Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Description of Banana
Uploaded by
JessicaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Description of Banana
Uploaded by
JessicaCopyright:
Available Formats
Banana
Banana is one food for the offerings in prayers in Bali. In some countries, bananas
used for cooking. Banana is vaiable in size, color, and firmness, but it usually elongated and
curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a rind which may be green, yellow, red,
purple, or brown when ripe. Plants are normally tall and fairly sturdy, and are often mistaken
for tress, but what appears to be a trunk is actually a fals stem. Bananas grow is a wide
variety variety of soils, as long as the soil is at least 60 cm deep, has good drainage and is not
compacted. The leaves of banana plants are big. The base of the petiole widens to form a
sheath; the tightly packed sheaths make up the pseudostem, which is all that supports the
plant. The edges of the sheath meet when it is first produced, making it tubular. As new
growth occurs in the centre of the pseudostem the edges are forced apart. Cultivated banana
plants vary in height depending on the variety and growing conditions. Leaves are spirally
arranged and may grow 2.7 metres long and 60 cm wide.They are easily torn by the wind,
resulting in the familiar frond look.
When a banana plant is mature, the corm stops producing new leaves and begins to
form a flower spike. A stem develops which grows up inside the pseudostem, carrying the
immature inflorescence until eventually it emerges at the top. Each pseudostem normally
produces a single inflorescence, also known as the "banana heart". After fruiting, the
pseudostem dies, but offshoots will normally have developed from the base, so that the plant
as a whole is perennial. In the plantation system of cultivation, only one of the offshoots will
be allowed to develop in order to maintain spacing. The inflorescence contains many bracts
(sometimes incorrectly referred to as petals) between rows of flowers. The female flowers
(which can develop into fruit) appear in rows further up the stem (closer to the leaves) from
the rows of male flowers. The ovary is inferior, meaning that the tiny petals and other flower
parts appear at the tip of the ovary. The banana fruits develop from the banana heart, in a
large hanging cluster, made up of tiers (called "hands"), with up to 20 fruit to a tier.
There is a protective outer layer (a peel or skin) with numerous long, thin strings (the
phloem bundles), which run lengthwise between the skin and the edible inner portion. The
inner part of the common yellow dessert variety can be split lengthwise into three sections
that correspond to the inner portions of the three carpels by manually deforming the
unopened fruit. In cultivated varieties, the seeds are diminished nearly to non-existence; their
remnants are tiny black specks in the interior of the fruit. Bananas are naturally slightly
radioactive, more so than most other fruits, because of their potassium content and the small
amounts of the isotope potassium found in naturally occurring potassium. The banana
equivalent dose of radiation is sometimes used in nuclear communication to compare
radiation levels and exposures.
Name
: Yessica Kristanti
NIM
: 1411105046
Speciality : Food Science and Technology
You might also like
- Fruit Berry Herbaceous Flowering Plants Genus Bananas Used For Cooking StarchDocument2 pagesFruit Berry Herbaceous Flowering Plants Genus Bananas Used For Cooking StarchSHOAIB MEMONNo ratings yet
- Classification of Horticultural CropsDocument14 pagesClassification of Horticultural Cropsmonkey luffy80% (5)
- Herbaceous Corm Trees Pseudostem Petiole Lamina: TiersDocument1 pageHerbaceous Corm Trees Pseudostem Petiole Lamina: TiersTommy2No ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document1 pageResearch Paper 1GUDIVADA LOKESH SAINATHNo ratings yet
- Group Members: - Nurul Farihin Mohd Radzi - Nurulatikah Ahmad - Fhatin Amira Musa - Wijayanti Akhmad - Syafiqah ShaariDocument21 pagesGroup Members: - Nurul Farihin Mohd Radzi - Nurulatikah Ahmad - Fhatin Amira Musa - Wijayanti Akhmad - Syafiqah ShaariEllie EllaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 7184258664312500997Document5 pagesInbound 7184258664312500997Aera YeolmaeNo ratings yet
- Banana Expert System - BotanyDocument4 pagesBanana Expert System - BotanybhushanNo ratings yet
- DWI LISTIYANI (17304241032) Pendidikan Biologi A 2017: Hypogaea)Document3 pagesDWI LISTIYANI (17304241032) Pendidikan Biologi A 2017: Hypogaea)Listiyani DwiNo ratings yet
- Sweet PataoDocument1 pageSweet PataoTanvi PawarNo ratings yet
- Scientific Name FinDocument10 pagesScientific Name FinJey VlackNo ratings yet
- Sweetpotato Germplasm Management - Ipomoea Batatas - Training ManualDocument218 pagesSweetpotato Germplasm Management - Ipomoea Batatas - Training ManualDianis ParedesNo ratings yet
- Submitted To Proff. Uzman Bashir Cheema Submitted by Arifa BashirDocument5 pagesSubmitted To Proff. Uzman Bashir Cheema Submitted by Arifa BashirMALIK ASAD Iqbal LaangNo ratings yet
- Banana: Musa (Genus) Cooking Banana Cavendish Banana Banana (Disambiguation)Document7 pagesBanana: Musa (Genus) Cooking Banana Cavendish Banana Banana (Disambiguation)CHRISTY ANNE M. CARILLANo ratings yet
- Banana - WikipediaDocument33 pagesBanana - WikipediaBryan Paul BautistaNo ratings yet
- Morphological Characteristics of Different Fodder BerseemDocument5 pagesMorphological Characteristics of Different Fodder BerseemMALIK ASAD Iqbal LaangNo ratings yet
- Bio Diversity-1Document6 pagesBio Diversity-1Habiba Rowshan (221011069)No ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument8 pagesIntroductionBanana LatteNo ratings yet
- SaukoDocument3 pagesSaukoBTS ARMYNo ratings yet
- Plant TravelersDocument3 pagesPlant Travelersahuddle1No ratings yet
- Sytemaseyt 1Document6 pagesSytemaseyt 1Sheena R. ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Basic Botany 2Document92 pagesBasic Botany 2Michael OduorNo ratings yet
- Ipil IpilDocument4 pagesIpil IpilJohn Rudolf CatalanNo ratings yet
- Sugar Cane Morphology - ProjectDocument6 pagesSugar Cane Morphology - Projectsulha mNo ratings yet
- List of PlantsDocument4 pagesList of PlantsKim KwonNo ratings yet
- PteridophytesDocument5 pagesPteridophytesAsif SultanNo ratings yet
- Weed Chart Algae: Weed Control - Identifying Lake Weeds Quick ReferenceDocument10 pagesWeed Chart Algae: Weed Control - Identifying Lake Weeds Quick ReferenceJUAN_LUIS_MENARESNo ratings yet
- PR Manual Agron 221Document27 pagesPR Manual Agron 221Ganpat Lal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sample To SendDocument6 pagesSample To SendRica Ehlaine CañetaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of VegetableDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of VegetableChocostar StaaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab 13Document49 pagesBio Lab 13Jackie Swift FuntanillaNo ratings yet
- Passion Fruit PDFDocument14 pagesPassion Fruit PDFamuronegaduNo ratings yet
- Reoport in BIOLOGYDocument7 pagesReoport in BIOLOGYpauletteNo ratings yet
- Crop Report: Potato (SDocument6 pagesCrop Report: Potato (SMikaela MarcosNo ratings yet
- BananaDocument25 pagesBananaDomagoj ButumovićNo ratings yet
- Lagundi (Vitex-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesLagundi (Vitex-WPS OfficeJay-ar TVNo ratings yet
- Fruit Vegetables - : TomatoDocument8 pagesFruit Vegetables - : TomatoPradya NarismaNo ratings yet
- Zinnia Elegans' Flower, and Zantedeschia Aethiopica's Flower. The Second Step WasDocument12 pagesZinnia Elegans' Flower, and Zantedeschia Aethiopica's Flower. The Second Step WasFita Nur JannahNo ratings yet
- Ontario Lawn Weed IdentificationDocument3 pagesOntario Lawn Weed IdentificationJohnny DNo ratings yet
- Mayeth B. VillanuevaDocument4 pagesMayeth B. VillanuevaMayeth VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- UmmeLaila (18arid2374) Practical Notebook HORT - 603Document15 pagesUmmeLaila (18arid2374) Practical Notebook HORT - 603UmmelailaNo ratings yet
- Amaranthaceae and AmaryllidaceaeDocument2 pagesAmaranthaceae and AmaryllidaceaeZaivie VillanobosNo ratings yet
- HW2Document4 pagesHW2Cza GuerraNo ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- Tugas Cas, Ruben, AnesDocument7 pagesTugas Cas, Ruben, AnesClara SitepuNo ratings yet
- Learn MarcottingDocument14 pagesLearn MarcottingJOVELYN Y. ALFORQUENo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 3Document90 pagesSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- Maldives 3Document30 pagesMaldives 3hanzo1260No ratings yet
- Classification of Botanical CropsDocument16 pagesClassification of Botanical CropsJhanno Belleña Edig DapitanonNo ratings yet
- Trees PresentationDocument7 pagesTrees PresentationAr Deepti ManojNo ratings yet
- HOR 211 2022 Batch EX NO. 3Document22 pagesHOR 211 2022 Batch EX NO. 3KuttyNo ratings yet
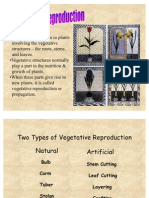
- Vegetative ReproductionDocument19 pagesVegetative ReproductionJane Sandra LimNo ratings yet
- Deskripsi MahoniDocument11 pagesDeskripsi MahoniDimas ArieyadiNo ratings yet
- Afrostain Banana Production GuideDocument21 pagesAfrostain Banana Production Guideonward marumuraNo ratings yet
- Types of Propagation and Classes of Plant PropagationDocument20 pagesTypes of Propagation and Classes of Plant PropagationJuliet Cayao SajolNo ratings yet
- Plantae Tracheobionta Spermatophyta Magnoliophyta Magnoliopsida Rosidae Sapindales Hippocastanaceae Aesculus L. Aesculus Glabra WilldDocument1 pagePlantae Tracheobionta Spermatophyta Magnoliophyta Magnoliopsida Rosidae Sapindales Hippocastanaceae Aesculus L. Aesculus Glabra Willdapi-24853125No ratings yet
- Scientific Name: Agapanthus Praecox Willd Common Name: Blue Lily or African Lily DescriptionDocument11 pagesScientific Name: Agapanthus Praecox Willd Common Name: Blue Lily or African Lily DescriptionJey VlackNo ratings yet
- 29 Edible Plants in The PhilippinesDocument0 pages29 Edible Plants in The PhilippinesChristine Carreon100% (3)
- Soal Akademik Tes Masuk Sma Plus Yasop Balige 2 019 Bahasa InggrisDocument12 pagesSoal Akademik Tes Masuk Sma Plus Yasop Balige 2 019 Bahasa Inggriswaqidi100% (1)
- Strawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument8 pagesStrawberry: For Other Species of Strawberry, See - For Other Uses, SeeIrene Joy GomezNo ratings yet
- Archaeological Finds of Ninth-And Tenth-Century Viking Foodstuffs Jorvík (York), Danelaw (England)Document3 pagesArchaeological Finds of Ninth-And Tenth-Century Viking Foodstuffs Jorvík (York), Danelaw (England)James RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organs Systems P1Document8 pagesPlant and Animal Organs Systems P1ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- International Coffee Organization: Ico Certificate of OriginDocument1 pageInternational Coffee Organization: Ico Certificate of OrigincahyoheriNo ratings yet
- Soil Biology The Soil Biology Primer ChaDocument21 pagesSoil Biology The Soil Biology Primer ChaRojotiana Marco RAKOTOMANANANo ratings yet
- Tomlinson 1992. Podocarpaceae ConeDocument18 pagesTomlinson 1992. Podocarpaceae ConejorbelocoNo ratings yet
- Ecology and Economic EntomologyDocument161 pagesEcology and Economic Entomologysushmetha venkatesanNo ratings yet
- Zahras Arabian Oud CatalogDocument66 pagesZahras Arabian Oud CatalogZahra GajNo ratings yet
- Harvesting: DNCRDPSC Technoguide Series 2020 No. 01Document2 pagesHarvesting: DNCRDPSC Technoguide Series 2020 No. 01tau econNo ratings yet
- Seed Longevity and DeteriorationDocument26 pagesSeed Longevity and DeteriorationAkhtar Abbas MagsiNo ratings yet
- English Conversation For Arabs: EgyptDocument38 pagesEnglish Conversation For Arabs: EgyptAnonymous ToHeyBoEbXNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge ALL PARTSDocument94 pagesGeneral Knowledge ALL PARTSSajid AliNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Morfologi Dan Anatomi Tipe StomataDocument9 pagesIdentifikasi Morfologi Dan Anatomi Tipe StomataDella AndreanaNo ratings yet
- Plant Fungal Diseases 3Document29 pagesPlant Fungal Diseases 3Mr FixerNo ratings yet
- Adaptations in Plants - Terrestrial HabitatDocument20 pagesAdaptations in Plants - Terrestrial Habitatatbatcha batNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Breeds of CowDocument9 pagesIndigenous Breeds of CowbruntigNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter Template General ApplicationDocument4 pagesCover Letter Template General ApplicationM SIREESHANo ratings yet
- Pectinase ReviewDocument13 pagesPectinase ReviewSyeda Mahfuza KhanomNo ratings yet
- 14 Rapeseed Muster DDocument20 pages14 Rapeseed Muster DMamata khandappagolNo ratings yet
- Reishi MushroomDocument5 pagesReishi MushroomBrij Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Perrier Sorem ActivityDocument18 pagesPerrier Sorem ActivityAnnisya FalensyNo ratings yet
- Oryza Glaberrima (African Rice) - As A Cereal Grain, It Is The MostDocument26 pagesOryza Glaberrima (African Rice) - As A Cereal Grain, It Is The MostAbiodun GbengaNo ratings yet
- Picture Description - in The KitchenDocument1 pagePicture Description - in The Kitchena1english academyNo ratings yet
- Science - Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesScience - Levels of OrganizationAlexNo ratings yet
- French Fries Home Made RecipeDocument2 pagesFrench Fries Home Made RecipeFrank KoningsNo ratings yet
- TÌM LỖI SAI trong đề thi THPT Quốc Gia (Phần 1)Document13 pagesTÌM LỖI SAI trong đề thi THPT Quốc Gia (Phần 1)Bùi Hồng QuảngNo ratings yet
- Simple Fractionation Through The Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Palm Kernel OilDocument8 pagesSimple Fractionation Through The Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Palm Kernel OilDevany Sofiana PurbaNo ratings yet
- Bagonbon National High School: Division of San Carlos CityDocument4 pagesBagonbon National High School: Division of San Carlos CityhomeylinNo ratings yet
- Recipe BookDocument16 pagesRecipe BookKaterina GeraliNo ratings yet