Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care for Pontine Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Kate CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care for Pontine Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Kate CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
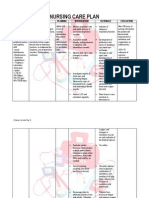
Cues and Clues
Objective:
1 Quadriplegia
2 Altered
consciousness
3 Slurring of speech
4 Weakness
of
shoulders
when
tested for Cranial
Nerve 11
5 Slight restlessness
6 O2 Saturation 94%
7 Vital Signs:
Blood Pressure
130/80 mmHg
Respiratory Rate
12 RPM
Nursing
Diagnosis
Altered
cerebral
tissue
perfusion due
to pontine
hemorrhage
secondary to
hypertension
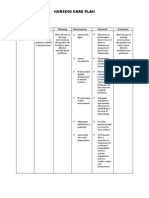
Nursing Care Plan for INEFFECTIVE CEREBRAL TISSUE PERFUSION
Goals and
Analysis
Interventions
Objectives
Blood is a connective Goal:
1 Monitor and
1
tissue composed of a effective
document
liquid extracellular matrix cerebral tissue
neurological status
called blood plasma that perfusion
frequently
dissolves and suspends
various cells and cell Within 7 hours
2 Monitor vital signs
2
fragments.
Blood of rendering
frequently, especially
transports oxygen from the therapeutic
heart rate, presence of
lungs and nutrients from nursing care, the
murmurs, pupils, and
the gastrointestinal tract. patient will:
respirations
The oxygen and nutrients have
subsequently diffuse from
3 Position client with
improvement
the
blood
into
the
head slightly elevated 3
in terms of
interstitial fluid and then
and in neutral
movement
into the body cells. Carbon have increased
position
dioxide and other wastes
O2 saturation
move in the reverse blood pressure
direction, from body cells
4 Instruct to prevent
of at least
to interstitial fluid to
straining at stool or
4
120/80
blood.
Blood
then
holding of breath.
have improved
transports the wastes to
cerebral tissue
various organsthe lungs,
perfusion
kidneys, and skinfor
5 Maintain bedrest,
elimination form the body.
provide quiet
5
Circulating blood helps
environment and
maintain homeostasis of
restrict visitors and
all
body fluids.
In
activities.
addition, blood osmotic
pressure influences the
6 Raise the beds
6
water content of cells,
siderails, and offer to
mainly
through
provide assistance
interactions of dissolved
when moving and/or
ions
and
proteins.
ambulating
However, a condition such
as renal failure causes
7 Provide interventions 7
alterations
in
tissue
that help with
perfusion,
particularly
relaxation, such as
reduction in arterial blood
guided imagery
flow that leads to deprived
Rationale
Evaluation
Determines current
need and enables
immediate response
when required
These are good
indicators of brain
function;
Irregularities signal
further
damage/problems.
Reduces arterial
pressure by
promoting venous
drainage and may
improve circulation
Goals were met,
therefore
nursing care
should be
continued.
Valsalva maneuver
increases intracranial
pressure and
increases risk for
further bleeding.
Prevents increase in
ICP and helps prevent
recurrence of stroke.
Provides safety to the
client
May help prevent
increases in ICP and
promote relaxation,
which prevents stress
After 7 hours of
rendering
therapeutic
nursing care, the
patient :
have
improvement
in terms of
movement
have increased
O2 saturation
blood pressure
of at least
120/80
had improved
cerebral tissue
perfusion
nutrition and oxygenation
at the cellular level.
Decreased tissue perfusion
can be transient with few
or minimal consequences
to the health of the patient.
If the decreased perfusion
is acute and protracted, it
can
have
devastating
effects on the patient.
Diminished cerebral tissue
perfusion may result in
further brain damage or
death if not responded to
immediately.
Encourage DBCE
and reposition
frequently.
Administer
supplemental oxygen
as needed
10 Administer
medications as
needed
11 Have an accurate
intake-output count
and monitor
laboratory studies,
especially PTT and
aPTT
Promotes
oxygenation and
prevents
complications
associated with
decreased brain tissue
perfusion
9 Promotes
oxygenation and
healing of the
cerebral tissue
10 Medications may be
needed together with
other interventions to
promote faster
healing and prevent
complications
11 Provides information
about the
effectiveness of the
drugs used to treat
the condition
You might also like
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- NCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisDocument142 pagesNCM 106 Acute Biologic CrisisEllamae Chua88% (8)
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Tissue PerfusionDocument16 pagesAlterations in Tissue PerfusionPatricia CaladoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Document9 pagesCardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Prince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Document9 pagesCardiovascular System Diseases Part 2Prince Rener Velasco PeraNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctionDocument63 pagesCritical Care Nursing Guide to Shock and Multi-Organ DysfunctiontikoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- ShockDocument1 pageShockmilayosoresNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Hypovolemic Shock Nursing Care Management and Study GuideDocument1 pageHypovolemic Shock Nursing Care Management and Study GuideRoselyn VelascoNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Case Study NCM 118' With YouDocument6 pagesI Am Sharing 'Case Study NCM 118' With YouQusai BassamNo ratings yet
- Nursing Study GuideDocument21 pagesNursing Study GuideYanahNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Presentation CvaDocument82 pagesCase Analysis Presentation CvaVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journaling 1Document12 pagesReflective Journaling 1Nosheen ShahNo ratings yet
- Cardiac FailureDocument63 pagesCardiac FailureNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument3 pagesAssessment: Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDelaine Mae MierNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis: Kidney Failure and Fluid Volume ExcessDocument74 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Kidney Failure and Fluid Volume ExcessSheela Khrystyn LeeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Case PresDocument6 pagesCase PresCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDocument15 pagesObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18No ratings yet
- Heart Failure NCPDocument9 pagesHeart Failure NCPMiriam EstradaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document2 pagesNCP 1faitheeeNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Idol L. Bondoc, M.D.,R.NDocument58 pagesLecturer: Idol L. Bondoc, M.D.,R.NidolbondocNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis92% (13)
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument16 pagesHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output RM 7Document9 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output RM 7api-283470660No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing - NeuroDocument19 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - NeuroChristian EstevesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarNo ratings yet
- NCP FORM For TetralogyDocument3 pagesNCP FORM For TetralogyGraceMelendres100% (3)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusioniammkrissa33% (3)
- SHOCKDocument17 pagesSHOCKChithra Saju100% (1)
- Ru For CVD BleesDocument30 pagesRu For CVD BleesKaye LeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJhevilin RM100% (1)
- Guidelines for Congestive Heart FailureDocument9 pagesGuidelines for Congestive Heart FailureAldo FerlyNo ratings yet
- Care of Client with CVA and Hypertension (Less than 40 charsDocument75 pagesCare of Client with CVA and Hypertension (Less than 40 charsVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemic Shock 09Document58 pagesHypovolemic Shock 09Joanne Bernadette Aguilar100% (2)
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument9 pagesAcute Coronary Syndromekimchi girlNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HF FinalDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan HF FinalCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Care PlanDocument6 pagesHeart Failure Care PlanOlivia Winkler StuartNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument25 pagesShockAvneet Maan100% (1)
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDocument14 pagesAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeeNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN for 8yo Male with CHDDocument5 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN for 8yo Male with CHDDonna Co IgNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Case StudyDocument8 pagesHeart Failure Case StudyDavid PayosNo ratings yet
- End-Stage Heart Disease Management and Palliative Care GuidelinesDocument44 pagesEnd-Stage Heart Disease Management and Palliative Care GuidelinesCyrille AgnesNo ratings yet
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionStephanie Louisse Gallega Hisole100% (2)
- MaeDocument9 pagesMaeCharmaigne Mae Padilla Sotelo100% (1)
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument2 pagesCardiogenic ShockChristine QuironaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in Patient With Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaDocument5 pagesNursing Care in Patient With Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary EdemaAyyu Sandhi100% (1)
- CHF Pathophys PaperDocument8 pagesCHF Pathophys PaperSarah SNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorder Case StudyDocument21 pagesRenal Disorder Case StudyXuehua GuanNo ratings yet
- By: Calaour, Carrey Dasco, Danica Amor Dimatulac, Kevin Lim, Shiela Marie Pagulayan, Sheena May Pua, Mar KristineDocument41 pagesBy: Calaour, Carrey Dasco, Danica Amor Dimatulac, Kevin Lim, Shiela Marie Pagulayan, Sheena May Pua, Mar Kristineceudmd3d100% (2)
- Case 1a Answer KeyDocument4 pagesCase 1a Answer KeyChettan Kerala100% (1)
- Case Study 9Document7 pagesCase Study 9Lindsay WishmierNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Internal Medicine Ali SaifDocument5 pagesTopic 10 Internal Medicine Ali SaifAnkit Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Should Blood Cultures Be Performed For Patients With Acute Prostatitis?Document4 pagesShould Blood Cultures Be Performed For Patients With Acute Prostatitis?Kate CruzNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors: Predisposing Factors:: Non-ModifiableDocument2 pagesPrecipitating Factors: Predisposing Factors:: Non-ModifiableKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Review ArticleDocument10 pagesReview ArticleKate CruzNo ratings yet
- 0084 03 PDFDocument23 pages0084 03 PDFKate CruzNo ratings yet
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Types of Seizures - Generalized vs PartialDocument1 pageTypes of Seizures - Generalized vs PartialKate CruzNo ratings yet
- D CAdfghjklDocument2 pagesD CAdfghjklKate CruzNo ratings yet
- 0084 03 PDFDocument23 pages0084 03 PDFKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Molecular Methods For Diagnosis of Viral Encephalitis: Roberta L. Debiasi and Kenneth L. TylerDocument23 pagesMolecular Methods For Diagnosis of Viral Encephalitis: Roberta L. Debiasi and Kenneth L. TylerKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Pag-Iwas Sa Pulmonya, Ating Kayang-Kaya!: Ust-SnDocument2 pagesPag-Iwas Sa Pulmonya, Ating Kayang-Kaya!: Ust-SnKate CruzNo ratings yet
- SDFGHJDocument1 pageSDFGHJKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Non Marital RelationshipDocument8 pagesNon Marital RelationshipKate CruzNo ratings yet
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- ART TherapyDocument3 pagesART TherapyKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial PartialsdffghbjnkmlDocument1 pagePsychosocial PartialsdffghbjnkmlKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Biblio Lung CancerDocument4 pagesBiblio Lung CancerKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Trust Vs MistrustDocument1 pageTrust Vs MistrustKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Biblio Lung CancerDocument4 pagesBiblio Lung CancerKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Family Coping Index AssessmentDocument2 pagesFamily Coping Index AssessmentKate CruzNo ratings yet
- E CIGDocument2 pagesE CIGKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Cardio RespiDocument57 pagesCardio RespiKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Role in Wellness: Nutrition For Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases Physical Health DimensionDocument8 pagesRole in Wellness: Nutrition For Cardiovascular and Respiratory Diseases Physical Health DimensionKate CruzNo ratings yet
- Viruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023Document27 pagesViruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023nazNo ratings yet
- Primary HyperparathyroidismDocument5 pagesPrimary HyperparathyroidismAbdul QuyyumNo ratings yet
- Clinician-rated Depression Scale Assesses SeverityDocument2 pagesClinician-rated Depression Scale Assesses SeverityRian Candra Ibrahim100% (1)
- Inner EngineeringDocument6 pagesInner Engineeringsuryasak427255% (11)
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesDocument3 pagesArterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesNayem Hossain HemuNo ratings yet
- 11 Best Herbs For Astral Projection - Insight StateDocument2 pages11 Best Herbs For Astral Projection - Insight Stateiamthe100% (1)
- Checkedterms 1Document29 pagesCheckedterms 1api-267016167No ratings yet
- Asbestos Controls and RegulationsDocument66 pagesAsbestos Controls and RegulationsvdiazsuarezNo ratings yet
- Schizoid Personality DisorderDocument9 pagesSchizoid Personality DisorderinsildaNo ratings yet
- Rare Disease Day QuizDocument2 pagesRare Disease Day QuizALD_LifeNo ratings yet
- HIV Structure and Life CycleDocument4 pagesHIV Structure and Life CycleNau MaanNo ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument63 pagesSpirometryAries DocNo ratings yet
- 2016 Pediatric HydrocephalusDocument15 pages2016 Pediatric HydrocephalusYudit Arenita100% (1)
- Day Care Centre: Benefits of Ambulatory SurgeryDocument17 pagesDay Care Centre: Benefits of Ambulatory SurgeryAnonymous ibmeej9No ratings yet
- Hypnotic Suggestibility and Its NatureDocument21 pagesHypnotic Suggestibility and Its NatureRaluka RalucaNo ratings yet
- ICT Project: "Curbing Malnutrition Among Filipino Children"Document7 pagesICT Project: "Curbing Malnutrition Among Filipino Children"Janea ArinyaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Dietary Patterns and Nutritional Knowledge With The Nutritional Status of Bajo Tribe Pregnant Women in Duruka District, Muna RegencyDocument5 pagesThe Relationship Between Dietary Patterns and Nutritional Knowledge With The Nutritional Status of Bajo Tribe Pregnant Women in Duruka District, Muna RegencytreesNo ratings yet
- AP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Document22 pagesAP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Jorge MarroneNo ratings yet
- Healthy Gut SummitDocument1 pageHealthy Gut Summitgreym111No ratings yet
- Chapter 004Document10 pagesChapter 004Erika Midkiff100% (2)
- IMI RANO Critieria Booklet Nov 2011Document18 pagesIMI RANO Critieria Booklet Nov 2011johnthomas75No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Exercises GHIJKPDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Exercises GHIJKPAry OrtizNo ratings yet
- Post Test NUR 219Document3 pagesPost Test NUR 219Naomi VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- IndianJPsychiatry618254-624277 172027Document16 pagesIndianJPsychiatry618254-624277 172027Fatma BakrNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis ADocument1 pageHepatitis AGary Detman100% (1)
- Assessment of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument13 pagesAssessment of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusBaso AgusofyangNo ratings yet
- Hovaguimian DysautonomiaDocument21 pagesHovaguimian DysautonomiaAnonymous tG35SYROzENo ratings yet
- Midterm Last TopicDocument3 pagesMidterm Last TopicLynette BalodNo ratings yet
- Cie 10 TotalDocument682 pagesCie 10 TotalGLADYS BAONo ratings yet