Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Homework 11
Uploaded by
Miftah ShidqiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Homework 11
Uploaded by
Miftah ShidqiCopyright:
Available Formats
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
Physics Homework 11
PR 11. Sifat Dasar dan Perambatan Cahaya serta Polarisasi Cahaya
Kerjakan soal di Halliday:
Bab 33 no 2, 41, 45, 49, 51, 53, 61, 65,70,79.
Bab 35 no. 2, 4, 10
BAB 33
2.) Project Seafarer was an ambitious program to construct an enormous
antenna, buried underground on a site about 10 000 km 2 in area. Its
purpose was to transmit signals to submarines while they were deeply
submerged. If the effective wavelength were 1.0 X 104 Earth radii, what
would be the (a) frequency and (b) period of the radiations emitted?
Ordinarily, electromagnetic radiations do not penetrate very far into
conductors such as seawater, and so normal signals cannot reach the
submarines.
c
f
=
a)
3 x 108
105 ( 6,4 x 106 )
4,688 x 103 Hz
1
b) T = f
1
4,688 x 103
213,31 s
41.) A beam of polarized light is sent into a system of two polarizing
sheets. Relative to the polarization direction of that incident light, the
polarizing directions of the sheets are at angles for the first sheet and
90 for the second sheet. If 0.10 of the incident intensity is transmitted by
the two sheets, what is ?
I =( I 0 cos2 ) sin2
I0
=( I 0 cos 2 ) sin 2
10
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
1
=cos2 sin 2
10
1
sin 2
=
10
2
2
=sin 2
10
2=39,232
=19,616
45.) When the rectangular metal tank in picture is filled to the top with an
unknown liquid, observer 0, with eyes level with the top of the tank, can
just see corner E. A ray that refracts toward at the top surface of the liquid
is shown. If D = 85.0 cm and L = 1.10 m, what is the index of refraction of
the liquid?
1=tan1
tan 1
L
D
1,1
0,85
52,306
n1=
n2 sin 2
sin 1
1 ( sin { 90 })
sin ( 52,306 )
1,264
49.) In picture shows light reflecting from two perpendicular reflecting
surfaces A and B. Find the angle between the incoming ray i and the
outgoing ray r
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
Jadi sudut antara i dan r adalah 180
51.) In picture light is incident at angle (1 = 40.1 on a boundary
between two transparent materials. Some of the light travels down
through the next three layers of transparent materials, while some of it
reflects upward and then escapes into the air. If n1 = 1.30, n2 = 1.40, n3
= 1.32, and n4 = 1.45, what is the value of (a) (5
in the air and (b) (4 in the bottom material?
n sin 1=nudara sin 5
a) 1
1,3 sin ( 40,1 )=1 sin 5
sin 5=0,837
5=56.862
b)
nudara sin 5=n1 sin 1=n2 sin 2=n3 sin 3=n 4 sin 4
1,45 sin 4=0,837
4 =35,257
53.) In picture, a ray is incident on one face of a triangular glass prism in
air. The angle of incidence is chosen so that the emerging ray also
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
makes the same angle with the normal to the other face. Show that the
index of refraction n of the glass prism is given by
where f is the vertex angle of the prism and if; is the deviation angle, the
total angle through which the beam is turned in passing through the
prism. (Under these conditions the deviation angle if; has the smallest
possible value, which is called the angle of minimum deviation.)
2 + =90
dan
+2 =180 ,
2=90
1
90 ( 180 )=
2
2
( 2 )
=2 ( 2 )=2
+
2
; Jadi
n=
sin
sin 2
+
2
sin
2
sin
61.) In Fig. 33-59, light ini-tially in material 1 refracts into
material 2, crosses that material, and is then incident at
the critical angle on the interface between materials 2
and 3. The indexes of refraction are n 1 = 1.60, n2 = 1.40,
and n = 1.20. (a) What is angle ? (b) If is in3
creased, is there refraction of light into material 3?
sehingga
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
a. n1 sin
= n2 sin
1,60 sin
= n2
n
1 3
n2
( )
(1,40 ) ( 1,20 )
2
n n
2
2
2
3
= 26,8
b. Dengan meningkatkan
akan menyebabkan penurunan sudut
cahaya pada bahan 2 dan 3 sehingga sudut kritis yang terjadi akan lebih
besar.
65.) Figure 33-61 depicts a sim-plistic optical fiber: a
plastic core (n1 =1.58) is surrounded by a plastic sheath
(n2 = 1.53). A light ray is incident on one end of the
fiber at angle 8. The ray is to undergo total
internal reflection at point A, where it encounters
sheath boundary. (Thus there is no loss of light
through that boundary.) What is the maxi-mum
value of 8 that allows total internal reflection at A?
sin =
Sin A = cos
n2
n1
Sin
1
n1
sin
(1,582
,n
udara = 1.
1si n2 '
n n
2
1
core-
1si n2 '
= sin A =
the
2
2
1
sin
n1
dengan n1 = 1,58 dan n2=1,53 maka
=arcsin
1,532) = 23,20
70.) In Fig. 33-64, a light ray in air is incident on a flat layer
material 2 that has an index of refraction n2 = 1,5.
Beneath material 2 is material 3 with an index of
refraction n3. The ray is incident on the air-material 2
interface at the Brewster angle for that interface. The
ray of light refracted into material 3 happens to be
incident on the material 2-material 3 interface at the
Brewster angle for that interface. What is the value of n3?
of
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
n2
n1
= (900
n3
n2
( )( )
( tan
Tan
= (tan
2
B1
) (tan
n3
n2
= = (tan
merupakan complement dari
B2
= tan (
besar dengan
)C = 1/ tan
sehingga persamaan menjadi:
pada gambar terlihat
sama
sehingga dapat dikatakan n3 = 1,0 alias medium
udara.
79.) (a) Prove that a ray of light incident on the surface of a sheet of plate
glass of thickness t emerges from the opposite face parallel to its initial
direction but displaced sideways, as in Fig. 33-69. (b) Show that, for small
angles of incidence 0, this displacement is given by
where n is the index of refraction of the glass and is measured in
radians.
a. Hukum pemantulan berlaku sin
munculnya maka n sin
;
= sin
= nsin
3
. Jika
adalah sudut
. n di udara 1 maka sin
=sin
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
Sudut muncul/
sejajar dengan sudut datang, x
adalah jarak antara sinar datang dengan sinar biasnya.
Panjang gelombang di kaca umpamakan C maka C cos
X=
Dsin
= t dan C= t/cos
= D sin ( -
radian, sin
cos
; sin
2,
. Sudut
t sin (2)
cos 2
X=
b. Jika semua sudutnya
dan
kecil (small) dan dalam
; sin
dan
1. n , so /n, nilai X menjadi
2
2
X
( n )
( n1 ) t
n
BAB 35
2.) In Fig. 35-30, a light wave along ray r l reflects once from a mir-ror and
a light wave along ray r2 reflects twice from that same mir-ror and once
from a tiny mirror at distance L from the bigger mirror. (Neglect the slight
and are initially exactly
tilt of the rays.) The waves have wavelength
out of phase. What are the (a) smallest, (b) second smallest, and (c) third
smallest values of L/ that result in the final waves being exactly in
phase?
Persamaan yang berlaku untuk lebar celah L=
2 m+1
dimana nilai m =
0,1,2,3....
a. Nilai terkecil m=0; L/
=
b. Nilai selanjutnya m= 1; L/ =
c. Nilai ketiga m= 2; L/ = 5/4
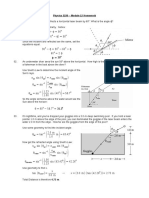
4.) In Fig. 35-31a, a beam of light in material 1 is incident on a boundary
at an angle of 30. The extent to which the light is bent due to refraction
depends, in part, on the index of refraction n 2 of material 2. Figure 35-31b
Petra Elang Pradana/ 1106023096
Teknik Perkapalan
gives the angle of refraction
versus n2 for a range of possible n2
values, from na = 1.30 to nb = 1.90.
speed of light in material 1 ?
Hukum snellius
n1=n2. Pada grafik , ketika
What
is
ketika
300 n2=1,5
Kecepatan dimedium v= c/n1 = 2,998
108 / 1,5 = 2
108 m/s
10.) In Fig. 35-33, a light ray is inci-dent at
angle 1 = 50 on a series of five transparent layers with parallel boundaries. For layers 1 and 3, L I =
20 pm, L3 = 25 pm, nl = 1.6, and n3 = 1.45.
(a) At what angle does the light emerge back
into air at the right? (b) How much time does the
light take to travel through layer 3?
a. Sudut keluar sama dengan sudut datang yaitu 500
b. Waktu yang dibutuhkan cahaya untuk melewati layer 3
t= nL/c = (1,45)(25 10-19m)/ (3 108 m/s)= 1,4 10-13 s
the
You might also like
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- BiprismDocument35 pagesBiprismAviral99No ratings yet
- FAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 23-Aug-2021 NA Problems1Document54 pagesFAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 23-Aug-2021 NA Problems1tejas paiNo ratings yet
- 17 InterferometersDocument84 pages17 InterferometersAnirban PaulNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Annex 2 - Delivery Format - Task 2Document13 pagesAnnex 2 - Delivery Format - Task 2Ever CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Student ENE423Document14 pagesLecture 3 Student ENE423reraisinNo ratings yet
- Week8 InterferometersDocument84 pagesWeek8 InterferometersArijit PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Ondas Electromagneticas en Medios CerradosDocument14 pagesOndas Electromagneticas en Medios CerradosANYELO DARIO TOVAR ROANo ratings yet
- As 23b OpticsDocument57 pagesAs 23b OpticsHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2. Section-A: Short QuestionsDocument5 pagesUnit - 2. Section-A: Short QuestionsKadis PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Document10 pagesUltrasonic Echography A-Scan and Ultrasonic B-Scan: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)SITI NURFATIHA JAMIANNo ratings yet
- Course: Physics (PH101) : Duration: 3 WeeksDocument2 pagesCourse: Physics (PH101) : Duration: 3 WeeksRajendra BisoiNo ratings yet
- ISAT 2011 PaperDocument30 pagesISAT 2011 PaperRavi LorventNo ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical FibresDocument31 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FibresWail HamedNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument19 pagesOptical FibreAbdul Qadir Mohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- SPPU PHYSICS QP Solution 2012-13 sem-IIDocument8 pagesSPPU PHYSICS QP Solution 2012-13 sem-IIHemantNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument72 pagesLecture 2 Electronic Structure of AtomsKEMPNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsDocument12 pages6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsNathanian50% (2)
- InterferenceDocument8 pagesInterferencerajesh.v.v.kNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document60 pagesCH 7Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- CH 35 FDocument19 pagesCH 35 FrobdebobNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesMidterm 1 SolutionsConrad DudeNo ratings yet
- ISAT-2011 Previous Year Question PaperDocument30 pagesISAT-2011 Previous Year Question Paperktktkt01No ratings yet
- Refraction 1Document8 pagesRefraction 1Sudharsan Gupta SudhirNo ratings yet
- be_first-year-engineering_semester-2_2018_december_applied-physics-ii-cbcgsDocument20 pagesbe_first-year-engineering_semester-2_2018_december_applied-physics-ii-cbcgsmahek guptaNo ratings yet
- Interference of light in thin films observed as different coloursDocument3 pagesInterference of light in thin films observed as different coloursNisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Interference: A. Double Slit InterferenceDocument22 pagesInterference: A. Double Slit InterferenceMade TamaraNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document4 pagesExercise 3JavierNo ratings yet
- Assignment-11 and SolutionDocument8 pagesAssignment-11 and SolutionadimeghaNo ratings yet
- Interference of LightDocument23 pagesInterference of LightShafin AnowarNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument15 pagesRefractionSudharsan Gupta Sudhir100% (1)
- Solution Physics QuizDocument3 pagesSolution Physics QuiztoaniltiwariNo ratings yet
- FAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000316 Reference Material I 15-Oct-2022 Module 1-Interference-01Document12 pagesFAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000316 Reference Material I 15-Oct-2022 Module 1-Interference-01Pritam PatraNo ratings yet
- REFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A LevelDocument47 pagesREFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A Levelssenyonjotrevor01No ratings yet
- Task 2 - Electromagnetic Waves in Bounded Open Media Individual WorkDocument11 pagesTask 2 - Electromagnetic Waves in Bounded Open Media Individual WorkSebastián HabibNo ratings yet
- Physical Optics: Interference of LightDocument6 pagesPhysical Optics: Interference of LightvinaykgkNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document19 pagesCH 13Eufemio MorenoNo ratings yet
- Newtons RingsDocument7 pagesNewtons RingsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledabood shabanehNo ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument38 pagesInterferenceAbror md FayiazNo ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument13 pagesInterferenceYugandhar VeeramachaneniNo ratings yet
- A00103781 Jose Rodriguez Copra3Document5 pagesA00103781 Jose Rodriguez Copra3SurFreestyleNo ratings yet
- 131 Refrac - CalcsDocument3 pages131 Refrac - CalcsWongXinXinNo ratings yet
- Astro 501 Fundamental Astronomy Problem Set 3 Due DateDocument5 pagesAstro 501 Fundamental Astronomy Problem Set 3 Due DateMax EisenhardtNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3: 1 2 CritDocument1 pageQuiz 3: 1 2 Critcab0oseNo ratings yet
- PHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Document14 pagesPHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Jason Tan100% (2)
- Anschp 35Document11 pagesAnschp 35pashelo001No ratings yet
- Physics2220 Solutions Module12Document3 pagesPhysics2220 Solutions Module12SeleneblueNo ratings yet
- HGDocument49 pagesHGZaheer Abbas QalooNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics: Dr. Chetan Kotabage Department of Physics Kls Gogte Institute of TechnologyDocument39 pagesApplied Physics: Dr. Chetan Kotabage Department of Physics Kls Gogte Institute of TechnologyTanishka BhiseNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2011Document30 pagesAieee 2011Shruti GaurNo ratings yet
- OQP Assignment Questions and SolutionDocument30 pagesOQP Assignment Questions and SolutionSagarika Padhi Sagarika PadhiNo ratings yet
- Compile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviDocument10 pagesCompile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviSelma Regita MahardiniNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics InterferenceDocument12 pagesWave Optics InterferenceYang Xiao XiaoNo ratings yet
- Midterm 04Document10 pagesMidterm 04Diego GuerraNo ratings yet
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiFrom EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsFrom EverandEssentials of Lasers: The Commonwealth and International Library: Selected Readings in PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Stat & Prob - OKDocument96 pagesStat & Prob - OKMiftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 10Document6 pagesPhysics Homework 10Miftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 11Document8 pagesPhysics Homework 11Miftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 11Document8 pagesPhysics Homework 11Miftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Physics Homework 10Document6 pagesPhysics Homework 10Miftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Movie ReviewDocument1 pageMovie ReviewMiftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- Physic Homework 13Document9 pagesPhysic Homework 13Miftah ShidqiNo ratings yet
- BelowsDocument35 pagesBelowstejassidhpuraNo ratings yet
- Mean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldDocument4 pagesMean Deviation - Wolfram MathWorldbraulio.dantas-1No ratings yet
- Worksheet On Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Quantum NumbersJannah Mae IsioNo ratings yet
- Cluster ExpansionDocument4 pagesCluster ExpansionflytrapsolNo ratings yet
- Teacher Guide Activity 2 AccelerationDocument4 pagesTeacher Guide Activity 2 AccelerationCanada Railway TimesNo ratings yet
- API 510 Pressure Vessel Inspector Certification Preparation CourseDocument4 pagesAPI 510 Pressure Vessel Inspector Certification Preparation CoursejbsantoNo ratings yet
- Interactions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument24 pagesInteractions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsEmmanuel Vachon LachanceNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFDocument28 pagesHeat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFhiren_mistry55No ratings yet
- Journal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingDocument4 pagesJournal of Environmental Sciences research on morphology changes of coking coal during cokingJohan Pranata BarusNo ratings yet
- Judo Bio MechanicsDocument11 pagesJudo Bio MechanicsAttilio Sacripanti100% (6)
- CH20005-Chemical Reaction Engineering:) C C CRDocument2 pagesCH20005-Chemical Reaction Engineering:) C C CRSunny KashyapNo ratings yet
- Book Review Electrochemistry: "Electrolysis". Pot-PourriDocument2 pagesBook Review Electrochemistry: "Electrolysis". Pot-PourriShashank ChandraNo ratings yet
- Notesch # 18Document11 pagesNotesch # 18ZeeshanMahdiNo ratings yet
- Bearings ShaftsDocument74 pagesBearings ShaftsCik MinnNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Concept of ViscosityDocument11 pagesCH 3 Concept of ViscosityJenny ChenNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes On Duplex SSDocument22 pagesTechnical Notes On Duplex SSBhyrappaNo ratings yet
- Cementing EquipDocument12 pagesCementing Equipzbhdzp100% (1)
- Solar System and Astronomy FactsDocument535 pagesSolar System and Astronomy FactsKavita KrishnamorthiNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Properties of Silver NanoparticlesDocument37 pagesAntimicrobial Properties of Silver NanoparticlesbasavarajitnalNo ratings yet
- Fluent 6.0 Staff Training Combustion and DPMDocument30 pagesFluent 6.0 Staff Training Combustion and DPMZakManNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Fracture Injection Tests in Ultra Low Perm FormationsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Fracture Injection Tests in Ultra Low Perm FormationsBolsec14No ratings yet
- Choice of Steel Material To Avoid Brittle Fracture For Hollow Section StructuresDocument204 pagesChoice of Steel Material To Avoid Brittle Fracture For Hollow Section Structuresg1n2No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266Document9 pagesChapter 22 Thermal Expansion: EXERCISE 122, Page 266NurulAinMatAron0% (1)
- Electrostatics PDFDocument51 pagesElectrostatics PDFSaksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Audio Processing Quiz 1Document2 pagesAudio Processing Quiz 1Tony BrooksNo ratings yet
- Skema Chemistry Paper 3Document8 pagesSkema Chemistry Paper 3nurul atiqahNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaDocument4 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaVenkat ChadalavadaNo ratings yet
- Art AnalysisDocument3 pagesArt AnalysisCheeny VelascoNo ratings yet
- Information Folder LUCCON PDFDocument9 pagesInformation Folder LUCCON PDFASHOKKUMAR ENo ratings yet
- Submodular Set Function - WikipediaDocument5 pagesSubmodular Set Function - WikipedianmahsevNo ratings yet