Professional Documents
Culture Documents
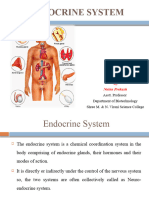
Glands
Uploaded by
Julia Gargano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesEndocrine glands are ductless glands that secrete hormones to regulate metabolic functions. Examples include the pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, and pancreas glands. The endocrine system uses hormones as slow-acting chemical messengers, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters as fast-acting chemical messengers. Hormones require receptor sites on target cells in order to take effect and regulate functions like blood sugar levels and body temperature through positive and negative feedback mechanisms.
Original Description:
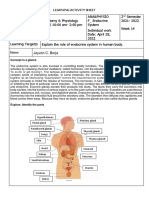
WHAT ARE YOU GLANDS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEndocrine glands are ductless glands that secrete hormones to regulate metabolic functions. Examples include the pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, and pancreas glands. The endocrine system uses hormones as slow-acting chemical messengers, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters as fast-acting chemical messengers. Hormones require receptor sites on target cells in order to take effect and regulate functions like blood sugar levels and body temperature through positive and negative feedback mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesGlands
Uploaded by
Julia GarganoEndocrine glands are ductless glands that secrete hormones to regulate metabolic functions. Examples include the pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, and pancreas glands. The endocrine system uses hormones as slow-acting chemical messengers, while the nervous system uses neurotransmitters as fast-acting chemical messengers. Hormones require receptor sites on target cells in order to take effect and regulate functions like blood sugar levels and body temperature through positive and negative feedback mechanisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
oEndocrine glands are
nDuctless glands that secrete hormones to regulate metabolic
functions
nTheir function is to work in conjunction with the nervous system to
control body activities
oExamples
nPituitary, adrenal, thyroid, pancreas
oEndocrine system is a slow acting regulatory system that uses
hormones as chemical messenger
oNervous system is a quick acting regulatory system that uses
neurotransmittors as chemical messenger
oAre chemical messengers that may stimulate or inhibit actions
oAmounts:
nHypersecretion is too much hormone
nHyposecretion is too little hormone
oHormones have no effect until they reach their target organs
oExocrine glands ducted gland that delivers secretions to target site
via ducts; effects are produced in regions of glands
oExamples:
nSweat
nSalivary
nsebaceous
What do hormones need in order to work?
oReceptor site on target cell
compare nonsteroid hormones to steroid hormones
oNonsteroid hormones
oMade of peptides (amino acids)
oBind to receptor molecule on outside of target cell membrane (causes
change)
oBiochemical changes occur inside cell
oCalled 1st messenger because it travels from gland to target organ
o1st messenger releases AMP (2nd messenger)
oAMP activates enzymes that change cells activities
oSteroid hormones
oHormones made of lipids
oCause changes in target cells by interacting with structures inside
cells
oSmall and can easily pass through membrane
nCan enter almost any cell of the body
oAffect only cells with appropriate receptor molecules
oCause change by gene regulation, causing section of DNA to turn on
oPositive feedback
Response results in increase production of hormone
Increase body temp increase temp
Increase blood sugar levels increase release of insulin
oNegative feedback
nResponse results in decrease or cessation of production of hormone
nInsulin causes blood sugar to reach desired level then production of
insulin stops
Describe how feedback mechanisms control blood sugar
oEat a meal increase blood sugar level
oIncreased blood sugar level causes pancreas to secrete insulin
oInsulin causes decrease in blood sugar stop release of insulin
Exocrine
Exocrine system: The exocrine system is a term that is sometimes used
to refer to the large variety of exocrine glands and their functions in the
human body. The exocrine system produces and excretes many different
types of secretions through ducts. These secretions flow to the surface of
the body or to the lining of a hollow structure in the body. The exocrine
secretions are involved in many important functions, such as sweating,
digestion and lubricating the eyes. There are many types of exocrine
glands in the exocrine system. Examples include the salivary glands, liver,
stomach, prostate, lacrimal glands, pancreas, sweat glands, sebaceous
glands, and mammary glands.
You might also like
- 5-17 Endocrine HandoutDocument10 pages5-17 Endocrine HandoutJohn Lawrence YbanezNo ratings yet
- Investigations of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesInvestigations of Endocrine SystemCharity ChilongaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Mechanism of Endocrine System, Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesFeedback Mechanism of Endocrine System, Reproductive Systemnhel gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-1Document90 pagesEndocrine System-1markmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Learning JournalDocument82 pagesLearning JournalAnnapurna RavelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Endocrinologyjimmybarack27No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endocrine SystemDocument45 pagesIntroduction To The Endocrine Systemវ៉ុន ដាលីន Von DalinNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS PROPER BestDocument370 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS PROPER BestronaronixstheboyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument95 pagesEndocrine SystemUmar Ilyasu JibrilNo ratings yet
- 3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansDocument35 pages3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansIMELDANo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Problem On EndocrineDocument48 pagesCare of Clients With Problem On EndocrineAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument133 pagesEndocrine SystemAudrey KenfacNo ratings yet
- Colegio Gimnasio Campestre San Sebastián: Docente: Edith Carolina Conde CarrilloDocument4 pagesColegio Gimnasio Campestre San Sebastián: Docente: Edith Carolina Conde CarrilloEdith CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Bio 225 Concordia NotesDocument5 pagesBio 225 Concordia NotesretterateNo ratings yet
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDocument3 pagesLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 10 Edition: Assessment of Endocrine System Key PointsDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System in FinfishesDocument43 pagesEndocrine System in FinfishesMisbah SayyedNo ratings yet
- Psychology AssignmentDocument6 pagesPsychology Assignmentbijina AnnNo ratings yet
- 439 en Intro 1Document74 pages439 en Intro 1Omotosho DavidNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyDocument20 pagesEndocrine System: 3.6 Functions, Definitions & VocabularyD AngelaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument30 pagesEndocrine SystemBrenda Domaneo BaseNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Endocrinology: H. KibichoDocument370 pagesEndocrinology Endocrinology: H. KibichoMursal RashidNo ratings yet
- 1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineDocument36 pages1 - Endocrine 1 (Introduction) - MedicineBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Consists of Glands That Secrete Chemical Called To Control Various Body ProcessesDocument23 pagesThe Endocrine System: Consists of Glands That Secrete Chemical Called To Control Various Body ProcessesSnhs SpsNo ratings yet
- Endocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Document61 pagesEndocine System Physiology 20-4-2020Farah AljayyousiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesEndocrine SystemNada DardeerNo ratings yet
- Exo and EndoDocument4 pagesExo and EndoJimboy MaglonNo ratings yet
- Natural EndocrineDocument121 pagesNatural EndocrinetanasedanielaNo ratings yet
- Activity 16 HormonesDocument16 pagesActivity 16 HormonesKendrix Aguiluz FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesEndocrine Systemkevin maheshNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PharmacologyDocument87 pagesEndocrine PharmacologyHarrison Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical MessengersDocument10 pagesEndocrine Glands The Producers of Chemical Messengersahmed100% (1)
- The Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Endocrine System Anaphy ReviewAdiel CalsaNo ratings yet
- Our Powerpoint On Homeostasis and Hormonal ControlDocument54 pagesOur Powerpoint On Homeostasis and Hormonal ControlNoel HymanNo ratings yet
- A Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesA Module On Human Body: Lesson V: The Endocrine Systemapi-3731377No ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Part 2Document31 pagesEndocrine System - Part 2Maryem NabawiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System and Hormones 1Document41 pagesEndocrine System and Hormones 1Jizaille Audrey Ho QuirongNo ratings yet
- CH 45Document9 pagesCH 45homamunfatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology DictionaryDocument7 pagesEndocrine Glands - Definition Examples Function Biology Dictionaryrania khanNo ratings yet
- Body RegulationsDocument36 pagesBody RegulationsZyra AbordsNo ratings yet
- Aminal BehaviorDocument6 pagesAminal BehaviorMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- System Glands Hormone: NeurotransmittersDocument6 pagesSystem Glands Hormone: NeurotransmittersShaheryar HasanNo ratings yet
- BT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatiDocument17 pagesBT101 - Introductory Biology (Endocrine/Exocrine) DR - Navin Gupta Dept of BSBE, IIT GuwahatirechinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.Document27 pagesLecture 1.abdelrazeq zarourNo ratings yet
- 07 Animal Physiology - Endocrine SystemDocument48 pages07 Animal Physiology - Endocrine SystemJerome Ysrael ENo ratings yet
- Chemical CoordinationDocument34 pagesChemical CoordinationThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination X-3Document60 pagesControl and Coordination X-3naveenshankarjee3No ratings yet
- PD22 Hap1 L03Document33 pagesPD22 Hap1 L03Ka Yan LAUNo ratings yet
- Introduction Endocrine Physiology 2Document52 pagesIntroduction Endocrine Physiology 2IshaqNo ratings yet
- Anatomy An D Physiology Endocrine SystemDocument53 pagesAnatomy An D Physiology Endocrine SystemMARIETA OPINIONNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportrtvb77smjhNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisDocument7 pagesEndocrine System (Vertebrate) : HomeostasisKaleem UllahNo ratings yet
- AnaPhysio Endocrine System Borja, JayvenDocument4 pagesAnaPhysio Endocrine System Borja, JayvenJboar TbenecdiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands Mini ProjectDocument7 pagesEndocrine Glands Mini ProjectJoy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Document34 pagesEndocrine System: Dr. Annette M. Parrott GPC BIOL1612Nathan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesEndocrine Systempranutan739No ratings yet
- Glandular SystemDocument18 pagesGlandular SystemAashishNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Scientific Posts: Csir-National Botanical Research InstituteDocument10 pagesScientific Posts: Csir-National Botanical Research InstituteYogesh KapilNo ratings yet
- Molecular ConnectionDocument4 pagesMolecular ConnectionCaryl Louise ParlanNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Steroid Hormone Receptor and Cell Membrane ReceptorDocument46 pagesDifference Between Steroid Hormone Receptor and Cell Membrane ReceptorJiten SharmaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and TeratologyDocument31 pagesGenetics and Teratologypandem soniyaNo ratings yet
- Glycated Albumin-A ReviewDocument12 pagesGlycated Albumin-A ReviewfarzanaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 NotesDocument54 pagesExam 1 NotesAnonymous If9p21kwZKNo ratings yet
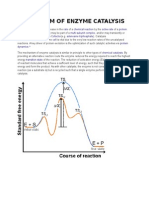
- Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis MadhuDocument9 pagesMechanism of Enzyme Catalysis MadhumengelhuNo ratings yet
- 499-Article Text-706-1-10-20220526-MutoniDocument8 pages499-Article Text-706-1-10-20220526-MutoniChristine MutoniNo ratings yet
- Bio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/05/2018Document15 pagesBio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/05/2018Atif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- CellPress Heliyon Protocol TemplateDocument9 pagesCellPress Heliyon Protocol TemplateSri HaryatiNo ratings yet
- Herculanum (Psicografia Wera Krijanowskaia - Espirito J. W. Rochester)Document52 pagesHerculanum (Psicografia Wera Krijanowskaia - Espirito J. W. Rochester)Alexsandro ClaudinoNo ratings yet
- Cici OralPresenterDocument11 pagesCici OralPresenterCiyciyRizhqhiy Ieyngiend BahageachellaluwNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction From Blood: Preparation of BuffersDocument2 pagesDna Extraction From Blood: Preparation of Buffershely shahNo ratings yet
- 1107 FullDocument107 pages1107 FullClara JensNo ratings yet
- Caspase 1 and Procaspase 1Document9 pagesCaspase 1 and Procaspase 1Audhy RaflesNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Midterm ReviewDocument38 pagesAP Bio Midterm ReviewCandice LongNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesLesson Planapi-576945442No ratings yet
- B&B List of VideosDocument22 pagesB&B List of VideosRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Milestones in Genetic EngineeringDocument2 pagesMilestones in Genetic EngineeringPaavni Sharma100% (4)
- Myo 5 ADocument26 pagesMyo 5 Aapi-221640706No ratings yet
- Data and Analysis For pBLUDocument2 pagesData and Analysis For pBLUS. SpencerNo ratings yet
- Paper I Unit Ii:-Gene Expression Rna Polymerase DefinitionDocument53 pagesPaper I Unit Ii:-Gene Expression Rna Polymerase DefinitionRithwik ZNo ratings yet
- Can We Live ForeverDocument4 pagesCan We Live ForeversherryNo ratings yet
- Materi KolinergikDocument62 pagesMateri KolinergikWira KrisnaNo ratings yet
- Nextera DNA Sample Prep Guide 15027987 ADocument40 pagesNextera DNA Sample Prep Guide 15027987 Asramirez77No ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- Human Genome ProjectDocument57 pagesHuman Genome ProjectIsma Velasco100% (1)
- 4 - The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins: © 2017 W. H. Freeman and CompanyDocument43 pages4 - The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins: © 2017 W. H. Freeman and CompanyRegis BetaNo ratings yet
- Site Directed MutagenesisDocument77 pagesSite Directed MutagenesisDanny Sebastian Thomas100% (1)
- Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesCell MembraneJenica CruzNo ratings yet