Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insulin - Pharmacology, Types of Regimens, and Adjustments
Uploaded by
Mohamed OmerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insulin - Pharmacology, Types of Regimens, and Adjustments
Uploaded by
Mohamed OmerCopyright:
Available Formats
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
NCBIBookshelf.AserviceoftheNationalLibraryofMedicine,NationalInstitutesofHealth.
DeGrootLJ,BeckPeccozP,ChrousosG,etal.,editors.Endotext[Internet].SouthDartmouth(MA):MDText.com,Inc.2000.
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustments
LisaKroon,PharmD,CDE
ProfessorandExecutiveViceChair,DepartmentofClinicalPharmacy,SchoolofPharmacy,UniversityofCaliforniaSanFrancisco,SanFrancisco,CA
kroonl@pharmacy.ucsf.edu
IraD.Goldfine,M.D.
ProfessorofMedicine,DepartmentofMedicine,DiabetesandEndocrineResearch,UniversityofCaliforniaSanFrancisco/Mt.ZionMedicalCenter,San
Francisco,CA
ira.goldfine@ucsf.edu
SinanTanyolac,M.D.
VisitingScientist,DepartmentofMedicine,UniversityofCaliforniaSanFrancisco,SanFrancisco,CA
stanyolac@gmail.com
LastUpdate:October1,2010.
INTRODUCTION
Withtheintroductionofseveralnewinsulinssince1996,insulintherapyoptionsfortype1andtype2diabeticshave
expanded.Insulintherapiesarenowabletomorecloselymimicphysiologicinsulinsecretionandthusachievebetter
glycemiccontrolinpatientswithdiabetes.Thischapterreviewsthepharmacologyofinsulins(usingacomparative
approach),typesofinsulinregimensandtherapeuticadjustmentofthem,andprovidesanoverviewofinsulinpump
therapy.
PHARMACOLOGY
In1922,Canadianresearcherswerethefirsttodemonstrateaphysiologicresponsetoinjectedanimalinsulininapatient
withtype1diabetes.In1955,insulinwasthefirstproteintobefullysequenced.Theinsulinmoleculeconsistsof51
aminoacidsarrangedintwochains,anAchain(21aminoacids)andBchain(30aminoacids)thatarelinkedbytwo
disulfidebonds[1] (Figure1).ProinsulinistheinsulinprecursorthatistransportedtotheGolgiapparatusofthebeta
cellwhereitisprocessedandpackagedintogranules.Proinsulin,asinglechain86aminoacidpeptide,iscleavedinto
insulinandCpeptide(aconnectingpeptide)botharesecretedinequimolarportionsfromthebetacelluponstimulation
fromglucoseandotherinsulinsecretagogues.WhileCpeptidehasnoknownphysiologicfunction,itcanbemeasured
andifpresent,indicatesapersonhasfunctioningbetacells.
Figure1
InsulinStructure
Insulinexertsitseffectonglucosemetabolismbybindingtoinsulinreceptorsthroughoutthebody.Uponbinding,
insulinpromotesthecellularuptakeofglucoseintofatandskeletalmuscleandinhibitshepaticglucoseoutput,thus
loweringthebloodglucose.(seeInsulinsignalingandaction:glucose,lipids,protein)
Commerciallyavailableinsulinsareusedforallpatientswithtype1diabetesinwhominsulinisrequiredforsurvival,
andforpatientswithtype2diabeteswhendiet/exercise,oralagentsandotherinjectablehypoglycemicagents(i.e.,
incretinemimeticagents/GLP1analogs)nolongerprovideadequateglucosecontrol.
SourcesofInsulin
WiththeavailabilityofhumaninsulinbyrecombinantDNAtechnologyinthe1980s,useofanimalinsulindeclined
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
1/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
dramatically.Beefinsulin,beefporkandporkinsulinarenolongercommerciallyavailable.TheFDAmayallowfor
personalimportationofbeefinsulinfromaforeigncountryifapatientcannotbetreatedwithhumaninsulin[2] .Beef
insulindiffersfromhumaninsulinby3aminoacidsandporkinsulindiffersbyoneaminoacid[3] .
Currently,intheUSA,mostinsulinsusedareeitherhumaninsulinand/oranalogsofhumaninsulin.Therecombinant
DNAtechniqueforhumaninsulininvolvesinsertionofthehumanproinsulingeneintoeitherSaccharomycescerevisiae
(bakersyeast)oranonpathogeniclaboratorystrainofEscherichiacoli(Ecoli)whichserveastheproduction
organism.Humaninsulinisthenisolatedandpurified[4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] .
InsulinAnalogs
RecombinantDNAtechnologyhasallowedforthedevelopmentandproductionofanalogstohumaninsulin.With
analogs,theinsulinmoleculestructureismodifiedslightlytoalterthepharmacokineticspropertiesoftheinsulin,
primarilyaffectingtheabsorptionofthedrugfromthesubcutaneoustissue.TheB26B30regionoftheinsulinmolecule
isnotcriticalforinsulinreceptorrecognitionanditisinthisregionthataminoacidsaregenerallysubstituted[12] .
Thus,theinsulinanalogsarestillrecognizedbyandbindtotheinsulinreceptor.Thestructuresofthreeinsulinanalogs
areshowninFigure2(insulinaspart,lisproandglulisine)andFigure3(insulinglargineanddetemir).
Figure2
InsulinAspart,GlulisineandLisproStructures
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
2/24
25/06/2015
Figure3
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
InsulinGlargineandDetemirStructures
Becauseinsulinanalogsaremodifiedhumaninsulin,thesafetyandefficacyprofilesoftheseinsulinshavebeen
comparedtohumaninsulin[13] .InsulinandIGF1receptorbindingaffinities(IGFinsulinlikegrowthfactor),
metabolicandmitogenicpotenciesofinsulinlispro,insulinaspart,insulinglargineandinsulindetemirrelativetohuman
insulinhasbeenassessed.Insulinlisproandaspartaresimilartohumaninsulinonalloftheaboveparameters,except
insulinlisprowasfoundtobe1.5foldmorepotentinbindingtotheIGF1receptorcomparedtohumaninsulin.Insulin
glarginewasfoundtohavea6to8foldincreaseinmitogenicpotencyandIGF1receptoraffinitycomparedtohuman
insulin.Insulindetemirwasfoundtotobemorethan5foldlesspotentthanhumaninsulininbiningtoIGF1.Whilethe
clinicalsignificanceofthesedifferencesisnotknown,theylikelydonotrepresentanysignificantconcern[14] .
Immunogenicity
Becauseporkandbeefinsulindifferfromhumaninsulinby1and3aminoacidsrespectively,theyaremore
immunogenicthanexogenoushumaninsulin.Olderformulationsofinsulinwerelesspure,containingisletcellpeptides,
proinsulin,Cpeptide,pancreaticpolypeptides,glucagons,andsomastostatin,whichcontributedtoimmunogenicityof
insulin[15] .Componentsofinsulinpreparations(e.g.,zinc,protamine)andsubcutaneousinsulinaggregatesarealso
thoughttocontributetoantibodyformation[16] .Commerciallyavailablehumaninsulinsarenowvirtuallyfreeof
contaminantsandcontain<1ppmofproinsulin(alsoreferredtoaspurified)[17] .Insulinsideeffectssuchas
localorsystemichypersensitivity,lipodystrophy,andantibodyproductioncausinginsulinresistance,arenowrarely
seenwithexogenoushumaninsulin[18] .Becauseoftheavailabilityofhumaninsulinandtheincreasedpotentialfor
animalsourceinsulintobeimmunogenic,animalsourceinsulinsarenowrarelyusedandpeoplewithdiabetesshouldbe
initiatedonhumaninsulin.
Therarehypersensitivityresponsestoinsulincanbeimmediatetype,localorsystemicIgEmediatedreactions[19] .
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
3/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Patientswhoexperienceatrueallergicreactiontoinsulinoftenhavereceivedinsulininthepast,andexperiencethe
allergicreactionafterinsulinisrestarted.Anotherallergicreactionseenwithanimalinsulinswasadelayedlocalreaction
thatwasIgGmediated[20] .InsulintherapycanalsoresultintheproductionofinsulinantibodiesoftheIgGclass,
whichneutralizeinsulin.AnimmunologicalinsulinresistancecanoccurinpatientswithveryhightitersofIgG
antibodies.
Lipodystrophyseenwithinsulinreferstotwoconditions:lipoatrophyandlipohypertrophy.Lipoatrophyisanimmune
mediatedconditioninwhichthereislossoffatattheinsulininjectionsites[21] .Lipoatrophyoccursmuchless
frequentlywithpurifiedhumaninsulins.Treatmentforpatientswhowereonananimalinsulinwasinjectionwithhuman
insulinattheatrophiedsite.Lipohypertrophyisanonimmunologicalsideeffectofinsulinresultingfromrepeated
administrationofinsulinatthesameinjectionsite.
Concentration
IntheUnitedStates,allinsulinsareavailableintheconcentrationof100units/ml(denotedasU100).Insulinsyringes
aredesignedtoaccommodatethisconcentrationofinsulin.Regularhumaninsulin(HumulinR,Lilly)isavailableina
moreconcentratedinsulin,U500(500units/ml),howeverthispreparationisusedprimarilyinaspecializedinstitutional
settingorforrarecasesofextremeinsulinresistance,whereverylargedosesofinsulin(generally>200unitsperday)
arerequired.SpecificsyringesforU500insulinarenotavailableandextremecautionmustbetakenaseachmarked
unitonaU100syringewillactuallydeliver5unitsofinsulin.
OutsidetheUnitedStates,alessconcentratedinsulinpreparation,U40,(40units/ml)isstillavailableandsometimes
used.SpecificU40syringesareusedwiththisinsulin.Itisimportantthatpatientstravelingfromonecountrytothe
next,beawareoftheconcentrationofinsulintheyuse,andthattheappropriatesyringeisused.
PhysicalandChemicalProperties
Regularhumaninsuliniscrystallinezincinsulindissolvedinaclearsolution.Itmaybeadministeredbyanyparenteral
route:subcutaneous,intramuscular,orintravenous.Insulinaspart,glulisineandlisproarealsosolublecrystallinezinc
insulin,butareintendedforsubcutaneous(subQ)injection.NPH,orneutralprotamineHagedorn,isasuspensionof
regularinsulincomplexedwithprotaminethatdelaysitsabsorption.Insulinsuspensionsshouldnotbeadministered
intravenously.Allinsulins,exceptinsulinglargine,areformulatedtoaneutralpH.
LongactingInsulinglargineisasoluble,clearinsulin,andhasapHof4.0.ItsacidicpHiscriticalforitssubQ
absorptioncharacteristicsandwillbediscussedfurtherunderpharmacokinetics.Insulinglargineshouldnotbemixed
withotherinsulins,andshouldonlybeadministeredsubcutaneously[22] .
InsulindetemirisalongactinginsulinanalogthathasafattyacidcoupledtoitsothatitbindstoalbumininthesubQ
tissueresultingindelayedabsorption,proloningitsdurationofaction.Likeinsulinglargine,insulindetemirshouldnot
bemixedwithotherinsulins,andshouldbeinjectedsubcutaneously.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
InsulinadministeredviaSCinjectionisabsorbeddirectlyintothebloodstream,withthelymphaticsystemplayinga
minorroleintransport[23] .TheabsorptionofhumaninsulinaftersubQabsorptionistheratelimitingstepofinsulin
activity.ThisabsorptionisinconsistentwiththecoefficientsofvariationofT50%(timefor50%oftheinsulindosetobe
absorbed)varying~25%withinanindividualandupto50%betweenpatients[24] [25] .Mostofthisvariabilityof
insulinabsorptioniscorrelatedtobloodflowdifferencesatthevarioussitesofinjection(abdomen,deltoid,gluteus,and
thigh)[26] .Forregularinsulin,theimpactofthisisa~2timesfasterrateofabsorptionfromtheabdomenthanother
subcutaneoussites[27] .Theclinicalsignificanceofthisisthatpatientsshouldavoidrandomuseofdifferentbody
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
4/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
regionsfortheirinjections.Forexample,ifapatientpreferstousetheirthighforanoontimeinjection,thissiteshouldbe
usedconsistentlyforthisinjection.Forsimplicity,however,theabdomenisoftenrecommendedasthepreferredsiteof
injectionbecauseitistheleastsusceptibletofactorsaffectinginsulinabsorption(seeTable1).Insulinaspart,glulisine
andlisproappeartohavelessdaytodayvariationinabsorptionratesandalsolessabsorptionvariationfromthe
differentbodyregions[28] [29] [30] [31] .Insulinglarginespharmacokineticprofileissimilarafterabdominal,
deltoidorthighSCadministration[32] .
AgeneralprincipleforfactorsthatcanalterinsulinabsorptionisthatwhenlocalbloodflowinthesubQtissueis
changed,theabsorptionrateofinsulinwillalsobeaffected.AfactorthatincreasessubQbloodflowwillincreasethe
absorptionrateandviceversa.SeeTable1forfactorsthataffectinsulinabsorption.
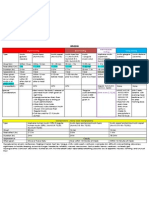
Table1
FactorsAffectingInsulinAbsorption([33][34][35])
Factor
Comment
Exerciseofinjectedarea
Strenuousexerciseofalimbwithin1hourofinjection.Clinicallysignificantforregular
humaninsulin.
Localmassage
WhileitisOKtopressontheinjectionsitetopreventseepage,thesiteshouldnotbe
rubbedvigorouslyormassaged.
Temperature
Heatcan
increaseabsorptionrate.Avoidthesauna,shower,hotbathsoonafterinjection.
Coldhastheoppositeeffect.
Siteofinjection
Insulinisabsorbedfasterfromtheabdomen.Lessclinicallyrelevantwithrapidacting
insulins,insulinglargineandinsulindetemir.
Lipohypertrophy
Injectionintohypertrophiedareasdelaysinsulinabsorption.
Jetinjectors
Increase
absorptionrate.
Insulinmixtures
Absorptionratesareunpredictablewhensuspensioninsulinsarenotmixedadequately(i.e.,
theyneedtoberesuspended).
Insulindose
Largerdoseshavedelayinactionand
increasedduration.
Physicalstatus(solublevs. Suspensioninsulinsmustbesufficientlyresuspendedpriortoinjectiontoreducevariability.
suspension)
Distribution
CirculatinginsulinisdistributedinequilibriumbetweenfreeinsulinandinsulinboundtoIgGantibodies[36] .The
presenceofinsulinantibodiescandelaytheonsetofinsulinactivity,reducethepeakconcentrationoffreeinsulin,and
prolongthebiologichalflifeofinsulin[37] .
Elimination
Thekidneysandliveraccountforthemajorityofinsulindegradation.Normally,theliverdegrades~60%ofinsulin
releasedbythepancreas(insulindeliveredthroughportalveinbloodflow)andthekidneys~3545%[38] .When
insulinisinjectedexogenously,thedegradationprofileisalteredsinceinsulinisnolongerdelivereddirectlytotheportal
vein.ThekidneyhasagreaterroleininsulindegradationwithsubQinsulin(~60%),withtheliverdegrading~3040%[
39] .
Becausethekidneysareinvolvedinthedegradationofinsulin,renaldysfunctionwillreducetheclearanceofinsulinand
prolongitseffect.Thisdecreasedclearanceisseenwithbothendogenousinsulinproduction(eithernormalproduction
orthatstimulatedbyoralagents)andexogenousinsulinadministration.Renalfunctiongenerallyneedstobegreatly
diminishedbeforethisbecomesclinicallysignificant[40] .
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
5/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Pharmacodynamics
Theonset,peak,anddurationofeffectarethemostclinicallysignificantdifferencesamongtheinsulins.Insulin
pharmacodynamicsreferstothemetaboliceffectofinsulin.Commerciallyavailableinsulinscanbecategorizedasrapid
acting,shortacting,intermediateacting,andlongacting.ThecurrentinsulinsavailableintheUnitedStatesarelistedin
Table2.Insulinpharmacodynamics(i.e.,onset,peakandduration)ofthevariousinsulins)areshowninTable3.Itis
importanttonotethatrangesarelistedfortheonset,peakandduration,accountingforintra/interpatientvariability.
Eachpatientwillhaveanindividualpatternofresponse.Byhavingthepatientselfmonitortheirbloodglucose
frequently,thepatientspecifictimeactionprofileofthespecificinsulincanbebetterappreciated.Figures4a4c[41] [
42] [43] [44]
graphicallyshowthetimeactivityprofilesforthevariousinsulins.
Table2I
nsulinsCommerciallyAvailableintheUS
Category/Nameof
Insulin
Source
BrandName(manufacturer)
Preparation(s)
RapidActing
InsulinLispro
InsulinAspart
InsulinGlulisine
Recombinant
DNARecombinant
DNA
RecombinantDNA
Humalog(Lilly)Novolog(Novo vial,cartridge,disposablepenvial,
Nordisk)
cartridge,disposablepen
Apidra(sanofiaventis)
vial,disposablepen
ShortActing
Regular
Human
RecombinantDNA
HumulinR(Lilly)NovolinR
(NovoNordisk)
vialvial
IntermediateActing RecombinantDNA
NPH
Human
HumulinN(Lilly)NovolinN
(NovoNordisk)
vial,disposablepenvial
LongActing
InsulinDetemir
InsulinGlargine
Recombinant
DNARecombinant
DNA
Levemir(NovoNordisk
)Lantus(sanofiaventis)
vial,disposablepenvial,cartridge,
disposablepen
InsulinMixtures
NPH/Regular
(70%/30%)
Human
Lispro
Protamine/Lispro
(50%/50%)
Lispro
Protamine/Lispro
(75%/25%)
Aspart
Protamine/Aspart
(70%/30%)
Recombinant
DNARecombinant
DNA
RecombinantDNA
RecombinantDNA
Humulin70/30(Lilly)Novolin
70/30(NovoNordisk)
HumalogMix50/50(Lilly)
HumalogMix75/25(Lilly)
NovologMix70/30(Novo
Nordisk
vial,disposablepenvial
vial,disposablepen
vial,disposablepen
vial,disposablepen
Note:Allinsulinanalogsareavailablebyprescriptiononly.OnAugust17,2009,NovoNordiskannouncedthe
NovolinInnoletR,N,and70/30devicesandtheNovolinR,Nand70/30PenFillcartridgeswouldnolongerbe
availableafterDecember31,2009.
Table3I
nsulinPharmacodynamics([45][46][47][48][49][50][51][52][53][54][55][56][57])
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
6/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Insulin
Onset(hr)
Peak(hr)
Duration(hr) Appearance
InsulinLispro
within15min 1
35
Clear
InsulinAspart
within15min 13
35
Clear
InsulinGlulisine .25.5
.51
Clear
Regular
24
58
Clear
NPH
12
410
14+
Cloudy
InsulinDetemir
34
68(thoughrelativelyflat) upto2024
Clear
InsulinGlargine
1.5
flat
24
Clear
LisproMix50/50 .25.5
.53
1424
Cloudy
LisproMix75/25 .255
.52.5
1424
Cloudy
AspartMix70/30 .1.2
14
1824
Cloudy
Note:Patientspecificonset,peak,durationmayvaryfromtimeslistedintable,
Peakanddurationareoftenverydosedependentwithshorterdurationofactionswith
smallerdosesandviceversa.
Figure4a
PharmacodynamicProfilesofaRapidInsulinAnalog(insulinlispro)andRegularInsulin.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
7/24
25/06/2015
Figure4b
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
PharmacodynamicProfilesofLongActingandIntermediateActing
BasalInsulins.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
8/24
25/06/2015
Figure4c
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
PharmacodynamicProfile:LisproNPLinComparisonwithNPH
DoseDependentEffect
ThepharmacodynamicsofregularandNPHareparticularlyaffectedbythesizeofthedose[58] .Largerdosescan
causeadelayinthepeakandincreasethedurationofaction.Forexample,injecting4unitsofNPHwillhavea
significantlydifferenttimeactionprofilecomparedto30unitsofNPH.
RapidActingInsulins
InsulinLispro(Humalog)
Insulinlispro[Lys(B28),Pro(B29)]isaninsulinanalogthatwasapprovedin1996(Humalog).TheB28(proline),B29
(lysine)aminoacidsequenceoftheinsulinmoleculeisreversedtobelysineprolineresultinginarapidabsorption,
within15minutes.Becauseitisabsorbedmorerapidly,itsonsetandpeakaresooner(anddurationshorter)comparedto
regularinsulin.Insulinlisproisalsoapprovedforinjectionimmediatelyafterameal.Becauseinsulinlisprocanbe
injectedjustbefore(orafter)themealversuswaiting30minuteswithregularinsulin,patientsmayfinditprovidesthem
withmoreflexibilityandconveniencefortheirmealtimeinsulininjection.Insulinlisprocanbemoreeffectivein
loweringpostprandialbloodglucoselevelsandhasareducedriskofhypoglycemiacomparedtoregularinsulin[59] [
60] [61]
.Thereasoninsulinlisproisassociatedwithlesshypoglycemiaisduetobettermatchingofinsulineffectand
foodabsorption[62] .Insulinlisprohasbeenstudiedforuseininsulinpumpsand,FDAapprovedforthisindicationin
2004.[63] [64] [65] .Intherarecaseofseverehumaninsulinallergy,insulinlisprohasbeenshowntobeless
immunogenic[66] .
InsulinAspart(Novolog)
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
9/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
InsulinaspartisahumaninsulinanalogapprovedJune7,2000(Novolog).TheB28aminoacidprolineissubstituted
withasparticacidresultinginarapidonsetofactivity.Insulinaspartshouldbeinjected510minutesbeforethemeal.
Advantageslistedaboveforinsulinlisproarethesameforinsulinaspart[67] .TheinsulinaspartisFDAapprovedfor
useininsulinpumps[68] [69] .
Whileonamolarbasisinsulinaspartandlisprohaveidenticalinvivopotencycomparedtoregularhumaninsulin,
higherpeakconcentrationsareachievedwiththerapidactinginsulins[70] .Thus,whilea1:1conversionisoftenused
fortheinitialswitchfromregularinsulintoinsulinaspart,glulisineorlispro,overtime,apatientsrapidacting
insulindosemayneedtobeadjusted,oftenreduced.Thisdosingchangeisalsoduetothebettermatchingofthepeakof
theinsulinwiththemeal,thusachievingbetterpostprandialcontrol.
InsulinGlulisine(Apidra)
Insulinglulisineisarapidactinginsulinanaloguethatdiffersfromhumaninsulininthattheaminoacidasparagineat
positionB3isreplacedbylysineandthelysineinpositionB29isreplacedbyglutamicacid.Chemically,itis3Blysine
29Bglutamicacidhumaninsulin.Wheninjectedsubcutaneously,itsonsetofactionismorerapidandachieveshigher
concentrationscomparedtohumaninsulinonaunitperunitbasis.Whenusedasamealtimeinsulin,thedoseshouldbe
givenwithin15minutesbeforeamealorwithin20minutesafterstartingameal.Insulinglulisinealsoisbeingusedin
insulinpumps[71] .InsulinglulisinehasbeenavailableinUSAsince2007andFDAapprovedin2004.
ShortActingInsulin(Regular)
Regularinsulinhasanonsetofactionof3060minutes.Itshouldbeinjectedapproximately30minutesbeforethemeal.
Adherencetothisschedulecanbeinconvenientanddifficultforsomepatients.
IntermediateActingInsulins(NPH)
NPH,whichstandsforNeutralProtamineHagedorn,wascreatedin1936byHansChristianHagedornandB.Norman
Jensen.Thesescientistsdiscoveredthattheeffectsofsubcutaneouslyinjectedinsulincouldbeprolongedbytheaddition
ofprotamine,aproteinthattheyobtainedfromthe"milt"orsemenofrivertrout.NPHinsuliniscategorizedasan
intermediateactinginsulin,whoseonsetofactionisapproximately2hours,peakeffectat614hours,anddurationof
actionupto24hours(dependingonthesizeofthedose).Intermediateactinginsulinscanserveabasalinsulinand/or
prandialinsulindependingontimeofadministration.NPHinsulinisavailableinvariouscombinationswitheither
regularinsulinorshortactinginsulins(Table2).
LongActingInsulins
Longactinginsulinsservetoprovideabasal(orbaseline)levelofinsulin.
InsulinGlargine(Lantus)
Insulinglargine(21AGly30BaLArg30BbLArghumaninsulin)isaninsulinanalogapprovedApril20,2000
(Lantus).Itconsistsoftwomodificationstohumaninsulin.TwoargininesareaddedtotheCterminusoftheBchain
shiftingtheisoelectricpointoftheinsulinfromapHor5.4to6.7[72] .Thischangemakestheinsulinmoresolubleat
anacidicpHandinsulinglargineisformulatedatapHof4.0[73] .ThesecondmodificationisattheA21position,
whereasparagineisreplacedbyglycine.Thissubstitutionpreventsdeamidationanddimerisationthatwouldoccurwith
acidsensitiveasparagine.Wheninsulinglargineisinjectedintosubcutaneoustissue,whichisatphysiologicpH,the
acidicsolutionisneutralized.Microprecipitatesofinsulinglargineareformed,fromwhichsmallamountsofinsulinare
releasedthroughouta24hourperiod,resultinginalowlevelofinsulinthroughouttheday[74] .Thebiologicalactivity
ofinsulinglargineisduetoitsabsorptionkineticsandnotadifferentpharmacodynamicactivity(e.g.,stimulationof
peripheralglucoseuptake)[75] .
Itiscriticalthatinsulinglarginenotbemixedinthesamesyringewithanyanotherinsulinorsolutionbecausethiswill
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
10/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
alteritspHandthusaffectitsabsorptionprofile.Lantusmaybegivenatanytimeofday.Insulinglarginehasbeen
showntohavelessnocturnalhypoglycemiawhenusedatbedtimecomparedwithNPHinsulin[76] [77] .
InsulinDetemir(Levemir)
Insulindetemirisalongactinghumaninsulinanalogformaintainingthebasallevelofinsulinitstradenameis
Levemir.ItisaninsulinanaloginwhichtheB30aminoacidisomittedandaC14fattyacidchain(myristicacid)is
boundtotheB29lysineaminoacid.Insulindetemirisslowlyabsorbedduetoitsstrongassociationwithalbumininthe
subQtissueandwhenitreachesthebloodstreamitagainbindstoalbumindelayingitsdistributiontotheperipheral
tissues.
Storage
Allinsulinshaveanexpirationdatewhichislabeledondirectlyontheproduct(vials,cartridges,disposablepensand
otherdeliverydevices)applieswhentheyareunopenedandrefrigerated.Unopened(i.e.,insulinnotcurrentlyinuse)
insulinshouldbestoredintherefrigeratorat36F46F(2C8C).Insulinshouldneverbefrozenorstoredinan
ambienttemperaturegreaterthan86F(30C).Aninsulinvialinusemaybekeptatroomtemperature,below86
F,or30C(insulinglulisineandNovoNordiskhumaninsulins,N,Rand70/30,shouldbestoredupto77F
only),for28days,orabout1month(exceptforinsulindetemirandNovoNordiskhumaninsulins,whichcanbekept
forupto42days).Insulincartridges,disposablepensandotherdeliverydevicescanhavedifferentstorage
recommendationsforroomtemperature.Onceopened,insulincartridgesandpensshouldnotberefrigerated.
AdverseEffects
Themostsignificantadverseeffectofinsulinishypoglycemia.IntheDCCT(DiabetesControlandComplications
Trial),intensiveinsulintherapywasassociatedwitha23foldincreaseinseverehypoglycemia(i.e.,apersonrequiring
assistance)[78] .Likewise,intheUKPDS(UnitedKingdomProspectiveDiabetesStudy),insulintherapyinthe
intensivelytreatedgroupresultedin1.8%rateofmajorhypoglycemicepisodescomparedto0.7%intheconventional
group[79] .Allpatientsreceivinginsulinshouldbeawareofthesymptomsofhypoglycemiaandhowtotreatit.
Weightgainisanothersignificantsideeffectofinsulintherapy.Inpart,theweightgaincanbearesultoffrequent
hypoglycemicepisodesinwhichpatientsoftenovertreat/overeatinresponsetohunger.Insulin,beingananabolic
hormone,alsopromotestheuptakeoffattyacidsintoadiposetissue.TheamountofweightgainintheDCCTand
UKPDSassociatedwithinsulintherapywas4.6kgand4.0kgrespectively[80] [81] .However,lessweightgainis
encounteredwithlongactinginsulinanalogs[82] [83] .
Trueallergicreactionsandcutaneousreactionsarerare(seeImmunogenicity).Toavoidlipohypertrophy,patientsshould
beinstructedtorotatetheirinsulininjectionsites,preferablyrotatingwithinonearea(e.g.,abdomenavoid2inchradius
aroundnavel)andnotreusingforoneweek[84] .
InJune2009,4retrospective,epidemiologicstudiesassessingtheriskofcancerfrominsulinuse,glargineinparticular,
werepublishedonlineattheEuropeanAssociationfortheStudyofDiabetes'journalwebsite3oftheseEuropean
studiesreportedanincreasedriskofcancerwithinsulinglargine.IntheGermanystudy,acorrelationbetweeninsulin
doseandcancerriskwasfoundforallinsulintypes(humaninsulin,aspart,lisproorglargine)howeverafteradjusting
fordose,insulinglarginewasfoundtohaveadosedependentincreasedriskofcancercomparedtohumaninsulin(e.g.,
HR1.09,1.19and1.31foratotaldailydosesof10units,30unitsand50unitsrespectively).[85] Themedianfollow
uptimewasonly1.63years(1.31yearsforinsulinglargine)andbodymassindexwasnotaccountedfor.TheSwedish
studyfoundastatisticallysignificantincreasedriskofbreastcanceronlyinwomenwhousedinsulinglarginealone(RR
1.99),butnotinthoseoninsulinglargineplusotherinsulins.[86] TheScotlandstudydemonstratedaincreasedriskof
cancer(HR1.55)forpatientsoninsulinglarginealone,whilethoseoninsulinglargineplusotherinsulinshadaslightly
lowerincidenceofcancer(HR0.81)comparedtohumaninsulinonlyuserswhichwasnotstatisticallysignificant.[87]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
[88]
11/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Finally,intheUKstudy,nolinkbetweeninsulinglargineandcancerwasfound.[88] Theseobservationalstudies
assessedlargepatientdatabasesandhavesignificant,inherentlimitationstogeneralizetheirconclusions,suchasthe
potentialfordifferentpretreatmentcharacteristicsofthegroups,selectionbias,thesmallnumbersofcancercasesfound,
andshortdurationoffollowup.Also,type2diabetesitselfisassociatedwithanincreasedriskofcolon,pancreasand
breastcancer.Furthermore,inarandomised,5year,openlabeltrialcomparingtheprogressionofretinopathyofNPH
andinsulinglargineusers,noincreasedriskofcancerwasfoundinthe1017patientsample.[89] Lastly,inananalysis
of31randomizedcontrolledtrialsfromthesanofiaventissafetydatabase(phase2,3,and4studies),insulinglargine
wasnotassociatedwithanincreasedriskofcancer,includingbreastcancer.[90] Ofnote,themainstudyaffectingthese
findingsistheRosenstocketalstudycomparingglarginetoNPHthathadanapproximate5yearduration,whereas19
ofthestudiesincludedhadveryshortdurations(approximately6months).OnJuly1,2009,theFDAissuedanearly
communicationaboutthesafetyofLantusandisworkingwiththemanufacturertoreviewthecollectivedataand
determinewhetheradditionalstudiesneedtobeperformed.Atthistime,thesedatadonotprovideconclusiveevidence
ofanincreasedriskofcancerassociatedwithinsulinglargine.
TYPESOFREGIMENS
GeneralPrinciples
Type1Diabetes
Withdecreasingbetacellfunctionresultingindecreasedinsulinproduction,peoplewithtype1diabetesmayrequire
insulinforsurvival.Ingeneral,insulinopenictype1diabeticsgenerallyrequire0.51.0unitsperkgofbodyweightper
dayofinsulin[91] .Insulintherapyisofteninitiatedat0.50.75units/kg/day[92] .Duringtheearlystagesoftype1
diabetes,patientswillrequirelessinsulinbecausethebetacellsarestillproducingsomeinsulininsulinrequirementscan
beintherangeof0.10.6unitsperkgperday[93] [94] .Intensiveinsulintherapy(definedas3insulininjections
daily)isindicatedforpeoplewithtype1diabetesasthishasbeenshowntoprovidebetterglycemiccontrolthan1or2
dailyinjectionsandreducethedevelopmentandprogressionofmicrovascularcomplications[95] .
Type2Diabetes
Manypatientswithtype2diabeteswilleventuallyrequireinsulintherapy.Sincetype2diabetesisassociatedwith
insulinresistance,insulinrequirementscanexceed1unit/kg/day.IntheUKPDS,by9yearslessthan25%ofpatients
treatedwithasulfonylureaasmonotherapywereabletomaintainA1Clevels<7.0%themajorityofpatientsrequired
insulintherapywithin9yearsofdiagnosis[96] .Wheninitiatinginsulintherapyinpatientswithtype2diabetes,insulin
isoftenusedincombinationwiththeoralmedicationsapatientistaking.Oftenanintermediatetolongactinginsulin
(e.g.,NPH,insulinglargine,orinsulindetemir)isaddedatbedtimeor70/30insulinbeforedinner[97] .Therationaleis
thatinsulin,bysuppressinghepaticglucoseoutputduringthenight,willcontrolthefastingbloodglucose(FPG),while
theoralmedication(s)continuestocontrolprandialglucoselevelsandglucosethroughouttheday[98] .Typically,a
startingdoseof10unitsisutilized,or~0.10.2units/kg[99] .Theintermediatetolongactinginsulinistitratedto
achievetheFPGtarget(seeAdjustmentsbelow).Ifthepatienthaspoorglycemiccontrolduringtheday,daytimeinsulin
caninitiatedtwicedailyregimenofinsulinormultipledailyinjectionscanbeused.Atthispoint,thepatientis
experiencingbetacellfailure.Ifthepatientistakinganinsulinsecretagogue(e.g.,glyburide,repaglinide,etc),itshould
bediscontinued,asinsulinwillnowbereplacedexogenously.However,theinsulinsensitizingoralagents(e.g.,
metforminshouldbecontinued)Anotheroptionistodiscontinuetheinsulinsecretagoguewheninsulintherapyisstarted
tosimplifythemedicationregimenandtoavoidpotentialhypoglycemia.[100] .
GoalsofTherapy
Beforestartingapatientoninsulin,oradjustingtheircurrentinsulintherapy,itisimportanttoestablishglycemicgoals
tailoredtothepatient.TheAmericanDiabetesAssociationcurrentlyrecommendsthefollowingglycemicgoals[101] :
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
12/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Preprandialplasmaglucose70130mg/dl
Postprandialplasmaglucose<180mg/dl
A1C<7%
Forexample,ifapatientspreprandialbloodglucoselevelshavebeeninthehigh200s,aninitialgoalmightbe
tolowerthemto150mg/dl.Uponachievingthis,alowergoalcanbeset(e.g.,90130mg/dl).IntheDCCT,
retinopathyinitiallyworsenedduringthefirstyearinpatients(withtype1diabetes)whoreceivedintensivetherapy[102
]
.Thisisthoughttobeduetorapidloweringofglucoselevels.Thusinpatientswithproliferativeretinopathyorthose
withhighA1C(e.g,>10%),slowerloweringofglucoseiswarranted[103] .Anotherexampleofindividualizing
glycemicgoalsisapatientwithhypoglycemicunawarenessglycemicgoalsshouldbelessaggressiveasglucoselevels
shouldnotborderaround70mg/dltooclosely.
ReplacementStrategies
PhysiologicInsulinReplacement
Afunctioningpancreasreleasesinsulincontinuously,tosupplyabasalamounttosuppresshepaticglucoseoutput
betweenmealsandovernight,andalsoreleasesabolusofinsulinprandiallytopromoteglucoseutilizationaftereating[
104]
.Replacinginsulininamannerthatattemptstomimicphysiologicinsulinreleaseisoftenreferredtoasthe
basal/bolusconcept.Thisphysiologicreplacementrequiresmultipledailyinjections(3ormore)oruseofaninsulin
pump.Basalinsulinrequirementsareapproximately50%ofthetotaldailyamount.Prandialinsulinis~1020%ofthe
totaldailyinsulinrequirementateachmeal[105] .Providingbasalbolusinsulinregimensallowpatientstohave
flexibilityintheirmealtimesandachievebetterglycemiccontrol.
NonPhysiologicInsulinReplacement
Wheninsulinisgivenonceortwicedaily,insulinlevelsdonotmimicphysiologicinsulinreleasepatterns.Forpeople
withtype2diabetes,inwhombasalinsulinreplacementisnotascritical,onceortwicedailyregimenscanstillwork
satisfactorilywithreasonableglycemiccontrolachieved.
ExamplesofRegimens
OnceDailyInsulinRegimen(forpatientswithtype2diabetesonoralagents)
NPH(Figure5a),insulinglargine(Figure5b),orinsulindetemiraremostoftengivenatbedtime(howeverinsulin
glarginecanbeadministeredanytimeoftheday)orforpatientwhoeatlargeamountsofcarbohydratesatdinner,an
insulinmixture,regularandNPHoraprexmixedinsulin,canbegivenpriortodinner(Figure5c).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
13/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Figure5a.
Figure5b.
Figure5c.
TwicedailyInsulinRegimen(SplitMixedandPreMixedRegimens)
Twothirdsoftheinsulindoseisgiveninthemorningbeforebreakfastandonethirdisgivenbeforedinner.Premixed
insulinscanbeusedoramixtureofashortactinginsulin(e.g.,regular,insulinaspart/glulisine/lispro)andan
intermediateactinginsulin(e.g.,NPH)(Figure6a)[106] .
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
14/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Figure6a.
2/3totaldailydoseatbreakfast:givenas2/3NPHand1/3Regular(orinsulinaspart/glulisine/lispro)
1/3totaldailydoseatdinner:dividedinequalamountsofNPHandRegular(orinsulinaspart/glulisine/lispro)
ForpatientswhoexperiencenocturnalhypoglycemiawhenNPHisadministeredatdinnerwithashortactinginsulin,
movingtheNPHdosetobedtimehelpsreducetheriskfornocturnalhypoglycemia[107] .Conversely,NPHatdinner
canresultinfastinghyperglycemiaduetodissipationofinsulinactivityandthedawnphenomenon.MovingtheNPH
dosetobedtimecanhelpresolvethisproblem[108] (Figure6b).Anobviouslimitationtousingpremixedinsulinis
reducedflexibilityindosingifthedoseisadjusted,bothtypesofinsulininthemixtureareadjusted.
Figure6b.
MultipleDailyInsulinInjectionRegimen:BasalplusPrandialInsulin
Manydifferenttypesofregimensarepossiblewithmultipledailyinjections.Regular,insulinaspart,glulisineandlispro
areusedtoprovideprandialinsulin.NPH,insulinglargine,andinsulindetemirareusedtoprovidebasalinsulin.
Regular,insulinaspart/glulisine/lisprobeforemealsandNPH,insulinglargineorinsulindetemiratbedtime
(Figure7a,7b).
Insulinaspart/glulisine/lisprobeforemealsandNPHtwicedaily(breakfastandbedtime)(Figure8).
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
15/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Figure7a.
Figure7b.
Figure8.
InsulinPumps
Insulinpumporcontinuoussubcutaneousinsulininfusion(CSII)therapyisanotheroptionforintensiveinsulintherapy.
Whilepumptherapyusedtobereservedforprimarilytype1diabetes,patientswithtype2diabetesarenowusing
insulinpumps[109] .Patientsinitiatedoninsulinpumptherapyneedtobeveryknowledgeableaboutdiabetes
managementandbepracticingselfmanagement.Patientsalreadyknowhowtocountcarbohydratesandadjusttheir
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
16/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
insulindoses.Potentialadvantagesofinsulinpumpsincludelessweightgain,lesshypoglycemia,andbettercontrolof
fastinghyperglycemiaduetothedawnphenomenoncomparedtomultipledailyinjections[110] [111] [112] [113] .
TimingofPrandialInsulinInjection
Thelagtimefrominjectingregularinsulinandeatingisapproximately30minuteswhileinsulinaspart/glulisine/lispro
canbeinjectedwithin15minutesofeating.Dependingonthelevelofhyperglycemiabeforemeals,thelagtimecanbe
increased.Rapidactinginsulinsallowpatientstoadjustinsulintomatchtheirlifestyleratherthanhavingtoadaptthe
timingofmealstoamorefixedinsulinregimen[114] .
Adjustments
Insulindosesshouldbeadjustedtoachieveglycemictargets.Itisalwaysbesttoerrontheconservativesidewhen
dosinginsulinatinitiationorwhenadjustingcurrentinsulintherapy.Typicallya1020%increaseordecreaseinan
insulindoseisappropriate.Ifapatientisexperiencinghypoglycemia,adjustmentoftheinsulindosecausingthe
hypoglycemiashouldbeaddressedpreferentiallyoverotherinsulindoseadjustments.Hyperglycemiaisadominoeffect:
ifapatientishyperglycemicinthemorning,chancesaretheyremainhyperglycemicthroughouttheday.Therefore,
adjusttheearliesttimeofhyperglycemiafirst[115] .
AdjustmentofIntermediatetoLongActingInsulin
Whenadoseofintermediateorlongactinginsulinisadjusted,itisrecommendedtowaitatleast25daysbeforefurther
changesinthedosetoassesstheresponse[116] .
AdjustmentofOnceDailyEveningInsulin
TheFPGisusedtoadjusttheintermediatetolongactinginsulingivenintheevening.Acommonweeklytitration
scheduleusedis[117] :
IftheFPGis>140mg/dl:Increaseby4units
IftheFPGis120140mg/dl:Increaseby2units
Forinsulinglargine,thefollowingtitrationschedulehasbeenstudiedandshowntocauselessnocturnalhypoglycemia
comparedtobedtimeNPHinsulin.Inthisstudy,insulinwastitrated,usingaforcedtitrationschedule,totargetaFPGof
100mg/dl[118] .
ForcedTitrationScheduleStartwith10unitsbedtimebasalinsulindoseadjustweekly
FPG(mg/dL)
Increaseinsulindose
100120
120140
140180
180
Decreaseinsulindose(e.g.,24units/day)ifhypoglycemiaoccurs.(modifiedrecommendationfromreference112)
SupplementalInsulinforCorrectionofHyperglycemia
Regularinsulin,insulinaspart/glulisine/lisprocanbeusedtocorrectforhyperglycemia[119] .Ingeneral,12unitsof
insulinwilllowerthebloodglucoseby3050mg/dl.Often1unitforevery50mg/dlabovetheglucosetargetisa
startingsupplementaldose,adjustingforinsulinsensitivity[120] .Anexampleofasupplementalinsulinregimenisas
follows:Forevery50mg/dlabovethepremealglucosetarget(e.g.,150mg/dl),add1unitofinsulin[121] .So,ifa
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
17/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
personspremealglucosewas250mg/dl,2unitsofinsulinwouldbeaddedtotheusualdoseofpremealinsulin.
Supplementalinsulincanalsobeusedforsnacks[122] .
CarbohydrateCounting
Amoresophisticatedtypeofinsulinregimenisoneinwhichapatientdosestheirprandialinsulinbasedonthenumber
ofcarbohydrateseatenatthemeal.Bylearninghowtocounttheircarbohydrates,anddosingtheirinsulinaccordingly,
patientsareaffordedflexibilityintheirmeals.Astartinginsulintocarbohydraterationoftenusedis1unitofinsulinfor
every15gramsofcarbohydrate[123] .Thisratioisadjustedbasedoninsulinsensitivityandmaybedifferentforeach
meal.Carbohydratecountingistoodifficultforsomepatients.Inthesepatients,mealportionsizesandestimatesof
carbohydrateservings(15grams)areconceptsthatcanbelearned.Medicalnutritiontherapyisacriticalcomponentof
therapyforpatientsoninsulin.
Acomprehensivediabeteseducationclass,thatteachesselfmanagementskills,suchashowtodoseprandialinsulinby
matchingittotheamountofcarbohydrateintakeareanexcellentresourcetofacilitatepatientsinadoptinganintensive
insulintherapyregimen[124] .
AdjustmentsforExercise
Exerciseimprovesinsulinsensitivity.Thus,whenapatientexercises,itisoftennecessarytodecreasetheinsulindose
(andincreasecaloricintake).Formorningexercise,theprebreakfastinsulindoseshouldbereduced(~25%depending
onthedurationandintensityoftheexercise).Forlatemorning/earlyafternoonandeveningexercise,theprelunchand
predinnerinsulindoseshouldbereducedrespectively[125] .Theeffectofexerciseoninsulinsensitivitycanlastfor
manyhourssoseveralinsulindosesmayneedtobeadjusted.
SelfMonitoringofBloodGlucose
Patientswhowerenotselfmonitoringtheirbloodglucose(SMBG)levelspriortoinsulinneedtobeeducatedhowtodo
this,howtointerprettheirglucosereadings,andhowtotreathypoglycemiaifitoccurs.Involvementofdiabetes
educatorisextremelyusefulwheninitiatingpatientsoninsulintoprovidecomprehensiveselfmanagementtraining.The
ADAcurrentlyrecommendthatpeoplewithtype1diabetesSMBGatleast3timesdailyandthosewithtype2diabetes
atleastdaily[126] .Mostglucosemetersarenowplasmareferenced,correlatingbettertotheADAsglycemic
goals.Plasmaglucoseconcentrationsareapproximately1015%higherthanwholebloodglucoseconcentrations[127] .
SICKDAYGUIDELINES
Acommonmisconceptionamongpatientsisthatiftheyaresickenoughthattheydonteatorevenvomit,they
shouldnottaketheirdiabetesmedications,insulinincluded.Patientsshouldbeinstructedtocontinuetheirinsulin
therapy,maintainfluidintake,eatsmallermealsastolerated,andtesttheirglucoselevelsevery14hours(ketonesas
wellforpeoplewithtype1diabetes).Insulintherapyshouldbeadjustedbasedontheglucoselevels.Iftheglucoseis
>240mg/dlwithmoderatetolargeketonuria,patientsshouldcontacttheirproviderimmediately[128] .
References
1. BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
2. FDA/CDERresourcespage.Frequentlyaskedquestionsaboutimportingbeeforporkinsulinforpersonaluse.Food
andDrugAdministrationwebsite.Availableat:http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/beefandporkinsulin/default.htm.
AccessedSeptember16,2006.
3. BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
4. May2004EliLillyandCompany.HumalogPackageInsert.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
18/24
25/06/2015
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
March2005EliLillyandCompany.HumalogMix75/25PackageInsert.
February2006SanofiAventisU.S.LantusPackageInsert.
October2005NovoNordisk,Inc.NovologPackageInsert.
November2005NovoNordiskInc.NovologMix70/30PackageInsert.
January2006EliLillyandCompany.HumalogMix50/50PackageInsert.
October2005NovoNordiskInc.LevemirPackageInsert.
November2005AventisPharmaceuticalsInc.ApidraPackageInsert.
KurtzhalsP,SchafferL,SorensenA,etal.2000Correlationsofreceptorbindingandmetabolicandmitogenic
potenciesofinsulinanalogsdesignedforclinicaluse.Diabetes49:9991005.[PubMed:10866053]
KurtzhalsP,SchafferL,SorensenA,etal.2000Correlationsofreceptorbindingandmetabolicandmitogenic
potenciesofinsulinanalogsdesignedforclinicaluse.Diabetes49:9991005.[PubMed:10866053]
HomePD,AshwellSG2002Anoverviewofinsulinglargine.DiabetesMetabResRev18Suppl3:S5763.
[PubMed:12324987]
SchernthanerG1993Immunogenicityandallergenicpotentialofanimalandhumaninsulins.DiabetesCare16
Suppl3:15565.[PubMed:8299472]
SchernthanerG1993Immunogenicityandallergenicpotentialofanimalandhumaninsulins.DiabetesCare16
Suppl3:15565.[PubMed:8299472]
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
SchernthanerG1993Immunogenicityandallergenicpotentialofanimalandhumaninsulins.DiabetesCare16
Suppl3:15565.[PubMed:8299472]
SchernthanerG1993Immunogenicityandallergenicpotentialofanimalandhumaninsulins.DiabetesCare16
Suppl3:15565.[PubMed:8299472]
SchernthanerG1993Immunogenicityandallergenicpotentialofanimalandhumaninsulins.DiabetesCare16
Suppl3:15565.[PubMed:8299472]
March2007sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.LantusPackageInsert.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
KroonLA,AssemiM,CarlisleBA.2009DiabetesMellitus.In:AppliedTherapeutics:TheClinicalUseofDrugs,
9thedition.KodaKimbleMA,YoungLY,AlldredgeBA,CorelliRL,GuglielmoBJ,KradjanWA,WilliamsBR,
eds.Lippincott,Williams&Wilkins:Baltimore,MD.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
March2009EliLillyandCompany.HumalogPackageInsert.
March2008NovoNordisk,Inc.NovologPackageInsert.
February2009sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.ApidraPackageInsert.
terBraakEW,WoodworthJR,BianchiR,etal.1996Injectionsiteeffectsonthepharmacokineticsand
glucodynamicsofinsulinlisproandregularinsulin.DiabetesCare19:143740.[PubMed:8941480]
March2007sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.LantusPackageInsert.
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
KurtzhalsP,SchafferL,SorensenA,etal.2000Correlationsofreceptorbindingandmetabolicandmitogenic
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
19/24
25/06/2015
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
potenciesofinsulinanalogsdesignedforclinicaluse.Diabetes49:9991005.[PubMed:10866053]
HomePD,AshwellSG2002Anoverviewofinsulinglargine.DiabetesMetabResRev18Suppl3:S5763.
[PubMed:12324987]
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
FrancisAJ,HanningI,AlbertiKG1985Theinfluenceofinsulinantibodylevelsontheplasmaprofilesandaction
ofsubcutaneouslyinjectedhumanandbovineshortactinginsulins.Diabetologia28:3304.[PubMed:3899818]
terBraakEW,WoodworthJR,BianchiR,etal.1996Injectionsiteeffectsonthepharmacokineticsand
glucodynamicsofinsulinlisproandregularinsulin.DiabetesCare19:143740.[PubMed:8941480]
NolteMS,Karam,J.H.2001PancreaticHormones&AntidiabeticDrugs.In:KatzungB(ed)BasicandClinical
Pharmacology,8thed.LangeMedicalBooks/McGrawHill,NewYork,pp711734.
RabkinR,RyanMP,DuckworthWC1984Therenalmetabolismofinsulin.Diabetologia27:3517.[PubMed:
6389240]
RoachP,WoodworthJR2002Clinicalpharmacokineticsandpharmacodynamicsofinsulinlispromixtures.Clin
Pharmacokinet41:104357.[PubMed:12403642]
RaveK,etal.2005Timeactionprofileofinhaledinsulinincomparisonwithsubcutaneouslyinjectedinsulinlispro
andregularhumaninsulin.DiabetesCare2810771082.[PubMed:15855570]
PlankJ,etal.2005.Adoubleblind,randomized,doseresponsestudyinvestigatingthepharmacodynamicand
pharmacokineticpropertiesofthelongactinginsulinanalogdetemir.DiabetesCare2811071112.[PubMed:
15855574]
LeporeM,etal.2000.Pharmacokineticsandpharmacodynamicsofsubcutaneousinjectionoflongactinghuman
insulinanalogglargine,NPHinsulin,andultralentehumaninsulinandcontinuoussubcutaneousinfusionofinsulin
lispro.Diabetes4921422148.[PubMed:11118018]
March2009EliLillyandCompany.HumalogPackageInsert.
March2009EliLillyandCompany.HumalogMix75/25PackageInsert.
March2007sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.LantusPackageInsert.
March2008NovoNordisk,Inc.NovologPackageInsert.
October2007NovoNordiskInc.NovologMix70/30PackageInsert.
May2007NovoNordiskInc.LevemirPackageInsert.
KurtzhalsP,SchafferL,SorensenA,etal.2000Correlationsofreceptorbindingandmetabolicandmitogenic
potenciesofinsulinanalogsdesignedforclinicaluse.Diabetes49:9991005.[PubMed:10866053]
HomePD,AshwellSG2002Anoverviewofinsulinglargine.DiabetesMetabResRev18Suppl3:S5763.
[PubMed:12324987]
KroonLA,AssemiM,CarlisleBA.2009DiabetesMellitus.In:AppliedTherapeutics:TheClinicalUseofDrugs,
9thedition.KodaKimbleMA,YoungLY,AlldredgeBA,CorelliRL,GuglielmoBJ,KradjanWA,WilliamsBR,
eds.Lippincott,Williams&Wilkins:Baltimore,MD,pp5017.
terBraakEW,WoodworthJR,BianchiR,etal.1996Injectionsiteeffectsonthepharmacokineticsand
glucodynamicsofinsulinlisproandregularinsulin.DiabetesCare19:143740.[PubMed:8941480]
FrancisAJ,HanningI,AlbertiKG1985Theinfluenceofinsulinantibodylevelsontheplasmaprofilesandaction
ofsubcutaneouslyinjectedhumanandbovineshortactinginsulins.Diabetologia28:3304.[PubMed:3899818]
NolteMS,Karam,J.H.2001PancreaticHormones&AntidiabeticDrugs.In:KatzungB(ed)BasicandClinical
Pharmacology,8thed.LangeMedicalBooks/McGrawHill,NewYork,pp711734.
RabkinR,RyanMP,DuckworthWC1984Therenalmetabolismofinsulin.Diabetologia27:3517.[PubMed:
6389240]
BinderC,BrangeJ1997Insulinchemistryandpharmacokinetics.In:PorteD,Jr.,SherwinR(eds)Ellenberg'sand
Rifkin'sDiabetesMellitus,5theditioned.AppletonandLange,Stamford,CT,p689.
PampanelliS,TorloneE,IalliC,etal.1995Improvedpostprandialmetaboliccontrolaftersubcutaneousinjection
ofashortactinginsulinanaloginIDDMofshortdurationwithresidualpancreaticbetacellfunction.Diabetes
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
20/24
25/06/2015
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
77.
78.
79.
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
Care18:14529.[PubMed:8722069]
BrunelleBL,LlewelynJ,AndersonJH,Jr.,GaleEA,KoivistoVA1998Metaanalysisoftheeffectofinsulin
lisproonseverehypoglycemiainpatientswithtype1diabetes.DiabetesCare21:172631.[PubMed:9773738]
LalliC,CiofettaM,DelSindacoP,etal.1999Longtermintensivetreatmentoftype1diabeteswiththeshort
actinginsulinanaloglisproinvariablecombinationwithNPHinsulinatmealtime.DiabetesCare22:46877.
[PubMed:10097931]
LalliC,CiofettaM,DelSindacoP,etal.1999Longtermintensivetreatmentoftype1diabeteswiththeshort
actinginsulinanaloglisproinvariablecombinationwithNPHinsulinatmealtime.DiabetesCare22:46877.
[PubMed:10097931]
ZinmanB,TildesleyH,ChiassonJL,TsuiE,StrackT1997InsulinlisproinCSII:resultsofadoubleblind
crossoverstudy.Diabetes46:4403.[PubMed:9032100]
KaufmanFR,HalvorsonM,KimC,PitukcheewanontP2000Useofinsulinpumptherapyatnighttimeonlyfor
children710yearsofagewithtype1diabetes.DiabetesCare23:57982.[PubMed:10834412]
RennerR,PfutznerA,TrautmannM,HarzerO,SauterK,LandgrafR1999Useofinsulinlisproincontinuous
subcutaneousinsulininfusiontreatment.Resultsofamulticentertrial.GermanHumalogCSIIStudyGroup.
DiabetesCare22:7848.[PubMed:10332682]
KumarD1997Lisproanalogfortreatmentofgeneralizedallergytohumaninsulin.DiabetesCare20:13579.
[PubMed:9283778]
RaskinP,GuthrieRA,LeiterL,RiisA,JovanovicL2000Useofinsulinaspart,afastactinginsulinanalog,asthe
mealtimeinsulininthemanagementofpatientswithtype1diabetes.DiabetesCare23:5838.[PubMed:
10834413]
March2008NovoNordisk,Inc.NovologPackageInsert.
BodeBW,StrangeP2001Efficacy,safety,andpumpcompatibilityofinsulinaspartusedincontinuous
subcutaneousinsulininfusiontherapyinpatientswithtype1diabetes.DiabetesCare24:6972.[PubMed:
11194244]
terBraakEW,WoodworthJR,BianchiR,etal.1996Injectionsiteeffectsonthepharmacokineticsand
glucodynamicsofinsulinlisproandregularinsulin.DiabetesCare19:143740.[PubMed:8941480]
February2009sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.ApidraPackageInsert.
BolliGB,OwensDR2000Insulinglargine.Lancet356:4435.[PubMed:10981882]
BolliGB,OwensDR2000Insulinglargine.Lancet356:4435.[PubMed:10981882]
HeinemannL,LinkeschovaR,RaveK,HompeschB,SedlakM,HeiseT2000Timeactionprofileofthelong
actinginsulinanaloginsulinglargine(HOE901)incomparisonwiththoseofNPHinsulinandplacebo.Diabetes
Care23:6449.[PubMed:10834424]
MudaliarS,MohideenP,DeutschR,etal.2002.Intravenousglargineandregularinsulinhavesimilareffectson
endogenousglucoseoutputandperipheralactivation/deactivationkineticprofiles.DiabetesCare25:1597602.
[PubMed:12196433]
YkiJarvinenH,DresslerA,ZiemenM.2000.Lessnocturnalhypoglycemiaandbetterpostdinnerglucosecontrol
withbedtimeinsulinglarginecomparedwithbedtimeNPHinsulinduringinsulincombinationtherapyintype2
diabetes.HOE901/3002StudyGroup.DiabetesCare23:11306.[PubMed:10937510]
RatnerRE,HirschIB,NeifingJL,GargSK,MeccaTE,WilsonCA2000Lesshypoglycemiawithinsulin
glargineinintensiveinsulintherapyfortype1diabetes.U.S.StudyGroupofInsulinGlargineinType1Diabetes.
DiabetesCare23:63943.[PubMed:10834423]
TheDiabetesControlandComplicationsTrialResearchGroup.1993.Theeffectofintensivetreatmentofdiabetes
onthedevelopmentandprogressionoflongtermcomplicationsininsulindependentdiabetesmellitus.NEnglJ
Med329:97786.[PubMed:8366922]
UKProspectiveDiabetesStudy(UKPDS)Group.1998.Intensivebloodglucosecontrolwithsulphonylureasor
insulincomparedwithconventionaltreatmentandriskofcomplicationsinpatientswithtype2diabetes(UKPDS
33).Lancet352:83753.[PubMed:9742976]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
21/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
80.
TheDiabetesControlandComplicationsTrialResearchGroup.1993.Theeffectofintensivetreatmentofdiabeteson
thedevelopmentandprogressionoflongtermcomplicationsininsulindependentdiabetesmellitus.NEnglJMed
329:97786.[PubMed:8366922]
81. UKProspectiveDiabetesStudy(UKPDS)Group.1998.Intensivebloodglucosecontrolwithsulphonylureasor
insulincomparedwithconventionaltreatmentandriskofcomplicationsinpatientswithtype2diabetes(UKPDS
33).Lancet352:83753.[PubMed:9742976]
82. MeneghiniLF,RosenbergKH,KoenenC,MerilainenMJ,LddekeHJ.2007.Insulindetemirimproves
glycaemiccontrolwithlesshypoglycaemiaandnoweightgaininpatientswithtype2diabeteswhowereinsulin
naiveortreatedwithNPHorinsulinglargine:clinicalpracticeexperiencefromaGermansubgroupofthe
PREDICTIVEstudy*Diabetes,ObesityandMetabolism9(3)418427.[PubMed:17391170]
83. RosenstockJ,DaviesM,HomePD,LarsenJ,KoenenC,SchernthanerG.2008.Arandomised,52week,treatto
targettrialcomparinginsulindetemirwithinsulinglarginewhenadministeredasaddontoglucoseloweringdrugs
ininsulinnaivepeoplewithtype2diabetes.Diabetologia51(3):408416.[PMCfreearticle:PMC2235909]
[PubMed:18204830]
84. ADA.2004.AmericanDiabetesAssociationPositionStatement.Insulinadministration.DiabetesCare27Suppl
1:S106109.[PubMed:14693942]
85. HemkinsLG,GrouvenU,BenderRetal.2009.Riskofmalignanciesinpatientswithdiabetestreatedwithhuman
insulinorinsulinsanalogues:acohortstudy.Diabetologia52:17321744.[PMCfreearticle:PMC2723679]
[PubMed:19565214]
86. JonassonJM,LjungR,TlbackMetal.2009.Insulinglargineuseandshorttermincidenceofmalignanciesa
populationbasedfollowupstudyinSweden.Diabetologia52:17451754.[PubMed:19588120]
87. ColhounHM,onbehalfoftheSDRNEpidemiologyGroup.2009.Useofinsulinglargineandcancerincidencein
Scotland:astudyfromtheScottishDiabetesResearchNetworkEpidemiologyGroup.Diabetologia52:17551765.
[PMCfreearticle:PMC2723678][PubMed:19603149]
88. CurrieCJ,PooleCD,2009.GaleEAMTheinfluenceofglucoseloweringtherapiesoncancerriskintype2
diabetes.Diabetologia52:17661777.[PubMed:19572116]
89. RosenstockJ,FonsecaV,McGillJBetal.2009.Similarriskofmalignancywithinsulinglargineandneutral
protamineHagedorn(NPH)insulininpatientswithtype2diabetes:findingsfroma5yearrandomized,openlabel
study.Diabetologia52:17781788.[PMCfreearticle:PMC2723677][PubMed:19609501]
90. HomePD,LagarenneP.2009.Combinedrandomisedcontrolledtiralexperienceofmalignanciesinstudiesusing
insulinglargine.Diabetologiadoi:10.1007/s0012500915305.[PMCfreearticle:PMC2776153][PubMed:
19756478]
91. HirschIB1999Type1diabetesmellitusandtheuseofflexibleinsulinregimens.AmFamPhysician60:234352,
23556.[PubMed:10593324]
92. HirschIB1999Type1diabetesmellitusandtheuseofflexibleinsulinregimens.AmFamPhysician60:234352,
23556.[PubMed:10593324]
93. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
94. 2002Practicalinsulin:Ahandbookforprescribingproviders.AmericanDiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
95. 1993TheDiabetesControlandComplicationsTrialResearchGroup.Theeffectofintensivetreatmentofdiabetes
onthedevelopmentandprogressionoflongtermcomplicationsininsulindependentdiabetesmellitus.NEnglJ
Med329:97786.[PubMed:8366922]
96. TurnerRC,CullCA,FrighiV,HolmanRR1999Glycemiccontrolwithdiet,sulfonylurea,metformin,orinsulin
inpatientswithtype2diabetesmellitus:progressiverequirementformultipletherapies(UKPDS49).UK
ProspectiveDiabetesStudy(UKPDS)Group.Jama281:200512.[PubMed:10359389]
97. HermannLS2000Optimisingtherapyforinsulintreatedtype2diabetesmellitus.DrugsAging17:28394.
[PubMed:11087006]
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
22/24
25/06/2015
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
98.
HermannLS2000Optimisingtherapyforinsulintreatedtype2diabetesmellitus.DrugsAging17:28394.[PubMed:
11087006]
99. DeWittDE,DugdaleDC2003Usingnewinsulinstrategiesintheoutpatienttreatmentofdiabetes:clinical
applications.Jama289:22659.[PubMed:12734138]
100. YkiJarvinenH2001Combinationtherapieswithinsulinintype2diabetes.DiabetesCare24:75867.[PubMed:
11315844]
101. ADA2009Standardsofmedicalcareindiabetes2009.DiabetesCare32Suppl1:S1361.[PMCfreearticle:
PMC2613589][PubMed:19118286]
102. 1993TheDiabetesControlandComplicationsTrialResearchGroup.Theeffectofintensivetreatmentof
diabetesonthedevelopmentandprogressionoflongtermcomplicationsininsulindependentdiabetesmellitus.N
EnglJMed329:97786.[PubMed:8366922]
103. RoachP,WoodworthJR2002Clinicalpharmacokineticsandpharmacodynamicsofinsulinlispromixtures.Clin
Pharmacokinet41:104357.[PubMed:12403642]
104. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
105. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
106. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
107. FanelliCG,PampanelliS,PorcellatiF,RossettiP,BrunettiP,BolliGB2002Administrationofneutralprotamine
Hagedorninsulinatbedtimeversuswithdinnerintype1diabetesmellitustoavoidnocturnalhypoglycemiaand
improvecontrol.Arandomized,controlledtrial.AnnInternMed136:50414.[PubMed:11926785]
108. FrancisAJ,HomePD,HanningI,AlbertiKG,TunbridgeWM1983Intermediateactinginsulingivenatbedtime:
effectonbloodglucoseconcentrationsbeforeandafterbreakfast.BrMedJ(ClinResEd)286:11736.[PMCfree
article:PMC1547399][PubMed:6404377]
109. RaskinP,BodeBW,MarksJB,etal.2003Continuoussubcutaneousinsulininfusionandmultipledailyinjection
therapyareequallyeffectiveintype2diabetes:arandomized,parallelgroup,24weekstudy.DiabetesCare
26:2598603.[PubMed:12941725]
110. MudaliarS,EdelmanSV2001Insulintherapyintype2diabetes.EndocrinolMetabClinNorthAm30:93582.
[PubMed:11727406]
111. BodeBW,SabbahHT,GrossTM,FredricksonLP,DavidsonPC2002Diabetesmanagementinthenew
millenniumusinginsulinpumptherapy.DiabetesMetabResRev18Suppl1:S1420.[PubMed:11921425]
112. BodeBW,TamborlaneWV,DavidsonPC2002Insulinpumptherapyinthe21stcentury.Strategiesfor
successfuluseinadults,adolescents,andchildrenwithdiabetes.PostgradMed111:6977quiz27.[PubMed:
12040864]
113. PickupJ,KeenH2002Continuoussubcutaneousinsulininfusionat25years:evidencebasefortheexpanding
useofinsulinpumptherapyintype1diabetes.DiabetesCare25:5938.[PubMed:11874953]
114. February2009.sanofiaventisU.S.LCC.ApidraPackageInsert.
115. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
116. ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
117. MudaliarS,EdelmanSV2001Insulintherapyintype2diabetes.EndocrinolMetabClinNorthAm30:93582.
[PubMed:11727406]
118. RiddleMC,RosenstockJ,GerichJ2003Thetreattotargettrial:randomizedadditionofglargineorhumanNPH
insulintooraltherapyoftype2diabeticpatients.DiabetesCare26:30806.[PubMed:14578243]
119. HollemanF,vandenBrandJJ,HovenRA,etal.1996ComparisonofLysB28,ProB29humaninsulinanalog
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
23/24
25/06/2015
120.
121.
122.
123.
124.
125.
126.
127.
128.
InsulinPharmacology,TypesofRegimens,andAdjustmentsEndotextNCBIBookshelf
andregularhumaninsulininthecorrectionofincidentalhyperglycemia.DiabetesCare19:14269.[PubMed:
8941477]
MudaliarS,EdelmanSV2001Insulintherapyintype2diabetes.EndocrinolMetabClinNorthAm30:93582.
[PubMed:11727406]
DeWittDE,HirschIB2003Outpatientinsulintherapyintype1andtype2diabetesmellitus:scientificreview.
Jama289:225464.[PubMed:12734137]
KongN,KitchenMM,RyderRE2000Theuseoflisproforhighsugarcontentsnacksbetweenmealsin
intensiveinsulinregimens.DiabetMed17:3312.[PubMed:10821304]
HirschIB1999Type1diabetesmellitusandtheuseofflexibleinsulinregimens.AmFamPhysician60:234352,
23556.[PubMed:10593324]
2002Traininginflexible,intensiveinsulinmanagementtoenabledietaryfreedominpeoplewithtype1diabetes:
doseadjustmentfornormaleating(DAFNE)randomisedcontrolledtrial.Bmj325:746.[PMCfreearticle:
PMC128375][PubMed:12364302]
ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
ADA2009Standardsofmedicalcareindiabetes2009.DiabetesCare32Suppl1:S1361.[PMCfreearticle:
PMC2613589][PubMed:19118286]
StahlM,BrandslundI,JorgensenLG,HyltoftPetersenP,BorchJohnsenK,deFineOlivariusN2002Can
capillarywholebloodglucoseandvenousplasmaglucosemeasurementsbeusedinterchangeablyindiagnosisof
diabetesmellitus?ScandJClinLabInvest62:15966.[PubMed:12004932]
ADA1998MedicalManagementofInsulinDependent(TypeI)DiabetesMellitus,3rdeditioned.American
DiabetesAssociation,Alexandria,VA.
Copyright20002015,MDText.com,Inc.
ThiselectronicversionhasbeenmadefreelyavailableunderaCreativeCommons(CCBYNCND)license.Acopyofthelicensecanbeviewedat
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/byncnd/2.0/.
BookshelfID:NBK278938
PMID:25905175
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278938/?report=printable
24/24
You might also like
- What to Do in Case Of.......: A Reference Diagnostic Guide in Thoracic Organ TransplantationFrom EverandWhat to Do in Case Of.......: A Reference Diagnostic Guide in Thoracic Organ TransplantationNo ratings yet
- Global Health Training in Graduate Medical Education: A Guidebook, 2Nd EditionFrom EverandGlobal Health Training in Graduate Medical Education: A Guidebook, 2Nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nalini Chilkov Curriculum VitaeDocument6 pagesDr. Nalini Chilkov Curriculum VitaeKriszen Dana AmpalayoNo ratings yet
- Clinical DiabetesDocument669 pagesClinical DiabetesedsideasNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Document369 pagesInternal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2hurbinamaggi76No ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Document369 pagesInternal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2asdf234234888100% (5)
- Williams PDFDocument18 pagesWilliams PDFEmilioHernándezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Insulin TherapyDocument23 pagesAn Introduction To Insulin TherapyOrion JohnNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument302 pagesEndocrinologyMichelle L Saphire80% (5)
- Histerectomia PDFDocument177 pagesHisterectomia PDFernestosandNo ratings yet
- Goiter Author and Editor InformationDocument2 pagesGoiter Author and Editor InformationfynneroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Medicine: 2nd EditionDocument1,709 pagesClinical Laboratory Medicine: 2nd EditionBeatriz BelottiNo ratings yet
- Endo Sub Consult 20Document662 pagesEndo Sub Consult 20Hamad Alablani100% (4)
- JANA Long Cytokines, Excitotoxin Autism PaperDocument56 pagesJANA Long Cytokines, Excitotoxin Autism PaperAnonymous CoUBbG1mLNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Books Obstetric AnesthesiaDocument190 pagesAnesthesia Books Obstetric AnesthesiaMarcus Menezes100% (1)
- Manual of Clinical Hematology: 3rd EditionDocument470 pagesManual of Clinical Hematology: 3rd Editionnguyenvanbang420No ratings yet
- Complementary and CMedicineDocument635 pagesComplementary and CMedicineLikoh TimothyNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic HemoglobinopathiesLaboratory Methods and Case StudiesDocument479 pagesDiagnostic HemoglobinopathiesLaboratory Methods and Case StudiesZia Uddin100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of DiseaseDocument1,079 pagesPathophysiology of DiseaseTony Ansah100% (5)
- OSCDDocument331 pagesOSCDmanselsap100% (1)
- Disaster Preparedness for Healthcare FacilitiesFrom EverandDisaster Preparedness for Healthcare FacilitiesRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (3)
- Colorectal Neoplasia and the Colorectal Microbiome: Dysplasia, Probiotics, and FusobacteriaFrom EverandColorectal Neoplasia and the Colorectal Microbiome: Dysplasia, Probiotics, and FusobacteriaNo ratings yet
- MKSAP 17 Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine PDFDocument192 pagesMKSAP 17 Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine PDFRoxana Enachescu100% (3)
- The Health Effects of Cannabis and CannabinoidsDocument487 pagesThe Health Effects of Cannabis and CannabinoidsMiguel Salas-GomezNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diagnosis of Endocrine DisordersFrom EverandGenetic Diagnosis of Endocrine DisordersRoy E. WeissNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Family-Centered Care in The Neonatal, Pediatric, and Adult ICUDocument114 pagesGuidelines For Family-Centered Care in The Neonatal, Pediatric, and Adult ICUGabriela LealNo ratings yet
- Indoor Tanning Medical Sign On FINALDocument15 pagesIndoor Tanning Medical Sign On FINALdfreedlanderNo ratings yet
- Noonan Syndrome: Characteristics and InterventionsFrom EverandNoonan Syndrome: Characteristics and InterventionsAmrit P.S. BhangooNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Handbook of Chronic Kidney Disease Management by John T Daugirdas PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Handbook of Chronic Kidney Disease Management by John T Daugirdas PDF Ebookwilliam.hoisington872100% (40)
- Handbook of Critical Care Nephrology 2021Document851 pagesHandbook of Critical Care Nephrology 2021Roberto Barbery100% (3)
- Transgender Medicine An Issue of Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America Vin Tangpricha Ebook Full ChapterDocument51 pagesTransgender Medicine An Issue of Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America Vin Tangpricha Ebook Full Chaptertamera.stone860100% (5)
- (4X - A5) - 08161373182 - Shelf-Life Obgyn 2015 PDFDocument358 pages(4X - A5) - 08161373182 - Shelf-Life Obgyn 2015 PDFcmbhganteng80% (5)
- Research in Occupational TherapyDocument752 pagesResearch in Occupational Therapylala_roxana100% (8)
- Respiratory Symptoms Campbell All ChapterDocument67 pagesRespiratory Symptoms Campbell All Chaptermelanie.grant662100% (15)
- Primary Care of The Child With A Chronic Condition e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesPrimary Care of The Child With A Chronic Condition e Book 5th Edition Ebook PDFthelma.brown536100% (39)
- American College of Physicians - MKSAP 19 - Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program. Rheumatology-American College of Physicians (2021)Document194 pagesAmerican College of Physicians - MKSAP 19 - Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program. Rheumatology-American College of Physicians (2021)Paulo VizcardoNo ratings yet
- MKSAP For Students 5Document362 pagesMKSAP For Students 5vado_727100% (2)
- Dilemmas in ERCP: A Clinical CasebookFrom EverandDilemmas in ERCP: A Clinical CasebookDaniel K. MulladyNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Document369 pagesInternal Medicine Essentials For Clerkship Students 2Sudhir Tyagi100% (31)
- Eating Disorders and Obesity Third Edition A Comprehensive Handbook 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesEating Disorders and Obesity Third Edition A Comprehensive Handbook 3rd Edition Ebook PDFrichard.gibson910100% (41)
- Ebook Clinical Gynecologic Oncology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Clinical Gynecologic Oncology PDF Full Chapter PDFalton.kanahele202100% (26)
- Clinical Gynecologic Oncology 9Th Edition Edition Philip J Disaia Full ChapterDocument51 pagesClinical Gynecologic Oncology 9Th Edition Edition Philip J Disaia Full Chaptertim.morrison630100% (12)
- Pathways Winter 2015Document24 pagesPathways Winter 2015taliancichNo ratings yet
- Oxford American Cardiology Library HypertensionDocument190 pagesOxford American Cardiology Library HypertensionWesker Albert100% (1)
- MKSAP 18 Infectious DiseaseDocument206 pagesMKSAP 18 Infectious Diseasemus100% (2)
- Effects of Lifestyle on Men's HealthFrom EverandEffects of Lifestyle on Men's HealthFaysal A. YafiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology During Pregnancy 2Nd Edition Donald Mattison Editor Full ChapterDocument67 pagesClinical Pharmacology During Pregnancy 2Nd Edition Donald Mattison Editor Full Chapterdoug.wiggins940100% (6)
- Gastrointestinal Oncology Principles and PracticesDocument794 pagesGastrointestinal Oncology Principles and Practicesjohny3333No ratings yet
- Full Download Book Breastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Professional PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Breastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Professional PDFgeorge.pittman905100% (14)
- Full Download Book Breastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Profession PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Breastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Profession PDFgeorge.pittman905100% (15)
- Vital Directions for Health & Health Care: An Initiative of the National Academy of MedicineFrom EverandVital Directions for Health & Health Care: An Initiative of the National Academy of MedicineNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Profession Ruth A Lawrence Full ChapterDocument67 pagesBreastfeeding A Guide For The Medical Profession Ruth A Lawrence Full Chapterjulia.swanson282100% (5)
- A Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic TestsDocument2,696 pagesA Manual of Laboratory & Diagnostic Testsnezzie38% (8)
- AcogDocument178 pagesAcogFernando Vigil Velásquez100% (1)
- The International Society for Gender Medicine: History and HighlightsFrom EverandThe International Society for Gender Medicine: History and HighlightsNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse Quick Reference 2e: For Healthcare, Social Service, and Law Enforcement ProfessionalsFrom EverandChild Abuse Quick Reference 2e: For Healthcare, Social Service, and Law Enforcement ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Implications of Stress and DepressionFrom EverandCardiovascular Implications of Stress and DepressionPaul D. ChantlerNo ratings yet
- Oncology Endpoints in A Changing Landscape-P&T Magazine SupplementDocument12 pagesOncology Endpoints in A Changing Landscape-P&T Magazine SupplementMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- How Do I Copy Ahow Do I Copy A Copy Protected Web Page Copy Protected Web PageDocument21 pagesHow Do I Copy Ahow Do I Copy A Copy Protected Web Page Copy Protected Web PageMohamed Omer33% (6)
- HAAD Application How To ApplyDocument22 pagesHAAD Application How To ApplyMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabia's Foreign Policy On Iran and The Proxy WarDocument10 pagesSaudi Arabia's Foreign Policy On Iran and The Proxy WarMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Adherence To TreatmentDocument11 pagesAdherence To TreatmentMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Canadians Still Waiting Too Long For Health CareDocument21 pagesCanadians Still Waiting Too Long For Health CareMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy OverviewDocument18 pagesPharmacy OverviewMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Why Do Some Individuals With Serious Mental Illness Refuse To Take Medication FinalDocument5 pagesWhy Do Some Individuals With Serious Mental Illness Refuse To Take Medication FinalMohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Generički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCDocument7 pagesGenerički Naziv Lijeka (Zabranjena Supstanca) Registrovani Preparati (Komercijalni Naziv) Zaštićeno Ime Lijeka Oznaka U LZS 2015 Oznaka U ATCДраган ЧолићNo ratings yet
- Penggunaan Insulin Pada Diabetes Tipe 2Document47 pagesPenggunaan Insulin Pada Diabetes Tipe 2pebbyfebrianNo ratings yet
- Insulin InfoDocument4 pagesInsulin Infomonoj5859No ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High Alert Instalasi Farmasi Rsud SumedangDocument4 pagesDaftar Obat High Alert Instalasi Farmasi Rsud SumedangKOMITE MEDIKNo ratings yet
- Insulin Therapy Guide 2Document3 pagesInsulin Therapy Guide 2AimanRiddleNo ratings yet
- Fornas GPDocument2 pagesFornas GPyosaNo ratings yet
- Obat Ed 2021 TerbaruDocument19 pagesObat Ed 2021 TerbaruIF RSYMCNo ratings yet
- Slide Lokakarya Insulin Makassar Sept 2004Document45 pagesSlide Lokakarya Insulin Makassar Sept 2004Dian SobaNo ratings yet
- Diabtes MelitusDocument1 pageDiabtes Melitusrendi adi saputraNo ratings yet
- Pump SuppDocument3 pagesPump SuppAkshit R ShahNo ratings yet
- PP Lantus & Apidra ID Dokter. Update Insulin in RamadhanDocument57 pagesPP Lantus & Apidra ID Dokter. Update Insulin in RamadhanAhmad Husain 'Ucenk' PalliNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesDiabetes Cheat Sheetmanuel iglesiasNo ratings yet
- 2017 05 GC Pocket CardDocument2 pages2017 05 GC Pocket Cardapi-312241089No ratings yet
- Human Insulin Vs Insulin AnalogDocument7 pagesHuman Insulin Vs Insulin AnalogWita Ferani Kartika100% (1)
- I School - DiaCareDocument1 pageI School - DiaCareWarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimen and Priciple of Intensive Insulin Theraphy 2Document41 pagesInsulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimen and Priciple of Intensive Insulin Theraphy 2Dinar Danan SukmawatiNo ratings yet
- Switching Between InsulinDocument2 pagesSwitching Between InsulinThoufiNo ratings yet
- List Obat Kronis BpjsDocument6 pagesList Obat Kronis BpjsHelmi AgustianNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Long Acting InsulinsDocument3 pagesComparison Between Long Acting InsulinsSiddiq MohammedNo ratings yet
- Insulin ChartDocument2 pagesInsulin ChartJohanNone100% (1)
- Ilmu Resep TA 2020 - 2021 Tutorials - MyDispenseDocument6 pagesIlmu Resep TA 2020 - 2021 Tutorials - MyDispenseNatanaelHendrySantosoNo ratings yet
- Insulin Chart 05032012 PDFDocument1 pageInsulin Chart 05032012 PDFTiffany CrittendenNo ratings yet
- Add-On Diabetes: by Roche Diabetes CareDocument17 pagesAdd-On Diabetes: by Roche Diabetes CareKatya GeorgievaNo ratings yet
- INSULINDocument6 pagesINSULINmilaNo ratings yet
- Insulin ChartDocument1 pageInsulin ChartSyedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Parenteral Drug Calculations PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 11 Parenteral Drug Calculations PDFjames smithNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management SystemDocument3 pagesDiabetes Management Systembeth2042No ratings yet
- Types of Insulin PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Insulin PDFRetno WulanNo ratings yet
- Brands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreDocument3 pagesBrands and Types of Insulin - Rapid-Acting, Long-Acting, and MoreNanda Asyura RizkyaniNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument4 pagesInsulinMonNo ratings yet