Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vessel Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Saad BakhtyarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vessel Nomenclature
Uploaded by
Saad BakhtyarCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendices
455
APPENDIX F
VESSEL NOMENCLATURE
Types of Vessels
Shop-Fabricated Pressure Vessels
1. Process vessels
a. Trayed columns
b. Reactors
c. Packed columns
2 . Drums and miscellaneous vessels
a. Horizontal
b. Vertical
3. Storage vessels
a. Bullets
b. Spheres
Field-Fabricated Pressure Vessels
0
Any of the above listed vessels can be field fabricated;
however, normally only those vessels that are too large
to transport in one piece are field fabricated.
Although it is significantly more expensive to field fabricate a vessel, the total installed cost may be cheaper than a
shop fab that is erected in a single piece due to the cost of
transportation and erection.
There are always portions of field fab vessels that are shop
fabricated. These can be as small as nozzle assemblies or
as large as major vessel portions.
Vessel Parts
Vessel Heads (End Closures)
1. Types
a. Hemi
b. Elliptical
c. Torispherical (flanged and dished)
d. Conical, toriconical
e. Flat (bolted or welded)
f. Misc. (flanged and flued)
g. Spherically dished covers
h. Closures (T-bolt, finger pin, quick opening)
2. Types of manufacture
a. Pressed
b. Spun
c. Bumped
d. Forged
e. Hot or cold formed
3 . Terminology
a. Knuckle radius
b. Crown radius
c. Dished portion
d. Straight flange
Vessel Supports
1. Types
Classification of Vessels
Function: Type of vessel, i.e., reactor, accumulator,
column, or drum
Material: Steel, cast iron, aluminum, etc.
Fabrication Method: Fielashop fabricated, welded, cast
forged, multi-layered, etc.
Geometry: Cylindrical, spherical, conical, etc.
Pressure: Internal, external, atmospheric
Heating Method: Fired or unfired
Orientation: Vertical, horizontal, sloped
Installation: Fixed, portable, temporary
Wall Thickness: Thidthick walled
Example: Vertical, unfired, cylindrical, stainless steel,
heavy-walled, welded reactor for internal pressure
a. Skirt (straight or conicaI)
b. Legs (braced or unbraced)
c. Saddles (attached or loose)
d. Rings
e. Lugs
f. Combination (lugs and legs, rings and legs, rings
and skirt)
Nozzles
1. Types
a. Integrally reinforced
b. Built-up construction
c. Pad type (studding outlet)
d. Sight glasses
e. Elliptical manways
456
Pressure Vessel Design Manual
2. Types of service
a. Manways
b. Inspection openings
c. PSV
e. Instrument connections
d. Vents
f. Drains
g. Process connections
Internals
1. Types
a. Trays, seal pans
b. Piping distributors
c. Baffles
d. Demisters
e. Packing
f. Liquid distributors
g. Vortex breakers
h. Bed supports
i. Coils
Flanges
1. Types
a. Slip on
b. Weld neck, long weld neck
c. Lap joint
d. Blind
e. Screwed
f. Plate flanges
g. Studding outlets
h. Reverse-type flange
i. Reducing flange
j. Graylock hub connector
k. Socket weld
2. Flange Facing
a. Flat face
b. Raised face
c. Finish (smooth, standard, serrated)
d. Ring joint
e. Tongue and groove
f. Male and female
Gaskets
1. Types
a. Ring, nonasbestos sheet
b. Flat metal
c. Spiral wound
d. Metal jacketed
e. Corrugated metal
f. Rings (hexagonal or oval)
g. Yielding metal gaskets (lens ring, delta ring, rectangular ring)
h. Elastomeric (rubber, cork, etc.)
Skirt
Bolt Chair
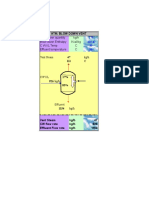
Figure F-1. Typical trayed column.
458
Pressure Vessel Design Manual
Glossary of Vessels Parts
Anchor Bolt Chairs: Gussets and plates welded to base
plate and skirt to provide for anchor bolt attachment.
Anchor Bolts: Bolts embedded in concrete foundation and
bolted to vessel anchor bolt chairs.
Base Plate: Flat plate welded to the bottom of vessel supports and bearing on the foundation.
Chimney Tray: A tray composed of chimneys extending
above the liquid level of the tray, permitting passage of
the vapors upward. The tray collects and removes all
liquid product from a specific portion of the vessel.
Column Davit: A hoisting device attached by means of
a socket to the top of fractionation columns. Used for
handling relief valves, bubble trays, bubble caps, etc.
Conical Head: Head formed in the shape of a cone.
Coupling: A fitting welded into the vessel to which the
piping is connected either by screwing or welding. This
type of fitting is generally used for pipe sizes 1%in. and
smaller.
Distributor Tray: A perforated tray that provides equal
distribution of liquid over the vessel area. Risers on the
tray extend above the liquid level to permit passage of
vapors rising upward.
Downcomers: Rectangular flat plates bolted, welded or
clamped to shell and trays inside of fractionation columns.
Used to direct process liquid and to prevent bypassing of
vapor.
Flanged and Dished (Torispherical) Head: Head formed
using two radii, one radius called crown radius, and
another called knuckle radius, which is tangent to both
the crown radius and the shell.
Flanges (or Pipe Flanges): Fittings used to connect pipes
by bolting flanges together.
Flat Head (or Cover Plate): Flat plate welded or bolted to
the end of a shell.
Fractionating Trays: Circular flat plates bolted, welded or
clamped to rings on the inside of fractionation columns.
Used to obtain vapor liquid contact, which results in fractionation.
Head: The end closure of a vessel.
Hemispherical Head: Head formed in the shape of a half
sphere.
Insulation Rings: Rings made of flat bar or angle attached
around the girth (circumference) of vertical vessels. Used
to support the weight of the vessel insulation.
Ladders and Cages: Rung-type ladders with cages built of
structural shapes to prevent a man from falling when
climbing the ladder. Bolted to and supported by clips on
the outside of the vessel. Used for vertical access to the
platforms.
Manhole Hinges or Davits: Hinges or davits attached to
manhole flange and cover plate which allow cover plate to
swing aside from the manhole opening.
Mist Eliminator (or Demister): A wire mesh pad held in
place between two light grids. The mist eliminator disengages liquids contained in the vapor.
Nozzle: Generally consists of a short piece of pipe welded in
the shell or head with a flange at the end for bolting to the
piping .
Pipe Supports and Guides: Supports and guides for
attached piping that is bolted to clips, which are welded
to the vessel.
Platforms: Platforms bolted to and supported by clips on
the outside of the vessel. Generally located just below a
manhole, at relief valves, and other valves or connections
that need frequent service.
Reinforcing Pad: Plate formed to the contour of shell or
head, welded to nozzle and shell or head.
Saddles: Steel supports for horizontal vessels.
Seal Pans: Flat plates bolted, welded, or clamped to rings
inside of fractionation column shell below downcomer of
lowest tray. Used to prevent vapor from bypassing up
through the downcomer by creating a liquid seal.
Shell: The cylindrical portion of a vessel.
Skirt: Cylinder similar to shell, which is used for supporting
vertical vessels.
Skirt Access Opening: Circular holes in the skirt to allow
workers to clean, inspect, etc., inside of skirt.
Skirt Fireproofing: Brick or concrete applied inside and
outside of slart to prevent damage to skirt in case of fire.
Skirt Vents: Small circular holes in the skirt to prevent
collection of dangerous gases within the skirt.
Stub-end: A short piece of pipe or rolled plate welded into
the vessel to which the piping is connected by welding.
Support Grid: Grating or some other type of support
through which vapor or liquid can pass. Used to support
tower packing (catalyst, raschig rings, etc.).
Support Legs: Legs made of pipe or structural shapes that
are used to support vertical vessels.
Toriconical Head: Head formed in the shape of a cone and
with a knuckle radius tangent to the cone and shell.
2:l Semielliptical Head: Head formed in the shape of a
half ellipse with major to minor axis ratio of 21.
Vacuum Stiffener Rings: Rings made of flat bar or plate, or
structural shapes welded around the circumference of the
vessel. These rings are installed on vessels operating under
external pressure to prevent collapse of the vessel. Also
used as insulation support rings.
Vessel Manhole: Identical to a nozzle except it does not bolt
to piping and it has a cover plate (or blind flange), which is
bolted to the flange. When unbolted it allows access to the
inside of the vessel. Generally 18in. or larger in size.
Vortex Breaker: A device located inside a vessel at the
outlet connection. Generally consisting of plates welded
together to form the shape of a cross. The vortex breaker
prevents cavitation in the liquid passing through the outlet
connection.
You might also like
- Hazen - William Coeficiente FBEDocument10 pagesHazen - William Coeficiente FBEOrlandoNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger (Shell and Tube) 5Document39 pagesHeat Exchanger (Shell and Tube) 5vvkvaranasiNo ratings yet
- Joint Efficiency - EDocument6 pagesJoint Efficiency - EPaul NeedhamNo ratings yet
- Painting SpecificationDocument11 pagesPainting SpecificationgaurangNo ratings yet
- Welding SymbolsDocument23 pagesWelding SymbolsgaurangNo ratings yet
- Intersecting Spherical Pressure TankDocument25 pagesIntersecting Spherical Pressure TankLuci Oktaria SitorusNo ratings yet
- Lifting LugsDocument11 pagesLifting LugsISEDAC21No ratings yet
- ES-20.14 Waste Heat PTT Public Co., LTD Recovery Units Engineering Standard REV: 02Document10 pagesES-20.14 Waste Heat PTT Public Co., LTD Recovery Units Engineering Standard REV: 02Nikki RobertsNo ratings yet
- ES-20.02 Quality Requirements PTT Public Co., LTD OF 23 For Pressure Vessel Engineering Standard REV: 01Document23 pagesES-20.02 Quality Requirements PTT Public Co., LTD OF 23 For Pressure Vessel Engineering Standard REV: 01Nikki RobertsNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Specification Sheet SI-BARG UnitsDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Specification Sheet SI-BARG Unitsshahbaz akramNo ratings yet
- ARTICLE - Tubular Drag Conveyors (R Sutton) 09-06Document12 pagesARTICLE - Tubular Drag Conveyors (R Sutton) 09-06Darko MarjanovicNo ratings yet
- SP-2069 Specification For Pressure VesselsDocument68 pagesSP-2069 Specification For Pressure Vesselsarjunprasannan7No ratings yet
- Types of Tube-To-TubesheetDocument1 pageTypes of Tube-To-TubesheetAnonymous AlhzFE9EVNNo ratings yet
- 4.16 Flanged Joints v6 PDFDocument44 pages4.16 Flanged Joints v6 PDFaprabhakar15No ratings yet
- Allowable Nozzle LoadsDocument7 pagesAllowable Nozzle LoadsZulkarnain NasrullahNo ratings yet
- Astm F436.04 PDFDocument6 pagesAstm F436.04 PDFWelington Volpatto MoraisNo ratings yet
- For Weight of PipeDocument5 pagesFor Weight of PipekathirNo ratings yet
- Compress EvaluateDocument23 pagesCompress EvaluateVishalDhiman100% (1)
- Pip Ctse1000-2018Document82 pagesPip Ctse1000-2018John BuntalesNo ratings yet
- Project Standard and Specifications Painting Specifications Rev01webDocument6 pagesProject Standard and Specifications Painting Specifications Rev01webhiyeonNo ratings yet
- Awwa d103 PotableDocument9 pagesAwwa d103 PotableAnonymous UArnIExNo ratings yet
- Saddle Stress CalculationsDocument8 pagesSaddle Stress CalculationsMuthuNo ratings yet
- Rork Plate RectangularDocument30 pagesRork Plate RectangularAscanio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Bolted Flange Design According To ASME Section VIII Division 1Document18 pagesBolted Flange Design According To ASME Section VIII Division 1LORENA REISNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: Training Program On GUIDED TOUR OF ASME CodesDocument120 pagesWelcome To: Training Program On GUIDED TOUR OF ASME CodesAndri Konyoa KonyoaNo ratings yet
- Chimney & Venting Sizing HandbookDocument50 pagesChimney & Venting Sizing HandbookCallGRNo ratings yet
- BPVC I p-2Document2 pagesBPVC I p-2Ingeniería Thermo PressionNo ratings yet
- Sample of Expansion LoopDocument1 pageSample of Expansion LoopalvinchuanNo ratings yet
- SP0793-0000-1M05-005 - Standard Specification For Welding Rev0 Marzo 2022Document19 pagesSP0793-0000-1M05-005 - Standard Specification For Welding Rev0 Marzo 2022Nestor De Jesus Pico TorresNo ratings yet
- ASME Section VIII Div 1 vs. Div 2 For Pressure VesselsDocument3 pagesASME Section VIII Div 1 vs. Div 2 For Pressure VesselsPoncho RmzNo ratings yet
- Coke Drum Skirt ExampleDocument10 pagesCoke Drum Skirt Example2009tamerNo ratings yet
- 100MT Tank Calculation 3300 Dia - WLDocument144 pages100MT Tank Calculation 3300 Dia - WLUmar AslamNo ratings yet
- Shell BoilerDocument12 pagesShell BoilerMochamad Fajar RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Straddle Principle For FlangesDocument1 pageStraddle Principle For Flangesameybarve67% (3)
- Dci Epe Bladder AccumulatorsDocument43 pagesDci Epe Bladder AccumulatorsMiguel YudegoNo ratings yet
- Jacketed PipingDocument4 pagesJacketed Pipingbinukumar100No ratings yet
- Lifting - Lug (Modification)Document11 pagesLifting - Lug (Modification)Sam LowNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Calculation - Primary Reformer Stack-R0Document22 pagesNozzle Calculation - Primary Reformer Stack-R0Aditya Jain100% (1)
- Design of Saddle Support For Horizontal Pressure Vessel PDFDocument5 pagesDesign of Saddle Support For Horizontal Pressure Vessel PDFnizam1372100% (3)
- 2019 ASME Section VIII Division 1 SynopsisDocument58 pages2019 ASME Section VIII Division 1 SynopsisCristian Xavier Avendaño BelloNo ratings yet
- How To Use Code Case in PV EliteDocument2 pagesHow To Use Code Case in PV EliteMukeshChopraNo ratings yet
- CAESAR II-Applications GuideDocument302 pagesCAESAR II-Applications GuideTakChi_LamNo ratings yet
- Asme Sec XDocument1 pageAsme Sec XSARSAN NDTNo ratings yet
- Acum#2 RoladoDocument1 pageAcum#2 RoladoJuan PabloNo ratings yet
- Stack Wind CalculationsDocument5 pagesStack Wind CalculationsJosé García100% (2)
- Expanded and WeldedDocument9 pagesExpanded and Weldedmasaminathan100% (1)
- TEMA Standards Inquiries 2020Document24 pagesTEMA Standards Inquiries 2020Nisarg Patel100% (1)
- A Regular ASME Design Checklist - Deconeq Engineering GroupDocument3 pagesA Regular ASME Design Checklist - Deconeq Engineering GroupAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Manual-M.asgaRZADEGANDocument79 pagesPressure Vessel Manual-M.asgaRZADEGANH BNo ratings yet
- 299 Elliptical Head Design Tool Ver E4 01Document1 page299 Elliptical Head Design Tool Ver E4 01Noman Abu-FarhaNo ratings yet
- Absorção ChillerDocument44 pagesAbsorção ChillergdaronaldoNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Adding A MaterialDocument11 pagesPV Elite Adding A Material9913489806No ratings yet
- What Is Design Interpretation?Document17 pagesWhat Is Design Interpretation?Qaisir MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Tank Jet MixersDocument2 pagesTank Jet MixersGabriela Axinte100% (1)
- Autopipe Vessel Guide 1-5Document5 pagesAutopipe Vessel Guide 1-5fiuto_rights_1404802No ratings yet
- A Fitting: Pipe Tubing FluidDocument7 pagesA Fitting: Pipe Tubing FluidAliNo ratings yet
- Design of Petroleum Refining Equipment-1Document20 pagesDesign of Petroleum Refining Equipment-1sherifelbayoumy266No ratings yet
- Vessel Heads BottomDocument9 pagesVessel Heads BottomFahad RockingNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Glossary of TermsDocument3 pagesHeat Exchanger Glossary of Termsusman_hafeez86No ratings yet
- Our Common Bond 2014Document84 pagesOur Common Bond 2014Yanpeng ZhangNo ratings yet
- Screw Compressor Minimum Capacity TableDocument1 pageScrew Compressor Minimum Capacity TableSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Primary NSW Ranked PDFDocument63 pagesPrimary NSW Ranked PDFSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- 2016 Icb CalendarDocument1 page2016 Icb CalendarSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- 11ETT001 Tech Talk Understanding ISO Cleanliness Codes Jan2011Document1 page11ETT001 Tech Talk Understanding ISO Cleanliness Codes Jan2011Saad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Em16-0032 Parentsnext Factsheets What Is Parents Next 01Document1 pageEm16-0032 Parentsnext Factsheets What Is Parents Next 01Saad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper - AlignmentDocument20 pagesWhitepaper - Alignmentmanbkk100% (2)
- Work Health and Safety ACT 2011 QLDDocument378 pagesWork Health and Safety ACT 2011 QLDSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper - AlignmentDocument20 pagesWhitepaper - Alignmentmanbkk100% (2)
- QGC Our Way HSSE InductionDocument1 pageQGC Our Way HSSE InductionSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Pipe Strain: 50 OrbitDocument11 pagesPipe Strain: 50 Orbitsaadbakhtyar2065No ratings yet
- Notes On API PlanDocument2 pagesNotes On API PlanSaad BakhtyarNo ratings yet
- Installation and Commissioning of API 650 Tanks (Presentation Without Audio)Document80 pagesInstallation and Commissioning of API 650 Tanks (Presentation Without Audio)Warlex100% (4)
- FEM Analysis For Spherical TanksDocument28 pagesFEM Analysis For Spherical TanksSaad Bakhtyar100% (2)
- Rab Interior Hotel FixDocument4 pagesRab Interior Hotel FixDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- Process-to-Process Delivery: SCTPDocument44 pagesProcess-to-Process Delivery: SCTPsalamudeen M SNo ratings yet
- Mediterranean Diet Toolkit A Guide To Healthy Eating (Handout)Document6 pagesMediterranean Diet Toolkit A Guide To Healthy Eating (Handout)Kley DesousaNo ratings yet
- Nimble 5e RulesDocument5 pagesNimble 5e Ruleswarpticus4100% (1)
- Week 3 PPT Day 1Document26 pagesWeek 3 PPT Day 1Zoila EscalonaNo ratings yet
- The Standard Book of SpellsDocument9 pagesThe Standard Book of SpellsOlgaPrangachiNo ratings yet
- Mack The KnifeDocument36 pagesMack The Knifesandrovergara100% (1)
- Two-Step Story Problems Freebie: by Jan GervaisDocument10 pagesTwo-Step Story Problems Freebie: by Jan Gervaisapi-311208292No ratings yet
- S.No Name of The Student Reg - No Elective ChoosenDocument3 pagesS.No Name of The Student Reg - No Elective ChoosenHarshaNo ratings yet
- La Guitarra Espanola - The Music of Santiago de Murcia - BookletDocument7 pagesLa Guitarra Espanola - The Music of Santiago de Murcia - BookletEloy Arósio25% (4)
- Trends and Issues in Young Adult LiteratureDocument49 pagesTrends and Issues in Young Adult LiteraturePhoebe RamosNo ratings yet
- RT-650 Provisional Manual - April 2008Document32 pagesRT-650 Provisional Manual - April 2008lula6894No ratings yet
- Kneehigh - Tristan & Yseult - Memory Aid For Students OnlineDocument49 pagesKneehigh - Tristan & Yseult - Memory Aid For Students Onlineapi-252232178100% (1)
- GM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFDocument5 pagesGM Bluetooth Starter Guide PDFTin_AmoNo ratings yet
- As&SH Combat Actions (Unofficial)Document1 pageAs&SH Combat Actions (Unofficial)TrysteroNo ratings yet
- Don Featherstone Colonial RulesDocument2 pagesDon Featherstone Colonial RulesA Jeff ButlerNo ratings yet
- Mario VIC.m3uDocument10 pagesMario VIC.m3uPabloDelgadilloNo ratings yet
- Samsung LN52A550P3FXZA TroubleshootingDocument38 pagesSamsung LN52A550P3FXZA TroubleshootingPterocarpousNo ratings yet
- Cultural ResonanceDocument15 pagesCultural ResonanceAdithya NarayanNo ratings yet
- Phonepe and Its FunctionalitiesDocument7 pagesPhonepe and Its FunctionalitiesSreeram BaddilaNo ratings yet
- Tauplitz Bergfalter 2012-13 GB-WWWDocument2 pagesTauplitz Bergfalter 2012-13 GB-WWWbcnv01No ratings yet
- Recipes From People's Pops by Nathalie Jordi, David Carrell, and Joel HorowitzDocument14 pagesRecipes From People's Pops by Nathalie Jordi, David Carrell, and Joel HorowitzThe Recipe Club0% (1)
- Utax Part List Cdc5520 Cdc5525 Eng Rev1Document49 pagesUtax Part List Cdc5520 Cdc5525 Eng Rev1arredaufficioNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Clasa A IV-aDocument2 pagesTest Paper Clasa A IV-aCrina MiklosNo ratings yet
- Weld Gun SpecificationDocument76 pagesWeld Gun SpecificationAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Film Outreach Engage BudgetDocument15 pagesFilm Outreach Engage BudgetJavier Garcia0% (1)
- Bra Book 240713Document7 pagesBra Book 240713Abhinav kumar100% (1)
- EC-BOS-8: Multi-Protocol Web Building ControllerDocument5 pagesEC-BOS-8: Multi-Protocol Web Building ControllerAngel Kevin Corral AvitiaNo ratings yet
- EE Band Perusal BK1Document68 pagesEE Band Perusal BK1Alfredo Arrautt100% (4)
- Summoner (Fullcaster) (5e Class)Document16 pagesSummoner (Fullcaster) (5e Class)Layon RodriguesNo ratings yet