Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition
Uploaded by
Snezana MihajlovicCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition
Uploaded by
Snezana MihajlovicCopyright:
Available Formats
GE Healthcare
Arrhythmia Recognition
Cardiac Conduction System
ECG Components
Electrical and Mechanical Events
LEFT
ATRIUM
Sinoatrial
Node
HIS Bundle
RIGHT ATRIUM
Left Bundle
Branch
Right Bundle
Branch
LEFT
VENTRICLE
RIGHT
VENTRICLE
VERTICAL
AXIS
1 Small Square = 1 mm (0.1 mV)
1 Small Square = .04 sec (40 msec)
1 Large Square = 5 mm (0.5 mV)
HORIZONTAL 1 Large Square = .2 sec (200 msec)
AXIS
2 Large Squares = 1 mV
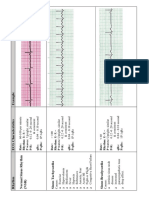
Sinus Rhythms
Mid
Diastole
5 Large Squares = 1 sec (1000 msec)
Atrial
Contraction
Isovolumic
Ventricular
Contraction
Supraventricular Rhythms
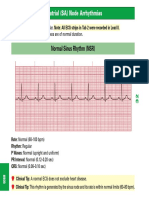
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Right Bundle Branch Block
Atrial Tachycardia
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
60 100 bpm
Regular
Before each QRS,
identical
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
140 250 bpm
Regular
Abnormal P before
each QRS
(difcult to see)
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
N/A
Irregular
Premature and
abnormal.
May be hidden
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
Sinus Arrhythmia
QRS
Isovolumic
Ventricular
Relaxation
Conduction Defects
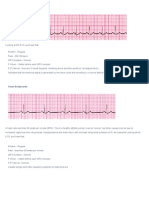
Premature Atrial Complexes PACs
Heart Rate
Ventricular
Ejection
QRS
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Before each QRS,
identical
0.12 to 0.20
0.12
RSR in V1
Left Bundle Branch Block
Atrial Flutter
Premature Atrial Complex Isolated PAC
Heart Rate
Usually
60 100 bpm
Rhythm
Irregular
P Wave
Before each QRS,
identical
PR Interval
(in seconds)
0.12 to 0.20
QRS
(in seconds)
< 0.12
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
QRS
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
N/A
Irregular
Premature and
abnormal.
May be hidden
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
A: 240 350 bpm
V: Varies with
conduction ratio
A: Regular
V: Regular,
group beating
or variable
Flutter (F) waves usually the negative component of the utter
wave in II, III, aVF and
positive in V1
N/A
< 0.12
Sinus Tachycardia
Premature Atrial Complexes (Atrial Bigeminy)
Every other beat is a PAC
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
> 100 bpm
Regular
Before each QRS,
identical
0.12 to 0.20
(in seconds)
< 0.12
Sinus Bradycardia
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
N/A
Irregular
Premature and
abnormal.
May be hidden
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Before each QRS,
identical
0.12 to 0.20
0.12
QS or rS in V1 and V2
ST elevation
Pre-excitation Syndrome
Atrial Fibrillation
QRS
Rhythm
PR Interval
QRS
(in seconds)
Heart Rate
P Wave
QRS
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
A: 350 650 bpm
V: Slow to rapid
Irregular
Absent
Fibrillatory (f) waves
N/A
< 0.12
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Before each QRS,
identical
< 0.12
Usually > 0.10
Delta wave
distorts initial QRS
First-Degree AV Block
Junctional Rhythm
Premature Atrial Complex with Aberrancy
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
< 60 bpm
Regular
Before each QRS,
identical
0.12 to 0.20
(in seconds)
QRS
(in seconds)
< 0.12
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
40 60 bpm
Regular
Inverted in inferior
leads; before, during
or after the QRS;
may be absent
< 0.12
< 0.12
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Before each QRS,
identical
> 0.20
< 0.12
Regular rhythm
Second-Degree AV Block Type I
(AV Wenckebach or Mobitz type I)
Sinus Arrest or SA Block
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
40 100 bpm
Irregular
Identical before
each QRS.
P to P interval
may be xed before
and after the pause
0.12 to 0.20
(in seconds)
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
N/A
Irregular
Premature and
abnormal.
May be hidden
0.12 to 0.20
< 0.12
Abnormal shape
QRS
(in seconds)
< 0.12
Nonconducted Premature Atrial Complex
Heart Rate
60 100 bpm
P Wave is buried in the T Wave.
Rhythm
P Wave
Usually AV May be sinus P wave
dissociation be- (AV dissociation)
cause of digitalis
toxicity
PR Interval
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Conduction
intermittent
Increasingly
prolonged
< 0.12
QRS dropped in a
repeating pattern
Second-Degree AV Block Type II
(Mobitz type II)
QRS
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
< 0.12
< 0.12
NOTE: Notch is not present in other T Waves
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
N/A
Irregular
Premature and
abnormal.
May be hidden
None
Absent
Junctional Tachycardia
QRS
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Sinus
Usually normal
and identical
(before and after a
blocked impulse)
Broad
0.12
Some P waves
are not conducted
Second-Degree AV Block 2:1 AV Block
Heart Rate
Rhythm
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Usually
<140 bpm
Regular
Inverted, absent or
after QRS
< 0.12
< 0.12
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Sinus
Normal or prolonged
Narrow or broad
2:1 AV conduction
Third-Degree (Complete) AV Block
Arrhythmia Recognition (poster 1 of 2)
This is part one of two posters to assist healthcare professionals in
recognizing basic arrhythmias. According to the Practice Standards
for Electrocardiographic Monitoring in Hospital Settings (Circulation.
2004;110:2721-2746) in general, the mechanisms of arrhythmias are
the same in both adults and children. However, the ECG appearance of
the arrhythmias may differ due to developmental issues such as heart
size, baseline heart rate, sinus and AV node function, and automatic
innervation.
ECG terminology and diagnostic criteria often vary from text to text and
from one teacher to another. There are often several terms describing
similar ndings (for example: Premature Atrial Contraction, Atrial
Premature Complex, Atrial Extrasystole, Supraventricular Ectopic Beat,
etc.) It is important to correlate the ECG interpretation with the clinical
observation of the patient.
Normal ECG Standards for Children by Age
Heart
Rate/Min
01d
13d
37d
7 30 d
1 3 mo
3 6 mo
6 12 mo
13 y
35y
58y
8 12 y
12 16 y
94 -155
(122)
91 - 158
(122)
90 - 166
(128)
106 - 182
(149)
120 - 179
(149)
105 - 185
(141)
108 - 169
(131)
89 - 152
(119)
73 - 137
(109)
65 - 133
(100)
62 - 130
(91)
60 - 120
(80)
PR Interval
Lead II
(Seconds)
0.08 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.13 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.15 0.08 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.17 0.09 - 0.18
(0.107)
(0.108)
(0.102)
(0.100)
(0.098)
(0.105)
(0.106)
(0.113)
(0.119)
(0.123)
(0.128)
(0.135)
QRS Interval
Lead V5
(Seconds)
0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.07 0.03 - 0.08 0.04 - 0.09 0.04 - 0.09
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.05)
(0.06)
(0.06)
(0.06)
(0.06)
(0.07)
All values 2nd 98th percentile; numbers in parentheses, means. Adapted from Pediatr Cardiol. 1979;1:123.
This poster includes Premature Ventricular Conduction, Pacemaker Lead
Placement, ST Segment Depression, Ventricular Rhythms, Pacemaker
Rhythms, Full Compensatory Pause and ECG Artifact. The ECG rhythm
strips display lead II as the top waveform and lead V1 as the bottom
waveform. Classic examples are shown for each rhythm to provide basic
visualization and avoid complexities. The intended use of this poster is
to compliment a text and/or course in addition to a reference guide for
arrhythmia recognition
The most common ECG rate, interval, and duration measurements are from the following publications:
Clinical Electrocardiography (Post Graduate Institute for Medicine).
Understanding Electrocardiography (Mary Boudreau Conover).
How to Quickly and Accurately Master Arrhythmia Interpretation (Dale Davis).
Principles of Clinical Electrocardiography (M. J. Goldman).
Basic Dysrhythmias Interpretation and Management (Robert Huszar).
An Introduction to Electrocardiography (Leo Shamroth).
Interpretation of Arrhythmias (Emanual Stein).
P Wave
PR Interval
(in seconds)
(in seconds)
QRS
Characteristics
Normal but not related
to QRS
N/A
Narrow or broad
AV dissociation
GE imagination at work
2027186-002
www.gehealthcare.com
You might also like
- ECG ReadingDocument11 pagesECG ReadingSuresh Shrestha100% (1)
- ArrhythmiaDocument2 pagesArrhythmiaChris Pritchard93% (30)
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocument16 pages11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhNo ratings yet
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- Cardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideDocument14 pagesCardiac Rhythms and Dysrhythmias GuideShawn Gaurav Jha100% (1)
- ECG Rythum Study Guide PDFDocument9 pagesECG Rythum Study Guide PDFArtika MayandaNo ratings yet
- Ecg Reading NotesDocument17 pagesEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2Document1 pageArrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2Gwen LylesNo ratings yet
- ECG Rhythms Guide: Normal, Abnormal & Example TracingsDocument9 pagesECG Rhythms Guide: Normal, Abnormal & Example Tracingsdiani arisandhi100% (1)
- DIT High Yield Questions PDFDocument13 pagesDIT High Yield Questions PDFjoshNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrhythmiassmurf096No ratings yet
- Cardiac pacing guide for beginnersDocument89 pagesCardiac pacing guide for beginnerssandwhale056No ratings yet
- Basic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswersDocument3 pagesBasic EKG Interpretation Exam AnswerstwdroppointNo ratings yet
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocument31 pagesECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani KayedNo ratings yet
- ECG AbnormalitiesDocument9 pagesECG Abnormalitiesbigabm062No ratings yet
- Cardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideDocument7 pagesCardiac Rhythm Abnormalities GuideAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular IV and VDocument6 pagesCardiovascular IV and VJessicaNo ratings yet
- Basics of EKG InterpretationDocument132 pagesBasics of EKG InterpretationArif Imam HidayatNo ratings yet
- ACLS Drug TherapyDocument8 pagesACLS Drug TherapySahrensNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation: Gel PDocument2 pagesEcg Interpretation: Gel PjuliperNo ratings yet
- EKG Flash CardsDocument5 pagesEKG Flash CardsRyann Sampino FreitasNo ratings yet
- BBB EcgDocument33 pagesBBB EcgLokbre YoasNo ratings yet
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation GuideDocument3 pagesECG Rhythm Interpretation Guideis_aradanas0% (1)
- Ekg Made EasyDocument7 pagesEkg Made Easystring44100% (3)
- Ekg PracticeDocument7 pagesEkg PracticeMichelle Cobb Matthews100% (1)
- Interpret ECG Rhythms & Manage ArrhythmiasDocument6 pagesInterpret ECG Rhythms & Manage Arrhythmiasjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- ACLS Class Packet PDFDocument9 pagesACLS Class Packet PDFImam GultomNo ratings yet
- Acls Book PDFDocument63 pagesAcls Book PDFSabir Khan67% (3)
- NSTEMIDocument29 pagesNSTEMIGeanina CreangaNo ratings yet
- Basic Arrythmia AnalysisDocument60 pagesBasic Arrythmia AnalysisZakky KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineDocument88 pagesAdvanced Ekg Interpretation: Micelle J. Haydel, M.D. LSU New Orleans Emergency MedicineRoroNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias Nursing InterventionsDocument7 pagesDysrhythmias Nursing InterventionsGail Lian Santos100% (1)
- Cardiac Murmurs and Maneuvers GuideDocument1 pageCardiac Murmurs and Maneuvers GuidePkernNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds: Mitral Regurgitation Congestive Heart FailureDocument6 pagesHeart Sounds: Mitral Regurgitation Congestive Heart FailurecindyNo ratings yet
- Ecg StripsDocument39 pagesEcg StripsNursyNurse100% (3)
- Dysrhytmia NotesDocument11 pagesDysrhytmia NoteshannahhwolfNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medical Procedures GuideDocument57 pagesEmergency Medical Procedures GuideDuane Liloc100% (1)
- EKG Practice PowerpointDocument25 pagesEKG Practice PowerpointDave Amarasinghe100% (2)
- Qrs Complexes: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramDocument49 pagesQrs Complexes: Fast & Easy Ecgs - A Self-Paced Learning ProgramMuhammad Hatta HamzahNo ratings yet
- EKG Basic Analysis GuideDocument1 pageEKG Basic Analysis Guideskeebs23No ratings yet
- EkgDocument94 pagesEkgCaprita LauraNo ratings yet
- The Six Second ECG: Annotated Answer KeyDocument9 pagesThe Six Second ECG: Annotated Answer KeyShimika Tomes100% (1)
- Ecg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointDocument37 pagesEcg Taking and Interpretation.... PowerpointJara Maris Moreno BudionganNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DrugsDocument8 pagesCardiac Drugsdawggj100% (2)
- ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesECG InterpretationAndrea AndradaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapDocument1 pageArrhythmia Pharmacology MindmapTesnikolaNo ratings yet
- Common Cardiac MedicationsDocument1 pageCommon Cardiac MedicationsPaige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation GuideDocument4 pagesECG Interpretation GuidePRaDo PATNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocument1 pagePoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFPierf-17No ratings yet
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocument1 pagePoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFMiko RamosoNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG InterpretationDocument82 pagesBasics of ECG Interpretationpopescuioana1No ratings yet
- BASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Document63 pagesBASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Sharmaine KimmayongNo ratings yet
- Sally Aburumman Bushra SaleemDocument75 pagesSally Aburumman Bushra SaleemAbdulrahman AlsayyedNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article 2043-1 PDFDocument8 pages2021 Article 2043-1 PDFSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Becattini 2018Document25 pagesBecattini 2018Snezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Movement Disorders in Children: Continuumaudio Interview Available OnlineDocument22 pagesMovement Disorders in Children: Continuumaudio Interview Available OnlineSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- ResenjaDocument40 pagesResenjaSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Complete Phrasal Verbs ListDocument137 pagesComplete Phrasal Verbs ListHermes®No ratings yet
- Global Perspectives on NOAC Treatment in Special PopulationsDocument54 pagesGlobal Perspectives on NOAC Treatment in Special PopulationsSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Activity OverviewDocument44 pagesActivity OverviewSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Rett Syndrome 2023 - Emerging Agents - Handout PDFDocument1 pageRett Syndrome 2023 - Emerging Agents - Handout PDFSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma HodgkinDocument84 pagesLymphoma HodgkinSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- E Case Internale MedicineDocument8 pagesE Case Internale MedicineSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- MS TelemedicinaDocument18 pagesMS TelemedicinaSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- About Cochrane - Trusted Evidence for Healthcare DecisionsDocument31 pagesAbout Cochrane - Trusted Evidence for Healthcare DecisionsSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Recognizing, Diagnosing, and Treating Mitochondrial DiseaseDocument57 pagesRecognizing, Diagnosing, and Treating Mitochondrial DiseaseSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Young Latina MS PatientDocument14 pagesYoung Latina MS PatientSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Neuroimaging in Acute StrokeDocument23 pagesNeuroimaging in Acute StrokeSnezana Mihajlovic100% (1)
- Collaborative Care in SMADocument58 pagesCollaborative Care in SMASnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Treatment Approaches in MS: Biomarkers Guide Decision-MakingDocument15 pagesTreatment Approaches in MS: Biomarkers Guide Decision-MakingSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- CIS Treating or Not TreatingDocument14 pagesCIS Treating or Not TreatingSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Dravet SyndromeDocument61 pagesDravet SyndromeSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Early Detection Key for SMA TreatmentDocument55 pagesEarly Detection Key for SMA TreatmentSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Traditional Treatments Vs Moder Treatments For ALSDocument63 pagesTraditional Treatments Vs Moder Treatments For ALSSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Management of MS in BlacksDocument15 pagesManagement of MS in BlacksSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Rett SyndromeDocument55 pagesRett SyndromeSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Precision in MSDocument62 pagesPrecision in MSSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Examining The CV Safety of FenfluramineDocument66 pagesExamining The CV Safety of FenfluramineSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Disparities in Alzheimer's Disease CareDocument58 pagesDisparities in Alzheimer's Disease CareSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Managing Dravet SyndromeDocument42 pagesManaging Dravet SyndromeSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument2 pagesPhrasal VerbsSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Dravet Syndrome OutcomesDocument62 pagesEnhancing Dravet Syndrome OutcomesSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Precision in MSDocument62 pagesPrecision in MSSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- Lingualied OcclDocument7 pagesLingualied Occlsiddu76No ratings yet
- Fortune Medicare Inc., V AmorinDocument4 pagesFortune Medicare Inc., V AmorinAlexandria ThiamNo ratings yet
- Maternity Record Keeping 4.0Document24 pagesMaternity Record Keeping 4.0ItaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Massachusetts HIX-IES System Review 021314Document22 pagesMicrosoft Massachusetts HIX-IES System Review 021314Shira SchoenbergNo ratings yet
- Literature Search StrategyDocument3 pagesLiterature Search StrategyhadiyudhaNo ratings yet
- XTRAC Psoriais Patient Brochure 071212Document2 pagesXTRAC Psoriais Patient Brochure 071212ravisagarNo ratings yet
- Order Denying Motion To Dismiss-1Document30 pagesOrder Denying Motion To Dismiss-1GovtfraudlawyerNo ratings yet
- Modifier Reference Guide PDFDocument15 pagesModifier Reference Guide PDFkhatNo ratings yet
- Gonzales Cannon Nov. 22 IssueDocument38 pagesGonzales Cannon Nov. 22 IssueGonzales CannonNo ratings yet
- Healthy LifestyleDocument2 pagesHealthy LifestyleCorey BrownNo ratings yet
- Medical Coding Fundamentals Study GuideDocument62 pagesMedical Coding Fundamentals Study GuideAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Individual Health Insurance CoveragesDocument25 pagesIndividual Health Insurance Coveragesmannajoe70% (1)
- CINI NewsletterDocument6 pagesCINI NewsletterChild in Need InstituteNo ratings yet
- DUPIXENT MyWay English Enrollment FormDocument5 pagesDUPIXENT MyWay English Enrollment FormJhoanna Marie MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Staying Active for Better HealthDocument1 pageStaying Active for Better HealthAntonia AntoNo ratings yet
- Learning Disability Eye Test LeafletDocument4 pagesLearning Disability Eye Test LeafletInclusionNorthNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)Document22 pagesAn Overview of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)Urlam Kumar71% (7)
- WCASevereConditionsFAQs 0Document4 pagesWCASevereConditionsFAQs 0Gail Ward100% (1)
- Cochlear Implantation Technique PDFDocument9 pagesCochlear Implantation Technique PDFKenric TamNo ratings yet
- Communicating using SBAR modelDocument1 pageCommunicating using SBAR modelchibimakuNo ratings yet
- To Err Is Human 1999 Report Brief PDFDocument8 pagesTo Err Is Human 1999 Report Brief PDFRenan LelesNo ratings yet
- Quality Standards for HealthcareDocument6 pagesQuality Standards for HealthcareLey EnhaimaNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Cures Act LetterDocument2 pages21st Century Cures Act LetterPeter SullivanNo ratings yet
- Mercer - Proposal RFP ResponseDocument46 pagesMercer - Proposal RFP ResponseAleeza KhanNo ratings yet
- Lepage Job WRKSHP 10-26-11Document2 pagesLepage Job WRKSHP 10-26-11Andi ParkinsonNo ratings yet
- Quality Manual: Sta. Rosa Hospital and Medical CenterDocument15 pagesQuality Manual: Sta. Rosa Hospital and Medical CenterRenz Marrion RolleNo ratings yet
- Omnicell Cerner Alliance Brochure enDocument2 pagesOmnicell Cerner Alliance Brochure enRonnie EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- J. DAFTAR PUSTAKADocument6 pagesJ. DAFTAR PUSTAKADewiNo ratings yet
- MankindDocument14 pagesMankindpriteshghogare80% (5)
- Assessment of RA 9994 implementation for senior citizensDocument12 pagesAssessment of RA 9994 implementation for senior citizenserroljohnescorial100% (1)