Professional Documents
Culture Documents
System Testing and Implementation
Uploaded by
khattak123456Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
System Testing and Implementation
Uploaded by
khattak123456Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
7. SYSTEM TESTING AND IMPLEMENTATION
System testing and implementation is the last step in software development.
So this last chapter discusses the system testing and implementation.
7.1 System Testing
System testing is an essential step for the development of a reliable and error-free
system. Once source code has been generated, software must be tested to uncover and
correct as many errors as possible before delivery to your customer. Your goal is to
design a series of test cases that have a high likelihood finding errors but how, there
are different methods that provides a systematic guidance for designing tests that,
Exercise the internal logic of software components, and
Exercise the input and output domains of the program to uncover errors in the
program function, behaviour, and performance.
Software testing is a crucial element of software quality assurance and
represents the ultimate review of specification, design, and code generation.
The work product is a set of test cases designed to exercise both internal logic
and external requirements is designed and documented, expected results are
defined, and actual results are recorded. The primary objectives of testing
software are to execute a program with the intent of finding an error; a good
test case will find an as-yet-undercover error, and a successful that uncover an
as-yet-undercover error.
7.2 Testing Strategies
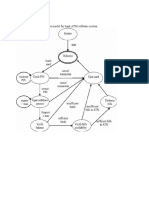
The basic strategies that were used for testing were following
• Specification Testing
• Black Box Testing
• White Box Testing
• Regression Testing
• Acceptance Testing
• Assertion Testing
• Unit Testing
Sales Tracking system
48
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
• System Testing
Unit testing
Module testing
Subsys testing
System testing
Acceptance testing
Component testing Integration testing User testing
Fig 7.1 Testing Strategies Diagram
7.2.1 Specification Testing
Even if the code testing is performed exclusively, it doesn’t ensure
against program failure. Code testing doesn’t answer whether the code meets
the agreed specifications document. It doesn’t also determine whether all
aspects of the design are implemented. Therefore, examining specifications
stating what program should do and how it should behave under various
conditions performs specification testing. Test cases are developed to test the
Sales Tracking system
49
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
range of values expected including both valid and invalid data. It helps in
finding discrepancies between the system and its original objective. During
this testing phase, all efforts were made to remove programming bugs and
minor design faults.
7.2.2 Black Box Testing
Black-box testing is conducted at the software interface. In Black Box
testing only the functionality was tested without any regard to the code
written. If the functionality, which was expected from a component, is
provided then black box testing is completed.
7.2.3 White Box Testing
White-box testing, sometimes called glass-box testing is a test case
design method hat uses the control structure of the procedural design to derive
test cases. In White Box testing internal code written in every component was
tested and it was checked that the code written is efficient in utilizing various
resources of the system like memory or the utilizing of input output
7.2.4 Regression Testing
In Regression testing the software was tested against the boundary
conditions. Various input fields were tested against abnormal values and it was
tested that the software does not behave abnormally at any time.
7.2.5 Acceptance Testing
In acceptance testing the software was checked for completeness that it
is ready. Normally the quality assurance department performs the acceptance
testing that the software is ready and can be exported.
7.2.6 Assertion Testing
Sales Tracking system
50
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
In assertion testing the software is tested against the possible
assertions. Assertions are used to check the program and various locations that
whether the state of the program at a particular point is the same as expected
or not.
7.2.7 Unit Testing
In unit testing we checked that all the individual components were
working properly. Before integration of the entire components unit testing is
essential because it gives a confidence that all the components individually are
working fine and ready to be integrated with the other ones.
7.2.8 System Testing
When all the units were working properly and unit testing was
performed then comes the time for system testing where we checked all the
integrated components as a whole and looked for possible discrepancies,
which could have arisen after the integration.
7.3 System Evaluation
The objectives of the system evaluation are to determine whether the desired
objective has been accomplished or not. Determining the merits or demerits of the
proposed system over the existing is also covered in the system evaluation. This is
concerned with the detailed study of the developed system, from implementation
point view. At the end, some suggestions for the improvement of the system are
coded.
7.4 Implementation
This phase consists of bringing the new system into operation and turning it over
the users. Briefly it involves following steps.
7.4.1 Training
It involves
Sales Tracking system
51
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
• User Groups.
• Administrators.
7.4.2 Installation of Computer Equipments
It involves
• Location.
• Power Supply.
• Space Requirement.
7.4.3Testing the New System
System testing of the developed system was performed in these three steps.
7.4.2.1 Unit Testing
In unit testing the different modules of software are tested
independently errors. This helps in locating errors, in coding and logic that
were contained within a particular module. For example testing of each tab
canvas individually for validates entries.
7.4.2.2 Integrated Testing
After unit testing, combined testing of all modules was carried out.
The purpose was to determine that all the modules are correctly interacting
with each other.
7.4.2.3 System Testing
Final testing was done on the entire system to check that whether
the desired specification and requirements are met or not. The main aim
here was to determine the inconsistencies in the developed system. Hence
the whole system was tested.
7.5 Put the New System into Operation
At this point, a final dress rehearsal sometimes runs. It is done in the following
ways.
Sales Tracking system
52
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
7.5.1 Direct/Crash Conversion
In this approach, an entire new system is installed. The old system is
completely dismantled, leaving the organization suddenly to rely on the new
system alone. The advantage of the crash conversion is that when the old
system is seriously inadequate or radically different from the new system and
when the conversion will be so rapid that it will not severely disrupt
operations. The crash conversion also has disadvantages i.e. the crash
conversion is risky, and even for minor problem can seriously delay the
implementation schedule. Careful planning and attention to detail are
necessary for a successful crash conversion.
7.5.2 Pilot Conversion
In this approach, the old manual system is replaced by the newly
computerized system stepwise. That is one subsystem is chosen as the lead or
prototype system and implemented before all others. Only when that
subsystem is completely operational can conversion of the next system can be
considered. This approach, reduce the chances of sudden ad total system
failure. But it may take along time and money than other approaches.
7.5.3 Parallel Conversion
In this approach the proposed system run concurrently with the
existing system, processing exactly the same data. If the new system has been
properly implemented, its results should be identical to the results of the
existing system. The parallel conversion should be conducted for a complete
processing cycle. The old system is available as a backup in the case of failure
of the new one. Result obtain from the new system can be compared to that
old system.
7.6 Proposed Change Over
Peeing in view the sensitivity of matter/data. It is suggested that system should
be run parallel to manual system.
Sales Tracking system
53
Chapter: 7 System Testing and Implementation
Sales Tracking system
54
You might also like
- Insurance SRS 1Document31 pagesInsurance SRS 1Akhil Sai100% (1)
- Final Payroll Management SystemDocument40 pagesFinal Payroll Management SystemLovely Jigs80% (10)
- ELMS Project ReportDocument42 pagesELMS Project ReportLuckinsi Samuel100% (1)
- Employee Appraisal System - DesignDocument20 pagesEmployee Appraisal System - Designanirudhgupta0989% (9)
- Different Diagrams of Online Shopping SystemDocument9 pagesDifferent Diagrams of Online Shopping SystemRXT STORMNo ratings yet
- Online Crime Managment System Project ReportDocument65 pagesOnline Crime Managment System Project ReportAnkitNo ratings yet
- Crime File Management System Project Report JAVADocument153 pagesCrime File Management System Project Report JAVAYaikob Kebede100% (2)
- A Project Report ON Crime Reporting: (HCL Info System LTD)Document89 pagesA Project Report ON Crime Reporting: (HCL Info System LTD)Amit Gupta82% (17)
- An Online Tax Management SystemDocument47 pagesAn Online Tax Management SystemThembo Jimmy87% (15)
- Srs of Student Result Management System PDFDocument14 pagesSrs of Student Result Management System PDFA Royal TrapNo ratings yet
- Hospital ManagementDocument36 pagesHospital ManagementraviNo ratings yet
- University Management SystemDocument17 pagesUniversity Management SystemPrithvi Raj0% (1)
- Library Management SystemDocument16 pagesLibrary Management SystemnoorNo ratings yet
- Online Crime Reporting System ReportDocument37 pagesOnline Crime Reporting System ReportTony Mwasaga100% (3)
- The History of 3D AnimationDocument11 pagesThe History of 3D AnimationAariff AlaviNo ratings yet
- Section 2 QuizDocument5 pagesSection 2 Quizdaemon29100% (1)
- Practical-1: AIM: Project Definition and Objective of The Specified Module and PerformDocument6 pagesPractical-1: AIM: Project Definition and Objective of The Specified Module and PerformMAITRY NIRAVBHAI SHAHNo ratings yet
- Employee Management & Attendance SystemDocument103 pagesEmployee Management & Attendance SystemAnonymous NmKcrDPPrNo ratings yet
- Complaint Management SystemDocument69 pagesComplaint Management SystemChaithra kNo ratings yet
- Online Bus Booking System PDFDocument69 pagesOnline Bus Booking System PDFArslan Syed90% (10)
- Project Report SampleDocument62 pagesProject Report SampleHimanshu Soni0% (1)
- OOSE Crime Management System PDFDocument35 pagesOOSE Crime Management System PDFsamuel100% (1)
- ERP System Documentation 123Document75 pagesERP System Documentation 123Victor KariukiNo ratings yet
- Online Crime Reporting System SypnosisDocument7 pagesOnline Crime Reporting System SypnosisShaikh Hasim AliNo ratings yet
- SRS Payroll Management SystemDocument9 pagesSRS Payroll Management SystemVaishnavi/ven .P100% (2)
- Synopsis of ProjectDocument24 pagesSynopsis of Projectannu priya100% (1)
- Online Job PortalDocument21 pagesOnline Job PortalDaring Aditya75% (16)
- Srs On Online Booking System PDFDocument9 pagesSrs On Online Booking System PDFZeeshan AbbasNo ratings yet
- 8-Benefits and Risks of Object Oriented Development-16-Dec-2019Material - I - 16-Dec-2019 - 7 - The - Benefits - of - Object-Oriented - DevelopmentDocument7 pages8-Benefits and Risks of Object Oriented Development-16-Dec-2019Material - I - 16-Dec-2019 - 7 - The - Benefits - of - Object-Oriented - DevelopmentAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv: 4.1 System Architecture: Satellite-Based NavigationDocument27 pagesUnit-Iv: 4.1 System Architecture: Satellite-Based NavigationAli Jama100% (1)
- Complete Final Project GuidelinsDocument151 pagesComplete Final Project GuidelinsZeeshan Anwer50% (2)
- Use Case Model of Crime Management SystemDocument15 pagesUse Case Model of Crime Management SystemMuzaffar Salik80% (5)
- SRS Document For Tourism PortalDocument16 pagesSRS Document For Tourism PortalArchana ra50% (2)
- coLLEGE Management SystemDocument7 pagescoLLEGE Management Systemzainab zainabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Online Car Rental System: Chapter-1Document29 pagesIntroduction To Online Car Rental System: Chapter-1RajaNo ratings yet
- SRS For Andriod ProjectDocument10 pagesSRS For Andriod ProjectAyan Basak90% (10)
- Crime Record Managment SystemDocument18 pagesCrime Record Managment Systemtsegab bekeleNo ratings yet
- Online Car Rental SystemDocument42 pagesOnline Car Rental Systempython developer100% (1)
- DFD Diagrams For Online ExamDocument12 pagesDFD Diagrams For Online Examprathap0% (1)
- Conference Management System 10Document4 pagesConference Management System 10vidhyasiva8350% (2)
- A Software Engineering Mini Project On Online Trading SystemDocument29 pagesA Software Engineering Mini Project On Online Trading SystemSai RamNo ratings yet
- Project Report Online Library Management SystemDocument18 pagesProject Report Online Library Management SystemVijith ChissNo ratings yet
- Drawbacks of The Existing SystemDocument7 pagesDrawbacks of The Existing SystemSachin Mohite100% (1)
- Fast Food Billing SystemDocument6 pagesFast Food Billing SystemSubhadeep ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of Inventory Management SystemDocument29 pagesSynopsis of Inventory Management SystemSANDIP DHARNo ratings yet
- Crop Management SystemDocument85 pagesCrop Management SystemThej VîsHñu100% (1)
- Web Services On Mobile Platform DocumentationDocument18 pagesWeb Services On Mobile Platform Documentationmukesh427100% (4)
- Software Engineering ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONDocument5 pagesSoftware Engineering ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONAkshatha ShettyNo ratings yet
- Dental Clinic SrsDocument8 pagesDental Clinic SrsAnkit Patel100% (2)
- SRS Student ManagementDocument16 pagesSRS Student ManagementShuja Shabbir100% (1)
- Electricity Bill Project ReportDocument77 pagesElectricity Bill Project ReportRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Hostel Management SystemDocument30 pagesHostel Management SystemFarwa50% (2)
- Project Management System AbstractDocument2 pagesProject Management System AbstractKang فوزي40% (5)
- Functional & Non-Functional RequirementsDocument12 pagesFunctional & Non-Functional RequirementsAminah ShahzadNo ratings yet
- TESTINGDocument10 pagesTESTINGAmodha InfoTech100% (1)
- Testing: E-Commerce Application TestingDocument12 pagesTesting: E-Commerce Application TestingHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH - 7Document39 pagesCH - 7TedlamillionNo ratings yet
- Develop Business Process Model For Bank ATM Software SystemDocument14 pagesDevelop Business Process Model For Bank ATM Software SystemFitawu TekolaNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument5 pagesTestingLal PrakashNo ratings yet
- Module 4 NotesDocument29 pagesModule 4 NotesSuchith ReddyNo ratings yet
- System TestingDocument3 pagesSystem TestingLakshmi AvadhanulaNo ratings yet
- UatDocument3 pagesUatAhmad BadaraniNo ratings yet
- How To Unlock HR User in Oracle Database 12cDocument11 pagesHow To Unlock HR User in Oracle Database 12camit_iihtdhn280No ratings yet
- Kelly CompDocument529 pagesKelly Compzerophick1No ratings yet
- A en GB - System 800xa Course GB850 PCDeviceLib SV5Document2 pagesA en GB - System 800xa Course GB850 PCDeviceLib SV5vantaipcNo ratings yet
- VAT Code and Percent Using BRF+Document8 pagesVAT Code and Percent Using BRF+Yazeed_GhNo ratings yet
- Part 4 - Contents: Cctalk Generic SpecificationDocument27 pagesPart 4 - Contents: Cctalk Generic SpecificationomottoNo ratings yet
- 16-Bit MCU and DSC Programmer's Reference Manual PDFDocument520 pages16-Bit MCU and DSC Programmer's Reference Manual PDFHabogillNo ratings yet
- Az 900Document135 pagesAz 900nombreNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Original Size of Objects in Digital Image by MatlabDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Original Size of Objects in Digital Image by MatlabJans Hendry100% (2)
- Xsquare Userman 1.00 EN 20120626 Web PDFDocument30 pagesXsquare Userman 1.00 EN 20120626 Web PDFLaurentiu IacobNo ratings yet
- Ucs Faults RefDocument866 pagesUcs Faults Refconnect2praveenNo ratings yet
- And Dev DatabaseDocument30 pagesAnd Dev DatabaseAnna LaClairNo ratings yet
- Module 1 PDFDocument49 pagesModule 1 PDFAjayNo ratings yet
- OS Lab ManualDocument27 pagesOS Lab ManualMohammed BilalNo ratings yet
- SasmithabanuDocument4 pagesSasmithabanuAnonymous 548VnpgrNo ratings yet
- Question Solution AC14 SolDocument127 pagesQuestion Solution AC14 SolMuhammad AshfaqNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Complex Systems, This Issue's Hot TopicDocument5 pagesReliability of Complex Systems, This Issue's Hot TopicShanmugeshwari MuthiahNo ratings yet
- Navisworks File FormatsDocument4 pagesNavisworks File FormatsaswanikaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Questions On Functions1Document12 pagesICSE Questions On Functions1Harsh100% (1)
- New ABAP Syntax - Training MaterialDocument81 pagesNew ABAP Syntax - Training MaterialTanuja PandharpureNo ratings yet
- 1requirements Elicitation1Document15 pages1requirements Elicitation1Jason LoNo ratings yet
- Cross Browser TestingDocument17 pagesCross Browser TestingKaushik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- "Examination Management System": Project Report OnDocument31 pages"Examination Management System": Project Report OnJackNo ratings yet
- Report On Mini ProjectDocument51 pagesReport On Mini ProjectAjay JachakNo ratings yet
- QUBO Tutorial Version1Document46 pagesQUBO Tutorial Version1Khalil KafrouniNo ratings yet
- Kivy Cookbook - Sample ChapterDocument33 pagesKivy Cookbook - Sample ChapterPackt PublishingNo ratings yet
- PHP Compile TestDocument12 pagesPHP Compile TestgoharhussainNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Questions On ThinApp - VMware ThinApp Blog - VMware BlogsDocument1 pageTop 10 Questions On ThinApp - VMware ThinApp Blog - VMware BlogsYamuna DeviNo ratings yet