Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BBT 2204 Lecture1
Uploaded by
Marl Mwegi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageA system is a set of components that interact to accomplish some objectives. It can consist of tools, machines, procedures & people and required order and management. -Ve feedback allows system to revert back to its initial state.
Original Description:
Original Title
bbt 2204 Lecture1.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA system is a set of components that interact to accomplish some objectives. It can consist of tools, machines, procedures & people and required order and management. -Ve feedback allows system to revert back to its initial state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageBBT 2204 Lecture1
Uploaded by
Marl MwegiA system is a set of components that interact to accomplish some objectives. It can consist of tools, machines, procedures & people and required order and management. -Ve feedback allows system to revert back to its initial state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
BBT 2204:
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Overview of information system
approach
Terminologies Used
Introduction
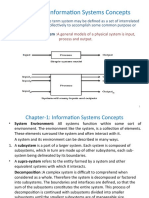
1. System---Its a set of components that interact to accomplish
some objectives. It can consist of tools, machines, procedures
& people & required order & management.
2. Boundaries---A boundary constitute of features that delimit
(define) or mark the extent of a system. I.e. separate those
things, which are part of systems from those outside system.
The things outside system constitute system environment.
System boundary provides scope for the system.
3. Environment--- the things outside the system, which may
affect what, goes on in the system, or which maybe affected by
what goes on inside the system.
4. System Objective---The purpose or goal of the system for
which it exists to achieve. A system may have one or several
objectives. For a CBIS, the system basically is designed to
transform data into information & distribute / disseminate the
information to the intended users.
5. Process and transformation---most systems are involved in
some transformation of something i.e. changing the state of
something into something else.
6. Inputs and outputs --- a system communicates with its
environment interims of input to and output from system i.e.
system transforms input into outputs.
7. Subsystems an inherent (inbuilt) property of systems where
large systems are seen to be made up of smaller parts known as
sub-systems. The study of systems involves the composing or
factoring them into small parts, resulting in a hierarchy.
8. State the behavior of system can be defined in terms of
notion of state. The state of a system is defined by values
appropriate to the systems attributes of state variables.
9. Control open systems normally adapt to changes in their
external stages. Control is the mechanism that implements
adaptation in most system. It is meant to regulate behavior of
system. Control is based on defined measures of performance
eg for an IS the time it takes to respond for the user query.
10. System Feedback
The types of feedback systems control is normally exercised within
a system through some form of feedback. Output from the process
of a system is feedback to the control mechanism. The control
mechanism then adjusts the control signal to the process on the
basis of data it received. Feedback can be +ve or ve. Ve feedback
allows system to amplify its behavior in a direction opposite of the
general direction. +Ve amplify the behavior in the same direction
the system is moving.
Example-in the marketing world 2 similar products, A & B, can be launched
with an equal advertising budget. The product that gets the best response
from consumers can then have its advertising budget increased. This is
known as +ve feedback if you choose to increase the budget of one with
poor response its ve feedback
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Develop Systems EffectivelyDocument24 pagesDevelop Systems EffectivelybernardNo ratings yet
- Overview of Information System Approach: Terminologies UsedDocument15 pagesOverview of Information System Approach: Terminologies Usedbambi2002No ratings yet
- Organisational Information SystemDocument15 pagesOrganisational Information SystemfiscordiaNo ratings yet
- SYSTEM ANALYSIS NotesDocument41 pagesSYSTEM ANALYSIS NotesAbass AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1.mis Chapter One Business Information SystemDocument32 pages1.mis Chapter One Business Information SystemEndash HaileNo ratings yet
- What a system isDocument9 pagesWhat a system isKatrina MilianNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument69 pagesSystem Analysis and Designsam mydaxNo ratings yet
- 'Introduction To System Analysis and DesignDocument120 pages'Introduction To System Analysis and DesignDipen TamangNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Overview of System Analysis & DesignDocument7 pagesLESSON 1 - Overview of System Analysis & DesignGlaiza PudaNo ratings yet
- System AnalysisDocument10 pagesSystem AnalysissybertechcomputerNo ratings yet
- SYS THEORY: Key ConceptsDocument7 pagesSYS THEORY: Key ConceptsMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- A System Exists Because It Is Designed To Achieve One or More ObjectivesDocument10 pagesA System Exists Because It Is Designed To Achieve One or More ObjectivesTsegaye ThomasNo ratings yet
- Mis NotesDocument53 pagesMis NotesJoab OgolaNo ratings yet
- Systems Theory and OrganizationDocument7 pagesSystems Theory and Organizationabbynimmo2013No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document54 pagesChapter 2Mostafa HossamNo ratings yet
- Foundation For Systems Development: Lesson 1: What Is An Information System?Document6 pagesFoundation For Systems Development: Lesson 1: What Is An Information System?May Ann Agcang SabelloNo ratings yet
- Mis Complete Notes PDFDocument53 pagesMis Complete Notes PDFannstine makenaNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Ch-1Document9 pagesSoftware Engineering Ch-1om chavanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mis NotesDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Mis NotesOtara Dan5No ratings yet
- SystemsDocument33 pagesSystemsStuti Aggarwal 2K21/BBA/148No ratings yet
- Sad - 1,2Document55 pagesSad - 1,2wigivi4421No ratings yet
- 601 - Unit 1Document14 pages601 - Unit 1Ch. Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On System Theory 12.09.20-1Document7 pagesLecture Notes On System Theory 12.09.20-1Seyon HunpeganNo ratings yet
- Mics NotesDocument185 pagesMics NotesSuchit GalaNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Unit 5Document13 pagesInformation Technology Unit 5Nandhini VirgoNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument23 pagesManagement Information SystemAlberto Nichols0% (1)
- Topic 5-6 Introduction To Systems DevelopmentDocument17 pagesTopic 5-6 Introduction To Systems Developmentvincent waithakaNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design - Notes Part1Document3 pagesSystem Analysis and Design - Notes Part1mouna0% (2)
- Abiyot Kiris Senior Secondary School: Ict Group AssignmentDocument19 pagesAbiyot Kiris Senior Secondary School: Ict Group AssignmentSolomon BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Systems Concept Characteristics of A System: UNIT-1Document49 pagesSystems Concept Characteristics of A System: UNIT-1GarimaNo ratings yet
- ITB - Unit 1 - NotesDocument21 pagesITB - Unit 1 - Notesdarinisri1352004No ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design Notes Complete Lecture NotesDocument67 pagesSystems Analysis and Design Notes Complete Lecture Notesbasma.mostafa1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1coding.addict007No ratings yet
- IT1 Assignment 1 - Systems AnalysisDocument3 pagesIT1 Assignment 1 - Systems AnalysisAlyssa Mae HonsonNo ratings yet
- System Analysis, Design and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesSystem Analysis, Design and DevelopmentSakibul Huda100% (1)
- Notes Unit - IDocument10 pagesNotes Unit - IAamin AftabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1vancedrandomNo ratings yet
- Unit01 Part02Document16 pagesUnit01 Part02Kabir SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Overview of System Analysis and DesignDocument9 pagesLecture 1: Overview of System Analysis and DesignShiena Marie NicolNo ratings yet
- Differences Between System Analysis and DesignDocument8 pagesDifferences Between System Analysis and DesignMarcel Fulgence LukangaNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument46 pagesManagement Information SystemMariam BisolaNo ratings yet
- Systems DevelopmentDocument10 pagesSystems Developmentsuper star videos SPsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Information System Concepts Revised TrisemesterDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Information System Concepts Revised Trisemesternafei almagdyNo ratings yet
- Chap1 SystemsDocument16 pagesChap1 SystemsNaman KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Information System ConceptsDocument35 pages1 Information System ConceptsSushila SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Introduction (Part-1)Document38 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction (Part-1)Ritu RajputNo ratings yet
- Unit - IiDocument5 pagesUnit - IiDeepak BhattNo ratings yet
- UCI 202 Topic 1 NotesDocument11 pagesUCI 202 Topic 1 Notesaroridouglas880No ratings yet
- 13-2 What Are The Core Activities in The Systems Development ProcessDocument3 pages13-2 What Are The Core Activities in The Systems Development ProcessSajakul Sorn100% (1)
- Introduction To MISDocument13 pagesIntroduction To MIScheldeanNo ratings yet
- 2017 BMS400 NotesDocument329 pages2017 BMS400 NotesRuth NyawiraNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design Module 1 Lesson 1Document12 pagesSystem Analysis and Design Module 1 Lesson 1Mary jane escuadroNo ratings yet
- System DesignDocument13 pagesSystem DesignHARIKIRAN PRNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design OverviewDocument98 pagesSystem Analysis and Design OverviewG.M. Sakhawat HossainNo ratings yet
- What is a SystemDocument12 pagesWhat is a SystemvivekkumarsNo ratings yet
- Computer Applications in Food and Dairy Processing 2005 Word NewDocument267 pagesComputer Applications in Food and Dairy Processing 2005 Word NewLofty N AmahNo ratings yet
- 17 Mics Final NotesDocument86 pages17 Mics Final NotesShraddha NepalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1studentsDocument50 pagesChapter 1studentsThitinaNo ratings yet
- Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Fuzzy Controlled Servo SystemsFrom EverandNature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Fuzzy Controlled Servo SystemsNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- Round Robin SchedulingDocument2 pagesRound Robin SchedulingMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- SYS THEORY: Key ConceptsDocument7 pagesSYS THEORY: Key ConceptsMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Form ReviewDocument5 pagesForm ReviewMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document14 pagesChapter 01Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in Management InformationDocument16 pagesEmerging Issues in Management InformationMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction: Bit 2319: Artificial IntelligenceDocument66 pagesLecture 1: Introduction: Bit 2319: Artificial IntelligenceMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Networking: 1.1 What Is A Network?Document6 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Networking: 1.1 What Is A Network?Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- A PointerDocument7 pagesA PointerMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Multiple TablesDocument45 pagesMultiple Tablesravikumar4itNo ratings yet
- 3.time Value of Money..F.MDocument21 pages3.time Value of Money..F.MMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- SPM NotesDocument108 pagesSPM NotesthreephasefaultNo ratings yet
- Database Systems Relational Algebra and CalculusDocument40 pagesDatabase Systems Relational Algebra and Calculussaurabhkher19No ratings yet
- Central BaDocument7 pagesCentral BaMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument3 pagesReferenceMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- MultimediajjjjjDocument222 pagesMultimediajjjjjMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Writing GuideDocument11 pagesWriting GuideCristina TomaNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument36 pagesProject Managementnoahzgambo319378% (9)
- Title PageDocument1 pageTitle PageMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Queuing TheoryDocument6 pagesQueuing TheoryMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Referencing Guide: Book With One AuthorDocument3 pagesReferencing Guide: Book With One AuthorMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- LFG 03 BodomoetalDocument16 pagesLFG 03 BodomoetalMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Inventory ControlDocument6 pagesInventory ControlMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Java Jukebox CourseworkDocument3 pagesJava Jukebox CourseworkMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Analysis and Design Course Book: Aron Trauring Class 2 April 12th, 2005Document39 pagesObject-Oriented Analysis and Design Course Book: Aron Trauring Class 2 April 12th, 2005Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- ChristDocument5 pagesChristMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Ooad Lab Manual 1Document119 pagesOoad Lab Manual 1Marl MwegiNo ratings yet
- 6409XDocument7 pages6409XMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Commerce Course OutlineDocument2 pagesElectronic Commerce Course OutlineMarl MwegiNo ratings yet
- 10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesDocument9 pages10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesPreeti KachhawaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development (INFANT)Document27 pagesGrowth and Development (INFANT)KasnhaNo ratings yet
- Marketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storesDocument18 pagesMarketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storescandyNo ratings yet
- 101 2015 3 B PDFDocument48 pages101 2015 3 B PDFJamesBandaNo ratings yet
- How To Think Like Da Vinci PDFDocument48 pagesHow To Think Like Da Vinci PDFTushar Walia100% (5)
- Data NormalisationDocument10 pagesData Normalisationkomal komalNo ratings yet
- Research Paper: EuthanasiaDocument10 pagesResearch Paper: Euthanasiahaha198502No ratings yet
- Drama GuidelinesDocument120 pagesDrama GuidelinesAnonymous SmtsMiad100% (3)
- Fear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyaDocument10 pagesFear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyashafaqkaziNo ratings yet
- Revenue Model of 12 Textile ShopsDocument34 pagesRevenue Model of 12 Textile ShopsSuhail Mohammed0% (1)
- Part 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFDocument7 pagesPart 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFMaksym BuchekNo ratings yet
- Ovl QC Manual-2012Document78 pagesOvl QC Manual-2012Sonu SihmarNo ratings yet
- Information Technology (Code No. 402) CLASS IX (SESSION 2019-2020)Document1 pageInformation Technology (Code No. 402) CLASS IX (SESSION 2019-2020)Debi Prasad SinhaNo ratings yet
- Manuel Figueroa v. The People of Puerto Rico, 232 F.2d 615, 1st Cir. (1956)Document8 pagesManuel Figueroa v. The People of Puerto Rico, 232 F.2d 615, 1st Cir. (1956)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CSR & Corporate FraudDocument18 pagesCSR & Corporate FraudManojNo ratings yet
- Existing culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaDocument9 pagesExisting culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaGilbert Gabrillo JoyosaNo ratings yet
- Jim Kwik - 10 Morning Habits Geniuses Use To Jump Start The Brain - YouTube Video Transcript (Life-Changing-Insights Book 15) - Stefan Kreienbuehl PDFDocument5 pagesJim Kwik - 10 Morning Habits Geniuses Use To Jump Start The Brain - YouTube Video Transcript (Life-Changing-Insights Book 15) - Stefan Kreienbuehl PDFCarlos Silva100% (11)
- Mayo ClinicDocument2 pagesMayo Clinicapi-3695725No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument7 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-212250493100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Moral Principle 1Document24 pagesChapter 4 Moral Principle 1Jerald Cernechez CerezaNo ratings yet
- Meditation - Buddhism and Science Aligned (Dr. Florian Lau, German Computer Scientist!)Document222 pagesMeditation - Buddhism and Science Aligned (Dr. Florian Lau, German Computer Scientist!)Mauro Sérgio Huguenin MarquesNo ratings yet
- MKT Cat ELT 2022 YoungAdultDocument36 pagesMKT Cat ELT 2022 YoungAdultnoah_mxNo ratings yet
- Final InternshipDocument64 pagesFinal Internshippradeep100% (2)
- Baptism of ApostlesDocument67 pagesBaptism of ApostlesaudubelaiaNo ratings yet
- Can Money Buy Happiness? How Wealth Impacts Life SatisfactionDocument3 pagesCan Money Buy Happiness? How Wealth Impacts Life SatisfactionShika RyaeshikaNo ratings yet
- KM UAT Plan - SampleDocument10 pagesKM UAT Plan - Samplechristd100% (1)
- The Ecology of School PDFDocument37 pagesThe Ecology of School PDFSravyaSreeNo ratings yet
- Notification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalDocument2 pagesNotification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalRomuald Leo PiongNo ratings yet
- CArib LitDocument8 pagesCArib LitNick FullerNo ratings yet