Professional Documents
Culture Documents
605 Nursing Care Plan 29-1: Patient With Asthma
Uploaded by
JonathonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
605 Nursing Care Plan 29-1: Patient With Asthma
Uploaded by
JonathonCopyright:
Available Formats
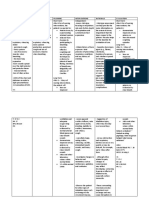
CHAPTER 29 Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
605
NURSING CARE PLAN 29-1
Patient with Asthma
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
PATIENT GOALS
Ineffective airway clearance related to bronchospasm, excessive mucus production, tenacious secretions, and fatigue
as evidenced by ineffective cough, inability to raise secretions, adventitious breath sounds
1. Maintains clear airway with removal of excessive secretions
2. Experiences normal breath sounds and respiratory rate
OUTCOMES (NOC)
Respiratory Status: Airway Patency
INTERVENTIONS (NIC) AND RATIONALES
Asthma Management
Determine baseline respiratory status to use as a comparison point.
Monitor rate, rhythm, depth, and effort of respiration to determine need for intervention and
evaluate effectiveness of interventions.
Observe chest movement, including symmetry, use of accessory muscles, and supraclavicular
and intercostal muscle retractions, to evaluate respiratory status.
Auscultate breath sounds, noting areas of decreased/absent ventilation and adventitious sounds,
to evaluate respiratory status.
Administer medication as appropriate and/or per policy and procedural guidelines to improve
respiratory function.
Coach in breathing/relaxation techniques to improve respiratory rhythm and rate.
Offer warm fluids to drink to liquefy secretions and promote bronchodilation.
Respiratory rate _____
Respiratory rhythm _____
Moves sputum out of airway _____
Ease of breathing _____
Measurement Scale
1 = Severely compromised
2 = Substantially compromised
3 = Moderately compromised
4 = Mildly compromised
5 = Not compromised
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
PATIENT GOALS
Anxiety related to difficulty breathing, perceived or actual loss of control, and fear of suffocation as evidenced by restlessness,
elevated pulse, respiratory rate, and blood pressure
1. Reports decreased anxiety with increased control of respirations
2. Experiences vital signs within normal limits
OUTCOMES (NOC)
Anxiety Level
INTERVENTIONS (NIC) AND RATIONALES
Anxiety Reduction
Restlessness _____
Increased blood pressure _____
Increased pulse rate _____
Increased respiratory rate _____
Verbalized anxiety _____
Facial tension _____
Measurement Scale
1 = Severe
2 = Substantial
3 = Moderate
4 = Mild
5 = None
Identify when level of anxiety changes to determine possible precipitating factors.
Use calm, reassuring approach to provide reassurance.
Stay with patient to promote safety and reduce fear.
Encourage verbalization of feelings, perceptions, and fears to identify problem areas so appropriate
planning can take place.
Provide factual information concerning diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis to help patient know
what to expect.
Instruct patient in the use of relaxation techniques to relieve tension and to promote ease of respirations.
NURSING DIAGNOSIS
PATIENT GOALS
Deficient knowledge related to lack of information and education about asthma and its treatment as evidenced by frequent
questioning regarding all aspects of long-term management
1. Describes the disease process and treatment regimen
2. Demonstrates correct administration of aerosol medications
3. Expresses confidence in ability for long-term management of asthma
OUTCOMES (NOC)
Asthma Self-Management
INTERVENTIONS (NIC) AND RATIONALES
Asthma Management
Describes causal factors _____
Initiates action to avoid and manage
personal triggers _____
Seeks early treatment of infections _____
Monitors peak flow routinely _____
Monitors peak flow when symptoms occur _____
Makes appropriate medication choices _____
Demonstrates appropriate use of inhalers,
spacers, and nebulizers _____
Self-manages exacerbations _____
Reports uncontrolled symptoms to health care
provider _____
Determine patient/family understanding of disease and management to assess learning needs.
Teach patient to identify and avoid triggers as possible to prevent asthma attacks.
Encourage verbalization of feelings about diagnosis, treatment, and impact on lifestyle to offer
support and increase compliance with treatment.
Educate patient about the use of the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) meter at home to promote
self-management of symptoms.
Instruct patient/family on antiinflammatory and bronchodilator medications and their appropriate
use to promote understanding of effects.
Teach proper techniques for using medication and equipment (e.g., inhaler, nebulizer, peak flow
meter)* to promote self-care.
Assist in the recognition of signs/symptoms of impending asthmatic reaction and implementation
of appropriate response measures to prevent escalation of attacks.
Establish a written plan with the patient for managing exacerbations to plan adequate treatment
of future exacerbations.
Measurement Scale
1 = Never demonstrated
2 = Rarely demonstrated
3 = Sometimes demonstrated
4 = Often demonstrated
5 = Consistently demonstrated
*See Tables 29-7, 29-8, 29-10 and Fig. 29-7.
You might also like
- Amanda AquiliniDocument2 pagesAmanda AquilinineoclintNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument34 pagesCase StudyJuzzy AnaydosNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Sas 21Document4 pagesSas 21Sistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Subjectives: Short Term Independent: Short TermDocument13 pagesSubjectives: Short Term Independent: Short TermMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Risk FactorsEdson John DemayoNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Situation:: Sbar For Copd Name: MR. Gomez 68 Yr Old, M Allergies-AmpicillinDocument5 pagesSituation:: Sbar For Copd Name: MR. Gomez 68 Yr Old, M Allergies-AmpicillinMrRightNo ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument9 pagesASTHMAmildred alidonNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument14 pagesGlaucomaWilliam SumoroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders Case StudyDocument4 pagesRespiratory Disorders Case StudyPremiums of the RoseNo ratings yet
- Managing COPD ExacerbationDocument17 pagesManaging COPD ExacerbationSean Menard Flores100% (1)
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome in a 5-Year-Old GirlDocument33 pagesGuillain-Barré Syndrome in a 5-Year-Old GirlYoel RayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanGabrielGitaNo ratings yet
- Risk For IneffectiveDocument6 pagesRisk For IneffectiveAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesACTIVITY 1: Nursing Care PlanChelsea JardelezaNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDDocument21 pagesAsthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDناصر دويكاتNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Pedia PDFDocument8 pagesDrugs Study Pedia PDFmark angeloNo ratings yet
- Revalida Review NotesDocument14 pagesRevalida Review NotesBryan Lloyd RayatNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 2Document1 pageConcept Map 2lanrevoiceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Eye & Ear IrrigationDocument34 pagesEye & Ear IrrigationdaisyNo ratings yet
- Day 15 - NCM-109 Children With Alteration in Oxygenation (A)Document50 pagesDay 15 - NCM-109 Children With Alteration in Oxygenation (A)Sheena Patricia ArasulaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsDocument6 pagesPredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors: Contributing FactorsKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Leadership, Management and Research Competency AppraisalDocument2 pagesNursing Leadership, Management and Research Competency AppraisalCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Disharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderDocument2 pagesDisharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderDianne Loregas SanchezNo ratings yet
- NSG 432cc Care PlanDocument8 pagesNSG 432cc Care Planapi-509642710100% (1)
- Vital SignsDocument38 pagesVital SignsSanjna Kumari (SNSR Senior Tutor/Lecturer)100% (1)
- Maternity Case StudyDocument31 pagesMaternity Case StudySyed Mohd Asri SabNo ratings yet
- Lower respiratory tract infectionsDocument8 pagesLower respiratory tract infections2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- RUBRIC Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningDocument4 pagesRUBRIC Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningElaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Asthma: A. DefinitionDocument6 pagesAsthma: A. DefinitionElvando SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Pontine BleedingDocument99 pagesPontine BleedingJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge and Practice Regarding Ventilator Associated Pneumonia VAP Critical Care Bundle Among Students of Selected Nursing Colleges of Distt. Mohali, PunjabDocument5 pagesA Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge and Practice Regarding Ventilator Associated Pneumonia VAP Critical Care Bundle Among Students of Selected Nursing Colleges of Distt. Mohali, PunjabEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Finished 2Document6 pagesConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- 5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pages5 Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlansMichelle Danica Vicente PaswickNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Adult Care Plan Impair Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAdult Care Plan Impair Gas ExchangeVic DangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document9 pagesDrug Study 2Justin PasaronNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesBronchitis in ChildrenVibhaSingh1No ratings yet
- University of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesUniversity of The East: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPATRICIA JEANNE JABIANNo ratings yet
- نسخة اختبارDocument318 pagesنسخة اختبارSami AlanziNo ratings yet
- Habit Rol TtsDocument9 pagesHabit Rol TtsGrecu IonutNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus InfographicDocument1 pageCorona Virus Infographicapi-510312435No ratings yet
- AfibDocument2 pagesAfibhakdogNo ratings yet
- ICU NCP AirwayDocument3 pagesICU NCP AirwayLisa TandogNo ratings yet
- Ret DemsDocument103 pagesRet DemsPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelDocument16 pagesOxygen Terapi Dan PrinsipelAmrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Sample 3Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Sample 3anon-333251No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaSteffanie Serrano100% (1)
- Dopamine Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDopamine Drug StudyHannah Philene D. CalubNo ratings yet
- Karl Pearson Correlation CoefficientDocument10 pagesKarl Pearson Correlation CoefficientBalaram ChampannavarNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis: Bronchial Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Bronchial Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeAndrea Chua BuadoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Care PlanDocument2 pagesAsthma Care Planwongfany100% (2)
- DX Asthma PDFDocument6 pagesDX Asthma PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Penuemonia Care PalnDocument2 pagesPenuemonia Care PalnVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Asthma NCPDocument4 pagesAsthma NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Cram SheetDocument8 pagesNCLEX Cram SheetKaloy Kamao100% (5)
- Medications - ADHDDocument1 pageMedications - ADHDJonathonNo ratings yet
- The BestDocument1 pageThe BestJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 54 - Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDocument13 pagesChapter 54 - Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39 - Introduction To The Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 39 - Introduction To The Reproductive SystemJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 - Muscle RelaxantsDocument12 pagesChapter 25 - Muscle Relaxantslarry blueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 047Document13 pagesChapter 047JonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 - Introduction To The Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesChapter 34 - Introduction To The Endocrine SystemJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 59 - Antiemetic AgentsDocument11 pagesChapter 59 - Antiemetic AgentsJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 57 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal SecretionsDocument11 pagesChapter 57 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal SecretionsJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 55 - Drugs Acting On The Lower Respiratory TractDocument13 pagesChapter 55 - Drugs Acting On The Lower Respiratory TractJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 58 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument12 pagesChapter 58 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal MotilityJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 56 - Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument11 pagesChapter 56 - Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemJonathonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Introduction To The ImmuneDocument13 pagesChapter 15 - Introduction To The ImmuneJonathonNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Care MapDocument7 pagesHyperthyroidism Care MapJonathonNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism Care MapDocument1 pageHyperthyroidism Care MapJonathonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PharmDocument2 pagesEndocrine PharmJonathonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PharmDocument2 pagesEndocrine PharmfranjoyNo ratings yet
- Care Map UtiDocument1 pageCare Map UtiJonathonNo ratings yet
- Incontinence Types ofDocument1 pageIncontinence Types ofJonathonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac System MedicationsDocument4 pagesCardiac System MedicationsfranjoyNo ratings yet
- Acs DXDocument2 pagesAcs DXJonathonNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument5 pagesCancerJonathonNo ratings yet
- Illeal Conduit Care MapDocument1 pageIlleal Conduit Care MapJonathonNo ratings yet
- Acs DXDocument6 pagesAcs DXJonathonNo ratings yet
- ECG HandoutDocument3 pagesECG HandoutJonathonNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics-AntiInfectives 2Document1 pageAntibiotics-AntiInfectives 2JonathonNo ratings yet
- Stages of DevelopmentDocument1 pageStages of DevelopmentJonathonNo ratings yet
- Pad Vs PVD ChartDocument1 pagePad Vs PVD ChartJonathonNo ratings yet
- Infection Control ChartDocument11 pagesInfection Control ChartbrittanyNo ratings yet
- Core StiffnessMcGill 2015Document12 pagesCore StiffnessMcGill 2015Hugo TintiNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Waste ManagementDocument14 pagesBiomedical Waste ManagementdivyeshkpatelNo ratings yet
- Duke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inDocument3 pagesDuke University Nurse Anesthesia Program (Acct #7042) Montgomery, Kelly Barton (Semester 7) Is Logged inkellyb11No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareDocument32 pagesSchizophrenia: Causes, Types, and Nursing CareNasriah Macadato100% (1)
- Intro CBTDocument12 pagesIntro CBTAria LevinsNo ratings yet
- Testimonial Theatre-Making: Establishing or Dissociating The SelfDocument9 pagesTestimonial Theatre-Making: Establishing or Dissociating The SelfLucretia DespinoiuNo ratings yet
- History of Ultrasound and Its Applications in GynecologyDocument28 pagesHistory of Ultrasound and Its Applications in Gynecologymichal ben meronNo ratings yet
- Preventing Illness and Living With Ill HealthDocument11 pagesPreventing Illness and Living With Ill HealthMonique MavronicolasNo ratings yet
- Quezon City - Ang Tahanan NG Quezon City3Document11 pagesQuezon City - Ang Tahanan NG Quezon City3Jalimay CabadingNo ratings yet
- CPAP ManualDocument43 pagesCPAP ManualTachira Julher RiveraNo ratings yet
- Art Therapy With Young Survivors of Sexual Abuse - Lost For WordsDocument215 pagesArt Therapy With Young Survivors of Sexual Abuse - Lost For WordskhalsomaliNo ratings yet
- User Manual LIS 1050 LT1370 Ing - Rev2Document27 pagesUser Manual LIS 1050 LT1370 Ing - Rev2AlexeyNo ratings yet
- Complete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument8 pagesComplete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Reverse AlzheimersDocument40 pagesReverse Alzheimersakajhon100% (9)
- Patellofemoral Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty PDFDocument8 pagesPatellofemoral Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty PDFSergiu PlescaNo ratings yet
- Pancha Karma (Sree Subramania Ayurvedic Nursing Home)Document15 pagesPancha Karma (Sree Subramania Ayurvedic Nursing Home)Sanand Ratnam Thekkayil100% (1)
- Health Assessment Exam 1 Study GuideDocument8 pagesHealth Assessment Exam 1 Study GuideDharati Patel100% (1)
- Research ProposalDocument6 pagesResearch Proposalapi-355503275No ratings yet
- Funcional Properties of Bioctive Peptides Derived From MeatDocument22 pagesFuncional Properties of Bioctive Peptides Derived From MeatJohanna RomeroNo ratings yet
- Sputum Culture TestDocument5 pagesSputum Culture TestpraveenASPNo ratings yet
- Nursing History Part 1. Demographic InformationDocument6 pagesNursing History Part 1. Demographic InformationAngelica VillalonNo ratings yet
- Cyanide PoisoningDocument5 pagesCyanide Poisoningriz04_fortitudessa5178No ratings yet
- Unit 1: Consumer HealthDocument23 pagesUnit 1: Consumer HealthGriffin AndersonNo ratings yet
- Effect of Sensorimotor Stimulation On Oropharyngeal DysphagiaDocument11 pagesEffect of Sensorimotor Stimulation On Oropharyngeal Dysphagiasneha duttaNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument14 pagesAtrial FibrillationNur Atiqah ZainalNo ratings yet
- Days Papers 2001Document341 pagesDays Papers 2001jorgefeitoza_hotmailNo ratings yet
- ArthrocentesisDocument4 pagesArthrocentesisAlejandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Best Personality Development Course Navi MumbaiDocument2 pagesBest Personality Development Course Navi MumbaiGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Ot StrokeDocument44 pagesOt StrokeDebora Astried F SipayungNo ratings yet