Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab 7 - Triaxial (Uu)
Uploaded by
NurulAdilahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 7 - Triaxial (Uu)
Uploaded by
NurulAdilahCopyright:
Available Formats
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
COURSE
BASIC SOIL MECHANICS
COURSE CODE
ECG303
LEVEL OF OPENNESS
CATEGORY
PARTIALLY OPEN ENDED
DEGREE OF OPEN-ENDED
(%)
33
PERIOD OF ACTIVITY
1 WEEK (WEEK 7)
TITLE
Unconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Test
1.1 Introduction
Level 1 laboratory activity refers to condition where the problem and ways &
means are guided and given to the students. However the answers to the
assignment are left to the students to solve using the group creativity and
innovativeness. It is hoped that the activity will slowly introduce and inculcate
independent learning amongst students and prepare them for a much harder task
of open-ended laboratory activities.
In this laboratory session, students will be introduced on how to determine the
shear strength parameters of soil using triaxial test.
1.2 Objective
The objective of the test is:
To determine the shear strength parameters for clay soil.
PREAMBLE
1.3 Learning Outcomes
At the end of the laboratory activity, students would be able to:
1. Conduct the unconsolidated undrained triaxial test to determine the shear
strength parameters for clay soil.
2. Analyse data correctly and present in typical format
3. Work in a group to produce technical report.
1.4 Theoretical Background
Triaxial test is more reliable because we can measure both drained and
undrained shear strength.
Generally 1.4 diameter (3 tall) or 2.8 diameter (6 tall) specimen is used.
Specimen is encased by a thin rubber membrane and set into a plastic
cylindrical chamber.
Cell pressure is applied in the chamber (which represents 3) by
pressurizing the cell fluid (generally water).
Vertical stress is increased by loading the specimen (by raising the platen
in strain controlled test and by adding loads directly in stress controlled
test, but strain controlled test is more common) until shear failure occurs.
Total vertical stress, which is 1 is equal to the sum of 3 and deviator
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
stress (d).
Measurement of d, axial deformation, pore pressure, and sample volume
change are recorded.
Depending on the nature of loading and drainage condition, triaxial tests
are conducted in three different ways.
UU Triaxial test
CU Triaxial test
CD Triaxial test
PROBLEM
STATEMENT
WAYS AND
MEANS
UU test measures the undrained shear strength of soils by means of axial
compression tests on cylindrical specimens in which no drainage is
permitted during the test.
2.0 Problem Statement
UU triaxial test gives shear strength of soil at different confining stresses. Shear
strength is important in all types of geotechnical designs and analyses. As a group
you are given a set of samples to determine the undrained parameters of the
soil.The group must carry out the test following the procedures outline and
subsequently analyse the data and present it in a proper technical format.
3.1 Apparatus
Strain controlled triaxial load frame
Triaxial cell assembly
Cell pressure supply panel
Scale
Balance sensitive to 0.1 g
Moisture cans
Oven
3.2 Procedures
1.
2.
3.
4.
Measure diameter, length, and initial mass of the specimen.
Measure the thickness of the rubber membrane.
Set a soil specimen in a triaxial chamber.
Increase the cell pressure to a desired value (70 kPa for the first case and
140 kPa in the second case).
5. Shear the specimen at the rate of 1%/min or 0.7 mm/min (for 70 mm
sample height).
In automated device, the software calculates it automatically based on the
soil type.
6. Record L, and d in every 10 seconds (computer does it automatically).
7. Continue the test until the deviator stress shows ultimate value or 20%
axial strain.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
Figure 1 triaxial compression testing device
8. After completion of the test, release the cell pressure to 0, vent the
pressure and bring the cell down by bring the lower platen down, drain the
cell, and clean the porous stone and the assembly.
9. Sketch the mode of failure.
10. Measure the weight of the soil specimen again, and put the specimen into
the oven.
11. Measure the weight again after 24 hours.
12. Repeat the test for the second specimen too (140 kPa of cell pressure and
third specimen 210 kPa of cell pressure).
USERS GUIDELINE FOR THE ELE TRIAXIAL DEVICE
(UU TRIAXIAL TEST)
A. POWER AND MAIN SUPPLY SETTINGS
(This step is already done)
1. Press the Power Display power button to the ON position. After
Stabilization (approx. 15 min.), push the Tare button to zero the display.
2. Turn on the laboratory vacuum supply. The associated amount of vacuum
available to your system will be displayed on the Vacuum Supply Gauge.
3. Turn on the laboratory compressed air supply. Viewing the Pressure
Supply gauge, adjust the Master Regulator until the desired maximum
supply pressure is reached.
The displayed pressure should be about 10 psi more than the required
cell pressure. Do Not exceed 150 psi (1034 KPa) pressure.
4. Turn on the laboratory water supply.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
B. FILLING OF THE DE-AIRED WATER TANK SYSTEM (This step is
already done)
1. Turn the De-Airing Water Control valve to the Fill position.
2. When the tank water level is about 1 from the top, turn the De-Airing
Water Control valve to the vent position (Very Slowly to allow water to
drain).
C. DE-AIRING THE WATER TANK
(This step is already done)
1. Turn the De-Airing Water Control valve to the Vacuum position.
2. Apply vacuum for 10-15 minutes and, at the same time, gently shake the
tank occasionally to enhance the removal of air from water.
3. Turn the De-Airing Water Control valve to the vent position.
D. FILLING THE BURETTE CHANNELS (This step is already done)
Set all five valves on the test cell to the closed position.
Set the De-Airing Water Control valve to the Pressure position.
Set the Burette/Annulus Input Control valve to the vent position.
Set the Annulus Control Switch to the open position (Normal).
Slowly turn the Burette/Annulus Flow Control valve to the Fill position.
When the water reaches the desired level, turn the Burette/Annulus Flow
Control valve to the Cell Operate position. Do not overfill. Water should
not be allowed to flow into the pressure tube at the top.
6. Repeat the above steps until two burette channels being used are filled to
the desired level.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Note: If the water level in the De-Aired Water Tank System drops to
about 1 from the bottom, repeat the filling and de-airing procedures
described above.
E. DE-AIRING THE BURETTE CHANNELS (This step is already done)
1. Set the Burette/Annulus Input Control valve for each channel to the
vacuum position. Under normal operating conditions, the de-airing
process should be completed in about 5-10 minutes.
2. After completion, set all Input Control valves back to the vent position.
F
PREPARATION OF THE SAMPLE
1. Trim the sample to be tested using a Miter Box.
2. Measure the height and diameter of the sample at various locations to get
an average value.
3. Measure the weight of the trimmed sample before test.
4. Wrap the sample in a plastic sheeting to prevent any moisture loss.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
5. Use the trimmings to get the Moisture Content of the sample before test.
PREPARATION FOR THE TRIAXIAL LOADING
Double click on the software icon DS7 on the desktop.
Click on the button New Test.
Select UU1 --Triaxial Quick Undrained Tests-AS.
Click on the button Select a Machine for the Test.
Fill in the spaces in this window and click on the button OK to the right
side of the screen. The fields marked * by their side can not be left blank
and the characters \ / * . , : ; @ # ~ ? can not be used while filling up the
spaces.
6. In the window Tests in Progress make sure that you select the test that
you want to run and then click on the button OK at the bottom of the
screen.
7. Switch on the Load cell machine using the button at the back.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
MONITORING THE TEST
1. In the Test Monitoring window, make sure that all the test data shown in
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
the upper left box is correct.
Click on the button Start Test Stage located to the upper right side of the
screen.
In the next window select Test Initialization and click on button OK in
the bottom.
In the Test Initialization window, enter the previously measured sample
Diameter, weight, and height.
The bulk density of the sample will be calculated automatically by the
software.
The information regarding the Membrane Thickness and Youngs Modulus
are default values and may not be changed, unless using a different kind
of membrane around the sample.
After entering all data click on the green button Confirm Setup Data.
This will bring you back to the Test Monitoring window.
Again click on button Start Test Stage located to the upper right side of
the screen.
This time select Compression from the menu and then click on button
OK at the bottom of the window.
COMPRESSION STAGE
From the previous stage you will be directed to the screen titled
Compression Stage for Undrained Test.
1. Vent Cell Pressure Transducer to Atmosphere and Reset:
a. Set the Burette/Annulus Input Control valve to the Pressure
Position.
b. Set the Annulus Control Switch valve to the on position.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
Set the Burette/Annulus Flow Control valve to the Cell Operate
position.
d. Make sure the cell pressure transducer is open to atmosphere and
wait for 10 seconds.
e. In the DS-7 software window, click on the red button Reset Cell
Pressure.
c.
2. Fill and Pressurise Cell. Select Material Type and Press Button to
Calculate Suggested Rate of Strain on Enter Directly:
a. Close the valve on the test cell marked CP.
b. Carefully place the sample on the Triaxial cell base pedestal.
c. Place the top pressure pad and use black O-rings to secure the
membrane around the base pedestal and top pressure pad.
d. Place the Triaxial cell cover over the sample and use the three rods to
secure it in place.
e. Open the knob at the top of the glass cylinder and attach the tube
marked CP to the knob marked water located at the bottom left of
the panel.
Open the valve on the test cell marked CP. This will gradually fill the
cell. Control the flow using the valve marked CP.
f. Close the knob at the top of the glass cylinder when the cell is filled
with water.
g. Detach the tube marked CP from the knob marked water and
attach it back to the knob marked CP on the panel.
h. Close the valve on the test cell marked CP.
i. Use the knob in the Set Pressure Control panel to increase the
pressure to the desired cell pressure level. Monitor the cell pressure
box in the DS-7 software to get the accurate reading.
j. Set the Burette/Annulus Input Control valve to Pressure position.
k. Slowly open the valve on the test cell marked CP. This will transfer
the cell pressure to the water inside the glass cylinder.
l. In the DS-7 software window, select the right Material Type to the
right side of the window and click on the button Calculate Rate of
Strain.
m. Input the calculated rate of displacement value from the computer
screen to the display window at the bottom of the test cell and press
Enter ().
3. Calculate Logger Sampling Rates (based on percentage of length of
specimen at failure):
a. On the DS-7 software window, fill up the boxes marked first
increments, upto, and second increments. This is the increment at
which the results will be captured by the transducers. The default
values are from the ASTM Standard. Set both for 0.01%.
4. Reset Force Transducer & Bring Piston just into contact with top cap:
a. Raise the sample using the key on the keypad on the loading frame
until the load piston just touches the top notch of the top plate above
the soil sample.
b. On the DS-7 software window, click on the red button marked Reset
Force Transducer.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
c.
This should reset the lower right window on the Test Monitoring
Window in the DS-7 software to 0.0 lbf.
5. Reset Axial Displacement & Start Compression at End of Count
Down:
a. Place the axial displacement transducer bottom touching the
horizontal rod and click on the button Reset Axial Displacement
Transducer on the DS-7 software window.
b. This should reset the lower left window on the Test Monitoring
window of the DS-7 software to 0.0 inches.
6. Click on the green Continue button at the bottom of the page of the
software window.
7. A window will appear that will instruct you to press enter (Green Button) to
start the Test Countdown. If everything is ready, click on the green button
Start Test Countdown.
8. Once the two whistles go, press the green button Run on the keypad at
the bottom of the test cell.
J
TO STOP THE TEST
1. To stop the loading at any time press the red button Stop on the keypad
of the load frame.
2. In the DS-7 software, on Test Monitoring window click on button End
Test Stage
3. Click on button Start Test Stage button.
4. Select Final Measurements and click on OK.
5. Enter all parameters that are available at this time
Final Specimen Weight (wet)
Final Specimen Weight (dry)
Initial Moisture Content from Trimmings
Lab Temperature during test
Particle Specific Gravity
6. Click on green button Confirm Data.
7. Click OK on the window stating FINAL STAGE IS NOW COMPLETE.
PRESS OK TO STORE THE TEST DATA READY FOR ANALYSIS OR
PRESS CANCEL TO PERFORM FURTHER STAGES.
8. Save the Raw data obtained from the test to a directory of your choice.
The software will prompt to a default directory.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
9. Click on button exit to exit from the software.
K DRAINING THE CELL
1. Turn the set Pressure Control knob in counterclockwise direction to
2.
3.
4.
5.
reduce the cell pressure.
Turn the Burette/Annulus Input Control valve to Bridge Off position.
Open the top knob of the glass cylinder in the load cell assembly.
Set the Burette/Annulus Flow control to drain position.
Open the valve on the test cell marked CP. This will drain the water from
the glass cylinder.
DISMANTLING THE CELL
1. Use the button on the keypad of the load frame to lower the sample
away from the load piston.
2. Unscrew the three rods from the sides of the glass cylinder and take out
the cylinder.
3. Dismantle the sample from the test cell and secure the membrane, top
and bottom end plates.
3.3 Data Acquisition
1. Calculate axial strain,
L
L
L = Vertical deformation of the specimen.
2. Calculate vertical load on the specimen.
You will get it directly from the force transducers.
3. Calculate corrected area of the specimen (Ac) Ac = A0
1
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
A0 = Initial cross-sectional area i.e. x D2/4
Calculate the stress on the specimen.
= Load
Ac
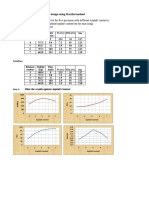
Plot d versus axial strain separately for three tests.
Plot d vs a for three tests in the same plot.
Plot Mohr circle based on 1 and 3 at failure. They should give the same
d value. Add one Mohr circle for unconfined compression test too.
Make a straight line, which is tangent to all Mohrs circles. This gives c u
with a horizontal line, i.e. u = 0. Therefore this test is called = 0 test.
cu = d
2
Figure 2 Total stress Mohr circle and failure envelope obtained from UU triaxial test
9. Calculate the moisture content of the specimen after the test.
10. Calculate the initial void ratio of the specimen (Use the equations provided
in the earlier classes).
UU Triaxial Test Laboratory Data Sheet
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
GENERAL INFORMATION
Tested by:
Lab partners/organization:
Client: CSUF
Boring no.: N/A
Recovery date:
Soil description:
I.
Date tested:
Project: Soils Lab
Recovery depth: N/A
Recovery method: N/A
II. TEST DETAILS
Initial specimen diameter, Do:
Initial specimen area, Ao:
Initial specimen length, Lo:
Initial specimen volume, Vo:
Moist mass of specimen after test, M:
Dry mass of specimen, Ms:
Moisture content, w:
Total unit weight, :
Dry unit weight, d:
Degree of saturation, S:
Membrane
type:
Standard
Rubber
Axial strain rate, 1/t:
Membrane
Deformation indicator: LVDT
Force indicator: LVDT
Cell pressure, 3:
Specimen
preparation
method:
Hand
Compaction
Notes, observations, and deviations from ASTM D2850 test standard:
Axial
Defor
mation
(L)
III. MEASUREMENTS
Axial
Load
(P)
AND
Axial
Strain
(1)
Corrected
Area
(A)
Deviator
Stress
()
CALCULATIONS
EQUATIONS:
a = L/Lo
A = Ao/(1-a)
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
3:
f:
1f:
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR GUDANG
= P/A
1f = 3 + f
GENERAL INFORMATION
Tested by:
Lab partners/organization:
Client: CSUF
Boring no.: N/A
Recovery date:
Soil description:
I.
II. TEST DETAILS
Axial
Deforma
tion (L)
Date tested:
Project: Soils Lab
Recovery depth: N/A
Recovery method: N/A
Axial
Load
(P)
Axial
Strain
(1)
Corrected
Area
(A)
Deviator
Stress
()
Initial specimen diameter, Do:
Initial specimen area, Ao:
Initial specimen length, Lo:
Initial specimen volume, Vo:
Moist mass of specimen after test, M:
Dry mass of specimen, Ms:
Moisture content, w:
Total unit weight, :
Dry unit weight, d:
Degree of saturation, S:
Membrane
type:
Standard
Rubber
Axial strain rate, 1/t:
Membrane
Deformation indicator: LVDT
Force indicator: LVDT
Cell pressure, 3:
Specimen preparation method: Hand Compaction
Notes, observations, and deviations from ASTM D2850 test standard:
III.
MEASUREMENTS
EQUATIONS:
AND
CALCULATIONS
a = L/Lo
A = Ao/(1-a)
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
3:
f:
1f:
Dis- March 2015
FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN AWAM
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA
SARAWAK
LABORATORY MANUAL
PASIR
GUDANG
= P/A
1f = 3 + f
RESULTS
4 Results, Analysis and Conclusion
The group is required to submit the technical report of the laboratory results
highlighting the data acquisition process, analysis carried out and the relevancy of
the set-out output to achieve the objective.
The report must be submitted 7 days after the completion of the test.
FKA, UiTM PASIR GUDANG
Dis- March 2015
You might also like
- Constant-Head Permeability Test Measures Sand Flow RateDocument5 pagesConstant-Head Permeability Test Measures Sand Flow RategmoozNo ratings yet
- Heron's Fountain Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesHeron's Fountain Physics ProjectsandsphilipNo ratings yet
- Soil Report 1Document3 pagesSoil Report 1Akkash RaviNo ratings yet
- Square Portal FrameDocument8 pagesSquare Portal FramenabilaNo ratings yet
- Field Density Lab ReportDocument21 pagesField Density Lab ReportAnonymous DR3NznNo ratings yet
- C6- Standard Consistency Cement PasteDocument4 pagesC6- Standard Consistency Cement PasteMuhamad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual On Geotechnical Engineering/Foundation Engineering/Soil Mechanics:Test of SoilDocument18 pagesLaboratory Manual On Geotechnical Engineering/Foundation Engineering/Soil Mechanics:Test of SoilSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Field and Laboratory Testing Procedures Final 07282008Document25 pagesChapter 05 Field and Laboratory Testing Procedures Final 07282008Bia Mughal100% (1)
- Determination of Field Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodDocument3 pagesDetermination of Field Density of Soil by Core Cutter MethodsiddiqueakbarNo ratings yet
- Consolidation: By. Rajesh S.GujarDocument33 pagesConsolidation: By. Rajesh S.Gujardarshan_dave17No ratings yet
- 3 Constant HeadDocument12 pages3 Constant HeadWHfamilyNo ratings yet
- Compaction TestDocument9 pagesCompaction TestArjun MulluNo ratings yet
- Constant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualDocument3 pagesConstant Head Permeability Test Lab ManualmmNo ratings yet
- Vane Shear Test: Quickly Measure Clay Soil Shear Strength in 38 CharactersDocument7 pagesVane Shear Test: Quickly Measure Clay Soil Shear Strength in 38 CharactersAriffudinAliNo ratings yet
- Lab7 ReportDocument4 pagesLab7 ReporthelensongyNo ratings yet
- Methods for Measuring Soil Consolidation RateDocument4 pagesMethods for Measuring Soil Consolidation RateSiva JothiNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Consolidation TestDocument5 pagesOne Dimensional Consolidation TestAzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- CompactionDocument15 pagesCompactionpp hsu100% (6)
- Cube TestDocument10 pagesCube Testridhuanzainal100% (1)
- Proctor Compaction TestDocument8 pagesProctor Compaction TestIreneNo ratings yet
- Bitumen ExtractorDocument7 pagesBitumen ExtractorNirmal NayakNo ratings yet
- L1-Physical Characteristic of SoilDocument78 pagesL1-Physical Characteristic of SoilTAN PANG ZORNo ratings yet
- Slump Test: Sourse /location:: CC Pavement Grade of Concrete:: M30 Water Cement Ratio:: 0.45Document37 pagesSlump Test: Sourse /location:: CC Pavement Grade of Concrete:: M30 Water Cement Ratio:: 0.45ChManikumarNo ratings yet
- Permeability 2 - Field TestDocument2 pagesPermeability 2 - Field TestNaufal HanifNo ratings yet
- BITUMEN LAB TEST CHARGESDocument7 pagesBITUMEN LAB TEST CHARGESRenga PandiNo ratings yet
- Determining Concrete Workability with Slump TestDocument6 pagesDetermining Concrete Workability with Slump Testjoshdax2No ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Vane Shear TestDocument16 pagesLaboratory Report Vane Shear Test'Sayed Asadullah93% (29)
- Namibia University of Science and Technology: School of Engineering Bachelor of Engineering: Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagesNamibia University of Science and Technology: School of Engineering Bachelor of Engineering: Civil EngineeringHi270693No ratings yet
- Swelling IndexDocument3 pagesSwelling IndexjitenderNo ratings yet
- Impact of JetDocument8 pagesImpact of JetOmar Faruqi100% (1)
- Direct Shear TestDocument11 pagesDirect Shear TestKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- 13-HPCL Vizag Soil Report-VOL.VDocument28 pages13-HPCL Vizag Soil Report-VOL.VDhananjay KumarNo ratings yet
- C 0) C' and ' C' and ' C' ' C C' Effective Undrained Cohesion C' Undrained Angle of Friction ' Effective Undrained Angle of Friction 'Document6 pagesC 0) C' and ' C' and ' C' ' C C' Effective Undrained Cohesion C' Undrained Angle of Friction ' Effective Undrained Angle of Friction 'Dr Wong Kim YuenNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength of Concrete CubesDocument3 pagesCompressive Strength of Concrete CubesoneakshayNo ratings yet
- Permiability Test Aim of The ExperimentDocument7 pagesPermiability Test Aim of The ExperimentArif AzizanNo ratings yet
- CBR TestDocument7 pagesCBR TestNanaNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis For Constant Head Permeability TestDocument3 pagesData Analysis For Constant Head Permeability TestJackyu TeeNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Penetration ReportDocument10 pagesBitumen Penetration Reportmuhd qayyumNo ratings yet
- Constent Head Permeability TestDocument11 pagesConstent Head Permeability TestAiryn Uyien100% (1)
- Chapter 1 (Sandy Lean Clay)Document17 pagesChapter 1 (Sandy Lean Clay)John Raymund TanugaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation TestDocument9 pagesConsolidation Testdatonizam0% (1)
- Specific Gravity of Bitumen.Document3 pagesSpecific Gravity of Bitumen.Bhaskar Pratim Das71% (7)
- Soil Mechanics Lab RecordDocument55 pagesSoil Mechanics Lab RecordshubhamNo ratings yet
- Consolidation TestDocument8 pagesConsolidation TestCasper da MagnificientNo ratings yet
- StudentDocument7 pagesStudentKartik AryanNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Crushing Value TestDocument4 pagesAggregate Crushing Value TestAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Atterberg LimitsDocument8 pagesAtterberg LimitsrbhavishNo ratings yet
- Compacting Factor TestDocument3 pagesCompacting Factor TestRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Geotech Vane Shear TestDocument78 pagesGeotech Vane Shear Test'Sayed AsadullahNo ratings yet
- Unconfined Compression TestDocument11 pagesUnconfined Compression TestAmiruddin JSNo ratings yet
- CIVL354 Notes 1 Soil CompactionDocument20 pagesCIVL354 Notes 1 Soil Compactionmusiomi2005No ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Triaxial - UuDocument11 pagesLab 7 - Triaxial - Uudixn__No ratings yet
- Unconsolidated UndrainedDocument9 pagesUnconsolidated UndrainedMohd Syafiq Akmal100% (2)
- UU Triaxial TestDocument11 pagesUU Triaxial Testprinces_anaNo ratings yet
- UU Triaxial TestDocument11 pagesUU Triaxial Testredz00100% (1)
- test-09(1)Document6 pagestest-09(1)Ateafac Anastasia NjuafacNo ratings yet
- LAB 11 - UU TRIAXIAL TEST (Level 1)Document6 pagesLAB 11 - UU TRIAXIAL TEST (Level 1)Doris AsmaniNo ratings yet
- Pressure Transient Formation and Well Testing: Convolution, Deconvolution and Nonlinear EstimationFrom EverandPressure Transient Formation and Well Testing: Convolution, Deconvolution and Nonlinear EstimationRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- The Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsFrom EverandThe Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsNo ratings yet
- 1.each of The Solids Shown in The Diagram Has The Same MassDocument12 pages1.each of The Solids Shown in The Diagram Has The Same MassrehanNo ratings yet
- FX15Document32 pagesFX15Jeferson MarceloNo ratings yet
- Nama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Document3 pagesNama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Yetri MulizaNo ratings yet
- Skuld List of CorrespondentDocument351 pagesSkuld List of CorrespondentKASHANNo ratings yet
- SQL Guide AdvancedDocument26 pagesSQL Guide AdvancedRustik2020No ratings yet
- Theory of Linear Programming: Standard Form and HistoryDocument42 pagesTheory of Linear Programming: Standard Form and HistoryJayakumarNo ratings yet
- ESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)Document20 pagesESA Knowlage Sharing - Update (Autosaved)yared BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaDocument35 pagesMarketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaMuamer ĆimićNo ratings yet
- Malware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisDocument27 pagesMalware Reverse Engineering Part 1 Static AnalysisBik AshNo ratings yet
- 3 - Performance Measurement of Mining Equipments by Utilizing OEEDocument8 pages3 - Performance Measurement of Mining Equipments by Utilizing OEEGonzalo GarciaNo ratings yet
- 17BCE0552 Java DA1 PDFDocument10 pages17BCE0552 Java DA1 PDFABHIMAYU JENANo ratings yet
- Marshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleDocument2 pagesMarshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleTewodros TadesseNo ratings yet
- Service and Maintenance Manual: Models 600A 600AJDocument342 pagesService and Maintenance Manual: Models 600A 600AJHari Hara SuthanNo ratings yet
- #3011 Luindor PDFDocument38 pages#3011 Luindor PDFcdouglasmartins100% (1)
- Evaluating Sources IB Style: Social 20ib Opvl NotesDocument7 pagesEvaluating Sources IB Style: Social 20ib Opvl NotesRobert ZhangNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Working CapitalDocument12 pagesEstimation of Working CapitalsnehalgaikwadNo ratings yet
- Report Emerging TechnologiesDocument97 pagesReport Emerging Technologiesa10b11No ratings yet
- Current Diagnosis and Therapy For Head and Neck MalignanciesDocument249 pagesCurrent Diagnosis and Therapy For Head and Neck MalignanciesMara TomaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management of a Client with Multiple Medical ConditionsDocument25 pagesNursing Care Management of a Client with Multiple Medical ConditionsDeannNo ratings yet
- Katie Tiller ResumeDocument4 pagesKatie Tiller Resumeapi-439032471No ratings yet
- Rounded Scoodie Bobwilson123 PDFDocument3 pagesRounded Scoodie Bobwilson123 PDFStefania MoldoveanuNo ratings yet
- Non Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGDocument7 pagesNon Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGLin ChrisNo ratings yet
- Guiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test BankDocument16 pagesGuiding Childrens Social Development and Learning 8th Edition Kostelnik Test Bankoglepogy5kobgk100% (27)
- Water Jet CuttingDocument15 pagesWater Jet CuttingDevendar YadavNo ratings yet
- Yellowstone Food WebDocument4 pagesYellowstone Food WebAmsyidi AsmidaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Computer ScienceradNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction: Question BankDocument12 pagesUnit-1: Introduction: Question BankAmit BharadwajNo ratings yet
- ASMOPS 2016 - International Invitation PHILIPPINEDocument4 pagesASMOPS 2016 - International Invitation PHILIPPINEMl Phil0% (3)
- FS2004 - The Aircraft - CFG FileDocument5 pagesFS2004 - The Aircraft - CFG FiletumbNo ratings yet
- STAT455 Assignment 1 - Part ADocument2 pagesSTAT455 Assignment 1 - Part AAndyNo ratings yet