: either
systemically well, but with a co-morbidity eg. peripheral vascular disease, chronic venous insufficiency or morbid obesity, which
may complicate or delay resolution of their infection. OR
may have a significant systemic upset such as acute confusion, tachycardia, tachypnoea, hypotension or may have unstable comorbidities that may interfere with a response to therapy or have a limb threatening infection due to vascular compromise.
Severe: have sepsis syndrome or severe life threatening infection e.g. necrotising fasciitis.
Cellulitis / soft tissue infections: Known MRSA
Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO
Moderate- Severe: Flucloxacillin 2g 6 hourly IV
Moderate- Severe: Clindamycin 900mg 8-hourly IV
Mild: Doxycycline 100mg 12 hourly PO sodium fusidate 500mg 8 hourly PO
Moderate: Teicoplanin 10mg / kg 12 hourly IV x 3 doses then 10mg 24 hourly IV
+ Sodium fusidate 500mg 8 hourly PO
OR
Vancomycin 1g 12 hourly IV (see therapeutic drug monitoring)
+ Sodium fusidate 500mg 8 hourly PO
Ceftriaxone 2g 12 hourly IV
If >55 years, immunocompromised or pregnant add Amoxicillin 2g 4 hourly IV
Mild / moderate: Metronidazole 400mg 8 hourly PO. Refer to full guidance
Chloramphenicol 25mg / kg 6 hourly IV.
If > 55yrs or immunocompromised add co-trimoxazole 1.44g 12 hourly IV
Severe disease: Refer to full local guidance
Review suitability for IV to oral switch within 48 hours and daily thereafter.
Criteria:
hydrated and drinking
adequate GI absorption
temperature <38C for >48 hrs
pulse <100 beats/min or return to baseline
resolution of tachypnoea and hypotension or return to baseline
no hypoxia or return to baseline
resolving WCC / CRP
no standing instruction for prolonged IV therapy e.g. osteomyelitis,
endocarditis, meningitis, bacteraemia
Oral formulation or suitable alternative is available
When prescribing
1.
2.
3.
4.
Must document in the medical notes and on the kardex the indication, drug
prescribed, dose, frequency, route and planned duration or review date.
Document baseline investigations requested.
Obtain samples for microbiological culture before administration of antibiotics
(where possible)
Review microbiology results and de-escalate therapy as appropriate (contact
micro if advice required)
Prudent antibiotic prescribing
To reduce emergence of multi resistant organisms and Clostridium difficile
associated diarrhoea:
De-escalate to narrow spectrum from broad spectrum empirical regimens
based on cultures where possible.
Avoid clindamycin, cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones outside guideline
limitations. Minimise carbapenems and long courses of antimicrobials
Penicillin allergy
Obtain a reliable history & document exact nature in case notes and on kardex
High risk:
History of: anaphylaxis, urticaria, early onset rash, angioedema, bronchospasm,
hypotension, laryngeal oedema, Stevens-Johnston or toxic epidermal necrolysis
Avoid penicillins, cephalosporins and other beta- lactam antibiotics.
Aztreonam may be less likely to cause hypersensitivity in penicillin sensitive
patients and can be used with caution (avoid aztreonam if allergic to
ceftazidime)
Low risk:
Minor non confluent, non pruritic rash restricted to a small area of the body, rashes
>72 hours after administration, nausea, diarrhoea:
Life threatening allergy very unlikely, therefore a trial of beta-lactam therapy
under observation may be considered as appropriate.
Consideration should be given to immunological proof of allergy (RAST test)
once patient has recovered from their infection.
5 7 days
5 7 days
Female 3 days/Male 7 days
7 10 days
Pyelonephritis 14 days
Depending on severity of
infection
Nitrofurantoin not advised in severe renal
impairment.
Review gentamicin requirement at day 3 4
followed by oral step down therapy to a
susceptible oral agent
Re-assess need for catheter; if it is required
change/remove under antibiotic cover.
Review gentamicin requirement at day 3.
Review at 48 hours
5 10 days
Depends on source &
severity
7 14 days
Depending on severity
Clinical features of NF are:
constant pain, bullous lesions, gas in the soft
tissues, systemic toxicity & rapid spread along the
facial planes.
NF is life-threatening, (take blood cultures and
send wound swab/debrided pus or tissue for
culture).
7 14 days
All dosing regimens assume normal renal and hepatic function. Check suitability of proposed regimen in pregnancy and breast-feeding
IV / Oral antibiotic switch guideline
7 days
COMMENT
Depends on pathogen
isolated
10 14 days
review daily refer to local
guidance
Therapeutic drug monitoring
Antibiotic
Teicoplanin levels
Only required for patients receiving prolonged courses > 7 days therapy
(assuming normal renal function). Patients with renal impairment and reduced
dose may need levels earlier.
Loading dose:
10 mg / kg doses 12-hourly for 3 doses (Round to nearest 200mg).
Maintenance dose:
10mg / kg / day 24-hourly in normal renal function. Adjust dose if renal
impairment.
Timing of first level:
Trough (pre dose) after 5-7 days of therapy completed. Give dose while
awaiting results of levels in normal renal function.
Expected range: 20-60mg / L.
Consult microbiologist.
Dosage
5mg / kg
Gentamicin
(once daily regimen) (in 100ml 5% glucose or 0.9% NaCl over 30-60
minutes)
Expected levels (mg/l)
Trough before 2nd dose i.e.
18-24 hours after first infusion
2-3
<1 (19-24 hours)
<2 (18 hours)
Levels prior to 18 hours after
last dose are not suitable
After 2- 3 doses
Gentamicin
(divided dosing)
Refer to local guidance
Vancomycin
*Monitor only if
given IV*
Creatinine Clearance (Cr Cl)
Cr Cl
Cr Cl < 50mL / min:
25mg / kg (up to 1g) stat then check levels at
24 hours before adjusting 2nd dose
accordingly
Give dose while awaiting results
of levels and adjust subsequent
dose accordingly
15mg / kg
Amikacin
(once daily regimen) (in 100ml 5% glucose or 0.9% NaCl over 1 hour)
> 50mL / min:
25mg / kg (up to 1g)
12-hourly
NB: slow infusion at a rate not to exceed 10mg / min
Re assay
interval (days)#
Timing of first level
Trough before 2nd dose i.e.
18-24 hours after first infusion
> 50mL / min only:
Trough before 3rd or 4th dose i.e.
>10 hours after 2nd or 3rd dose
Trough <2
Peak 5-10
2-3
Trough 10-15
2-3
2-3
<5
Levels prior to 18 hours after
last dose are not suitable
Trough 10-20 for more severe
infections
Levels sent <10 hours after
last dose are not suitable
Assuming renal function not impaired and initial results are within expected range and/or no other changes affecting levels e.g. changes in renal / hepatic function
drug interactions etc.
BT13-802
2010/2014
You might also like
- 2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisDocument1 page2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisTeng Huei LeeNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide June2013 PDFDocument2 pagesPocket Guide June2013 PDFSergeyGruntov100% (1)
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationFrom EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin & Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci: Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmDocument78 pagesVancomycin & Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci: Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., Pharmkharbosham100% (1)
- OS217 LEC06 Rational Antibiotic UseDocument6 pagesOS217 LEC06 Rational Antibiotic Usegenerics54321No ratings yet
- (CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsDocument6 pages(CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsHanifa Shereen B. AliNo ratings yet
- Empiric Treatment Guidelines Common InfectionsDocument9 pagesEmpiric Treatment Guidelines Common InfectionsShiza Batool100% (1)
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Blood DisordersDocument1 pageDrugs in Blood DisordersSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Classification of DrugsDocument10 pagesClassification of DrugsSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDocument8 pagesKlasifikasi Dan Mekanisme ABDeboyjackNo ratings yet
- NHS Antibiotice PDFDocument2 pagesNHS Antibiotice PDFHoratiu OanaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics 101Document49 pagesAntibiotics 101Tony VoNo ratings yet
- Penicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsDocument1 pagePenicinillase - Sensible: Inhibit Clasification AntibioticsАндрій ДанильцівNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic and NephriticDocument27 pagesNephrotic and Nephritictam meiNo ratings yet
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNo ratings yet
- EDT007Document110 pagesEDT007mahchusNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- A New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMDocument26 pagesA New Way of Mnemonics - Hypertension-cough-asthma-NSAID - WMKartik Mendiratta100% (1)
- Drug Side EffectsDocument2 pagesDrug Side EffectsAngelic khanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Chronic Heart FailureDocument2 pagesTreatment of Chronic Heart FailureShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Primary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Document10 pagesPrimary Care Antibiotic Guideline FINAL May 2015Atta Muhammad MemonNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Meds For HypertensionDocument3 pagesMeds For HypertensionZonicsNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic TableDocument5 pagesAntibiotic TableLiana Et Murat KalabalikNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDocument16 pagesThe Principles of Antibiotic Therapy: S. Aureus Streptococcus PneumoniaeDianne Chua100% (7)
- AntibioticsDocument4 pagesAntibioticsTan Geok Eng100% (1)
- Abx FinalDocument3 pagesAbx Finalyanks1120No ratings yet
- Antibiotics NotesDocument7 pagesAntibiotics NotesmuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- IMG EmpAposterDocument1 pageIMG EmpAposterChiu LeoNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactam AntibioticsDocument1 pageBeta Lactam AntibioticsCourtney TownsendNo ratings yet
- KDT Only ClassificationsDocument72 pagesKDT Only ClassificationsDebashis ParidaNo ratings yet
- Farmakokinetika Klinik Vancomycin: Riri Tifani 1201108Document21 pagesFarmakokinetika Klinik Vancomycin: Riri Tifani 1201108Rahmatul HusnaNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Resuscitation Pharmacology: Dr. Beny Hartono, SPJP, FihaDocument44 pagesResuscitation Pharmacology: Dr. Beny Hartono, SPJP, FihaAna AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Trials SummaryDocument12 pagesTrials SummaryReda SoNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Drugs SummaryDocument13 pagesAntibacterial Drugs SummaryNeo Ramagaga100% (1)
- With Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument1 pageWith Dr. Susan Lipsett: Community Acquired PneumoniaJayantiNo ratings yet
- Classification of The DrugsDocument50 pagesClassification of The DrugsGlena SalamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A - Drugs Used in Coagulation CascadeDocument13 pagesPharmacology A - Drugs Used in Coagulation CascadeselflessdoctorNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuideDocument6 pagesAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFDocument1 pagePharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inNo ratings yet
- DRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousDocument1 pageDRUG of CHOICE - InfectiousJoseph De JoyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Auc With Answers 1Document64 pagesVancomycin Auc With Answers 1api-493355126No ratings yet
- PCOL Maps PDFDocument11 pagesPCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- UAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuDocument19 pagesUAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDocument14 pagesPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorNo ratings yet
- 01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFDocument26 pages01 - Pharmacotherapy Pearls For Emergency Neurological Life Support PDFawinsyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of DiureticsDocument75 pagesPharmacology of DiureticsAhmed BassettNo ratings yet
- Pain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Document3 pagesPain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Ryan TurnerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AntimycobacterialDocument7 pagesPharmacology of Antimycobacterialselflessdoctor100% (1)
- Therapeutic Hypothermia Niraj BharuchDocument31 pagesTherapeutic Hypothermia Niraj BharuchNiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading EMPEROR-ReducedDocument21 pagesJournal Reading EMPEROR-ReducedLolii Con Harhazyuku100% (1)
- PHM - Hematologic DrugsDocument3 pagesPHM - Hematologic DrugsJeanne Rodiño100% (3)
- THE RELATIONSHIP OF BODY MASS INDEX AND HYPOALBUMINEMIA WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackDocument1 pageTHE RELATIONSHIP OF BODY MASS INDEX AND HYPOALBUMINEMIA WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Correlation of BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackDocument1 pageCorrelation of BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between Depression and Falls Among Elderly Patient Hospitalized at Geriatric Ward in Sanglah HospitalDocument1 pageCorrelation Between Depression and Falls Among Elderly Patient Hospitalized at Geriatric Ward in Sanglah HospitalAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- AGE BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN in Hospitalized Elderlty Abstrack Penelitian 2 ExtendedDocument4 pagesAGE BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN in Hospitalized Elderlty Abstrack Penelitian 2 ExtendedAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Penelitian Sri Rejeki-Correlation of Sepsis and Albumin SerumDocument1 pagePenelitian Sri Rejeki-Correlation of Sepsis and Albumin SerumAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Correlation of BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackDocument1 pageCorrelation of BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN WITH INFECTION IN GERIATRIC POPULATION AbstrackAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia NosokomialDocument29 pagesPneumonia NosokomialAngela NovanthiaNo ratings yet
- ATS GuidelinesDocument46 pagesATS Guidelinesapi-3847280100% (1)
- AGE BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN in Hospitalized Elderlty Abstrack Penelitian 2Document1 pageAGE BODY MASS INDEX AND ALBUMIN in Hospitalized Elderlty Abstrack Penelitian 2Anonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- New Targets in Malaria Parasite Chemotherapy A Review TropikDocument6 pagesNew Targets in Malaria Parasite Chemotherapy A Review TropikAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Infdis - Jiv365.full TropikDocument3 pagesInfdis - Jiv365.full TropikAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- DR Dewi Dian Early Detection of Bacterial Infection in Acute Febrile IllnessDocument9 pagesDR Dewi Dian Early Detection of Bacterial Infection in Acute Febrile IllnessAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- For Practitioner: Jaundice Obstructive SyndromDocument5 pagesFor Practitioner: Jaundice Obstructive SyndromArsy Mira PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kriteria Baru SleDocument10 pagesJurnal Kriteria Baru SleDr Edi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Nilai Workshop BagusDocument2 pagesNilai Workshop BagusAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- DHF 1 PDFDocument7 pagesDHF 1 PDFPutriIndahNo ratings yet
- Infdis - Jiv365.full TropikDocument3 pagesInfdis - Jiv365.full TropikAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- DR Dewi Dian Early Detection of Bacterial Infection in Acute Febrile IllnessDocument9 pagesDR Dewi Dian Early Detection of Bacterial Infection in Acute Febrile IllnessAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Prof Tuty The Etiology of Acute Febrile Illness Requiring Hospitalization - Docx2Document3 pagesProf Tuty The Etiology of Acute Febrile Illness Requiring Hospitalization - Docx2Anonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Cervical Thyroid Carcinoma-Review of The Literature With Illustrative Case SeriesDocument8 pagesEctopic Cervical Thyroid Carcinoma-Review of The Literature With Illustrative Case SeriesAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- DR Agus Specimen CultureDocument2 pagesDR Agus Specimen CultureAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH LENGKAP BIDS-6 Final Abstrak Siap PrintDocument14 pagesMAKALAH LENGKAP BIDS-6 Final Abstrak Siap PrintAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Uni CoverageDocument11 pagesJURNAL Uni CoverageAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Uni CoverageDocument11 pagesJURNAL Uni CoverageAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Uni CoverageDocument11 pagesJURNAL Uni CoverageAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- JURNAL Uni CoverageDocument11 pagesJURNAL Uni CoverageAnonymous s4yarxNo ratings yet
- Jurnal KeperawatanDocument9 pagesJurnal KeperawatanDewa DiningratNo ratings yet
- Highway-And-Railroad-Engineering SummaryDocument15 pagesHighway-And-Railroad-Engineering SummaryRodin James GabrilloNo ratings yet
- ZF-FreedomLine TransmissionDocument21 pagesZF-FreedomLine TransmissionHerbert M. Zayco100% (1)
- Arduino Oscilloscope ProjectDocument12 pagesArduino Oscilloscope ProjectSathya Narayan100% (1)
- The Acceptability of Rubber Tree Sap (A As An Alternative Roof SealantDocument7 pagesThe Acceptability of Rubber Tree Sap (A As An Alternative Roof SealantHannilyn Caldeo100% (2)
- Significance of GodboleDocument5 pagesSignificance of GodbolehickeyvNo ratings yet
- CBSE DetailsDocument6 pagesCBSE DetailsNARESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Flight Vehicle Design:: Example 2 (Uav)Document43 pagesFlight Vehicle Design:: Example 2 (Uav)Anmol KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document8 pagesLecture 12Mechanical ZombieNo ratings yet
- Emw 2007 FP 02093Document390 pagesEmw 2007 FP 02093boj87No ratings yet
- Ham Radio Balu N ManualDocument7 pagesHam Radio Balu N Manualcolinbeeforth100% (1)
- Douluo Dalu Volume 05 - Star Dou Forest PDFDocument141 pagesDouluo Dalu Volume 05 - Star Dou Forest PDFRay Joseph LealNo ratings yet
- EPCC Hydrocarbon Downstream L&T 09.01.2014Document49 pagesEPCC Hydrocarbon Downstream L&T 09.01.2014shyaminannnaNo ratings yet
- Honeycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Document3 pagesHoneycomb Kevlar 49 (Hexcel)Julia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesmarichuNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - 4th WeekDocument40 pagesLec 4 - 4th Weekrajpoot aliNo ratings yet
- Manual PipsDocument5 pagesManual PipsOzzyNo ratings yet
- DudjDocument4 pagesDudjsyaiful rinantoNo ratings yet
- Dawn of Solar PV CookingDocument5 pagesDawn of Solar PV CookingAbhinav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Faa Registry: N-Number Inquiry ResultsDocument3 pagesFaa Registry: N-Number Inquiry Resultsolga duqueNo ratings yet
- 1962 Gibson Johnny SmithDocument5 pages1962 Gibson Johnny SmithLuisNo ratings yet
- Native Data Sheet Asme b73.1Document4 pagesNative Data Sheet Asme b73.1Akhmad Faruq Alhikami100% (1)
- The Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsDocument10 pagesThe Indian Mining Sector: Effects On The Environment & FDI InflowsMehul MandanakaNo ratings yet
- H107en 201906 r4 Elcor Elcorplus 20200903 Red1Document228 pagesH107en 201906 r4 Elcor Elcorplus 20200903 Red1mokbelNo ratings yet
- Combined Shear and TensionDocument16 pagesCombined Shear and TensionDAN MARK OPONDANo ratings yet
- 123 09-Printable Menu VORDocument2 pages123 09-Printable Menu VORArmstrong TowerNo ratings yet
- Math COT 3Document18 pagesMath COT 3Icy Mae SenadosNo ratings yet
- Considerations For Impeller Trimming - Empowering Pumps and EquipmentDocument8 pagesConsiderations For Impeller Trimming - Empowering Pumps and Equipment김기준No ratings yet
- Owner'S Manual: 2023 Chassis CabDocument444 pagesOwner'S Manual: 2023 Chassis CabDmitry DimasNo ratings yet
- Immigrant Italian Stone CarversDocument56 pagesImmigrant Italian Stone Carversglis7100% (2)
- Determinants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesDeterminants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Apurv ChitranshNo ratings yet