Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2002 Trial
Uploaded by
taylorsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2002 Trial
Uploaded by
taylorsCopyright:
Available Formats
2002
Higher School Certificate
Trial Examination
Total Marks 100
General Instructions
Reading time 5 minutes
Working time 3 hours
Board approved calculators may be
used
Write using black or blue pen
Draw diagrams using pencil
Write your student number and/or
name at the top of every page
Section I
Total marks (75)
This section has two parts, Part A and Part B
Part A
Total marks (15)
Attempt questions 1 15
Allow about 30 minutes for this part
Part B
Total marks (60)
Attempt questions 16 31
Allow about 1 hour 45 minutes for this part
Section II (Pages 15 19)
Total marks (25)
Attempt ONE question from questions 32 36
Allow about 45 minutes for this section
This paper MUST NOT be removed from the examination room
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ..
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Section I
Total marks (75)
Part A
Total marks (15)
Attempt questions 1 15
Allow about 30 minutes for this part
Select the alternative A, B, C or D that best answers the question and indicate your choice
with a cross (X) in the appropriate space on the grid below.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Page 2 of 2
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
1. Mammalian blood needs to be maintained within a specific pH range. pH is the
term used to describe:
(A) the concentration of salt
(B) the acidity of a substance
(C) enzyme substrate concentration
(D) the metabolic rate of an organism
2. The group of organisms which are all Australian native ectotherms is:
(A) kangaroo, kookaburra, echidna
(B) echidna, long necked tortoise, green tree frog
(C) frilled lizard, echidna, kangaroo
(D) long necked tortoise, frilled lizard, green tree fro g
3. Blood in the pulmonary artery compared to blood in the aorta will have:
(A) more oxygen and more carbon dioxide
(B) more oxygen and less carbon dioxide
(C) the same concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide
(D) less oxygen and more carbon dioxide
4. The enzyme in humans that converts maltose to glucose is called maltase. If the
temperature of a system using this enzyme dramatically increases, the most likely
effect will be:
(A) a buffer system will maintain the temperature to allow the enzyme to function
normally
(B) no effect since enzymes are not affected by temperature
(C) the enzyme may denature and not be able to convert maltose to glucose
(D) the increased temperature will increase the rate of glucose production
5. John F. Kennedy, the president of the United States of Americ a, who was
assassinated in 1963, had Addisons Disease. This meant that his adrenal gland did
not secrete enough aldosterone and he needed to have hormone replacement therapy
to regulate:
(A) the levels of carbon dioxide in the blood
(B) his ability to maintain metabolic and physiological responses to his environment
(C) his body temperature
(D) the correct salt levels in the blood
Page 3 of 3
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
6. One side of a DNA strand has the following sequence of bases:
A-T-T-G-C-A
Where A = adenine, T = thymine, G = guanine, C = cytosine and U = uracil.
The complementary base sequence of the DNA molecule would be:
(A) T-A-A-C-G-T
(B) A-T-T-G-C-A
(C) T-U-UC-G-T
(D) U-A-A-C-G-U
7. The process of artificial insemination involves:
(A) placing a fertilised egg cell into the uterus of another member of the same sp ecies
(B) artificially placing semen, containing sperm, from a male into a female of the
same species
(C) artificially placing the nucleus of a sperm cell into an egg cell of the same species
(D) removing the nucleus of an egg cell and replacing it with the nucleus of a sperm
cell from the same species
8. Which of the following would probably NOT cause mutations to occur?
(A) ultra-violet light
(B) chemicals such as thalidomide and Agent Orange
(C) inbreeding of close relatives
(D) radiation emitted from nuclear power plants
9. It is thought that swans evolved to have long necks mainly through:
(A) changes in their physical environment
(B) competition for limited food resources
(C) constant stretching to reach food on the bottom of aquatic environments
(D) changes in their chemical environment
Page 4 of 4
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
10. While experimenting with garden pea plants, Gregor Mendel discovered that the
factor for green seedpods appeared to be dominant over the factor for yellow seedpods. In
one experiment, Mendel bred pea plants and produced 800 seedpods from a cros s
between a heterozygous green seedpod plant and a yellow seedpod plant. His expected
results would have been:
(A) 800 green pods and 0 yellow pods
(B) 600 green pods and 200 yellow pods
(C) 400 green pods and 400 yellow pods
(D) 200 green pods and 600 yellow pods
11. The change in scientific thinking most likely attributed to Macfarlane Burnet is:
(A) certain diseases are transmitted by insect vectors; and these are one of the greatest
reasons for current human disease occurrence
(B) the bodys mechanism for fighting disease relies on cells with receptors for
recognising self
(C) scientific techniques may be used in the understanding and prevention of diseases
caused by microbes
(D) certain diseases of humans are caused by environmental factors only
12. Prions are a unique causative agent of disease in that they:
(A) are acellular
(B) do not respond to antibiotics
(C) are proteins which initiate the immune response
(D) lack nucleic acids
13. Applications of research into high blood pressure by the National Health and Medical
Research Council has halved the number of strokes and reduced the number of heart
attacks. This kind of epidemiological data provides evidence that vascular disease is
partly:
(A) genetic
(B) infectious
(C) avoidable
(D) environmental
Page 5 of 5
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
14. A hospital laboratory technician was examining some culture plates. She noticed a
colony from a strain of relatively harmless gut bacteria called enterococcus growing on a
culture medium containing three different antibiotics. Enterococci are also commonly
found in wounds infected with the dangerous bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (Golden
Staph).
Use your understanding of bacteria and the problem of antibiotic resistance to decide
which of the following statements is most correct.
(A) There is no way of killing this enterococcus bacterium now that it has become
resistant to antibiotics
(B) Even though the enterococcus bacterium is relatively harmless, the laboratory
technician should still report her observation, as genetic information controlling
resistance to these antibiotics could be transferred from enterococcus to diseasecausing bacteria, like Staphylococcus aureus, by transduction or conjugation
(C) The enterococcus bacterium could still cause harm to humans by feeding on these
antibiotics, when they were prescribed by doctors, and so prevent these
antibiotics from protecting against disease-causing bacteria, like Staphylococcus
aureus
(D) If people ingested these enterococcus bacteria with their food, these people would
become resistant to the antibiotics.
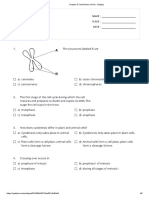
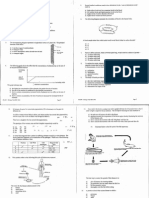
15. A scientist drew the following two graphs for enzyme activity.
Which row in the table below gives possible correct matches for these graphs?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Condition X
Increasing temperature
Increasing substrate concentration
Increasing temperature
Increasing pH
Condition Y
Increasing substrate concentration
Increasing pH
Increasing pH
Increasing temperature
Page 6 of 6
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Section I (continued)
Part B 60 marks
Attempt questions 16 31
Allow about 1 hour and 45 minutes for this part
Answer the questions in the spaces provided.
Marks
Question 16 (4 marks)
Recent media coverage has created some controversy over hormone replacement therapy.
Outline the use of hormone replacement therapy in people who cannot secrete
aldosterone and discuss the importance of this therapy.
4
Question 17 (4 marks)
4
Define the term enantiostasis and discuss its importance to estuarine-living organisms.
Page 7 of 7
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Question 18 (2 marks)
Marks
Identify the forms in which oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the human
circulatory system.
Question 19 (4 marks)
(a) Describe homeostasis.
1
................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................
(b) Explain, using an example, the TWO stages of homeostasis.
3
Question 20 (3 marks)
Explain the requirement for feedback mechanisms in organisms. Illustrate your answer
with a specific example that identifies the relevant stimuli and responses, and any
receptors and effectors involved.
3
Page 8 of 8
....
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Marks
Question 21 (3 marks)
Darwin and Wallace developed the theory of evolution which involves the process of
natural selection and isolation. This includes the processes of both divergent and
convergent evolution.
(a) Give an example of TWO organisms that demonstrate the process of convergent
evolution.
(b) Briefly explain why convergent evolution occurs and identify the result of convergent
evolution.
Question 22 (3 marks)
Name ONE transgenic species that you have studied. Briefly state the process used and
why it was developed.
Please turn over
Page 9 of 9
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Question 23 (6 marks)
Marks
Genetic variation within a species is important for the survival of the species in a
changing environment. The processes of meiosis and sexual reproduction are
instrumental in creating this variation. Name and briefly describe THREE ways variation
is created in the formation of gametes and sexual reproduction.
Question 24 (2 marks)
Alisa bought two genetically identical bottlebrush plants that were produced from
cuttings of the same parent plant. She planted one by itself in the middle of her front yard
and the other next to the fence in her back garden. After two years, she noticed the one in
the front was very bushy and full of foliage all around the plant and the one in the back
garden had leaves and branches growing primarily from one side of the plant. However,
the one in the front yard had leaves that were yellowish in colour and unhealthy looking
while the one in the backyard had good healthy looking green leaves.
Briefly explain how the environment may have affected the expression of the genes
controlling the leaf colour and plant shape.
Page 10 of 10
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Question 25 (3 marks)
Marks
Explain the need to maintain biodiversity and identify TWO current efforts to monitor
biodiversity.
Question 26 (3 marks)
Use an example to outline how the bodys natural microflora prevents disease when an
imbalance occurs.
Question 27 (4 marks)
(a) Describe a method which could be performed in the school laboratory to model
Pasteurs Classic Swan-Neck Flask Experiment to identify the role of microbes in decay.
(Use diagrams if it helps to describe the method)
3
(b) State the hypothesis being investigated in (a) above.
Page 11 of 11
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Question 28 (4 marks)
Marks
Two alternative methods of immunisation against measles involve injecting:
(i)
antigens of the pathogen
OR
(ii)
vaccine containing antibodies separated from human blood serum.
Assess the effectiveness of each method of immunisation.
4
Question 29 (5 marks)
2
(a) For a NAMED human disease identify the pathogen and its insect vector.
(b) Draw a simple diagram of the life cycle of the pathogen. Identify where prevention OR
control of the disease would be most effective.
Question 30 (4 marks)
The bodys Third Line of Defence can provide immunity against certain diseases.
4
Describe and explain this statement in terms of cells and cell products.
Page 12 of 12
....
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Marks
Question 31 (6 marks)
During your Biology course, you performed first-hand investigations using the light
microscope.
Assume that you are given a prepared human blood cells microscope slide.
(a) Explain the methods you would use to observe thi s slide under high power of your
microscope.
(b) Draw scaled diagrams to demonstrate the difference between red and white blood
cells, in terms of size and shape.
End of Section 1
Please turn over
Page 13 of 13
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Section II
25 marks
Attempt ONE question from Questions 32 36
Allow about 45 minutes for this section
Answer the question in a writing booklet. Extra writing booklets are available.
Question 32 Communication ................................ .............................. 15
*Questions for other option topics are available upon request. Email: andy@invertigo.com.au
Page 14 of 14
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Question 32 Communication (25 marks)
Marks
(a)
(i) What is the function of the iris in the eye?
(ii) State the name of the light sensitive pigment in rods in the human eye and also the
colours to which the pigment is most sensitive.
(b)
(i) What information would you need about the distribution of rods and cones in the eyes
of animals to predict which animals are active at night?
(ii) Compare the visual acuity of a human with that of most insects.
(c) Distinguish between myopia and hyperopia and describe technologies that can be
used to correct these conditions.
(d) The diagram below shows part of the human ear.
Outline the path of a sound wave through the external, middle and inner ear and identify
and justify which parts are most likely to be affected by chronic exposure to sounds of
different frequencies.
(e)
3
(i)
Explain the cause of colour blindness in humans.
(ii)
Describe cataracts and how this condition can be corrected using technology.
(iii)
Identify the types of energy transfer occurring in a conventional hearing aid.
End of Question 32.
Page 15 of 15
3
1
STUDENT NUMBER/NAME: ............
Page 16 of 16
You might also like
- 2009 HSC Exam BiologyDocument34 pages2009 HSC Exam Biologyeducator56100% (1)
- 2006 CSSA Biology TrialsDocument32 pages2006 CSSA Biology TrialsMickey NgoNo ratings yet
- Biology Trial 2020 Exam Choice-2Document37 pagesBiology Trial 2020 Exam Choice-2No.2 EijiNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Questions ARC 2006Document28 pagesBiology HSC Questions ARC 2006timeflies23No ratings yet
- Properties of Life: Biology Is The Science That Studies Life. What Exactly Is Life? This May Sound Like A SillyDocument27 pagesProperties of Life: Biology Is The Science That Studies Life. What Exactly Is Life? This May Sound Like A SillySandra Nicole RiveraNo ratings yet
- Biocomp Exam 1998Document15 pagesBiocomp Exam 1998Архи́пNo ratings yet
- Bio 8.2Document10 pagesBio 8.2zwindows123456789No ratings yet
- 2019 Australian Science Olympiad Exam: BiologyDocument28 pages2019 Australian Science Olympiad Exam: BiologyYinyin ZhuNo ratings yet
- A Local EcosystemDocument26 pagesA Local EcosystemsandnifflerNo ratings yet
- Seba BiologyDocument114 pagesSeba BiologymwansaNo ratings yet
- Cells Cell Transport - TeachersDocument13 pagesCells Cell Transport - TeachersNickNo ratings yet
- Uneb 2009 Biology TheoryDocument103 pagesUneb 2009 Biology TheoryBASOGA DAVIDNo ratings yet
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Document73 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Bikash Ranjan RayNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document19 pagesCH 06cyberyeung0% (1)
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010Document10 pagesAP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010yulianaholicNo ratings yet
- Chs Alarm ScaffoldDocument1 pageChs Alarm ScaffoldGREG.THWAITESNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Science Topic B1.1 Classification, Variation and Inheritance Test 13 - 14Document10 pagesEdexcel GCSE Science Topic B1.1 Classification, Variation and Inheritance Test 13 - 14Paul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Sri Lankan Biology Olympiad Model Questions 2009: InstructionsDocument6 pagesSri Lankan Biology Olympiad Model Questions 2009: InstructionsScience Olympiad BlogNo ratings yet
- A Local Ecosystem Topic TestDocument7 pagesA Local Ecosystem Topic TestJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Organization of The CellDocument15 pagesChapter 4-Organization of The CellKevin Ang100% (1)
- Cosmos Magazine, Issue 94 (March 2022)Document116 pagesCosmos Magazine, Issue 94 (March 2022)NajaNo ratings yet
- Oten BiologyDocument798 pagesOten BiologyZarinaNo ratings yet
- Sri Lankan Biology Olympiad 2011Document7 pagesSri Lankan Biology Olympiad 2011Science Olympiad Blog100% (1)
- HSC Biology 2012 Half Yearly ExamDocument25 pagesHSC Biology 2012 Half Yearly ExamRiemann100% (3)
- Biology: Pearson Edexcel GCEDocument8 pagesBiology: Pearson Edexcel GCEyat yat szeNo ratings yet
- 1999 AP Biology TestDocument25 pages1999 AP Biology TestTalal NabulsiNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Key Stages and ProcessesDocument8 pagesCell Division: Key Stages and ProcessesCarin TanNo ratings yet
- AQA Practical Handbook FinalDocument35 pagesAQA Practical Handbook FinaljannyankiriNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology Mock Exam 1B_Dec 2018_MARKSCHEMEDocument11 pagesYear 11 Biology Mock Exam 1B_Dec 2018_MARKSCHEMEtechang1No ratings yet
- VCE Biology 2019 Exam SolutionsDocument11 pagesVCE Biology 2019 Exam SolutionsMy Name is JeffNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Biology Test 2 Membrane StructureDocument4 pagesYear 12 Biology Test 2 Membrane StructureKome AgeinNo ratings yet
- IB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterDocument13 pagesIB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterweeNo ratings yet
- A Level H2 Biology SyllabusDocument27 pagesA Level H2 Biology SyllabusTerry YauNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2003 Biology Prelim YearlyDocument19 pagesJames Ruse 2003 Biology Prelim YearlyDogNo ratings yet
- VCE 2 WorksheetsDocument38 pagesVCE 2 WorksheetsneetiNo ratings yet
- Science Illustrated Australia - February 2017Document84 pagesScience Illustrated Australia - February 2017Anthony Mello100% (1)
- HSC Chemistry 2009 exam paperDocument32 pagesHSC Chemistry 2009 exam paperomhreemaimhreemNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument13 pagesFood TestsBilal Shahid100% (1)
- Chapter 5 ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Problemswalt richards0% (1)
- 2014 SpringEvoExam2Document4 pages2014 SpringEvoExam2Emi PhillipsNo ratings yet
- 2012 OpenExam AnsKeyDocument11 pages2012 OpenExam AnsKeymartynapetNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologyTallyNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Syllabus-NewDocument20 pagesIb Biology Syllabus-NewVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- HKCE BioDocument289 pagesHKCE BioKaito Magic100% (1)
- Ecology Revision QuestionsDocument3 pagesEcology Revision QuestionsMadeleine Agius100% (1)
- Indian National Biology Olympiad 2015Document50 pagesIndian National Biology Olympiad 2015Science Olympiad BlogNo ratings yet
- The Transport System IB Qq'sDocument12 pagesThe Transport System IB Qq'sJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Formative assessment on inheritance in goatsDocument4 pagesFormative assessment on inheritance in goatsTarshihiNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: July 2016 Biology: Section - I (Botany)Document3 pagesBoard Question Paper: July 2016 Biology: Section - I (Botany)Rohit GhereNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Grade 11 BiologyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Grade 11 BiologyEva100% (1)
- NQE 2007 Biology SolutionsDocument2 pagesNQE 2007 Biology SolutionsmartynapetNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationDocument25 pagesHeredity and VariationDre ParkerNo ratings yet
- 083 - Chromatography and Its Uses in BiologyDocument3 pages083 - Chromatography and Its Uses in Biologylastjoe71No ratings yet
- Module: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument30 pagesModule: Cell Structure and FunctionJohn Daniel Paulino GumbanNo ratings yet
- James Ruse Agricultural High School HSC Biology Ass. Task 2 Term 1 2006Document3 pagesJames Ruse Agricultural High School HSC Biology Ass. Task 2 Term 1 2006taylorsNo ratings yet
- 2002 James Ruse Term 4Document7 pages2002 James Ruse Term 4Tasnova ShafiNo ratings yet
- 12 SC Eggs Trial 2004Document25 pages12 SC Eggs Trial 2004Tasnova ShafiNo ratings yet
- 2002 Barker TrialDocument25 pages2002 Barker Trialtimeflies23No ratings yet
- 2001 James Ruse TrialDocument6 pages2001 James Ruse TrialtaylorsNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification Ort From ChickenDocument14 pagesIsolation and Identification Ort From Chickenthanh ba matNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Abattoir DepartmentDocument37 pagesVeterinary Abattoir DepartmentToyahabi NyunyutabisNo ratings yet
- Pearl Culture LectureDocument28 pagesPearl Culture LectureMahesh GKNo ratings yet
- Portal Vein - WikipediaDocument23 pagesPortal Vein - WikipediaNaqeeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Optra GateDocument48 pagesOptra Gateadam adamekNo ratings yet
- Here are the answers to the multiple choice questions in English:1. B2. D 3. A4. D5. B6. A7. D8. B 9. A10. D11. B12. B13. BDocument15 pagesHere are the answers to the multiple choice questions in English:1. B2. D 3. A4. D5. B6. A7. D8. B 9. A10. D11. B12. B13. BJean Ysrael MarquezNo ratings yet
- GST English6 2021 2022Document13 pagesGST English6 2021 2022Mariz Bernal HumarangNo ratings yet
- GRADE VI Science Baseline TestDocument4 pagesGRADE VI Science Baseline TestanthfranzNo ratings yet
- Wolf Island: Story VocabularyDocument2 pagesWolf Island: Story VocabularyNAJLAA ALENEZINo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition by RizzoDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition by Rizzoa475993205No ratings yet
- Department of Pedodontics: Submitted By: Shayoni Sen Bds Ivth YearDocument29 pagesDepartment of Pedodontics: Submitted By: Shayoni Sen Bds Ivth YearFarzana ShereenNo ratings yet
- Crochet Giraffe Amigurumi PDF PatternDocument8 pagesCrochet Giraffe Amigurumi PDF PatternBlumenNo ratings yet
- Skrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument6 pagesSkrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaYulia FondaNo ratings yet
- Sexual DictionaryDocument47 pagesSexual DictionaryYigit DemirelNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesBlood Circulatory SystemSyeda Fizza Abbas AlnaqawiNo ratings yet
- MER-KA-BA MeditationDocument10 pagesMER-KA-BA MeditationmutationxNo ratings yet
- Reincarnation Blues - 50 Page FridayDocument58 pagesReincarnation Blues - 50 Page FridayRandom House Publishing Group100% (2)
- Deep Magic II - Rune MagicDocument24 pagesDeep Magic II - Rune MagicWhiskey100% (1)
- Science 6 q2 Lamp v3Document8 pagesScience 6 q2 Lamp v3marvin susminaNo ratings yet
- OFFICE LISTDocument186 pagesOFFICE LISTBhuvaneswariNo ratings yet
- The Physical Self: The Human Body Is The Best Work of Art. ' - Jess C. ScottDocument15 pagesThe Physical Self: The Human Body Is The Best Work of Art. ' - Jess C. ScottJaycee TualaNo ratings yet
- Bcspca Factsheet Life of An Egg Laying Hen PDFDocument2 pagesBcspca Factsheet Life of An Egg Laying Hen PDFAnonymous 2OMEDZeqCDNo ratings yet
- Iodine - The Universal and Holistic Super Mineral - Dr. Gabriel CousensDocument32 pagesIodine - The Universal and Holistic Super Mineral - Dr. Gabriel CousensJ.J.100% (7)
- Monkey Puzzle Story Class 1 Vocabulary LessonDocument2 pagesMonkey Puzzle Story Class 1 Vocabulary LessonАнжела КашафутдиноваNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument119 pagesThe Reproductive SystemAshis karmakar100% (10)
- Unit 2BDocument4 pagesUnit 2BGiang Nguyen Thi ThuNo ratings yet
- A Most Potent Brew PDFDocument4 pagesA Most Potent Brew PDFSpawnOf Larry100% (4)
- Inp Eval ExamDocument3 pagesInp Eval Examd1choosenNo ratings yet
- Kelas 9 UasDocument7 pagesKelas 9 UasAsep BambangNo ratings yet
- DINAS PENDIDIKAN DAN KEBUDAYAAN KOTA TANGERANG UPT KECAMATAN PERIUK PENILAIAN AKHIR SEMESTER SEMESTER GANJIL TAHUN PELAJARAN 2019 – 2020 BAHASA INGGRISDocument4 pagesDINAS PENDIDIKAN DAN KEBUDAYAAN KOTA TANGERANG UPT KECAMATAN PERIUK PENILAIAN AKHIR SEMESTER SEMESTER GANJIL TAHUN PELAJARAN 2019 – 2020 BAHASA INGGRISNungki MaharaniNo ratings yet