Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inverter Experiments
Uploaded by
visalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inverter Experiments
Uploaded by
visalCopyright:
Available Formats
Inverter
Laboratory exercise 3
Inverter (DC AC)
An inverter is an electrical device that converts DC to AC power by switching the DC
input voltage in a pre-determined sequence so as to generate AC output voltage.
Applications: AC motor control, uninterruptible power supply (UPS), etc.
3.1 Width control of Single-phase inverter
V1
V11
V3
V13
V2
V12
up
U
ip
V4
V14
Pic 1 Single-phase inverter (RL load, = , UpRMS = U)
control angle
Pic 2 Single-phase inverter (RL load, < , UpRMS < U)
An effective load voltage (Single-phase inverter):
U pRMS U
(3.1)
Inverter
3.2 Width control of Three-phase inverter
A basic three-phase inverter consists of three single-phase inverter switches each
connected to one of the three load terminals.
V1
V01
V3
V03
V5
i p1
V05
L1
up1
u1- 2
L2
L3
V4
V04
V6
V06
V2
3xR
V02
Pic 3 Three-phase inverter
Pic 4 Six-step switching sequence and waveform of voltage ( = 180 = )
Up1 phase voltage, U1-2 line voltage
Inverter
An effective load voltage only for R load (Three-phase inverter):
U 3 pRMS 180
1
u 2 t dt
T
2
3
2
2
1
2
U
U dt U dt ...
3
3
3
2
U 0,47 U
3
7
U 3 pRMS 150
U 0,44 U
6
1
U 3 pRMS 120
U 0,41 U
6
U 3 pRMS 180
(3.2)
3.3 Pulse-width modulation (PWM)
Amplitudes of the triangular wave (carrier) and sine wave (modulating, desired) are
compared to obtain PWM waveform (output voltage of inverter).
PWM is the usual method used to achieve variable voltage and frequency (can be
controlled independently) of AC motor. Change of frequency means change of motor speed.
Pic 5 PWM
3.4 Variable-frequency drive (VFD)
A VFD is a system for controlling the rotational speed of an AC motor by controlling the
frequency of the electrical power supplied to the motor.
A VFD system generally consists of an operator interface, a frequency controller and an
AC motor.
Inverter
Pic 6 VFD system
Tasks
1. Width control of single-phase inverter with RL load: display waveforms of voltage
and current. Measure and calculate URMS (3.1) for = 180, 150, 120.
2. PWM control of single-phase inverter with RL load: display waveforms of voltage and
current.
3. Width control of three-phase inverter with R load and AC motor load: display
waveforms of voltage and current. Measure and calculate URMS (3.2) for R load and
= 180, 150, 120.
4. PWM control of three-phase inverter with AC motor load: display waveforms of
voltage and current for various switching frequencies.
D1
D3
D5
V1
V01
V3
V03
V5
V05
L1
L2
L1
L2
L3
L3
TR
V4
D4
D6
V04
V6
V06
V2
D2
Pic 7 Wiring diagram of Variable frequency controller (see Pic 6)
Device:
L1 L3
D1 D6
C
3-phase supply
Rectifier (6-pulse)
electrolyte capacitor
V1 V6
V01 V06
M 3~
Three-phase inverter
AC motor
Optional reference:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variable-frequency_drive
VFD system description
V02
M
3
3 x 400 V
50 Hz
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- SVPWM Thesis Prepared by DeekshitDocument81 pagesSVPWM Thesis Prepared by Deekshitchunduri_rambabuNo ratings yet
- AVR-ModelingDocument3 pagesAVR-ModelingsamkousNo ratings yet
- Auto Sync & Load ShareDocument24 pagesAuto Sync & Load Shareravi_kumar_100% (1)
- Auto Sync & Load ShareDocument24 pagesAuto Sync & Load Shareravi_kumar_100% (1)
- Electrical Calculation SheetsDocument4 pagesElectrical Calculation SheetsHusamHaskoNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument59 pagesInduction MotorAkama Kulasekara100% (3)
- Speed Control of Induction MotorDocument33 pagesSpeed Control of Induction MotorMaham NaeemNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Phase Controlled Rectifiers UsingDocument10 pagesSimulation of Phase Controlled Rectifiers UsinggubiliNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - Iduction Motor Drive Using Slip Power RecoveryDeepak BansalNo ratings yet
- TG-5 Relay SettingDocument10 pagesTG-5 Relay Settingbasil100% (1)
- Module 3 HVDC System ControlDocument14 pagesModule 3 HVDC System ControlMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Scalar Control of Ac DrivesDocument38 pagesScalar Control of Ac Drivessureshy-ee213No ratings yet
- Electrical Design AnalysisDocument2 pagesElectrical Design AnalysisEnegue Nilyab Soled SeyerNo ratings yet
- 023 Electrical ChecklistDocument1 page023 Electrical ChecklistJunard Lu HapNo ratings yet
- GTO-Based 48-Pulse STATCOM DynamicsDocument7 pagesGTO-Based 48-Pulse STATCOM DynamicsEngr Imtiaz Hussain GilaniNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Difference Between Frances Turbine and Kaplan TurbineDocument6 pagesDifference Between Frances Turbine and Kaplan TurbineHiongyiiNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesDocument5 pagesPrinciplesSachin RohillaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorDocument6 pagesModeling and Simulation of Frequency Converter Used in Speed Control of Asynchronous MotorLelosPinelos123No ratings yet
- Single Phase Bridge VSIDocument13 pagesSingle Phase Bridge VSIRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- VVC ControlDocument14 pagesVVC ControlRyte EchanoNo ratings yet
- Variable Speed DeriveDocument18 pagesVariable Speed DeriveEngr. Naveed MazharNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument89 pagesPower Electronicsneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument6 pagesAc Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FRoss ShawNo ratings yet
- Control AC Voltage Using ThyristorsDocument8 pagesControl AC Voltage Using ThyristorsAnucha YieNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode InvertersDocument22 pagesSwitch Mode InvertersVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Control Strategy for Three-Phase PWM Boost RectifierDocument18 pagesControl Strategy for Three-Phase PWM Boost RectifierHoàngMạnhTuấnNo ratings yet
- Fixed Frequency Sliding Mode Modulator For Current Mode PWM InvertersDocument7 pagesFixed Frequency Sliding Mode Modulator For Current Mode PWM InvertersPaulo UchihaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document89 pagesUnit 4Syed MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Prosedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDocument10 pagesProsedur Percobaan Motor SinkronSinkron Generator SinkronDara AmeliaNo ratings yet
- L2. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDocument104 pagesL2. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersShivaram Vadla100% (2)
- Multi-Modular Multi-Level Pulse Width Modulated Inverters: Mon W LDocument6 pagesMulti-Modular Multi-Level Pulse Width Modulated Inverters: Mon W LveguruprasadNo ratings yet
- Different Control Techniques of Dynamic VoltageDocument6 pagesDifferent Control Techniques of Dynamic VoltageSrinivas ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 InvertersDocument43 pagesUnit-4 InvertersbalafetNo ratings yet
- Project Status Review Semester: 7 EE (Group No: 2) Project I (2170001)Document51 pagesProject Status Review Semester: 7 EE (Group No: 2) Project I (2170001)UmangNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Dynamic Response Simulation of Gto-Based StatcomDocument4 pagesModeling and Dynamic Response Simulation of Gto-Based StatcomSadaf AnjumNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document89 pagesUnit 4Prafull BNo ratings yet
- SPWMDocument5 pagesSPWMKiran Kumar NallamekalaNo ratings yet
- DC Motors Speed Control - ModDocument9 pagesDC Motors Speed Control - ModAnuja VargheseNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost Ec2404Document65 pagesBuck Boost Ec2404Sai ChandhraNo ratings yet
- DC Drives and AC ControllerDocument27 pagesDC Drives and AC ControllerHolloGramNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryDocument9 pagesUnified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryAshutoshBhattNo ratings yet
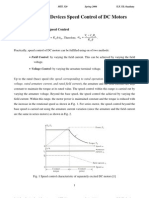
- 2.2 Conventional Methods of Speed Control: Unit-Ii DC DrivesDocument47 pages2.2 Conventional Methods of Speed Control: Unit-Ii DC DrivesrajeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Anil ParmarNo ratings yet
- Q02201300137Document8 pagesQ02201300137Vikas PatelNo ratings yet
- PWMDocument3 pagesPWMRakesh S ThodupuzhaNo ratings yet
- Improving The Power Quality by MLCI Type DSTATCOM: P. Manoj Kumar Y. Sumanth S. N. V. GaneshDocument5 pagesImproving The Power Quality by MLCI Type DSTATCOM: P. Manoj Kumar Y. Sumanth S. N. V. GaneshsarathNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibraryDocument22 pagesUnified Power Flow Controller (Phasor Type) : LibrarypavanNo ratings yet
- Application Note 24 A Simplified Test Set For Op Amp CharacterizationDocument12 pagesApplication Note 24 A Simplified Test Set For Op Amp CharacterizationpvickyNo ratings yet
- Cours Electronique de Puissance 2Document28 pagesCours Electronique de Puissance 2AigounNo ratings yet
- Ssemd PPT1Document205 pagesSsemd PPT1control 4uonlyNo ratings yet
- Psim SVMDocument9 pagesPsim SVMNarendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Adjust Excitation Equipment Voltage RegulatorsDocument12 pagesAdjust Excitation Equipment Voltage RegulatorskirananneNo ratings yet
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument211 pages02 Power Electronicsకృష్ణ మురళి100% (2)
- Control 3-Phase AC Drive with DSPDocument5 pagesControl 3-Phase AC Drive with DSPaman srivastavaNo ratings yet
- DR TutkaneDocument66 pagesDR Tutkanesaisrikanths5168No ratings yet
- Motor DrivesDocument61 pagesMotor DrivesSatesh NairNo ratings yet
- Ac Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument22 pagesAc Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDasari SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power ControlDocument73 pagesReactive Power Controlمحمد سليمانNo ratings yet
- Voltage RegulatorDocument31 pagesVoltage RegulatorMamidi Satya narayanaNo ratings yet
- Chopper Control DC Drive - 090075mDocument8 pagesChopper Control DC Drive - 090075mIsuru Pasan Dasanayake100% (1)
- An Adaptive Hy Steresis-Band Current Control Technique of A Voltage-Fed PWM Inverter For Machine Drive SystemDocument7 pagesAn Adaptive Hy Steresis-Band Current Control Technique of A Voltage-Fed PWM Inverter For Machine Drive SystemJandfor Tansfg Errott100% (1)
- PS 9213-Inverter AnalysisDocument18 pagesPS 9213-Inverter AnalysisvelukpNo ratings yet
- Exp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part IDocument7 pagesExp 11 Single Phase Inverter Part Iusmpowerlab0% (1)
- A New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesDocument7 pagesA New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesBharathkumars89No ratings yet
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Piotroski1 - Screener2Document4 pagesPiotroski1 - Screener2visalNo ratings yet
- Piotroski1 - Screener3Document4 pagesPiotroski1 - Screener3visalNo ratings yet
- Piotroski Score - Screener1Document4 pagesPiotroski Score - Screener1visalNo ratings yet
- REIMAGINING TODAY FOR A BETTER TOMORROWDocument264 pagesREIMAGINING TODAY FOR A BETTER TOMORROWSavy DhillonNo ratings yet
- HD44780Document23 pagesHD44780api-19831863No ratings yet
- Substation Enclosed Switchgear PCC FundamentalsDocument85 pagesSubstation Enclosed Switchgear PCC FundamentalsAlezsander RguezArNo ratings yet
- LV 25-pDocument4 pagesLV 25-pqais652002No ratings yet
- Induction Motor Parameter MeasurementDocument10 pagesInduction Motor Parameter Measurementvaljir23No ratings yet
- Cable Specifications For Control WiringDocument1 pageCable Specifications For Control WiringvisalNo ratings yet
- Safety Precautions in SubstationsDocument1 pageSafety Precautions in SubstationsvisalNo ratings yet
- Kuhnke PDFDocument112 pagesKuhnke PDFDan FlorescuNo ratings yet
- Fault Current Limiters Report On The Activities of CIGRE WG A3.10Document9 pagesFault Current Limiters Report On The Activities of CIGRE WG A3.10Sameer MalikNo ratings yet
- Palas ResumeDocument2 pagesPalas ResumeBLADE VLOGSNo ratings yet
- System proS Enclosed Starters GuideDocument38 pagesSystem proS Enclosed Starters GuideJuan Martin Alderete GobbatoNo ratings yet
- DC-AC Converter: PWM Inverter Operation and DesignDocument13 pagesDC-AC Converter: PWM Inverter Operation and Designnataphon kabkaewNo ratings yet
- Wsu Genprotintro 1slideperpage 160118Document137 pagesWsu Genprotintro 1slideperpage 160118PervimNo ratings yet
- 02 Analysis of Faults Notes PDFDocument38 pages02 Analysis of Faults Notes PDFJi Chou ChenNo ratings yet
- MEP Preliminary Program R00 - Local Authority MatrixDocument2 pagesMEP Preliminary Program R00 - Local Authority MatrixVarun AryaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EE 525Document2 pagesSyllabus EE 525Sajal JainNo ratings yet
- Master Panel Wiring DiagramDocument2 pagesMaster Panel Wiring DiagramShakik AhammodNo ratings yet
- Power Systems GATE 20 QuestionsDocument4 pagesPower Systems GATE 20 QuestionsOnly PersonalNo ratings yet
- BILL OF MATERIALSDocument8 pagesBILL OF MATERIALSPritam SinghNo ratings yet
- SELCO T-Line Generator Control Protection MonitoringDocument8 pagesSELCO T-Line Generator Control Protection MonitoringJesse GuoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: TransformersDocument5 pagesChapter 2: TransformerskhuzaimNo ratings yet
- ARMAN Feeds & Fisheries LTD: Morjal, Raipura, NarsingdiDocument2 pagesARMAN Feeds & Fisheries LTD: Morjal, Raipura, NarsingdiTanvirul islam fahimNo ratings yet
- SMGR 2004Document2 pagesSMGR 2004dennis dancunNo ratings yet
- LV Fuse Technical DetailsDocument8 pagesLV Fuse Technical DetailsMohan KNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Interruptor Siemens GMI PDFDocument20 pagesCatálogo Interruptor Siemens GMI PDFhesse21No ratings yet
- Em-Ii Assignment: Excitation of Synchronous GeneratorsDocument3 pagesEm-Ii Assignment: Excitation of Synchronous GeneratorsZain Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- NDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFDocument81 pagesNDB2 Series MCB Datasheet PDFjahabarsathickNo ratings yet
- Defect Management Guidelines - DraftDocument18 pagesDefect Management Guidelines - DraftqianghoNo ratings yet
- Siemens SentronDocument62 pagesSiemens SentronGonzalo PadillaNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Systems ClassificationsDocument16 pagesWind Energy Systems ClassificationsSubheesh KTNo ratings yet
- Brochure Inverter SG825865BEN A02-05.13Document4 pagesBrochure Inverter SG825865BEN A02-05.13zarun1No ratings yet