Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Notes Psasdmr
Uploaded by
David AntonitoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Notes Psasdmr
Uploaded by
David AntonitoCopyright:
Available Formats
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
REVISION NOTES (Science PMR)
The composition of Air
General composition of air is as follows.
Components
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Inert gases + other
substances
Water vapour, dust and
microorganisms
Percentages
78
21
0.03
O.97
Varies
Air is a mixture of gases because
The mixing of its component are done without any chemical reactions
The components can be easily separated by physical ways
The component gases maintains its different properties in mixture and when separated
too.
The composition of air varies from one place to another. For example forest area contains
more oxygen compared to industrial area.
Energy + Carbon Dioxide +
Water Vapour
5.2 The properties of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The properties of oxygen
soluble in water
not soluble in sodium hydroxide solution
does not react with lime water
is a neutral gas (no changes with hydrogen carbonate indicator and litmus paper)
soluble in alkaline pyrogallol solution
supports combustion (glowing splinter lights up)
The properties of Carbon dioxide
more soluble in water than oxygen
very soluble in sodium hydroxide solution
reacts with lime water (turns cloudy)
is acidic (hydrogen carbonate changes from red to yellow and litmus paper changes from
blue to red)
not soluble in alkaline pyrogallol solution
does not support combustion
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Oxygen is needed for Respiration
Glucose + Oxygen
Respiration
Inhalation (breathe in) obtains oxygen for respiration and exhalation (breathe out)
removes carbon dioxide and water vapour from the body.
The energy obtained through respiration is used for the activities carried out by the body.
The Differences between Inhaled and Exhaled Air
Inhaled Air
Contains more
oxygen
Contains less water
vapor
Temperature varies
according to the
surrounding
Exhaled Air
Contains more
carbon dioxide
Contains more
water vapor
Temperature of the
body
5.4 Oxygen is needed for Combustion
Fuel
Air
Heat
Allows combustion
(Without any of these, combustion would not occur)
Examples of substances that can burn easily are
Organic substances (ex: alcohol)
Substances containing alcohol
Hydrocarbons (compounds containing hydrogen and carbon)
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Products of combustion depending on the type of fuel used:
Carbon + Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide + energy
Hydrocarbon + Oxygen
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
5.5 Air Pollution
happens when air contains pollutants that are harmful to living things and non living
things
Sources of Air pollutants
Construction activities
Power Generating stations
Motor Vehicles
Industrial Activities
Smoking
Open Burning
Agricultural Activities
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Effects of Air Pollution
Causes
Asbestos
Particles
Lead
Carbon
monoxide
Sulphur
dioxide
Soot and
Dust
Acid rain
Haze
Excessive
carbon
dioxide
Cigarette
smoke (tar,
nicotine
and carbon
monoxide)
Effects
Lung cancer
Mental disabilities in
children
Blood carries less oxygen
Eye irritation and
respiratory problems
Make buildings dirty,
close up stomata
(difficulty for respiration
and photosynthesis)
Corrodes and quickens
rusting, makes soil less
fertile and kills aquatic
animals
Reduces the rate
photosynthesis
Greenhouse effect and
global warming
Causes cancer
How to prevent and control air pollution
Role of society (prevent CFC Products and open burning)
Education (educate the public by having forums and campaigns)
Using Modern Technology (use Catalytic converters or fix filters on the smoke ducts of
chimneys)
Law Enforcement (take legal action against owners of pollutants)
Replanting
Save electricity
Stop smoking
5.6 The Importance of Clean Air
Guarantees good health
Benefits future generations
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Survival of human beings and other living organisms
FORM 2
The World through Our Senses
1.1 Sensory Organs and the Functions
Sensory organ
Skin
Nose
Tongue
Ears
Eyes
Sense
Touch
Smell
Taste
Sounds
Light
Word Check:
Sensory organs organs that detect stimuli
Stimuli (stimulus) reaction by the body due to changes in the environment
Sense ability of the organs to detect stimuli
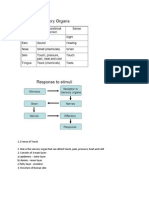
The Pathways for Response in Human Beings
Stimulus
Sensory organs are stimulated by the receptors
Nerve impulses are sent to the nerves
Brain receives impulses from the nerves and interprets and decides how to respond
Brain initiates nerve impulses
The nerves carry the nerve impulses to the effectors
The effectors responses
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
1.2 The Sense of Touch
Parts of the
Human Skin
Pain receptor
Heat receptor
Functions
Detects the slightest pain
Detects an increase in
temperature
Cold receptor Detects the decrease in
temperature
Pressure
Detects any forceful
receptor
pressure against the skin
Touch
Detects any touch and
receptor
identifies the texture of
an object
The sensitivity of the skin depends
The number of receptors present (more receptors makes skin more sensitive)
The thickness of the epidermis (thicker epidermis makes skin less sensitive)
1.3 The Sense of Smell
Word Check:
Nostrils holes in the nose
Nasal cavity hollow space in the nose
Mucus warm liquid moistens air before it enters the lungs
The Pathways for Smell Detection
The presence of chemicals in inhaled air
Air enters the nasal cavity
Air dissolves in the mucus
Smell receptors are stimulated
Impulses are sent to the brain
Brain detects the smell
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Tate and Sense
Word check:
Saliva chemical substance produced by the tongue
Taste buds taste buds are the taste receptors present on the tongue
The Pathways for Taste Detection
Saliva acts on the food that we chew
Taste receptors are stimulated
Nerve impulses are initiated and travels to the brain
Brain detects the taste
1.4 The Sense of Hearing
The Pathway in the Mechanism of Hearing
Sound waves are directed into the auditory canal to the eardrum
Eardrum vibrates and transfers the vibration to the ossicles which transfers to the oval window
Fluid in the cochlea vibrates and stimulates the receptors
Nerve impulses are initiated
Nerve impulses are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve
Brain interprets the sound
Parts of the ear which are not related to hearing
Semicircular canals helps maintain body balance
Eustachian tube helps balance the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
The Sense of Sight
The Function of each part of the Human eye
Parts
Ciliary
body
Suspensory
ligaments
Aquenous
humour
Functions
Allows changes in the focal
length of the lens
Holds the lens and connects
it to Ciliary body
Refract light and focus
image on retina and
maintain shape and pressure
of the eyes
Conjunctiva Protects the cornea
Pupil
Allow light to enter the eye
Cornea
Allow light to enter and
focuses it onto retina
Iris
Control the size of the pupil
and the amount of light
entering the eye
Eye lens
Bends and focus light to
form image on the retina
Vitreous
Jelly like material that
humour
maintains the shape of the
eye and refracts light on the
retina
Sclera
Protects and maintains the
shape of the eye
Choroid
Supply nutrients and oxygen
to the eye
Retina
Detects light stimuli and
send nerve impulses to the
brain
Yellow spot Most sensitive to light,
detects the images of objects
formed and changes them
into nerve impulses
Blind spot
Not sensitive to light, no
receptor cells here and it is
the spot where the optic
nerve leaves the eyeball
Optic nerve Sends impulses from the
retina to the brain
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
The Pathway in the Mechanism of Sight
Light enters the eye through pupil
Lights are refracted by the cornea, aqueous humour, eye lens and vitreous humour
Inverted and smaller image is formed on the retina
Photoreceptors are stimulated to initiate impulses
Optic nerve sends the impulses to the brain
Brain converts the inverted image into an upright image
Light and Sight
Properties of Light
Is a form of energy
Travels in straight line
It is reflected when it hits an opaque surface
It is refracted when it travels from transparent material to another
Word check:
Reflection happens when light hits an opaque surface
Refraction happens when light travels from one transparent material to another
Common defects of vision and ways to overcome them
Common
defects
Shortsightedness
Longsightedness
Astigmatism
Colour
blindness
Presbyopia
www.skorminda.com
Ways to overcome the
defects
Wear glasses with
concave lenses
Wear glasses with convex
lenses
Wear glasses with
cylindrical lenses
Cannot be corrected
Wear glasses with bifocal
lenses
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Stereoscopic and Monocular Visions
Stereoscopic
Vision
Both eyes at the
front and are used
to look at the
object
Monocular Vision
Eyes are at the
sides of the head
and only one eye is
used to look at the
object
The visual fields of The visual fields of
both eyes overlap
both eyes do not
(smaller)
overlap (wider)
More accuracy to
No accuracy to
estimate position
estimate position
and distance
and distance
Sound and Hearing
Properties of Sound
It is produced by vibrations
Needs medium to travel (solids, liquids or gases according to the rate sound travels
through it)
Do not travel in vacuum
1.5 Plants Responses to Stimuli
Plants respond to
Light
Gravity
Water
Touch
Types of responses
Positive tropism parts of the plant grows towards the stimulus
Negative tropism parts of the plant grows away from the stimulus
Types of tropisms
Phototropism plants response to light
Geotropism plants response to gravity
Hydrotropism plants response to water
Thigmotropism plants response to touch
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Interdependence among Living Organisms and the Environment
Word Check:
Species a group of similar organisms
Population the number of a species in a habitat
Community different populations in a habitat
Ecosystem various communities that interacts with non living things in the environment
Biological control the use of natural predators to control the population of pest species
Chemical control the use of chemicals to control the population of a pest species
A balanced ecosystem is a ecosystem that
Stable
Does not change much over a period of time
Have continuous supply of basic needs
Interaction between Living Organisms
Types of
interaction
Competition
- Intraspecific
competition
- Interspecific
competition
Symbiosis
Commensalisms
-Mutualism
-Parasitism
Prey predator
www.skorminda.com
Explanation
Living things compete
for their basic needs
- Competition among the
same species
- Competition among
different species
Relationship between 2
organisms of the same
species that live and
interact with each other
- One organism
(commensal) benefits
while the other (host) do
not benefit
-both organisms benefit
- One organism
(parasite) benefits while
the other (host) is
harmed
Predators are the ones
that kill the other
animals (carnivores)
Prey are the one get
killed (carnivores,
omnivores or herbivores)
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Word Check:
Food chain shows the feeding relationship between living organisms
Food web- shows a combination of food chains
Producers green plants (able to produce their own food)
Consumers animals that eats other living things [primary (animals that eats green
plants), secondary (animals that eats the primary consumers) and tertiary (animals that
eat the secondary consumers)]
Decomposers living things that breaks down dead animals and plants into simpler
substances
Energy flow in a food Web
Sunlight is the main source of energy
Energy flows from primary consumers to secondary consumers and finally to the tertiary
consumers.
Some energy is lost in the process through respiration, excretion and defecation.
Therefore the amount of energy decreases along the food chain
4.4 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food
Carbon dioxide + water
Sunlight
Chlorophyll
Glucose + oxygen
Conservation and Preservation
Word Check:
Preservation steps to maintain living things and their environment in their original and
balanced state
www.skorminda.com
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Conservation proper usage of natural resources to protect living organisms in the
habitat
Aims of Conservation and Preservation
To protect living things from destruction and extinction
Natural resources are not depleted
Promising ecosystem for the future generations
Natural habitats are preserved
4.6 Role of Human Beings in a Balanced Nature
Steps to preserve and conserve the environment
Maintain forest reserves and rehabilitation centres
Law enforcement
Reduce, reuse and recycle
Public awareness
Deforestation
Build marine parks
Word Check:
Electrostatics study of static electricity change through friction/ rubbing
Electrostatic force reaction when charged objects are brought together (same charges
would repel and different charges would attract)
Electroscope equipment used to test charges (+ve or -ve)
2 materials are rubbed together
Positively
charged when
losses electron
Electricity
Word Check:
Electricity a form of energy
www.skorminda.com
Negatively
charged when
receives
electron
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
Electric current the rate of flow of electrons (charges) from the positive to the negative
terminal (measured using Ammeter)
Electrons the electrical charges that flows and causes the electrical current
Electric voltage the force that pushes electrons through a wire (measured using
Voltmeter)
Word Check:
Conductor materials that allows heat or electricity to pass through them
Insulator materials that do not allow heat or electricity to pass through them
Resistance (ohms) the characteristic of a conductor that opposes the electric current (the
flow of electrons)
Resistor reduces the current flow through a circuit (fixed resistor has fixed resistance
and variable resistor has variable resistance)
Resistance
The higher the resistance, the lower the voltage
The lower the resistance, the higher the voltage
Factors affecting resistance
Length (the longer the higher)
Diameter (the smaller the surface area of conductor the higher the resistance)
Type of the conductor (good conductor has low resistance and vice versa)
Current, Voltage and Resistance
R = Resistance in ohm
V = Voltage in volts
I = current in Amperes
R = V/ I
Series Circuit and Parallel Circuit
Series Circuit
Has one path for
www.skorminda.com
Parallel Circuit
Has more than 2
PUSAT TUISYEN SKOR MINDA
electric current
The current that
flows are the same
The total voltage
supplied is shared
among the bulbs in
the circuit
Effective
resistance = sum of
resistance in each
bulb
paths for electric
current
The current
supplied by the
source is equal to
the current that
flows in the circuit
Each bulb uses the
total voltage
supplied
Effective
resistance decrease
when number of
resistors increases
Word Check:
Magnet material that produces a magnetic field
Magnetic field area surrounding the magnet on which the magnetic force acts
Magnetic substances materials that are attracted to magnet
Non magnetic substances materials that are not attracted to magnet
Properties of magnetic field lines
Begins at north pole and ends at south pole
They do not cross each other
www.skorminda.com
You might also like
- Kidsdiscoverchemistry DLDocument20 pagesKidsdiscoverchemistry DLAngela Navarro100% (2)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- Yearly Plan f5 MathsDocument20 pagesYearly Plan f5 MathsRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Definitive Ozone GuideDocument24 pagesDefinitive Ozone GuideAnonymous YcAZv5qF67100% (4)
- Exploring Science Active Book 8Document58 pagesExploring Science Active Book 8Raistlin Chan Ching Kit50% (2)
- Biology Revision GuideDocument22 pagesBiology Revision GuidePoornima AthikariNo ratings yet
- Air and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthFrom EverandAir and Your Health: Clean Air Is Vital to Your HealthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- STEM 5.9D 2.0 Explain STEMscopedia Eng PDFDocument5 pagesSTEM 5.9D 2.0 Explain STEMscopedia Eng PDFspaghett 1No ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument12 pagesScience Form 1 NoteRaemah Ibrahim0% (1)
- BioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisDocument34 pagesBioIGCSE 07 PhotosynthesisNADIANo ratings yet
- SWATHVRITTA PAPPER 2 PART A - WatermarkDocument108 pagesSWATHVRITTA PAPPER 2 PART A - WatermarkchandusgNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemAnonymous 5hYhEkINo ratings yet
- Swastha - Paper II BothDocument140 pagesSwastha - Paper II BothSAMUEL MNo ratings yet
- स्वस्थवृत्त Paper II Part A सामाजिक स्वस्थवृत्तDocument108 pagesस्वस्थवृत्त Paper II Part A सामाजिक स्वस्थवृत्तsaiyed bushra gNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Logger?Document9 pagesWhat Is Data Logger?Nurul natihahNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 1Document26 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 1EeJun LeeNo ratings yet
- What Is This ? How Can You Detect The Presence?Document79 pagesWhat Is This ? How Can You Detect The Presence?Nurul Ain Mat HussinNo ratings yet
- Biology: 1.1 Respiration, What Is It?Document5 pagesBiology: 1.1 Respiration, What Is It?api-309429111No ratings yet
- Short Notes Science TalkDocument9 pagesShort Notes Science Talkfairy_elieNo ratings yet
- Pluto JMT2023Document17 pagesPluto JMT2023krishangmahesh.rajNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Apshara Ghimire Ashma Panthi Bipana KC Echha Shrestha Kalpana AcharyaDocument22 pagesAir Pollution: Apshara Ghimire Ashma Panthi Bipana KC Echha Shrestha Kalpana AcharyaAlphaNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Danieal Ashraff Bin Shamsataria Class: 2B2 Homeroom: Eridanus ADocument14 pagesName: Muhammad Danieal Ashraff Bin Shamsataria Class: 2B2 Homeroom: Eridanus AMuhammad Danieal AshraffNo ratings yet
- The Special SensesDocument25 pagesThe Special Senseshed-ikaquinoNo ratings yet
- Gernal Science Presentation Group EDocument25 pagesGernal Science Presentation Group EKainaat AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Atm Chem Final Group ProjectDocument56 pagesAtm Chem Final Group ProjectSantosh SatputeNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument44 pagesEnvironmentkles insgkkNo ratings yet
- IrritabilityDocument30 pagesIrritabilityAnnesley RobanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Is2023Document24 pagesPhotosynthesis Is2023Sarah Gwyneth ABRIOLNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesisSarah Gwyneth ABRIOLNo ratings yet
- OmkarDocument25 pagesOmkarMarket with meNo ratings yet
- What Is The Oxygen Cycle?: Human BodyDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Oxygen Cycle?: Human BodyJEANY ROSE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- StimulusDocument3 pagesStimulusMiracle LakeNo ratings yet
- CYCLESDocument10 pagesCYCLESJE-ANN LUGPITNo ratings yet
- Conjunctiva Lines The EyelidsDocument3 pagesConjunctiva Lines The EyelidsApril Hilarylynn Lawa JagunosNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxides The BodyDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxides The Bodyvenu gopalNo ratings yet
- Photocellresp 1Document30 pagesPhotocellresp 1api-371983348No ratings yet
- Aoc 03 (2017-18)Document29 pagesAoc 03 (2017-18)therealsumanNo ratings yet
- Grade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114Document12 pagesGrade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114onmd2435No ratings yet
- Presentation: A Zero Harm CompanyDocument33 pagesPresentation: A Zero Harm CompanyIssac JohnNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Rajvardhan Rishi (Setb137) Nikhil (Setb103) Arjun Mandge (Setb138) DIPAK (SETB105) Shivshankar (Setb114)Document22 pagesPresented By:: Rajvardhan Rishi (Setb137) Nikhil (Setb103) Arjun Mandge (Setb138) DIPAK (SETB105) Shivshankar (Setb114)Atul UttamNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument3 pagesEnglishNesyaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryEthan PhilipNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentTeamireab DestaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Document24 pagesUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution, 2019 IIDocument18 pagesAir Pollution, 2019 IIPubg BoyNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Environmental AwarenessDocument8 pagesClimate Change and Environmental AwarenessNovi Marie Dela Cruz100% (1)
- BodyDocument40 pagesBodyaziz9091No ratings yet
- 4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingDocument71 pages4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingoliviaNo ratings yet
- Increase Your Oxygen With OzoneDocument3 pagesIncrease Your Oxygen With OzoneRaj SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- 9 DONE Air PollutantsDocument8 pages9 DONE Air PollutantsSumaiya ImamNo ratings yet
- 9 RespirationDocument3 pages9 RespirationKavin ManimaranNo ratings yet
- OxygenDocument2 pagesOxygenAdib AdibahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10biologyDocument8 pagesChapter 10biologyAleena kazmiNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document25 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Saraswati PNo ratings yet
- Oxygencycle 160312034323Document11 pagesOxygencycle 160312034323Romyross JavierNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution (2) 4) Methane Comes FromDocument4 pagesAir Pollution (2) 4) Methane Comes FromMuneebNo ratings yet
- Hormons &environDocument7 pagesHormons &environrincyNo ratings yet
- Transformations: I) Draw The Image For Each of TheDocument12 pagesTransformations: I) Draw The Image For Each of TheRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Ylp Maths f4Document16 pagesYlp Maths f4RenSaacNo ratings yet
- W1 Mon15Document4 pagesW1 Mon15KelvinYongNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: PJPK Revision For Term 2 Examination, SegakDocument1 pageMathematics: PJPK Revision For Term 2 Examination, SegakRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Model SPM Model SPM Model SPMDocument4 pagesModel SPM Model SPM Model SPMRenSaacNo ratings yet
- (Worksheet) Chapter 5 - VariationsDocument21 pages(Worksheet) Chapter 5 - VariationsRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3RenSaacNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structures Are Found in Various Places in NatureDocument3 pagesCrystal Structures Are Found in Various Places in NatureRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structures Are Found in Various Places in NatureDocument3 pagesCrystal Structures Are Found in Various Places in NatureRenSaacNo ratings yet
- It Is Well Wit My SoulDocument1 pageIt Is Well Wit My SoulRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Dancing IceDocument2 pagesDancing IceRenSaacNo ratings yet
- 962 CoverDocument1 page962 CoverRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Bubbles Prints What You NeedDocument1 pageBubbles Prints What You NeedRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: 7.0 Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesMathematics: 7.0 Acids and BasesRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Cabbage ChemistryDocument3 pagesCabbage ChemistryRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document2 pagesWeek 1RenSaacNo ratings yet
- ThursDocument4 pagesThursRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Theme/Learning Area Interaction Between Chemicals Measuring & Using NumbersDocument8 pagesTheme/Learning Area Interaction Between Chemicals Measuring & Using NumbersRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Amazing DetergentDocument1 pageAmazing DetergentRenSaacNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument1 pageMathematicsRenSaacNo ratings yet
- MonDocument7 pagesMonRenSaacNo ratings yet
- MonDocument3 pagesMonRenSaacNo ratings yet
- PostDocument2 pagesPostRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Class: 5G Date: 27 Jun 2014 Time: 07:00 A.M. - 8:10 A.M. Subject: Theme: Learning Objective: Students Will Be Taught ToDocument2 pagesClass: 5G Date: 27 Jun 2014 Time: 07:00 A.M. - 8:10 A.M. Subject: Theme: Learning Objective: Students Will Be Taught ToRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 I Standard Form ENHANCEDocument14 pagesChapter 9 I Standard Form ENHANCERenSaacNo ratings yet
- RPH Kump 5Document2 pagesRPH Kump 5RenSaacNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Yearly Teaching Plan 2014Document30 pagesForm 4 Yearly Teaching Plan 2014RenSaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: RATE OF REACTION: SpeedDocument4 pagesChapter 1: RATE OF REACTION: SpeedRenSaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: RATE OF REACTION: SpeedDocument4 pagesChapter 1: RATE OF REACTION: SpeedRenSaacNo ratings yet