Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elastomeric Bearing - 15m Span
Uploaded by
mnsawantCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastomeric Bearing - 15m Span
Uploaded by
mnsawantCopyright:
Available Formats
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
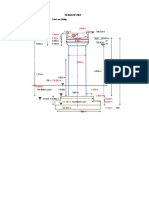
DESIGN OF ELASTOMERIC BEARING
The bridge is having simply support span. each support has three no. of elastomeric bearings.
CALCULATION OF BEARING LOADS
Normal Case
Max. Reaction on a bearing
(Refer STAAD output)
Due to DL of RCC girder and slab (from design calc.) =
Due to Diaphragm =
Due to SIDL =
Total DL + SIDL =
On outer Bearing
On inner Bearing
25.00
0.92
25.92
9.67
35.59
t
t
t
t
t
25.00
3.06
28.06
0.54
28.60
t
t
t
t
t
Due to Live load (impact -1.1) =
Max.
Min.
37.99
-1.20
t
t
52.89
-0.35
t
t
Total Maximum load =
Total Minimum load =
Max.
Min.
73.58
34.39
t
t
81.49
28.25
t
t
Calculation of horizontal forces :-Horizontal force from superstructure
3 Nos. elastomeric bearings are proposed on each support.
Braking force =
(100 x 0.2 )
20.00
10.00
Total Horizontal force transferred from superstructure =
20.00 / 2
This force is resisted by three bearing provided at each end
Thus longitudinal force on each bearing =
10.00
3.33 t
0.075
( Hor. seismic coeff.)
5.99
Seismic Transverse Case
h
Seismic force on Dead load =
5.99
t,
say
Its lever arm above bearing level =
1.01
m (approx.)
Thus moment at bearing level =
5.99
1.01
6.02
Tm
Seismic force on SIDL =
19.88
0.075
1.49
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
Its lever arm above bearing level =
1.80
Thus moment at bearing level =
1.49
1.80
2.68
Tm
Total live load reaction at support=
67.0
Seismic force on LL (50%)
33.5
0.075
2.51
Its lever arm above bearing level =
2.765
Thus moment at bearing level =
2.51
6.95
Tm
10.00
2.77
Total transverse force =
This force is resisted by three bearing provided at each end
Thus transverse force on each bearing =
10.00
Total transverse moment =
x ^2 =
x ( 2.90^2 + 0^2 )
15.65
Tm
3.33 t
16.82 m^2
Hence, Vertical load on inner bearing =
15.65
0.000
= (+/-) 0.00
Hence, Vertical load on outer bearing =
15.65
0.172
= (+/-) 2.70
Thus,
Maximum load on outer bearing (50% LL) =
25.92 +
9.67
+ 19.00 +
2.70
57.29
Minimum load on outer bearing =
25.92 +
9.67
-0.60
-2.70
32.29
+ 26.44 +
0.00
55.04
0.00
28.42
Maximum load on inner bearing
28.06 +
0.54
Minimum load on inner bearing =
28.06 +
0.54
-0.18
The design vertical load (minimum) =
28.42
t (Governing)
10.00
Horizontal force from superstructure
3 Nos. elastomeric bearings are proposed on each support.
Braking force (50%) =(100 x 0.2) x 0.5 =
Total Horizontal force transferred from superstructure =
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
10.00 / 2
5.00
+ 19.00
54.59
-0.60
34.99
+ 26.44
55.04
-0.18
28.42
This force is resisted by three bearing provided at each end
Thus longitudinal force on each bearing =
5.00
1.67 t
Seismic Longitudinal Case
Maximum load on outer bearing
25.9 +
9.67
Minimum load on outer bearing =
25.92 +
9.67
Maximum load on inner bearing
28.06 +
0.54
Minimum load on inner bearing =
28.06 +
0.54
The design vertical load (minimum) =
28.42
t (Governing)
7.48
10.00
12.48
Horizontal force from superstructure (seismic)
Horizontal force Dead load and SIDL(seismic) =
5.99
1.49
Braking force (50%) =(100 x 0.2)x0.5
Total Horizontal force transferred from superstructure =
7.48
10.0
/ 2
This force is resisted by three bearing provided at each end
Thus longitudinal force on each bearing =
12.48
4.16 t
Movement at bearing (@ 0.5 x 10^-3 )
=
0.5 x 10^-3 x 14.0 x 10^3 x0.5
3.50
mm
Rotation as per clause :916.3.5 IRC:83(part-II)
Dead Load rotation
Mmax
d
=
Grade of concrete
400 Mmax L /(Ec I )
=
83.78
t-m
=
10^-3
rad
(refer design calculations of superstructure)
M 30
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
5000x
fck
2791654 t/m2
Moment of inertia
x
x
83.78
2791654
t-m
(refer design calculations of superstructure)
400
0.5
0.2882 (refer design of superstructure)
x
14.000 x
x
0.2882
0.001
0.001166 rad
Live Load rotation
Mmax
149.41
0.00104
Total rotation
0.0011663
###
0.0022 rad
NOTE NO. DN-18
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
STAAD SPACE ANALYSIS OF SUPERSTRUCTURE FOR SIDL
INPUT WIDTH 79
UNIT MTON METRE
*
JOINT COORDINATE
*
101 0.0 0.0 0.000 109 14.0 0.0 0.000
201 0.0 0.0 1.450 209 14.0 0.0 1.450
301 0.0 0.0 4.350 309 14.0 0.0 4.350
401 0.0 0.0 7.250 409 14.0 0.0 7.250
501 0.0 0.0 8.700 509 14.0 0.0 8.700
*
701 0.0 0.0 0.725 709 14.0 0.0 0.725
801 0.0 0.0 2.900 809 14.0 0.0 2.900
901 0.0 0.0 5.800 909 14.0 0.0 5.800
1001 0.0 0.0 7.975 1009 14.0 0.0 7.975
*
110 -0.50 0.0 0.00; 111 14.50 0.0 0.0
210 -0.50 0.0 1.450; 211 14.50 0.0 1.450
310 -0.50 0.0 4.350; 311 14.50 0.0 4.350
410 -0.50 0.0 7.250; 411 14.50 0.0 7.250
510 -0.50 0.0 8.700; 511 14.50 0.0 8.700
*
710 -0.50 0.0 0.725; 711 14.50 0.0 0.725
810 -0.50 0.0 2.900; 811 14.50 0.0 2.900
910 -0.50 0.0 5.800; 911 14.50 0.0 5.800
1010 -0.50 0.0 7.975; 1011 14.50 0.0 7.975
*
MEM INCIDENCE
101 101 102 108
201 201 202 208
301 301 302 308
401 401 402 408
501 501 502 508
*
701 701 702 708
801 801 802 808
901 901 902 908
1001 1001 1002 1008
*
109 110 101; 110 109 111
209 210 201; 210 209 211
309 310 301; 310 309 311
409 410 401; 410 409 411
509 510 501; 510 509 511
*
709 710 701; 710 709 711
809 810 801; 810 809 811
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
77.
78.
79.
80.
81.
82.
83.
84.
85.
86.
87.
88.
89.
90.
91.
92.
93.
94.
95.
96.
SHEET NO.
909 910 901; 910 909 911
1009 1010 1001; 1010 1009 1011
*
2101 101 701 2109
2201 201 801 2209
2301 301 901 2309
2401 401 1001 2409
*
3101 701 201 3109
3201 801 301 3209
3301 901 401 3309
3401 1001 501 3409
*
MEMBER PROPERTIES
*DUMMY MEMBER
101 TO 110 501 TO 510 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
701 TO 710 801 TO 810 901 TO 910 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
1001 TO 1010 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
209 210 309 310 409 410 PRI YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
*
301 TO 308 401 TO 408 201 TO 208 PRIS AX 1.3645 IX 1E-10 IY .4673 IZ .2882
* DIAPHRAGM
2201 TO 2301 BY 100 2209 TO 2309 BY 100 3201 TO 3301 BY 100 3209 TO 3309 BY 100 PRIS AX 0.52932 IX 1E-10 IY 0.01429 IZ 0.05910
2101 2401 2109 2409 3101 3401 3109 3409 PRIS AX 0.17732 IX 1E-10 IY 0.009599 IZ 0.000715
* SLAB
2102 TO 2108 2202 TO 2208 2302 TO 2308 2402 TO 2408 3102 TO 3108 3202 TO 3208 3302 TO 3308 3402 TO 3408 PRIS AX 0.3850 IX 1E-10 IY 0.09826 IZ 0.001553
*
SUPPORTS
201 301 401 PINNED
209 309 409 FIXED BUT FX FZ MX MY MZ
*
CONSTANTS
E 3.0E6
DEN 2.4
*
LOAD 1 SIDL
MEMBER LOAD
***WEARING COAT
*
0.2*(2.9/2+1.225) = 0.535 T/M
*
0.2*2.9 = 0.58 T/M
201 TO 210 401 TO 410 UNI GY -0.535
301 TO 310 UNI GY -0.58
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
97.
98.
99.
100.
101.
102.
103.
104.
105.
119.
120.
**CRASH BARRIER
101 TO 110 501 TO 510 UNI GY -0.50
*
LOAD 2 SELF WT OF DIAPHRAGM (WT. 0.88X0.40X2.4=0.845 T/M)
MEMBER LOAD
2201 TO 2301 BY 100 3201 TO 3301 BY 100 2209 TO 2309 BY 100 3209 TO 3309 BY 100 UNI GY -0.845
*
PERFORM ANALYSIS
LOAD LIST 1
PRINT SUPPORT REACTION
JOINT
LOAD
201
301
401
209
309
409
1
1
1
1
1
1
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
9.67
.54
9.67
9.67
.54
9.67
FORCE-Z
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
121. LOAD LIST 2
122. PRINT SUPPORT REACTION
JOINT
LOAD
201
301
401
209
309
409
2
2
2
2
2
2
123. FINISH
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
.92
3.06
.92
.92
3.06
.92
FORCE-Z
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
.00
NOTE NO. DN-18
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
SHEET NO.
STAAD SPACE ANALYSIS OF SUPERSTRUCTURE FOR LIVE LOAD 70R WHEELED
INPUT WIDTH 79
UNIT MTON MET
*
JOINT COORDINATE
*
101 0.0 0.0 0.000 109 14.0 0.0 0.000
201 0.0 0.0 1.450 209 14.0 0.0 1.450
301 0.0 0.0 4.350 309 14.0 0.0 4.350
401 0.0 0.0 7.250 409 14.0 0.0 7.250
501 0.0 0.0 8.700 509 14.0 0.0 8.700
*
701 0.0 0.0 0.725 709 14.0 0.0 0.725
801 0.0 0.0 2.900 809 14.0 0.0 2.900
901 0.0 0.0 5.800 909 14.0 0.0 5.800
1001 0.0 0.0 7.975 1009 14.0 0.0 7.975
*
110 -0.50 0.0 0.00; 111 14.50 0.0 0.0
210 -0.50 0.0 1.450; 211 14.50 0.0 1.450
310 -0.50 0.0 4.350; 311 14.50 0.0 4.350
410 -0.50 0.0 7.250; 411 14.50 0.0 7.250
510 -0.50 0.0 8.700; 511 14.50 0.0 8.700
*
710 -0.50 0.0 0.725; 711 14.50 0.0 0.725
810 -0.50 0.0 2.900; 811 14.50 0.0 2.900
910 -0.50 0.0 5.800; 911 14.50 0.0 5.800
1010 -0.50 0.0 7.975; 1011 14.50 0.0 7.975
*
MEM INCIDENCE
101 101 102 108
201 201 202 208
301 301 302 308
401 401 402 408
501 501 502 508
*
701 701 702 708
801 801 802 808
901 901 902 908
1001 1001 1002 1008
*
109 110 101; 110 109 111
209 210 201; 210 209 211
309 310 301; 310 309 311
409 410 401; 410 409 411
509 510 501; 510 509 511
*
709 710 701; 710 709 711
809 810 801; 810 809 811
NOTE NO. DN-18
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
77.
78.
79.
80.
81.
82.
83.
84.
85.
86.
87.
88.
89.
90.
91.
92.
93.
94.
95.
96.
SHEET NO.
909 910 901; 910 909 911
1009 1010 1001; 1010 1009 1011
*
2101 101 701 2109
2201 201 801 2209
2301 301 901 2309
2401 401 1001 2409
*
3101 701 201 3109
3201 801 301 3209
3301 901 401 3309
3401 1001 501 3409
*
MEMBER PROPERTIES
*DUMMY MEMBER
101 TO 110 501 TO 510 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
701 TO 710 801 TO 810 901 TO 910 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
1001 TO 1010 PRIS YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
209 210 309 310 409 410 PRI YD 0.05 ZD 0.05
*
301 TO 308 401 TO 408 201 TO 208 PRIS AX 1.3645 IX 1E-10 IY .4673 IZ .2882
* DIAPHRAGM
2201 TO 2301 BY 100 2209 TO 2309 BY 100 3201 TO 3301 BY 100 3209 TO 3309 BY 100 PRIS AX 0.52932 IX 1E-10 IY 0.01429 IZ 0.05910
2101 2401 2109 2409 3101 3401 3109 3409 PRIS AX 0.17732 IX 1E-10 IY 0.009599 IZ 0.000715
* SLAB
2102 TO 2108 2202 TO 2208 2302 TO 2308 2402 TO 2408 3102 TO 3108 3202 TO 3208 3302 TO 3308 3402 TO 3408 PRIS AX 0.3850 IX 1E-10 IY 0.09826 IZ 0.001553
*
SUPPORTS
201 301 401 PINNED
209 309 409 FIXED BUT FX FZ MX MY MZ
*
CONSTANTS
E 3.0E6 ALL
*
DEFINE MOVING LOAD FILE DML.TXT
**
TYP 1 CLA 1.0
TYP 2 CL70R 1.0
*
**** CASE 1 : CLASS 70R MOST ECCENTRIC
LOAD GENERATION 100
TYPE 2 -13.9 0.0 6.855 XINC 0.30
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
97.
98.
99.
100.
102.
103.
104.
105.
106.
107.
108.
109.
110.
111.
112.
*
**** CASE 2 : CLASS 70R ONE WHEEL OVER G2
LOAD GENERATION 100
TYPE 2 -13.9 0.0 6.280 XINC 0.30
**** CASE 3 : CLASS 70R TRAIN SYMMETRIC TO G2
LOAD GENERATION 100
TYPE 2 -13.9 0.0 5.315 XINC 0.30
*
*** CASE 4 : CLASS A MOST ECCENTRIC
LOAD GENERATION 100
TYPE 1 -19.30 0.0 8.075 XINC 0.35
*
PERFORM ANALYSIS
LOAD LIST 50 51 52
PRINT SUPPORT REACTION LIST 409
JOINT
LOAD
409
50
51
52
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
FORCE-Z
33.51
34.54
26.64
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
113. LOAD LIST 64 65 66
114. PRINT SUPPORT REACTION LIST 209
JOINT
LOAD
209
64
65
66
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
FORCE-Z
-.99
-1.09
-.60
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
115. LOAD LIST 250 251 252
116. PRINT SUPPORT REACTION LIST 309
JOINT
LOAD
309
250
251
252
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
FORCE-Z
46.17
48.08
35.48
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
117. LOAD LIST 200 201 202
118. PRINT SUPPORT REACTION LIST 309
JOINT
LOAD
309
200
201
202
FORCE-X
.00
.00
.00
FORCE-Y
.00
-.32
-.13
FORCE-Z
.00
.00
.00
MOM-X
.00
.00
.00
MOM-Y
.00
.00
.00
MOM Z
.00
.00
.00
NOTE NO. DN-18
119. FINISH
SHEET NO.
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
A. Design Data - Normal case
Max. Vertical Load Nmax =
814880 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Min. vertical load Nmin =
282480 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Horz. force in Long. dir. hl from supstr. =
Horz. force inTrans. dir. ht from supstr. =
Rotation in Long. dir.bd =
Rotation in Trans. dir.ld=
33333 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
0N
0.0022 refer (refer calculation of bearing loads)
0 rad
Translation in long. dir. bd =
3.50 mm
Translation in Trans. dir. ld =
Concrete grade of pedestal M
0 mm
30 Mpa
Permissble stress in bearing o =
7.5 Mpa
Increased permissible stress as per cl.
307.1 of IRC:21 subject to a maximum
value f 10 Mpa as per cl. 916.3.5
B. Bearing Data
10.00 Mpa
Overall length of bearing in trans. dir.lo
380 mm
Overall width of bearing in long. dir. bo
380 mm
6 mm
Side cover c
Thickness of individual layer of elastomer hi
Thickness of top/bottom layer of elastomer
he
10 mm
Total no. of internal layers n
5 mm
6
Thickness of steel laminate hs
3 mm
Effective width b = bo -2c
368 mm
Effective length l = lo -2c
368 mm
Effective plan area A = l * b
Modulus of rigidity of ealstomer G
Assuming that condition of
required area will be satisfied
should be hi/2 subject to max of
6mm
135424 mm2
1.0 Mpa
3. Design of Bearing
1. Check for base Pressure
Maximum Base pressure on pedestal
m(max)= Nmax/A
6.02 Mpa <
10.00 Mpa
O.K
2.09 Mpa >
2.00 Mpa
2. Checks to be made if standard size is not used as per cl.916.3.3
O.K
Minimum Base pressure on pedestal m(min)=
Nmin/A
1. Ratio of length to width lo/bo
2. Height of elastomer h = n*hi+2*he
1.000 < 2
70 mm
bo/5 =
76
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
bo/10 =
Also total ht. Of bearing ho =
n*hi+2*he+ (n+1)*hs
38
91 mm
3. Shape factor S = A/(l+b)*2*hi
9.20 should be >6 and <12
O.K
3. Check for translation as per cl. 916.3.4
Shear strain of bearing d= bd= bd/h+md or d=(bd2+ld2)1/2 if ld is co-exixting
Total horizontal force on bearing as per clause 214.5.4 of IRC:6 = hl+ Vr * lic
where Vr is shear rating of elastomer bearing = G * A/ho
1488.17582 N/mm
& lic is movement of bearing equal to bd or ld for either direction
Total horz. Force in long. direction Hl = hl + Vr * bd
38542 N
Total horz. Force in trans. direction Ht = ht + Vr * ld
0N
Shear strain in long. dir. bd= bd/h+Hl/A
0.33
Shear strain in trans. dir. ld= ld/h+Ht/A
0.00
Shear strain of bearing d= bd or (bd +ld )
2
2 1/2
if ld is co-exixting =
0.33 0.7
O.K
4. Check for Rotation as per cl. 916.3.5
As per provisions of this clause total angle of rotation d bi,maxn
where d = bd or incase of ld co-existing d = (bd *b+ld *l)/b
0.0022
bi,max = 0.5*m*hi/b*S2 =
0.002
for which m = 10 Mpa as per codal provision
=m (max)/10
0.602
Total angle of rotation d =
0.002206 bi,maxn =
5. Check for Friction as per cl. 916.3.6
0.005796 O.K
As per provisions of this clause total shear straind< 0.2 + 0.1m
where m is minimum bearing presssure
m(min)= Nmin/A
2.09 Mpa 2 Mpa
Now shear strain d=
0.335 0.2+0.1 m=
0.409
O.K
(calculated above)
6. Check for Total Shear stress as per cl. 916.3.7
As per provision of his clause c 5 Mpa
Here,
c is shear stress due to axial compression = 1.5 * m(max) /S
is shear stress due to horizontal defromation = d
is shear stress due to rotation=0.5*(b/hi)2*bi
0.98 Mpa
0.33 Mpa
or = 0.5*(b2*bi+l2*li)/hi2 whereli co-exists
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
now bi is as calculated earlier 0.5 * m * hi / (b*S2)=
0.002
also li is as given by 0.5 * m * hi / (l*S )=
0.000
Therefore = 0.5*(b *bi+l *li)/h =
2
2
i
1.09 Mpa
Now total shear stress c
2.40
Check for pedestal size
Side of pedestal in long. dir.
Side of pedestal required in trans. dir.
307.1 of IRC:21
680
680
114
5.0
O.K
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
A. Design Data - Seismic trans. Case
Max. Vertical Load Nmax =
550440 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Min. vertical load Nmin =
284240 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Horz. force in Long. dir. hl from supstr. =
16667 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Horz. force inTrans. dir. ht from supstr. =
33320 N
Rotation in Long. dir.bd =
0.0017 refer (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Rotation in Trans. dir.ld=
0 rad
Translation in long. dir. bd =
3.50 mm
Translation in Trans. dir. ld =
Concrete grade of pedestal M
0 mm
30 Mpa
Permissble stress in bearing o =
7.5 Mpa
Increased permissible stress as per cl.
307.1 of IRC:21 subject to a maximum
value f 10 Mpa as per cl. 916.3.5
B. Bearing Data
10.00 Mpa
Overall length of bearing in trans. dir.lo
380 mm
Overall width of bearing in long. dir. bo
380 mm
6 mm
Side cover c
Thickness of individual layer of elastomer hi
Thickness of top/bottom layer of elastomer
he
10 mm
Total no. of internal layers n
5 mm
6
Thickness of steel laminate hs
3 mm
Effective width b = bo -2c
368 mm
Effective length l = lo -2c
368 mm
Effective plan area A = l * b
Modulus of rigidity of ealstomer G
Assuming that condition of
required area will be satisfied
should be hi/2 subject to max of
6mm
135424 mm2
1.0 Mpa
3. Design of Bearing
1. Check for base Pressure
Maximum Base pressure on pedestal
m(max)= Nmax/A
4.06 Mpa <
10.00 Mpa
O.K
2.10 Mpa >
2.00 Mpa
2. Checks to be made if standard size is not used as per cl.916.3.3
O.K
Minimum Base pressure on pedestal m(min)=
Nmin/A
1. Ratio of length to width lo/bo
2. Height of elastomer h = n*hi+2*he
1.000 < 2
70 mm
bo/5 =
76
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
bo/10 =
38
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
Also total ht. Of bearing ho =
n*hi+2*he+ (n+1)*hs
91 mm
3. Shape factor S = A/(l+b)*2*hi
9.20 should be >6 and <12
O.K
3. Check for translation as per cl. 916.3.4
Shear strain of bearing d= bd= bd/h+md or d=(bd2+ld2)1/2 if ld is co-exixting
Total horizontal force on bearing as per clause 214.5.4 of IRC:6 = hl+ Vr * lic
where Vr is shear rating of elastomer bearing = G * A/ho
1488.17582 N/mm
& lic is movement of bearing equal to bd or ld for either direction
Total horz. Force in long. direction Hl = hl + Vr * bd
21875 N
Total horz. Force in trans. direction Ht = ht + Vr * ld
33320 N
Shear strain in long. dir. bd= bd/h+Hl/A
0.21
Shear strain in trans. dir. ld= ld/h+Ht/A
0.25
Shear strain of bearing d= bd or (bd2+ld2)1/2 if ld is co-exixting =
0.32 0.7
O.K
4. Check for Rotation as per cl. 916.3.5
As per provisions of this clause total angle of rotation d bi,maxn
where d = bd or incase of ld co-existing d = (bd *b+ld *l)/b
0.0017
bi,max = 0.5*m*hi/b*S =
2
0.002
for which m = 10 Mpa as per codal provision
=m (max)/10
0.406
Total angle of rotation d =
0.001686 bi,maxn =
5. Check for Friction as per cl. 916.3.6
0.003915 O.K
As per provisions of this clause total shear straind< 0.2 + 0.1m
where m is minimum bearing presssure
m(min)= Nmin/A
2.10 Mpa 2 Mpa
Now shear strain d=
0.32 0.2+0.1 m=
0.41
O.K
(calculated above)
6. Check for Total Shear stress as per cl. 916.3.7
As per provision of his clause c 5 Mpa
Here,
c is shear stress due to axial compression = 1.5 * m(max) /S
is shear stress due to horizontal defromation = d
is shear stress due to rotation=0.5*(b/hi) *bi
2
now bi is as calculated earlier 0.5 * m * hi / (b*S2)=
0.66 Mpa
0.32 Mpa
or = 0.5*(b *bi+l *li)/hi2 whereli co-exists
2
0.002
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
also li is as given by 0.5 * m * hi / (l*S2)=
0.000
Therefore = 0.5*(b *bi+l *li)/h =
2
2
i
1.09 Mpa
Now total shear stress c
2.07
Check for pedestal size
Side of pedestal in long. dir.
Side of pedestal required in trans. dir.
307.1 of IRC:21
680
680
114
5.0
O.K
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
A. Design Data - Seismic long. Case
Max. Vertical Load Nmax =
550440 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Min. vertical load Nmin
284240 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
Horz. force in Long. dir. hl from supstr. =
Horz. force inTrans. dir. ht from supstr. =
Rotation in Long. dir.bd =
Rotation in Trans. dir.ld=
41612 N (refer calculation of bearing loads)
0N
0.0017 refer (refer calculation of bearing loads)
0 rad
Translation in long. dir. bd =
3.500 mm
Translation in Trans. dir. ld =
Concrete grade of pedestal M
0 mm
30 Mpa
Permissble stress in bearing o =
7.5 Mpa
Increased permissible stress as per cl.
307.1 of IRC:21 subject to a maximum
value f 10 Mpa as per cl. 916.3.5
B. Bearing Data
10.00 Mpa
Overall length of bearing in trans. dir.lo
380 mm
Overall width of bearing in long. dir. bo
380 mm
6 mm
Side cover c
Thickness of individual layer of elastomer hi
Thickness of top/bottom layer of elastomer
he
10 mm
Total no. of internal layers n
5 mm
6
Thickness of steel laminate hs
3 mm
Effective width b = bo -2c
368 mm
Effective length l = lo -2c
368 mm
Effective plan area A = l * b
Modulus of rigidity of elastomer G
Assuming that condition of
required area will be satisfied
should be hi/2 subject to max of
6mm
135424 mm2
1.0 Mpa
3. Design of Bearing
1. Check for base Pressure
Maximum Base pressure on pedestal
m(max)= Nmax/A
4.06 Mpa <
10.00 Mpa
O.K
2.10 Mpa >
2.00 Mpa
2. Checks to be made if standard size is not used as per cl.916.3.3
O.K
Minimum Base pressure on pedestal m(min)=
Nmin/A
1. Ratio of length to width lo/bo
2. Height of elastomer h = n*hi+2*he
1.000 < 2
70 mm
bo/5 =
76
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
bo/10 =
38
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
Also total ht. of bearing ho =
n*hi+2*he+ (n+1)*hs
91 mm
3. Shape factor S = A/(l+b)*2*hi
9.20 should be >6 and <12
O.K
3. Check for translation as per cl. 916.3.4
Shear strain of bearing d= bd= bd/h+md or d=(bd2+ld2)1/2 if ld is co-exixting
Total horizontal force on bearing as per clause 214.5.4 of IRC:6 = hl+ Vr * lic
where Vr is shear rating of elastomer bearing = G * A/ho
1488.17582 N/mm
& lic is movement of bearing equal to bd or ld for either direction
Total horz. Force in long. direction Hl = hl + Vr * bd
41612 N
Total horz. Force in trans. direction Ht = ht + Vr * ld
0N
Shear strain in long. dir. bd= bd/h+Hl/A
0.36
Shear strain in trans. dir. ld= ld/h+Ht/A
0.00
Shear strain of bearing d= bd or (bd +ld )
2
2 1/2
if ld is co-exixting =
0.36 0.7
O.K
4. Check for Rotation as per cl. 916.3.5
As per provisions of this clause total angle of rotation d bi,maxn
where d = bd or incase of ld co-existing d = (bd *b+ld *l)/b =
0.001686
bi,max = 0.5*m*hi/b*S2 =
0.002
for which m = 10 Mpa as per codal provision
=m (max)/10
0.406
Total angle of rotation d =
0.0017 bi,maxn =
5. Check for Friction as per cl. 916.3.6
0.003915 O.K
As per provisions of this clause total shear straind< 0.2 + 0.1m
where m is minimum bearing presssure
m(min)= Nmin/A
2.10 Mpa 2 Mpa
Now shear strain d=
0.357 0.2+0.1 m=
0.410
O.K
(calculated above)
6. Check for Total Shear stress as per cl. 916.3.7
As per provision of his clause c 5 Mpa
Here,
c is shear stress due to axial compression = 1.5 * m(max) /S
is shear stress due to horizontal defromation = d
is shear stress due to rotation=0.5*(b/hi) *bi
2
0.66 Mpa
0.36 Mpa
or = 0.5*(b *bi+l *li)/hi2 whereli co-exists
2
SHEET NO.
NOTE NO. DN-18
now bi is as calculated earlier 0.5 * m * hi / (b*S2)=
0.002
also li is as given by 0.5 * m * hi / (l*S )=
0.000
Therefore = 0.5*(b *bi+l *li)/h =
2
2
i
1.09 Mpa
Now total shear stress c
2.11
Check for pedestal size
Side of pedestal in long. dir.
Side of pedestal required in trans. dir.
307.1 of IRC:21
680
680
114
5.0
O.K
hi
hs
8
10
12
16
grade
3
3
4
6
stress
20
25
30
35
40
5
6.2
7.5
8.5
8.5
Print out not to be taken
You might also like
- A Modern Guide To Fingerings For The FluteDocument60 pagesA Modern Guide To Fingerings For The FluteTzeng100% (19)
- Bridge Abutment Pier Design As Per IRCDocument41 pagesBridge Abutment Pier Design As Per IRCjibendra mishra88% (43)
- Stability Analysis of Head Wall of Culvert 22-04-20Document20 pagesStability Analysis of Head Wall of Culvert 22-04-20Navarun Vashisth100% (1)
- Design of Abutment Excel SheetDocument33 pagesDesign of Abutment Excel Sheetbkvs12340% (5)
- Calculation Minor Bridges-1Document128 pagesCalculation Minor Bridges-1nandini100% (6)
- Toe Wall DesignDocument3 pagesToe Wall DesignKamlesh Parihar100% (1)
- Star Wars Saga Edition - Legacy Era Campaign GuideDocument225 pagesStar Wars Saga Edition - Legacy Era Campaign GuideArcAngelD92% (13)
- Design of Bridge PierDocument12 pagesDesign of Bridge PierSunita Chaurasia88% (8)
- Pile Foundation As Per IRC 112Document59 pagesPile Foundation As Per IRC 112ARVIND SINGH RAWAT0% (1)
- Box Culvert-Structural DesignDocument5 pagesBox Culvert-Structural Designsiva100% (1)
- SLRB Design of 7.45m Clear Span For IRC Class A LoadingDocument15 pagesSLRB Design of 7.45m Clear Span For IRC Class A Loadingpaaji100% (9)
- Design of Plum Concrete Breast Wall Design Note No: SAI/TKD-219016/PKG-5/DN/STR/BW-04Document9 pagesDesign of Plum Concrete Breast Wall Design Note No: SAI/TKD-219016/PKG-5/DN/STR/BW-04Rishikesh Majumdar100% (2)
- Box Culvert Limit StateDocument52 pagesBox Culvert Limit StateMahadev Sastry88% (8)
- Design of Gap SlabDocument15 pagesDesign of Gap Slabvivek100% (1)
- IRC Conc Bridge DesignDocument16 pagesIRC Conc Bridge Designovikbasu100% (1)
- Box Culvert Limit StateDocument45 pagesBox Culvert Limit StateMahadev Sastry0% (2)
- Calculation of Water Current ForcesDocument4 pagesCalculation of Water Current Forcesvasu7900No ratings yet
- RDSO B 11754 4R1 (Mod)Document1 pageRDSO B 11754 4R1 (Mod)shibnath lahiriNo ratings yet
- BRG 1266 (1550x597)Document1 pageBRG 1266 (1550x597)Nilay GandhiNo ratings yet
- Propped Cantilever Retaining Wall-IsDocument1 pagePropped Cantilever Retaining Wall-Isscshekar0% (1)
- Review Test 1: Units 1-3: VocabularyDocument5 pagesReview Test 1: Units 1-3: Vocabularyjulmay2No ratings yet
- Design of Box Culvert With CushionDocument18 pagesDesign of Box Culvert With CushionPrafulla MallaNo ratings yet
- Design of Elastomeric Bearings For Solid Slab DeckingsDocument8 pagesDesign of Elastomeric Bearings For Solid Slab Deckingsvasu7900No ratings yet
- Design of PierDocument11 pagesDesign of PierNaveen Yadav100% (6)
- Design of RCC PierDocument10 pagesDesign of RCC Piervijayunity40% (5)
- Toe Wall Design Final PDFDocument2 pagesToe Wall Design Final PDFDADADADGGG50% (2)
- RCC Detail Design of Abutment and PierDocument20 pagesRCC Detail Design of Abutment and Piershashibhushan singh100% (1)
- Design of Counterfort Type AbutmentDocument58 pagesDesign of Counterfort Type AbutmentSM Consultants100% (1)
- Box Type MNB 2x4 EstimationDocument26 pagesBox Type MNB 2x4 EstimationAjay Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bow String Girder QuantityDocument3 pagesBow String Girder Quantityvsballa25% (4)
- Designed Date Details Checked Title DocnoDocument4 pagesDesigned Date Details Checked Title DocnovivekNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC Box 2 X 4.0 M X 4.5mDocument17 pagesDesign of RCC Box 2 X 4.0 M X 4.5mvinoraam100% (1)
- Slab Culvert Estimate 5MDocument4 pagesSlab Culvert Estimate 5MRoman Pandit100% (1)
- 2 8 16 - Caculation As Per IRC 112Document228 pages2 8 16 - Caculation As Per IRC 112snehar redkar100% (8)
- BOX CULVERT LSM 1 X 5 X 3 PDFDocument67 pagesBOX CULVERT LSM 1 X 5 X 3 PDFamitkukna100% (2)
- Bridge Abutment Des.Document91 pagesBridge Abutment Des.Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- Nhai RCC Slab BridgeDocument21 pagesNhai RCC Slab BridgeBilal A BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Box CulvertDocument22 pages2 Cell Box Culvertabhijeet sahuNo ratings yet
- Standard For Pedestal Below Bridge BearingsDocument2 pagesStandard For Pedestal Below Bridge BearingsSwopnil KalikaNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Bearing DesignDocument22 pagesElastomeric Bearing DesignRudra Sharma50% (2)
- 3.0 Effective Width of Tyres and Load Distribution For IRC Class Special Vehicle 385 T (SV Class)Document2 pages3.0 Effective Width of Tyres and Load Distribution For IRC Class Special Vehicle 385 T (SV Class)vivekNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Pier Cap With 30.050 M Overall Length of Superstructure in Curved Alignment - R0 - DN-D07Document25 pagesDesign Calculation of Pier Cap With 30.050 M Overall Length of Superstructure in Curved Alignment - R0 - DN-D07Partha Gangopadhyay100% (1)
- Superstructure Design: Maligaon R.O.B Design of PSC Superstructure Superstructure/1Document47 pagesSuperstructure Design: Maligaon R.O.B Design of PSC Superstructure Superstructure/1Er Arabinda Kumar DharNo ratings yet
- Design of Pot Ptfe Bearing (Free Bearing) As Per Irc 83:2002 (Part 3)Document7 pagesDesign of Pot Ptfe Bearing (Free Bearing) As Per Irc 83:2002 (Part 3)DPJAIN INFRASTRUCTURENo ratings yet
- Dead Load Calculation For RCC T-Girder DeckDocument3 pagesDead Load Calculation For RCC T-Girder Deckvasu7900100% (1)
- Design - PCC Toe WallDocument10 pagesDesign - PCC Toe Wallsiddharth yadavNo ratings yet
- PipeDocument30 pagesPipepudumai100% (1)
- Design of 10m Clear Span Slab BridgeDocument53 pagesDesign of 10m Clear Span Slab BridgeD.V.Srinivasa Rao100% (4)
- Box Culvert 1x2.0x2.0mDocument72 pagesBox Culvert 1x2.0x2.0mnandu523100% (1)
- Abutment DesignDocument3 pagesAbutment DesignMalay Kumar DebNo ratings yet
- Bridge Bearing DesignDocument2 pagesBridge Bearing DesignYoshua Yang100% (1)
- PSC Girder-25m R0Document148 pagesPSC Girder-25m R0infra120100% (1)
- Spayed Wing Wall BBS 155+586 RHSDocument1 pageSpayed Wing Wall BBS 155+586 RHSHegdeVenugopal100% (1)
- Pier Design FinalDocument86 pagesPier Design Finalsanjay verma100% (1)
- Pier Cap Staging Analysis - 1Document6 pagesPier Cap Staging Analysis - 1Saiarpan V Joshi67% (3)
- Is 12720 2004 PDFDocument14 pagesIs 12720 2004 PDFBishowkumar Shrestha100% (1)
- PSC Girder DesignDocument26 pagesPSC Girder DesignLokesh M Yadav100% (5)
- Tank Design PDFDocument89 pagesTank Design PDFcecgootyNo ratings yet
- Tank DesignDocument89 pagesTank DesignDietrich von BismarckNo ratings yet
- Tank DesignDocument89 pagesTank DesignRafael ReyesNo ratings yet
- 6600mgwa JKT Psi - FatDocument6 pages6600mgwa JKT Psi - FatanandakoeNo ratings yet
- Anchor and Base Plate CalculationDocument6 pagesAnchor and Base Plate Calculationselahattin_erturk06No ratings yet
- asset-v1-CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+type@asset+block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Document42 pagesasset-v1-CornellX+ENGR2000X+2T2016+type@asset+block@F-1 Engine Model Calculations Non-Proprietyary Non-ITAR Rev2Axel DominiqueNo ratings yet
- DC Regulation 1991Document355 pagesDC Regulation 1991niyaz09aNo ratings yet
- Hollow Sections Book WardenierDocument199 pagesHollow Sections Book WardenierANUSSBAUMER100% (3)
- ERNDIM2020EQACataloguean SEGASACE644740 18 09 2019Document21 pagesERNDIM2020EQACataloguean SEGASACE644740 18 09 2019mnsawantNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide EbookDocument218 pagesUltimate Guide EbookChaitanya Sheth100% (3)
- Planning Design & Construction of Grade Separator - DelhiDocument15 pagesPlanning Design & Construction of Grade Separator - DelhimnsawantNo ratings yet
- MCGM BLDG Sor 13.11Document210 pagesMCGM BLDG Sor 13.11tops123100% (1)
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways Government of IndiaDocument200 pagesMinistry of Road Transport & Highways Government of IndiamnsawantNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Series Analytical and Precision Balances Data SheetDocument4 pagesPioneer Series Analytical and Precision Balances Data SheetmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Serviceability Limit States, Bar Anchorages and Lap Lengths in ACI 318-08 and BS 8110-97 - Comparative Study-ICJ-Nov 2013 PDFDocument11 pagesServiceability Limit States, Bar Anchorages and Lap Lengths in ACI 318-08 and BS 8110-97 - Comparative Study-ICJ-Nov 2013 PDFTimothy Voo Khi SingNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksDocument112 pagesSeismic Design of Liquid Storage TanksMunna Bhai100% (1)
- Mumbai-Storm Water DrainageDocument0 pagesMumbai-Storm Water DrainagemnsawantNo ratings yet
- Initial Draft For Clinical Establishment Act MaharashtraDocument21 pagesInitial Draft For Clinical Establishment Act MaharashtramnsawantNo ratings yet
- STEELW Results CombinatioDocument2 pagesSTEELW Results CombinatioD.V.Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Thane DSR 2010-2011 PDFDocument289 pagesThane DSR 2010-2011 PDFmnsawant100% (1)
- Construction Process of Segmental BridgesDocument47 pagesConstruction Process of Segmental BridgesmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Seismic Retrofit of Steel BridgesDocument4 pagesSeismic Retrofit of Steel BridgesmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Bearings and Expansion Joints-Case StudiesDocument6 pagesRelevance of Bearings and Expansion Joints-Case StudiesmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Goa NBS Report2011 PDFDocument9 pagesGoa NBS Report2011 PDFmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Softened Truss ModelDocument1 pageSoftened Truss ModelmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response of Substructures Under Earthquake Force Ppr12.145elrDocument21 pagesDynamic Response of Substructures Under Earthquake Force Ppr12.145elrmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Minimum Flexural Ductility Design of High-StrengthDocument11 pagesMinimum Flexural Ductility Design of High-StrengthmnsawantNo ratings yet
- Buckling Sefi 346 PDFDocument3 pagesBuckling Sefi 346 PDFmnsawantNo ratings yet
- AISI Appendix BDocument9 pagesAISI Appendix Brk_vijay81No ratings yet
- Not For SaleDocument1 pageNot For SalemnsawantNo ratings yet
- Not For SaleDocument1 pageNot For SalemnsawantNo ratings yet
- Second MoveDocument2 pagesSecond MovemnsawantNo ratings yet
- Not For SaleDocument1 pageNot For SalemnsawantNo ratings yet
- 124 2R-94 PDFDocument1 page124 2R-94 PDFfarhadamNo ratings yet
- Corus - Celsius Hot Finished SHS CT06v8 03 2006Document24 pagesCorus - Celsius Hot Finished SHS CT06v8 03 2006mnsawantNo ratings yet
- IdkDocument4 pagesIdkvishnu priyaNo ratings yet
- Signal Elektronik Ürün Katalogu (Signal Electronic Product Catalog)Document60 pagesSignal Elektronik Ürün Katalogu (Signal Electronic Product Catalog)gitarist666No ratings yet
- WWW Archdaily Com 772447 What Is Architecture PDFDocument3 pagesWWW Archdaily Com 772447 What Is Architecture PDFslavkoNo ratings yet
- Viva La Vida: ColdplayDocument11 pagesViva La Vida: ColdplayLiliana Quesado100% (1)
- English Functional Skill (Expressions in Summary) Class Xii ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 - 2008 (Odd Semester and Even Semester)Document22 pagesEnglish Functional Skill (Expressions in Summary) Class Xii ACADEMIC YEAR 2007 - 2008 (Odd Semester and Even Semester)emiliapuspitasari100% (2)
- 500 Cabinets - A Showcase of Design & CraftsmanshipDocument419 pages500 Cabinets - A Showcase of Design & CraftsmanshipMohammed HosnyNo ratings yet
- 12 Website DesignDocument29 pages12 Website DesignAien RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Stiffnesstester 170122185612Document20 pagesStiffnesstester 170122185612Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Plain Power Looms Into Continuous Weft Feeding LoomsDocument2 pagesConversion of Plain Power Looms Into Continuous Weft Feeding Loomssenthilkumar100% (1)
- Service ManualDocument87 pagesService ManualvimannNo ratings yet
- Key Test Your English 6Document1 pageKey Test Your English 6Leo ShenNo ratings yet
- Document Transmittal: SAW-CWCO-TR149 15 January 2013Document8 pagesDocument Transmittal: SAW-CWCO-TR149 15 January 2013Budi IndraNo ratings yet
- Westminster Walk - Walk London - Google MapsDocument5 pagesWestminster Walk - Walk London - Google MapsFastalNo ratings yet
- 112Document8 pages112Rishi ShahNo ratings yet
- Vishniac's Photo Archive Lands at Magnes, Including Unseen Israel Images - Jweekly 2018.11.20Document4 pagesVishniac's Photo Archive Lands at Magnes, Including Unseen Israel Images - Jweekly 2018.11.20spagnoloachtNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 3 EmpowermentDocument16 pagesQuarter 4 Module 3 EmpowermentDeey Lanne Casuga RufintaNo ratings yet
- Om SemDocument89 pagesOm SemRezki AshidiqiNo ratings yet
- PDF IprDocument10 pagesPDF IprUjjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- Arbor Press Drawings PDFDocument16 pagesArbor Press Drawings PDFCalixto Milla EsauNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek Language, Writing and AlphabetsDocument15 pagesAncient Greek Language, Writing and Alphabetstoza vitaminozaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 The Concept Hero and Role of Nation Building EssayDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 The Concept Hero and Role of Nation Building EssayJonah DelmundoNo ratings yet
- Free Floral Butterfly Cross Stitch Pattern 95b90c0Document3 pagesFree Floral Butterfly Cross Stitch Pattern 95b90c0parhelia syntaNo ratings yet
- Latex PresentationDocument26 pagesLatex PresentationHassan HusseinNo ratings yet
- Project 1: Semester September 2017Document51 pagesProject 1: Semester September 2017Miauriz RizNo ratings yet
- The Passionate Shephered To His LoveDocument4 pagesThe Passionate Shephered To His LoveKirk Kervin OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Frisius, Regnier GemmaDocument3 pagesFrisius, Regnier GemmacreeshaNo ratings yet
- Papango Eng Amer LittDocument26 pagesPapango Eng Amer LittReden OriolaNo ratings yet