Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk For Diseases Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Rick Frea100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
8K views1 pageKnow what patients are at risk for DIC, ARDC, PE, pneumonia, etc.
Original Title
Risk for Diseases Cheat Sheet
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKnow what patients are at risk for DIC, ARDC, PE, pneumonia, etc.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(5)100% found this document useful (5 votes)
8K views1 pageRisk For Diseases Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Rick FreaKnow what patients are at risk for DIC, ARDC, PE, pneumonia, etc.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
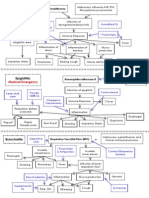
Signs of Pneumonia: High Risk for DIC:
1. Shortness of breath 1. Infection in blood (Sepsis)
2. Rapid, shallow breathing 2. Severe tissue injury, as in
3. Auscultation: Isolated crackles or crackles/ronchi throughout burns, head injury, trauma.
4. SpO2 levels decreasing below patient normal value 3. Recent surgery or anesthesia
5. Cough: either dry or productive (green, brown, yellow, bloody) 4. Reaction to transfusions
6. Chest pain that worsens with deep breath or when coughing 5. Labor & delivery problems
7. Fever, shaking, chills 6. Liver disease
8. Lab Values: Increased WBC and/or increased neutrophils
9. X-Ray High Risk for ARDS:
10. Organisms in sputum 1. Aspiration
11. Pt. may be pale, dusky, blue 2. Pneumonia
12. Diaphoretic, loss of appetite, fatigue and (in elderly) confusion 3. Sepsis
4. Transfusion
5. Lung contusion
Early signs of Sepsis: (#1 killer in of Critical Care patients)
6. Inhalation injury
1. Suspected Infection
7. Near Drowning
2. Two out of four:
8. Chemical inhalation
a. Temp>100.4, <96.8
Signs of ARDS
b. HR>90
1, SOB
c. RR >20 or PCO2<32
2. Labored
d. WBC >12,000 or <4000 or 10% bands
3. Cyanosis
3. SBP <90 after 20-30cc/kg fluid bolus (1.5-3 liters of fluid)
4. Tachypnea
4. Elevated lactic acid ( LDH, Lactate)
5. Decreased BP (Shock)
5. Decreased platelets
6. Organ failure
6. Decreased PO2 below patient normal
7. Rales/ crackles (fluid)
4. Altered mental status not due to drugs may signify organ failure.
8. ABG = Respiratory Acidosis
Signs of Severe Sepsis:
9. Chest X-Ray
1. Patient receiving antibiotics & needs Vasopressor (this is a
dangerous sign).
2. Pt showing signs of organ failure in 2 + systems for <= 24 hrs. High Risk for PE:
3. ARDS, DIC, MSOF 1. Prolonged bed rest, long car
Criteria for Organ Failure: car or plane rides, etc.
1. Cardiovascular: 2. Surgery, especially pelvic
a. SBP <= 90 3. Child birth
b. MAP <= 70 for 1 hour or CVP >8-12 4. Massive trauma
c. CK, CKMB, Troponin elevated 5. Cancer
2. Hemodynamics: 6. Stroke
a. Platelets <80,000 7. Heart attack
b. 50% decrease in platelets over 3 days 8. Heart surgery
3. Renal: 9. Fracture of hip or femur
a. UOP < 20cc/hour (with CVP >8-12) Signs of PE:
b. High Creatinin and BUN , GFR >29 1. Tachypnea: increased rate
c. Increased electrolytes (High K, Mg, and Na) and depth. (70% of cases)
d. Increased Uric Acid 2. Rales (50% of cases)
e. Metabolic Acidosis 3. ABG is normal
f. Increased BP 4. Dyspnea at rest
g. Prolonged bleeding 5. Diaphoretic
4. Hepatic: 6. Chest pain occurs suddenly &
a. Jaundice may worsen with deep breath,
b. High AST and ALT, Biliruben, Gamma-Gt cough, movement
c. Decreased Albumin 7. Cough began suddenly,
d. Coagulation abnormalities may be bloody sputum
5. Metabolic: 8. Tachycardia (30% of cases)
a. <=7.30 9. Anxiety
b. BE >= 5 10. Bluish or dusky skin
c. Lactate >2.0 once CVP> 8-12 11. D-Dimer (70% false positive).
6. Respiratory: 12. V/Q Scan (best indicator 87%)
a. PaO2/FiO2 <= 250 13. Treatment – preventative
b. Early ABG = Respiratory Alkalosis due to high RR (support ventilation,
a. Later ABG = Metabolic Alkalosis due to low perfusion anticoagulants)
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cheatsheet 5Document1 pageCheatsheet 5Rick Frea80% (5)
- Cheetsheet 6Document1 pageCheetsheet 6Rick Frea92% (12)
- Cheatsheet 4Document1 pageCheatsheet 4Rick FreaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Haemodynamic Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesHaemodynamic Pocket GuideDarryl Betts85% (13)
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Acid-Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid-Base WorksheetMayer Rosenberg100% (18)
- (SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac CycleDocument1 page(SVR) Measures Systemic Resistance and Reflects Afterload of Left Ventricle Average Perfusion of A Cardiac Cyclesarah_stover_1100% (4)
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidejenwiley318096% (73)
- Respiratory DysfunctionDocument1 pageRespiratory Dysfunctionoxidalaj100% (3)
- RT ConsultDocument5 pagesRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- CO2 Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesCO2 Pocket GuideDarryl Betts100% (7)
- Critical Care NoteDocument10 pagesCritical Care NoteHanis Rozib99% (69)
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Matt McGlothlin85% (13)
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Document9 pagesLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- Critical Care Survival GuideDocument2 pagesCritical Care Survival Guidetringalama100% (4)
- Electrolyte CompleteDocument6 pagesElectrolyte CompleteTofan Ana100% (2)
- Cardiac AssessmentDocument7 pagesCardiac AssessmentBryan Mae H. Degorio75% (4)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocument6 pagesCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- ABG InterpretationDocument1 pageABG Interpretationnulall100% (18)
- Types of Assisted VentilationDocument1 pageTypes of Assisted VentilationJerry G100% (2)
- Lab Values Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesLab Values Cheat SheetJamie Lebon100% (4)
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument9 pagesPulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- Commonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1Document9 pagesCommonly Used Lab Values at A Glance Chem 7 1annatw100% (10)
- ABG Made EasyDocument10 pagesABG Made EasyMayer Rosenberg100% (38)
- RT Consult Form Side #1Document2 pagesRT Consult Form Side #1Rick Frea100% (2)
- Hemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFDocument8 pagesHemodynamic Management Pocket Card PDFjenn1722No ratings yet
- Common Cardiac MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Cardiac MedicationsPaige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageVentilation Cheat Sheetlizzy59683% (6)
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart Failurehannahhwolf100% (3)
- Lower Respiratory Study SheetDocument13 pagesLower Respiratory Study SheetJune Rhoades100% (2)
- Spotlight On Cardiac DrugsDocument2 pagesSpotlight On Cardiac Drugspauerish100% (2)
- Cardiac Meds ChartDocument1 pageCardiac Meds ChartCharlotte Louise75% (4)
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFDocument3 pagesCardiac Dysrhythmia Chart Med Surg NUR4 PDFlml100% (1)
- Sbar 1Document2 pagesSbar 1Nurse Betty100% (2)
- FLASH CardsDocument3 pagesFLASH Cardsclarheena100% (2)
- Critical Care Medication Infusion ChartDocument2 pagesCritical Care Medication Infusion ChartEgi Munandar100% (1)
- Critical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableDocument7 pagesCritical Care - Hemodynamic Monitoring TableVictoria Romero100% (2)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmDocument19 pagesPediatric Advanced Life Support: I. PALS System Approach AlgorithmIsabel Castillo100% (1)
- Medication Work Sheet For MedSurgDocument5 pagesMedication Work Sheet For MedSurgRyanMitchell100% (2)
- Nurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARDocument1 pageNurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARashdmb217No ratings yet
- RT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyFrom EverandRT!: Reflections on a Career in Respiratory TherapyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Respiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesFrom EverandRespiratory Care Review: An Intense Look at Respiratory Care Through Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1From EverandRespiratory Therapy: 66 Test Questions Student Respiratory Therapists Get Wrong Every Time: (Volume 1 of 2): Now You Don't Have Too!: Respiratory Therapy Board Exam Preparation, #1No ratings yet
- Haemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideFrom EverandHaemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument9 pagesPulmonary Function TestsRick Frea0% (1)
- RT Consult Form Side #1Document2 pagesRT Consult Form Side #1Rick Frea100% (2)
- Mechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilator Management ProtocolRick Frea100% (2)
- RT ConsultDocument5 pagesRT ConsultRick Frea100% (2)
- RT Consult Form Side #2Document1 pageRT Consult Form Side #2Rick Frea100% (1)
- Inhaler LexiconDocument4 pagesInhaler LexiconRick Frea100% (2)
- RsbiDocument1 pageRsbiRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolDocument3 pagesEmergency Room Aerosolized Medication ProtocolRick Frea67% (3)
- Cheatsheet 3Document1 pageCheatsheet 3Rick Frea100% (1)
- Peek Flow FlowsheetDocument3 pagesPeek Flow FlowsheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet 1Document1 pageCheat Sheet 1Rick Frea100% (9)
- Tidal Volumes Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTidal Volumes Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Cheatsheet 2Document1 pageCheatsheet 2Rick Frea86% (7)
- Ventilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Document1 pageVentilator Graphics Cheat Sheet (Part 1)Rick Frea100% (2)
- Neonatal Special ConsiderationsDocument1 pageNeonatal Special ConsiderationsRick Frea100% (1)
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocument1 pageNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Capnography Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCapnography Cheat SheetRick Frea100% (1)
- Pediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesDocument1 pagePediatric Respiratory Distress GuidelinesRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetDocument1 pageNeonatal Ventilator Vent Set-Up CheatsheetRick Frea50% (2)
- Static Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetDocument1 pageStatic Compliance & RSBI CheatsheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramDocument6 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramRick Frea100% (5)
- Indicators For Calling A DoctorDocument1 pageIndicators For Calling A DoctorRick Frea100% (1)
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocument1 pageNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Neo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNeo-Peds Intubation Cheat SheetRick FreaNo ratings yet
- Lab CheatsheetDocument1 pageLab CheatsheetRick Frea86% (7)
- Meningocele PDFDocument1 pageMeningocele PDFDumora FatmaNo ratings yet
- Test/Sign Procedure (+) INDDocument8 pagesTest/Sign Procedure (+) INDDesi SmithNo ratings yet
- Scar Management in Burn Injuries Using Drug Delivery and 2018 Advanced DrugDocument20 pagesScar Management in Burn Injuries Using Drug Delivery and 2018 Advanced DrugDIOGENESNo ratings yet
- Date: 01 January 2017 Time: 01:45hrs Location: 53 Water Street, Georgetown, GuyanaDocument4 pagesDate: 01 January 2017 Time: 01:45hrs Location: 53 Water Street, Georgetown, Guyanajanson wilsonNo ratings yet
- Breech PresentationDocument85 pagesBreech Presentationwidya vannesaNo ratings yet
- Accident ReconstructionDocument10 pagesAccident ReconstructionsilviovictorNo ratings yet
- Injury Report 2011Document20 pagesInjury Report 2011Andrea ContiNo ratings yet
- NACM Welded Chain SpecificationsDocument12 pagesNACM Welded Chain SpecificationsAmpera marzelaNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Body ImageDocument11 pagesDisturbed Body ImageNdel LindaNo ratings yet
- BQ China Harbour-7bq1Document35 pagesBQ China Harbour-7bq1Dedi SutediNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Vulnerable Periwound SkinDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Vulnerable Periwound SkinPaty Antuña YarzaNo ratings yet
- Repaso 1 Anatomy Andominal Wall 0 CavityDocument7 pagesRepaso 1 Anatomy Andominal Wall 0 CavityAngelitza AlmodóvarNo ratings yet
- Chainsaw Safety Checklist Yes No N/A F/IDocument2 pagesChainsaw Safety Checklist Yes No N/A F/IKate Hopley20% (5)
- Maryland Triage System: Tag, Start, and JumpstartDocument39 pagesMaryland Triage System: Tag, Start, and JumpstartRizkanu ArshiNo ratings yet
- Hanging PositionDocument13 pagesHanging Positionmaliha ahmad0% (1)
- Gymnastics Tension Exercises - OdtDocument5 pagesGymnastics Tension Exercises - Odtbeppo33No ratings yet
- Ming MethodDocument2 pagesMing Methodwalterego58No ratings yet
- Verbos Regulares e IrregularesDocument13 pagesVerbos Regulares e IrregularesElisethrcNo ratings yet
- 2018 Friday Cal Dietz PDFDocument41 pages2018 Friday Cal Dietz PDFMolli100% (1)
- Archetype Hype PowerpointDocument20 pagesArchetype Hype Powerpointapi-287706625No ratings yet
- FF60 Bloodbones PDFDocument115 pagesFF60 Bloodbones PDFSean Mclaren100% (1)
- Abused and Neglected Children FdneDocument26 pagesAbused and Neglected Children FdneRonit ChandNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talk Chemical GlovesDocument6 pagesToolbox Talk Chemical GlovesBomber Man100% (1)
- M2series ServiceManual E2Document77 pagesM2series ServiceManual E2geeta181No ratings yet
- July 2016Document3 pagesJuly 2016Rama sekarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The BreastDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The BreastCharisse TaylanNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sports InjuriesDocument34 pagesIntroduction of Sports Injuriesadarsh raj gaur100% (3)
- Language Focus Unit 8: Present Perfect: Affirmative and Negative Present Perfect: QuestionsDocument2 pagesLanguage Focus Unit 8: Present Perfect: Affirmative and Negative Present Perfect: QuestionsMarianNo ratings yet
- Airbags and Collisions EssayDocument2 pagesAirbags and Collisions EssayDianaNo ratings yet
- Kinesiotaping TechniquesDocument26 pagesKinesiotaping TechniquesSuhana hidayat100% (1)