Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Feeding Techniques To Improve Bandwidth of MPA: Meenu Chinwan, Harshpreet Kaur
Uploaded by
dhvbkhnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Feeding Techniques To Improve Bandwidth of MPA: Meenu Chinwan, Harshpreet Kaur
Uploaded by
dhvbkhnCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE)
ISSN: 2231-2307, Volume-3, Issue-1, March 2013
Feeding Techniques to Improve Bandwidth of
MPA
Meenu Chinwan, Harshpreet Kaur
AbstractThe comprehensive study of MPA shows its
important role in the modern wireless communication devices.
Detailed literature review of past few decades papers on MPA, the
MPA has emerged into wide range of communication field.
Inherently the patch antenna is narrowband; various techniques
were developed to enhancement of bandwidth. Different
parameter affect the efficiency of antenna .Specification of MPA
has low weight, low profile. This is Omni-directional antenna
whose fabrication is easy.
Index TermsPatch design, Electromagnetic wave, and
radiation, Microstrip, Antenna
I. INTRODUCTION
Antenna is also called as transducer which transceivers
electromagnetic waves. Micro strip contains a patch which is
called as radiating patch. Various feed techniques has been
compared &it was found that co-axial feed is best among all,
& provide better performance. The size of antenna increases
due to the physical dimensions on the edge. Resonant
condition is obtained by using less than half the wavelength of
micro strip line. Lithographic pattern is used to design patch
II. MICROSTRIP PATCH CONFIGURATION
A. Microstrip Patch Antenna
A micro strip patch antenna has a patch which is
conducting in nature .The geometry of conducting patch is of
planar & non-planar nature. The structures of microstrip patch
antenna have dielectric substrate on one side & ground plane
on other side.MPA requires semi-hemispherical coverage for
narrowband microwave wireless links.MPA planar
configuration &ease of integration is widely used as array
elements. The patch used in MPA is of different shape and
structure which shows different properties of radiation.
Among all structure generally rectangular and circular patch
are preferred. Due to their structure which can easily
separated &simple estimation rectangular patch is used in
various applications. While the circular patch antenna shows
symmetric radiation pattern. The length of patch L is given by
the following expression:
on the dielectric substrate (
.Microstrip patch antenna
are basically work on narrowband various bandwidth
enhancement techniques has been introduced to increase the
bandwidth [1].
L 0.49
Fig 2 Micro strip patch antenna
Fig 1 Micro strip patch antenna
Manuscript received March 2013.
Meenu Chinwan, Department of Electronics and Communication, GRD
Institute of Management and Technology, Dehradun, India,
Harshpreet Kaur, Department of Electronics and Communication,
GRD Institute of Management and Technology, Dehradun, India,
B. Microstrip or Printed Dipole Antenna
The basic difference in the MPA & printed dipole antenna
is in their length-to-width ratio. The dipoles used in the
printed dipole antenna have 0.05o times width [2]. Different
parameter such as radiation resistance, bandwidth, and
cross-polar radiation vary according to the width of dipole
used. The main advantage of dipole antenna that is best for
higher frequencies and the requirement for attaining
significant bandwidth the substrates used must be electrically
thick. The VSWR is normally 2 in dipole antenna.
170
Feeding Technique to Improve Bandwidth of MPA
The excitations of the radiating patch depend upon the feed
current & patch mode.
Fig 3 Micro strip Dipole Antenna
C. Printed Slot Antenna
The structures of Printed slot antenna consist of a slot in the
ground plane of a grounded substrate. Many of MPA are
analyze in the form of printed slot antenna theoretically.
Among many design few are of most use namely rectangular
slot, annular slot, rectangular ring slot & tapered slot. Feeding
techniques can be micro strip line or co-planar waveguide.
The specific
features of slot antenna are generally
bidirectional radiators & they radiate on both side of slot.
Fig 5 Co-axial Probe Feed
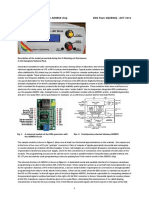
B. Micro Strip Line Feed
A Micro strip line is a simple conducting strip which is
directly connects to the radiating patch [3]. Micro strip lines
are easy in fabrication, matching by means of controlling the
position of the microstrip line. The fig 4 shows the diagram of
this by hfss software .Main disadvantages are thickness of
substrates is increase. High spurious radiation & surface wave
narrowband. If we increase the thickness of dielectric
substrate the corresponding surface wave & spurious
radiation will also increase. The patch is excited by the edged
coupled microstrip line with current density
magnetic field.
Fig 4 Geometry of Printed Slot Antenna
D. Micro Strip Travelling Wave Antenna
A MPA contain a chain-shape conductor which is periodic
in nature & to support TE mode a feed of long micro strip line
is used. At the other end resistive load is matched to the
traveling wave antenna so as to neglect the standing wave
which appears on antenna. This traveling wave is so formed
that must lie in any direction from broad side to end fire.
Coupling
EZJZdv cos (
III. FEEDING TECHNIQUES
Feeding is a techniques in which excitation is provided by
the direct or indirect contact to make the patch radiate.
A. Co-axial Probe Feed
Co-axial probe feeding is provided by direct contact. The
structure of co-axial probe feeding consists of two conductors
[4]. The inner conductor is attached with patch and the outer
conductor is attached to the ground plane. The fig 3 shows the
diagram of this by hfss software there are few advantages of
this is that the fabrication impedance matching is easy. The
increases in probe length result in more inductive input
impedance due to which impedance matching problem occur.
171
Fig 6 Micro strip line feed
&
as
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE)
ISSN: 2231-2307, Volume-3, Issue-1, March 2013
C. Aperture Coupled Feed
Aperture coupling feed consist of two dielectric substrates.
Both dielectric have different dielectric constant &are
separated by ground plane. The fig 5 shows the diagram of
this by hfss software .The top dielectric substrate constant is
high. The ground plane in between these two dielectric
substrates is used for the isolation of the feed from the
radiation of the radiating patch. The line feed &lower
substrate are electromagnetically coupled to the patch through
the aperture. Coupling depends on size, shape &location of
aperture.
Coupling=
M.Hdv sin (X0/l)
IV. MICROSTRIP ANTENNA CHARACTERSTICS
Many characteristics such as radiation patterns, gain&
beam width affect the micro strip patch antenna behavior but
apart from these there are some other parameters which play
very important role in the calculation of MPA.
V. CONCLUSION
This paper presents a survey of the different structures used
to accomplish the behavior of MPA by HFSS. By introducing
slots in the patch, the dual-frequency operation can be
achieved in a rectangular patch antenna. This dual-frequency
operation is not accomplished at the expense of any other
feature such as cross polarization or distorted radiation
patterns.
VI. ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors are grateful to their colleague for their
immense support & corporation.
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
Fig 7 Aperture Coupled Feed
D. Proximity Coupling Feed
Proximity is non-conducting type of feed technique .The
fig 8 shows the diagram of this by hfss software. In this
particular configuration, the impedance matching is
controlled by length of feeding stub &width-to-length ratio
[5]. The coupling in the proximity is of capacitive in nature. It
have double layer of dielectric substrate on which the
radiating patch is placed due to which bandwidth is enhanced.
[4]
[5]
[6]
Ramesh Garg, Prakash Bartia, Inder Bahl, Apisak Ittipiboon,
Microstrip Antenna Design Handbook, 2001, pp 168, 253316
Artech House Inc. Norwood, MA.
Alla I. Abunjaileh, Ian C. Hunter, Andrew H. Kemp,Multi Band
Matching Technique for Microstrip Patch Antenna Receivers,
School of electronic and electrical engineering, The University of
Leeds IEEE, EUMC.2007.4405174.
Yasir Ahmed, Yang Hao and Clive Parini, A 31.5 GHZ Patch
Antenna Design for Medical Implants, University of London,
International Journal of Antennas & Propagation, volume 2008,
(2008), article ID 167980.
S. Satthamsakul, N. Anantrasirichai, C. Benjangkapraset, and T.
Wakabayashi, Rectangular Patch Antenna with inset feed and
modifier ground plane for wide band antennas, IEEE, Aug, 2008.
Richard C. Johnson, Henry Jasik, Antenna Engineering Handbook
Second Edition 1984, pp 71 to 714, McGraw Hill, Inc. NY, USA.
Pozar, D. M., Microstrip Antennas, Proc. IEEE, Vol. 80, 1992, pp.
79 91
Meenu Chinwan received the Bachelors degree in
E.C.E from Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology,
Dehradun, Uttrakhand in 2011. She is currently
pursuing Masters degree in Wireless and Mobile
Communication from GRD Institute of Mangement
and Technology, Dehradun. Her research area is
Antenna and Wave Propagation.
Harshpreet Kaur received the Bachelors degree in
E.C.E from Lovely Institute of Technology,
Phagwara, Punjab in 2011. She is currently pursuing
Masters degree in Wireless and Mobile
Communication from GRD Institute of Mangement
and Technology, Dehradun. Her research area is
Digital Communication.
Fig 8 Proximity Coupling Feed
172
You might also like
- Bandwidth Enhancement of Circular Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Different Feeding TechniquesDocument6 pagesBandwidth Enhancement of Circular Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Different Feeding TechniquesinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericFrom EverandRadio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericNo ratings yet
- Ext 20185Document5 pagesExt 20185Bouhafs AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Design and Characterization of Corporate Feed Rectangular Microstrip Patch Array AntennaDocument6 pagesDesign and Characterization of Corporate Feed Rectangular Microstrip Patch Array AntennaimaculateNo ratings yet
- A Microstripe Slotted Patch Antenna Using Amc: Manju Saini, Sachin Singla, Koneesh AggarwalDocument5 pagesA Microstripe Slotted Patch Antenna Using Amc: Manju Saini, Sachin Singla, Koneesh AggarwalNag ChallaNo ratings yet
- Design of Series Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using HFSS SimulatorDocument4 pagesDesign of Series Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna Array Using HFSS SimulatoridescitationNo ratings yet
- IISRT - Divyasri GovindharajanDocument6 pagesIISRT - Divyasri GovindharajanIISRTNo ratings yet
- Circularly Polarized ArrowheadDocument12 pagesCircularly Polarized ArrowheadNatwar LalNo ratings yet
- Yagi GudaDocument10 pagesYagi GudaAnil Babu NamalaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Coaxial Probe Feed TechniqueDocument3 pagesPerformance Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Coaxial Probe Feed TechniqueInternational Jpurnal Of Technical Research And Applications100% (1)
- Master of Engineering: Dissertation-I PresentationDocument25 pagesMaster of Engineering: Dissertation-I Presentation21212011 manasNo ratings yet
- Design and Study of Inset Feed PDFDocument7 pagesDesign and Study of Inset Feed PDFVijaya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna Design and Simulation For Single S - Band Frequency Using ADSDocument8 pagesRectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna Design and Simulation For Single S - Band Frequency Using ADSMylavarapu SriprithamNo ratings yet
- Appli and TypesDocument5 pagesAppli and Typessuhag_73No ratings yet
- Performance Comparison of Microstrip Antenna Feeding TechniquesDocument5 pagesPerformance Comparison of Microstrip Antenna Feeding TechniquesFazil MohamedNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Microstrip Patch Antenna Using MetamaterialDocument6 pagesA Survey On Microstrip Patch Antenna Using MetamaterialAlejandro-SBNo ratings yet
- Microstrip Patch Antenna Technology GuideDocument7 pagesMicrostrip Patch Antenna Technology GuideRahul AryanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Micro Strip Antenna Using Hfss SoftwareDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Micro Strip Antenna Using Hfss SoftwareSaikrishnaChokkapuNo ratings yet
- Aperture Coupled Patch AntennaDocument5 pagesAperture Coupled Patch Antennasreelakshmi.ece eceNo ratings yet
- Analysis Different Methods of Microstrip Antennas Feeding For Their Electrical ParametersDocument5 pagesAnalysis Different Methods of Microstrip Antennas Feeding For Their Electrical ParametersIrfanullahKhanNo ratings yet
- Circularly Polarized Circular Patch Antenna With Coplanar Parasitic ElementsDocument4 pagesCircularly Polarized Circular Patch Antenna With Coplanar Parasitic ElementseditorinchiefijcsNo ratings yet
- A New Reduced Size Microstrip Patch Antenna With Fractal Shaped DefectsDocument9 pagesA New Reduced Size Microstrip Patch Antenna With Fractal Shaped DefectssharmabinNo ratings yet
- Review Paper For Circular Microstrip Patch Antenna: ISSN 2249-6343Document4 pagesReview Paper For Circular Microstrip Patch Antenna: ISSN 2249-6343Charan Macharla'sNo ratings yet
- Design and Comparison of Dual Coaxial and Edge Feed Square Micro Strip Patch Antenna For Wind Profiling Radar Applications at 430 MHZDocument10 pagesDesign and Comparison of Dual Coaxial and Edge Feed Square Micro Strip Patch Antenna For Wind Profiling Radar Applications at 430 MHZIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument44 pagesFrequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch AntennaJenath SathikbashaNo ratings yet
- Review of Some Investigations On Rectangular Microstrip Antennas With Embedded SlotsDocument8 pagesReview of Some Investigations On Rectangular Microstrip Antennas With Embedded SlotsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Design of Aperture Coupled Fed Micro-Strip Patch Antenna For Wireless CommunicationDocument3 pagesDesign of Aperture Coupled Fed Micro-Strip Patch Antenna For Wireless CommunicationALEX_125No ratings yet
- Project-Antenna ArrayDocument17 pagesProject-Antenna ArraysushantNo ratings yet
- Final Report ETE 300 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal Report ETE 300 PDFETE 18No ratings yet
- Bandwidth Enhancement in Multipatch Microstrip Antenna ArrayDocument6 pagesBandwidth Enhancement in Multipatch Microstrip Antenna ArrayInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Design of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 10.3 GHZ For X-Band ApplicationsDocument7 pagesDesign of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 10.3 GHZ For X-Band ApplicationsAbdulhakam abubakarNo ratings yet
- An Ten ADocument13 pagesAn Ten At.sin48No ratings yet
- Simulation of A Rectangular Patch AntennaDocument9 pagesSimulation of A Rectangular Patch AntennaragvshahNo ratings yet
- Broadband Planar Antennas For Mobile Communications Base StationsDocument8 pagesBroadband Planar Antennas For Mobile Communications Base StationsKhaled Abou ElseoudNo ratings yet
- 8.design of An S-Band Rectangular Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument8 pages8.design of An S-Band Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antennasrinivas08427No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Dual Band Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument27 pagesDesign and Simulation of Dual Band Microstrip Patch AntennaAnany SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Patch Antenna Performance FeedsDocument13 pagesRectangular Patch Antenna Performance FeedsyaswanthNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna With Triple Slot For X BandDocument10 pagesDesign and Simulation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna With Triple Slot For X BandIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Broadband Microstrip Patch Antennas for 3GDocument5 pagesBroadband Microstrip Patch Antennas for 3Galokcena007No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Microstrip Patch Arrayantenna For Wireless Communications at 24 GHZDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation of Microstrip Patch Arrayantenna For Wireless Communications at 24 GHZdeepaneceNo ratings yet
- Kumar 2018Document5 pagesKumar 2018PRASANTH KUMAR JNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Directivity of Multilayer Microstrip AntennaDocument6 pagesEnhanced Directivity of Multilayer Microstrip AntennaBhooshan PattanashettiNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Compact Dual Band U-Slot Mi 2018 Coax ProbeDocument3 pagesDesign and Analysis of Compact Dual Band U-Slot Mi 2018 Coax ProbeRaaz yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Aperture Coupled Microstrip Antenna Design and Analysis Using Matlab IJERTV8IS060302Document5 pagesAperture Coupled Microstrip Antenna Design and Analysis Using Matlab IJERTV8IS060302Brijesh SoniNo ratings yet
- Effect of Slots in Ground Plane and Patch On MicroDocument4 pagesEffect of Slots in Ground Plane and Patch On MicronikitaNo ratings yet
- CPW-Fed Capacitive Coupled Slot Antenna: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Omputer and Ommunication NgineeringDocument6 pagesCPW-Fed Capacitive Coupled Slot Antenna: Nternational Ournal of Nnovative Esearch in Omputer and Ommunication NgineeringNag ChallaNo ratings yet
- Microstrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationDocument20 pagesMicrostrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationBrhane DadsoNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2Document0 pages02 Chapter 2Dr-Pritam Singh BakariyaNo ratings yet
- Final PPT AmarDocument21 pagesFinal PPT Amarashishvasekar0% (1)
- Final Report ETE 300 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal Report ETE 300 PDFETE 18No ratings yet
- Micro-Strip Antennas ExplainedDocument22 pagesMicro-Strip Antennas Explainedaarthi100No ratings yet
- A Study of Different Feeding Mechanisms in Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument5 pagesA Study of Different Feeding Mechanisms in Microstrip Patch AntennaWARSE JournalsNo ratings yet
- Microstrip AntennaDocument6 pagesMicrostrip AntennaJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Optimization of Microstrip Patch Antenna-A Basic OverviewDocument11 pagesBandwidth Optimization of Microstrip Patch Antenna-A Basic OverviewEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Microstrip Patch Antenna ArrayDocument6 pagesThesis On Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrayangelarobertswilmington100% (1)
- Metodos de DiseñoDocument4 pagesMetodos de DiseñoAlex Jarrin RNo ratings yet
- E Shaped Patch Antennaanalysis IJERTV3IS120861Document4 pagesE Shaped Patch Antennaanalysis IJERTV3IS120861BT20ECE109Nikhil VanjariNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report: Microstrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationsDocument26 pagesSeminar Report: Microstrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationsDebdeep Sarkar100% (1)
- Symetric 1layer 6 M Controled 5GHz 2 - Parameter ListDocument1 pageSymetric 1layer 6 M Controled 5GHz 2 - Parameter ListdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Phase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LineDocument7 pagesPhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinePhase Shifter Loaded LinedhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromDocument23 pagesGas ChromMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Wireless Sensor Network Motes: Sachin Gajjar Nilav Choksi Mohanchur Sarkar Kankar DasguptaDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of Wireless Sensor Network Motes: Sachin Gajjar Nilav Choksi Mohanchur Sarkar Kankar DasguptadhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Antenna Measurements in The Presence of Multipath Waves: Progress in Electromagnetics Research PIER 30, 157-178, 2001Document22 pagesAntenna Measurements in The Presence of Multipath Waves: Progress in Electromagnetics Research PIER 30, 157-178, 2001dhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- High-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsDocument3 pagesHigh-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Rectennas for Wireless Energy HarvestingDocument4 pagesRectennas for Wireless Energy Harvestingvmbharani9740No ratings yet
- A Design of Rectangular Linear Polarized Microstrip Patch Antenna at 1 GHZDocument3 pagesA Design of Rectangular Linear Polarized Microstrip Patch Antenna at 1 GHZdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- High-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsDocument3 pagesHigh-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Wideband Circularly Polarized Array Using Linearly Polarized ElementsDocument12 pagesWideband Circularly Polarized Array Using Linearly Polarized ElementsSree HariNo ratings yet
- A Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array With Butler MatrixDocument4 pagesA Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array With Butler MatrixdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Analusis and Design of A Microtrip Reflectarray Using Patches of Variable SizeDocument4 pagesAnalusis and Design of A Microtrip Reflectarray Using Patches of Variable SizedhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Wideband Circularly Polarized Array Using Linearly Polarized ElementsDocument12 pagesWideband Circularly Polarized Array Using Linearly Polarized ElementsSree HariNo ratings yet
- A Novel Compact Butler Matrix Without Phase Shifter: Ge Tian, Jin-Ping Yang, and Wen WuDocument3 pagesA Novel Compact Butler Matrix Without Phase Shifter: Ge Tian, Jin-Ping Yang, and Wen WudhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- High-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsDocument3 pagesHigh-Efficiency Harmonically-Terminated Rectifier For Wireless Powering ApplicationsdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.: (Reciprocal) Directional CouplersDocument11 pagesLecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.: (Reciprocal) Directional CouplersdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Zhan 2001Document5 pagesZhan 2001dhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- PT-MT Kurs NotuDocument300 pagesPT-MT Kurs NotuBahadir TekinNo ratings yet
- Rfid 2008Document12 pagesRfid 2008Mitch NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Lý Thuyết Và Kỹ Thuật Anten - Phan AnhDocument546 pagesLý Thuyết Và Kỹ Thuật Anten - Phan AnhHocVanHanh91% (11)
- Microstrip Patch Antenna DesignDocument19 pagesMicrostrip Patch Antenna DesignNgoc Lan Nguyen50% (2)
- Circuit Simulation of Varactor Loaded Line Phase Shifter: V C V CDocument4 pagesCircuit Simulation of Varactor Loaded Line Phase Shifter: V C V CdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Metamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedDocument94 pagesMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImprovedMetamaterial Inspired ImproveddhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 coupler Lecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerDocument66 pagesLecture 8 coupler Lecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerLecture 8 couplerdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Zhan 2001Document5 pagesZhan 2001dhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Microstrip PatchDocument4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Microstrip PatchdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- Report PDFDocument21 pagesReport PDFdhvbkhnNo ratings yet
- MRF24J40 Data SheetDocument156 pagesMRF24J40 Data SheetnntuonNo ratings yet
- EW430 CompilerReferenceDocument312 pagesEW430 CompilerReferenceMurali ThangarajNo ratings yet
- JSS Academy Electrical Engineering AssignmentDocument2 pagesJSS Academy Electrical Engineering Assignmentamit621988No ratings yet
- IEEE Device Numbers & Functions GuideDocument2 pagesIEEE Device Numbers & Functions GuideIman MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- ADXL337Document17 pagesADXL337Anlles ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in AC CircuitsDocument75 pagesQuestion Bank in AC CircuitsJose Ricardo Garfin Jr.50% (10)
- C POWER ACB Manual PDFDocument172 pagesC POWER ACB Manual PDFVishab Fred80% (5)
- Digital DDS Generator With AD9850 Chip DDS From SQ5RWQDocument4 pagesDigital DDS Generator With AD9850 Chip DDS From SQ5RWQag1tatorNo ratings yet
- 1000 KVA Type Test From ERDA, IndiaDocument9 pages1000 KVA Type Test From ERDA, IndiasaikatNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Liquid Level SensorDocument24 pagesUltrasonic Liquid Level Sensormadhuri12345678No ratings yet
- Solenoid and CoilsDocument6 pagesSolenoid and CoilsBalgo BalgobinNo ratings yet
- T1 Datasheet DZ BZX55C-SeriesDocument3 pagesT1 Datasheet DZ BZX55C-SeriesAlex GrigorieNo ratings yet
- Sensor Signal ConditioningDocument366 pagesSensor Signal Conditioningwagnalang1639100% (1)
- Solera Opus v1.2.0 Error ListDocument3 pagesSolera Opus v1.2.0 Error ListMickey A CouvertierNo ratings yet
- HT capacitor bank technical specifications comparisonDocument2 pagesHT capacitor bank technical specifications comparisonJAY PARIKHNo ratings yet
- Circuit Construction Kit Ac Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enDocument4 pagesCircuit Construction Kit Ac Virtual Lab HTML Guide - enkavithaNo ratings yet
- Build A High-Frequency Portable Spectrum Analyzer Using Two Filter ICsDocument5 pagesBuild A High-Frequency Portable Spectrum Analyzer Using Two Filter ICsagmnm1962No ratings yet
- NOR Logic - WikipediaDocument7 pagesNOR Logic - WikipediaRangeen DuniyaNo ratings yet
- Abb Artu 2014Document404 pagesAbb Artu 2014haldrik5966No ratings yet
- Fire PumpDocument8 pagesFire PumpMani KumarNo ratings yet
- Mini Project Report-2Document26 pagesMini Project Report-2Remya Ramakrishnan0% (2)
- How to perform basic calculations on an electronic calculatorDocument2 pagesHow to perform basic calculations on an electronic calculatorProduccion TAMNo ratings yet
- SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR PRINCIPLESDocument21 pagesSYNCHRONOUS MOTOR PRINCIPLEStesfuNo ratings yet
- Handout For Electronics Electrical Engineering & MeasurementDocument2 pagesHandout For Electronics Electrical Engineering & MeasurementscribdrayanNo ratings yet
- AecDocument8 pagesAecGanesan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Amplifier ExperimentDocument22 pagesHigh Frequency Amplifier Experimentthuantndtvt2883No ratings yet
- 0 IntroductionDocument10 pages0 Introductionmahir faisalNo ratings yet
- Transformerless Split Inductor Neutral Point Clamped Three Level PV Grid Connected InverterDocument6 pagesTransformerless Split Inductor Neutral Point Clamped Three Level PV Grid Connected InvertersivalingakumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety in Mines: Work Regulations 1989. Approved Code of PracticeDocument21 pagesElectrical Safety in Mines: Work Regulations 1989. Approved Code of PracticeAyu Wanda SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Solar Mobile Charging NewDocument15 pagesWireless Solar Mobile Charging New18WJ1A03L4 RAVI MechNo ratings yet
- 4TWX4036 Service FactsDocument4 pages4TWX4036 Service FactsAlejandro OrdoñezNo ratings yet