Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problemas VHDL
Uploaded by
Eudomar Junior Gutierrez Beltran0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views4 pagesproblemas de vhdl
Original Title
Problemas Vhdl
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentproblemas de vhdl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views4 pagesProblemas VHDL
Uploaded by
Eudomar Junior Gutierrez Beltranproblemas de vhdl
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO 1
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE ING. ELECTRONICA
PROBLEMAS RESUELTOS DE VHDL
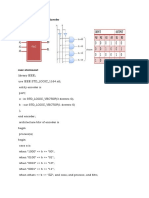
Ejemplo#1: MEMORIA RAM GENERICA
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_arith.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity SRAM is
generic(
w:
d:
a:
port( Clock:
Enable:
Read:
Write:
Read_Addr:
Write_Addr:
Data_in:
Data_out:
);
end SRAM;
integer:=4; -- ancho de palabra
integer:=4; -- n de palabras
integer:=2);-- ancho direccin
in std_logic;
in std_logic;
in std_logic;
in std_logic;
in std_logic_vector(a-1 downto 0);
in std_logic_vector(a-1 downto 0);
in std_logic_vector(w-1 downto 0);
out std_logic_vector(w-1 downto 0)
architecture behav of SRAM is
type ram_type is array (0 to d-1) of std_logic_vector(w-1 downto 0);
signal tmp_ram: ram_type;
begin
-- Lectura
process(Clock, Read)
begin
if (Clock'event and Clock='1') then
if Enable='1' then
if Read='1' then
Data_out <= tmp_ram(std2n(Read_Addr));
else
Data_out <= (Data_out'range => 'Z');
-- Todos los bits de Data_out se ponen a 'Z'
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
-- Escritura
process(Clock, Write)
begin
if (Clock'event and Clock='1') then
if Enable='1' then
if Write='1' then
tmp_ram(std2n(Write_Addr)) <= Data_in;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end behav;
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO 2
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE ING. ELECTRONICA
Ejemplo#2: SUMA DE 2 VECTORES
library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all;
package ope_aritmeticas is
function vector_to_natural (v:in std_logic_vector) return
natural;
function natural_to_vector (nat : in natural; length : in
natural)
return std_logic_vector;
procedure vector_add ( v1, v2 : in std_logic_vector;
v_result : out std_logic_vector);
end ope_aritmeticas;
package body ope_aritmeticas is
function vector_to_natural (v:in std_logic_vector) return
natural is
variable aux : natural:=0;
begin
for i in v'range loop
if v(i)='1' then
aux := aux + (2**i);
end if;
end loop;
return aux;
end vector_to_natural;
function natural_to_vector (nat : in natural; length : in
natural)
return std_logic_vector is
variable v: std_logic_vector(length-1 downto 0);
variable cociente, aux, i, resto: natural;
begin
aux:= nat;
i:=0;
while (aux/=0) and (i<length) loop
cociente := aux/2;
resto := aux mod 2;
if resto=0 then v(i):='0';
else v(i):='1';
end if;
i := i+1;
aux := cociente;
end loop;
for j in i to length-1 loop
v(j):='0';
end loop;
return v;
end natural_to_vector;
procedure vector_add ( v1, v2 : in std_logic_vector;
v_result : out std_logic_vector) is
variable suma,long: natural;
begin
long:=v1'length;
suma:= vector_to_natural(v1) + vector_to_natural(v2);
v_result := natural_to_vector(suma,long);
end vector_add;
end ope_aritmeticas;
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO 3
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE ING. ELECTRONICA
library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all;
use work.ope_aritmeticas.all; -- Para poder utilizar el paquete
entity sum is
port (v1,v2: in std_logic_vector;
v_result : out std_logic_vector);
end sum;
architecture beh of sum is
begin
p1: process(v1, v2)
variable suma: natural;
begin
vector_addu(v1,v2,suma);
v_result<= suma;
end process p1;
end beh;
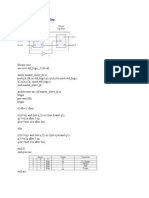
Ejemplo#3: REGISTRO DE 8 BITS
entity biestable is
port (clk, reset, C: in bit;
D: out bit);
end biestable;
architecture arch of biestable is
begin
process(clk, reset)
begin
if reset=1 then D<=0;
elsif (clkevent and clk=1) then D<=C;
end if;
end process;
end arch;
entity registro_8 is
port (clk, reset: in bit; A: in bit_vector(7 downto 0);
B: out bit_vector(7 downto 0));
end registro_8;
architecture estructural of registro_8 is
component biestable
port(clk, reset, c: in bit; d: out bit);
end component biestable;
signal F: bit_vector(7 downto 0);
begin
gen: for i in 0 to 7 generate
u: biestable port map(clk, reset, A(i),F(i));
end generate gen;
B <= F;
end estructural;
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO 4
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE ING. ELECTRONICA
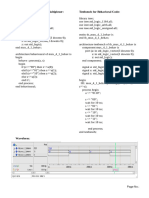
Ejemplo#4: CONTROLADOR DE MOTOR PASO A PASO
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_arith.all;
entity motor is
port(
clk : in std_logic;
en, dir : in std_logic;
a, b, c, d : out std_logic);
end fsmf;
architecture funcional of motor is
type estados is (s1, s2, s3, s4);
signal state : estados;
begin
process (clk)
begin
if (clk'event and clk = '1') then
case state is
when s1 => a <= '1'; b <= '0';
if (en = '0') then
state <= s1;
elsif (dir = '0') then
state <= s2;
else
state <= s4;
end if;
when s2 => a <= '1'; b <= '0';
if (en = '0') then
state <= s2;
elsif (dir = '0') then
state <= s3;
else
state <= s1;
end if;
when s3 => a <= '0'; b <= '1';
if (en = '0') then
state <= s3;
elsif (dir = '0') then
state <= s4;
else
state <= s2;
end if;
when s4 => a <= '0'; b <= '1';
if (en = '0') then
state <= s4;
elsif (dir = '0') then
state <= s1;
else
state <= s3;
end if;
end case;
end if;
end process;
end funcional;
c <= '1'; d <= '0';
c <= '0'; d <= '1';
c <= '0'; d <= '1';
c <= '1'; d <= '0';
You might also like
- VHDL CodeDocument34 pagesVHDL CodeHimanshu Thakur100% (1)
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- VHDL FileDocument25 pagesVHDL Filenitin_280890No ratings yet
- UNIX Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandUNIX Shell Programming Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Digital Lab Cs 6211 VHDL ProgramsDocument13 pagesDigital Lab Cs 6211 VHDL ProgramsMurugan GNo ratings yet
- VHDL ProgramDocument5 pagesVHDL ProgramJaswanth TejaNo ratings yet
- VHDL Programs LabDocument20 pagesVHDL Programs LabVasu SiriNo ratings yet
- Problemas Resueltos de VHDLDocument4 pagesProblemas Resueltos de VHDLVictor Jesus Sanz Flores0% (1)
- Problemas Resueltos de VHDLDocument4 pagesProblemas Resueltos de VHDLVictor Jesus Sanz FloresNo ratings yet
- Final LabDocument25 pagesFinal LabRAMYA VATHSALYA PNo ratings yet
- VHDL Codes For Various Combinational CircuitsDocument6 pagesVHDL Codes For Various Combinational CircuitsKaranNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos Facultad de Ingeniera Electronica Y ElectricaDocument16 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos Facultad de Ingeniera Electronica Y ElectricaEmerson KleemNo ratings yet
- Writing VHDL For RTL Synthesis: 1 StructureDocument9 pagesWriting VHDL For RTL Synthesis: 1 StructuremmalgiNo ratings yet
- V HDL SampleDocument5 pagesV HDL Sampleppat2006No ratings yet
- INFORME PRACTICA No 2Document30 pagesINFORME PRACTICA No 2MAURICIO REYES ROSERONo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: Design Combinational CKT Using Architecture ModelDocument36 pagesUNIT-3: Design Combinational CKT Using Architecture Modelankit_4382No ratings yet
- E Cad Lab ManualDocument51 pagesE Cad Lab ManualRajesh DoradlaNo ratings yet
- VHDLDocument13 pagesVHDLSrijeeta SenNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 AIM: Design A Half Adder ProgramDocument10 pagesExperiment-1 AIM: Design A Half Adder Programjai_007No ratings yet
- MDS I ManualDocument41 pagesMDS I ManualPanku RangareeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: AIM: Design The Following Combinational Circuits Using VHDL and Test The Circuits Using TestDocument83 pagesExperiment No.1: AIM: Design The Following Combinational Circuits Using VHDL and Test The Circuits Using Testdelinquent_abhishekNo ratings yet
- Rogram No: 1 AIM: Write HDL Code To Realize All The Logic GatesDocument32 pagesRogram No: 1 AIM: Write HDL Code To Realize All The Logic GatesPranav LatkarNo ratings yet
- Informe 4Document10 pagesInforme 4terran94No ratings yet
- Unit 3: Combinational Circuit DesignDocument30 pagesUnit 3: Combinational Circuit DesignKarn AroraNo ratings yet
- VHDL From BotrosDocument17 pagesVHDL From BotrossanjanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment-3: Aim: Activity1 Truth TableDocument7 pagesExperiment-3: Aim: Activity1 Truth TableHimanshu Rajan jainNo ratings yet
- VHDL Codes For A 4 Bit Parallel To Serial ConverterDocument9 pagesVHDL Codes For A 4 Bit Parallel To Serial ConverterAshutosh YadavNo ratings yet
- Library IEEEDocument4 pagesLibrary IEEEAdeel HanifNo ratings yet
- Resolved Signals and Generate Statement: Dr. Yann-Hang Lee Yhlee@asu - EduDocument24 pagesResolved Signals and Generate Statement: Dr. Yann-Hang Lee Yhlee@asu - EduChutiyaNo ratings yet
- Cad of Electronics LabDocument4 pagesCad of Electronics LabVaibhav PandeyNo ratings yet
- TP3-VHDL SolutionsDocument3 pagesTP3-VHDL SolutionsfalaNo ratings yet
- Ecad & Vlsi Lab ManualDocument28 pagesEcad & Vlsi Lab ManualSharath Kumar S SNo ratings yet
- Half AdderDocument11 pagesHalf AdderTahsin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Compteur 4 Bits: Exercices de VHDLDocument8 pagesCompteur 4 Bits: Exercices de VHDLHamza BadrNo ratings yet
- VHDL Registers, Buses, Etc: 0Document21 pagesVHDL Registers, Buses, Etc: 0ssfofoNo ratings yet
- Intro Vhdl1Document30 pagesIntro Vhdl1pandaros000No ratings yet
- VLSI Lab Assignment (VHDL) PRITAM PANIGRAHIDocument6 pagesVLSI Lab Assignment (VHDL) PRITAM PANIGRAHISunny TiwaryNo ratings yet
- VHDL Code For D FF Using Behavior ModelDocument20 pagesVHDL Code For D FF Using Behavior ModelAdithya ChakilamNo ratings yet
- Examples 11Document8 pagesExamples 11melwynthomasNo ratings yet
- Ejemplos VHDL Latch: Ieee Ieee STD - LOGIC - 1164Document6 pagesEjemplos VHDL Latch: Ieee Ieee STD - LOGIC - 1164MoriartyNo ratings yet
- Program I: To Simulate and Gate: Digital Circuits and Systems - Ii LabDocument72 pagesProgram I: To Simulate and Gate: Digital Circuits and Systems - Ii LabVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- VHDL TutorialDocument14 pagesVHDL TutorialMohan Kumar SmkNo ratings yet
- VHDL Lab FileDocument48 pagesVHDL Lab FileAnkit Gupta100% (1)
- VHDL TD - CorrigéDocument6 pagesVHDL TD - CorrigéSahsah AbdeslamNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 Mux 4 1Document3 pagesExpt 2 Mux 4 1Steven VazhappullyNo ratings yet
- MemoriaSRAM Chasi GutierrezDocument16 pagesMemoriaSRAM Chasi GutierrezJonathan Chasi0% (1)
- Programme No.10 AIM-To Design A D - Flip Flop CODE - Following Is The VHDL Code For Simulation of D Flip FlopDocument8 pagesProgramme No.10 AIM-To Design A D - Flip Flop CODE - Following Is The VHDL Code For Simulation of D Flip FlopAnkit GoelNo ratings yet
- Dcs-Ii Lab File: - Anupam Sobti 17/EC/09Document19 pagesDcs-Ii Lab File: - Anupam Sobti 17/EC/09Ankit GoelNo ratings yet
- Divisor de Frecuencia en VHDLDocument1 pageDivisor de Frecuencia en VHDLJosé LuisNo ratings yet
- Deber Digitales Nombre: Jossuet Farfan A. Codigo VHDLDocument7 pagesDeber Digitales Nombre: Jossuet Farfan A. Codigo VHDLJossuet GallagherNo ratings yet
- VHDL ManualDocument19 pagesVHDL ManualDr.B.Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Ec-452 VHDL CadDocument39 pagesEc-452 VHDL Cadkishorereddy416No ratings yet
- Vlsi Lab NewDocument28 pagesVlsi Lab NewVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1: Aim: Program of VHDL To Study The Not GateDocument75 pagesExperiment-1: Aim: Program of VHDL To Study The Not GatejaigodaraNo ratings yet
- VHDL Code For Halfadder: - Logic - XorDocument30 pagesVHDL Code For Halfadder: - Logic - XorAnushNo ratings yet
- VHDL ExamplesDocument23 pagesVHDL ExamplestkpradhanNo ratings yet
- BE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertFrom EverandBE EXPERT IN JAVA Part- 2: Learn Java programming and become expertNo ratings yet
- Learn C Programming through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into C ProgramsFrom EverandLearn C Programming through Nursery Rhymes and Fairy Tales: Classic Stories Translated into C ProgramsNo ratings yet