Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ADSL Manual Part 4.5
Uploaded by
Anonymous PqHsNUCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ADSL Manual Part 4.5
Uploaded by
Anonymous PqHsNUCopyright:
Available Formats
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Introduction
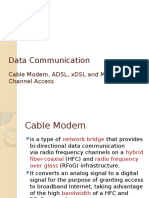
Digital Subscriber Line, DSL or xDSL, is a high speed internet that uses the wires (copper) of a
local telephone network. It enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines by utilizing
frequencies that are not used by a voice telephone call.
The Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), also referred to as the Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS).
Advantages of DSL:
Offers high speed internet connection.
The phone line can be used simultaneously for voice calls and for internet connection.
Does not necessarily require new wiring; it uses the existing telephone line.
Disadvantages of DSL:
Works better when closer to the provider's central office (exchange) . The farther away from the
CO, the weaker the signal becomes.
The service is not available everywhere.
Common DSL Types
Asymmetric DSL -ADSL
ADSL is a form of DSL wherein the downstream is greater than the upstream.The downstream is
used for communicating from the central office to the end user. The upstream band is used for
communication from the end user to the telephone central office. With standard ADSL, the band from
25.875 kHz to 138 kHz is used for upstream communication, while 138 kHz 1104 kHz is used for
downstream communication.
Standard ADSL utilizes the 1.1 MHz band while ADSL2+ utilizes the 2.2 MHz band.
The limit for ADSL service is 18,000 feet (5,460 meters), though for speed and quality of service
reasons many ADSL providers place a lower limit on the distances for the service.
Symmetric DSL -SDSL
Receives and sends data at the same speed. While SDSL also requires a separate line from your
phone, it uses only a single line.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Distance Limitations
(Using 24-Gauge Wire)
None
Connection
Maximum Transfer Rate
56 K Analogue Modem
56 kbit/s
Up to 128 Kbps (2 BRI)
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
(Multilink PPP)
10-30 Mbit/s Downstream
30 miles / 48 Km
128 kbit/s to 10 Mbit/s Upstream
over coaxial cable
(Shared bandwidth)
Up to 8Mbps downstream
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
Up to 640Kbps upstream
Up to 12Mbps downstream
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
Up to 1Mbps upstream
Up to 24Mbps downstream
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
Up to 1Mbps upstream
T1 - 1.544 Mbit/s (2 wire pairs)
2.2 miles / 3.6 Km
E1 - 2.048 Mbit/s (3 wire pairs)
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
T1 - 1.544 Mbit/s
2 miles / 3 Km
E1 - 2.048 Mbit/s
13 - 52 Mbit/s Downstream
1,000 ft/304 m
1.5 - 2.3 Mbit/s Upstream
4,500 ft/1371 m
Up to 34 Mbit/s if symmetric
depending on speed
An asymmetric service, rate-adaptive DSL
1.5 - 8 Mbit/s Downstream
3.4 miles / 5.4 Km
Up to 1.544 Mbit/s Upstream
ISDN
Cable Internet
ADSL
ADSL 2
ADSL 2+
HDSL
SDSL
VDSL
R-ADSL
Speed comparison of different DSL types as well as other internet types.
Frequency plan for ADSL. The red area is the frequency range used by normal voice telephony (PSTN), the green
(upstream) and blue (downstream) areas are used for ADSL.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL Set-Up
Typical ADSL network set up.
ADSL Modem
An ADSL modem or DSL modem is a device used to connect a single computer or a router to an
ADSL phone line, in order to use the ADSL service. ADSL modems use frequencies from 25 kHz to
above 1MHz, in order not to interfere with voice service which is primarily 0-4 kHz.
Filters
A filter performs two main tasks. First, it prevents high frequency noise from appearing at the
telephone and potentially decreasing voice quality. These filters are low-pass (LP) filters. It blocks
everything above 4 Khz preventing the data signals from interfering with standard telephone calls, since
all voice conversations take place below 4 KHz.
Second, it prevents the telephone equipment from interfering with the modem by preventing
harmonics, overtones and changes in impedance caused by the telephone equipment.
DSLAM
Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) allows telephone lines to make faster
connections to the Internet. It is a network device, located near the customer's location, that connects
multiple customer Digital Subscriber Lines to a high-speed Internet backbone line using multiplexing
techniques.
Factors Affecting ADSL
The actual download speed achievable for ADSL is subject to but not limited to the distance from the
local telephone exchange (cable length), network configuration and traffic, the quality of the customers
copper phone line, EMI, cabling and equipment.
Attenuation
Attenuation is the reduction, degradation or weakening of a signal's intensity or strength by
transmission through a medium. Usually reported in dB with respect to distance traveled through the
medium with a correspnding attenuation coefficient represented in dB/km.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Attenuation and Speed values with respect to distance from the exchange (ADSL2+).
20dB and below
20dB - 30dB
30dB - 40dB
40dB - 50dB
50dB - 60dB
60dB and above
- Outstanding
- Excellent
- Very good
- Good
- Poor and may experience connectivity issues
- Bad and will experience connectivity issues
SNR Margin/Noise Margin.
Noise Margin (also called SNR Margin) is the relative strength of the DSL signal to Noise ratio. 6dB
is generally the lowest dB manufacturers specify in order for the modem to be able to sync.
The following is the comparison of the different Noise Margin Values and their effect on the DSL
connection:
6dB or below is bad and will experience no sync or intermittent sync problems
7dB-10dB is fair but does not leave much room for variances in conditions
11dB-20dB is good with no sync problems
20dB-28dB is excellent
29dB or above is outstanding
Typical Set-up and Connection Procedures
On the customer side, the DSL modem is connected to a phone line. On the other end, it is
connected to a DSLAM. When the DSL modem is powered up, it goes through a sync procedure. The
actual process varies from modem to modem but can be generally described as:
1. The modem does a self-test.
2. The modem checks the connection between the modem and the computer. This is usually the
Ethernet port or a USB port or wireless.
3. The modem then attempts to synchronize with the DSLAM. Data can only come into the computer
when the DSLAM and the modem are synchronized. Modems have an indicator labeled "DSL" which
can be used to tell if the modem is synchronized. During synchronization the light flashes; when
synchronized, the light stays lit, usually with a green color.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
TPG ADSL
TPG ADSL Set-up
Before a customer can register for ADSL services with TPG, they must have a phone
line which is part of Telstras network.
Customer will need to nominate a specific phone number to have the ADSL service
installed
TPG offers/supports 3 types of DSL products, these are:
1. ADSL - Works on Telstras infrastructure
Telstra offers the following connections (quoted in Kilo Bits per
second): 1500k/256k; 512k/128k; 256k/64k; 8000k/384k
- Downstream = 4X Upstream
2. SDSL - Works on Telstras infrastructure
- Plans offered by Telstra: 512k/512k
- Downstream = Upstream
3. ADSL2+ - Works on TPG infrastructure
Download speeds of up to 24 Mbps and upload speeds of up to
1Mbps
- Also offered as Naked DSL
DSL connections can be accessed from anywhere on the premise as long as the line that
is attached to the ADSL modem/router is the one that was nominated at registration time.
When ADSL is installed on the nominated service number, it is referred to as there are
CODES on the line.
Since DSL speeds are quoted in Bits per second, to get an approximate figure in
Kilobytes/sec, divide by 10.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL2+ OVERVIEW
The theoretical maximum speed of ADSL2+ is 24Mbps (24,000 Kilobits per second)
download and 1Mbps upload.
The actual download speed achieved depends on many factors such as the distance
from the local telephone exchange, EMI (Electromagnetic Interference), the quality of the
copper phone line and broadband equipment.
When a customer joins a TPG ADSL2+ plan, we physically transfer the customer from
Telstra DSLAM to a TPG DSLAM port in the telephone exchange, allowing for ADSL2+
speeds.
Customers that live more than 3.5kms from the exchange may not notice any significant
increase in service speed on ADSL2+, however will experience a more stable and
reliable connection if using an ADSL2+ compatible modem/router. Most metro customers
live within 3.5kms of their exchange.
The graph indicates the potential connection speed obtainable for ADSL2+ based on the distance from the local
phone exchange, using an ADSL2+ compatible modem/router.
If the customers ADSL modem/router is only ADSL1 compatible, the maximum speed
achievable would be up to 8Mbps even on ADSL2+ plans. While, ADSL2 compatible
modem/routers can achieve a maximum download speed of up to 12Mbps even on
ADSL2+ plans.
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
TPG LAYER 2 TYPES (ADSL, ADSL2+ and SDSL)
TPG DSL connections (ADSL, ADSL2+ and SDSL) are classified as Layer 2 using PPPoE as
connection type
In a PPPoE connection, a Username and a Password is required for authentication. Similar
to how dial up works. When a customer authenticates to the TPG network successfully, TPG
will assign them an IP address and DNS for their connection
There are 2 types of Layer 2 Fixed (2F) and Dynamic (2D)
2F customers get assigned the SAME IP every time they authenticate to TPG radius servers
2D customers get assigned an IP from the pool of available TPG IPs. This gets done at
random so every time the customer reconnects, they may get a DIFFERENT IP
TPG Layer 2 types.
To authenticate, all ADSL customers use <UN>@L2TP.tpg.com.au (2F) or
<UN>@PPP.tpg.com.au (2D) as their username and their normal TPG password to gain
access to broadband service via their ADSL modem
Domain name is needed in Telstra network for right forwarding to ISPs
For most customers it does not matter which extension they use however it is recommended to
keep to the rule
The extension of the username is not case sensitive
ADSL2+ customers DO NOT require a domain extension to their UN
All Layer 2 accounts come with a back up dial up account charged at $1.10 per hour, capped at
$16.99 per month. These charges are separate from ADSL charges
Customers can use their back up dial up account and their ADSL at the same time and should
not cause any authentication issues
For email or back up dial up, the username and password are left unchanged (no extension
needed)
ADSL MODEM, MODEM/ROUTER, ROUTER
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL
Modem
No routing capability, only a pass through device, hence only 1 PC at a time
Can be setup in PPPoE or Bridged
Has no web interface (GUI)
Phone line gets connected directly to it from the wall socket
Usually have USB only connection option. Thus, a driver needs to be installed. This would come
with the package. USB modems are powered by the USB port of the PC
Connection and disconnection of Internet is done similarly with 56k dial-up connections
Modem setup on PPPoE mode:
1. Customer installs the driver and selects the PPPoE option
2. A dialler will be automatically created by the driver on the desktop and it is through this
dialler that the customer needs to authenticate.
3. In the username section of the dialler they need to put their username (with the specified
extension). Normal password is used.
There is no noise heard (handshake) from the modem when dialling as this is an
authentication process only
The customer will not be charged a local call every time they dial up
Once authenticated, the connection icon should appear on the Task Bar
As soon as this is done, the customer can get connection to the internet
If the connection is disconnected or the PC is turned off, the customer needs to go through the
connection process again
The internet remains connected if the PC stays on too
Examples are Dlink DSL 200 and Netcomm NB2
ADSL Modem/Router
Often referred to as router
It can handle routing hence it is more intelligent than a modem, thus 1 or more PC can be
connected
Can be setup in PPPoE or Bridged
Has a web interface (GUI)
Phone line gets connected directly to it from the wall socket
Have a LAN and a WAN side.
The LAN side talks to the PC or the local network and the WAN side talks to the outside world
A router can be connected to a PC via Ethernet, USB or Wireless connection. Depending on the
model, the router could have 1,2 or all 3 options
Ethernet connection on Modem Routers
Uses a Network Interface Card (NIC) and Ethernet cable
To configure a modem/router, the interface (GUI) needs to be accessed. A browser is
used to log into the configuration page by browsing the modem/routers LAN address
(gateway address)
The routers WAN side needs to be configured to talk to the outside world.
Examples are Netcomm NB6+4, Dynalink RTA1320, RTA 1025W, RTA 1046VW
USB connection on Modem Routers
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
The driver needs to be installed first and will create a virtual LAN card. Then the
modem/router needs to be configured
The LAN and WAN side of the router needs to be accessed via the interface by browsing
the gateway address
Sometimes the gateway address will be different depending if the connection is USB or
Ethernet
Examples are Linksys AM300, Dynalink RTA1320
ADSL Wireless Modem Routers
All the features of ADSL modem/router with wireless technology
If the router is to have a wireless connection to the PC, then the PC needs to have a
wireless adapter. TPG sells these:
PCI Wireless Adapter Needs to be installed in the PC
PCMCIA Wireless Card for Notebooks
USB Wireless Adapter your PC or notebook needs to have a free USB port
Examples are Dynalink RTA1025W, Dynalink RTA1046VW
Router
TPG does not support these
Used in networks to allow for multiple PCs
Not to be confused with ADSL modem/router. This is not an ADSL modem/router, hence there
is no phone line that is attached to this device
Factory Default
Standard settings that the manufacturer has the router in when purchased off the shelf
You can reset a router to factory defaults either via its interface or manual reset at the back
panel of the router, if available.
A power cycle of the router (turning it off then on) will not cause the router to loose its
configuration
10
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
PPPOE CONNECTION SET-UP
A modem/router setup in PPPoE mode does the authentication. Once authenticated, the
modem/router holds the Public IP assigned by TPG (whether dynamic or fixed)
The customers username, password and DNS settings are held on the modem/router. Once
the modem/router is turned off, no computer will have internet access
The NAT (Network Address Translation) feature must be enabled (enabled at factory default).
This allows for the LAN side to talk to the WAN side. Since the Public IP is held at the router
and the computer holds a private IP
In this example we will assume the following:
- UN: adsl1234@L2TP.tpg.com.au
- Password: secret
- Computer is connected directly to the router via ethernet connection
- The router is at factory default and the LAN IP 192.168.1.1
1. Browse to 192.168.1.1and log into the router
interface. You are accessing the router via its LAN
side. The LAN side is the interface between the router
and your PC (Either go to the NIC>TCP/IP and
specify a private IP or allow for a private IP to be
assigned by DHCP):
2. Configure the router on the WAN side (for this you
may need to look at the manuals for the type of router
your dealing with. These are available from
helpdesk.tpg.com.au or helpdesk.tpg.com.au/kb). The
WAN side is the connection between your router and
the Telstra Network.
Connection Type: PPPoE LLC
Username: adsl1234@L2TP.tpg.com.au
Password: secret
VPI: 8
VCI: 35
Security Protocol: PAP
NAT: enabled
Mux Type: LLC
Modulation: G.dmt for ADSL and ADSL 2+ for
ADSL2+ customers
3. Save and reboot the router
Internet
TPG
Network
Telstra
Exchange
WAN
Router
192.168.1.1
LAN
NIC
PC
11
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
You should now have:
Internet
TPG
Network
Telstra
Exchange
All the info in step 2
WAN
Router
LAN
Customer IP: 192.168.1.2
Gateway: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
192.168.1.1
NIC
PC
COMMANDS
Windows
Linux
ping
ping
nslookup
nslookup
tracert
traceroute
ipconfig
/sbin/ifconfig
winipconfig
na
Sends out 4 packets to see if what you are pinging will respond
- ping <IP>
- ping <URL>
- ping <IP/URL> -t will do a continuous ping test
Gives you the IP of the URL or URL of the IP
- nslookup <URL>
- nslookup <IP>
Traces path from source to destination (URL or IP)
- tracert <URL>
- tracert <IP>
- Reports the PCs TCP/IP information like IP, GW, SM
- ipconfig /all is used for XP and 2000 to show extended version of
TCP/IP settings. For Win95 ipconfig all is used
- Performs the same function as ipconfig but only for Win98 and ME
winipconfig all can also be used to show more detailed information
Note: A Firewall on Host machine/router or NAT on router may block ICMP (ping) request.
12
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Ping 203.213.34.218
Ping test OK!
Pinging 203.213.34.218 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 203.213.34.218: bytes=32 time=16ms TTL=22
Reply from 203.213.34.218: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=22
Reply from 203.213.34.218: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=22
Reply from 203.213.34.218: bytes=32 time=16ms TTL=22
Ping statistics for 203.213.34.218:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
There was no packet loss
to the destination Host
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 15ms, Maximum = 16ms, Average = 15ms
It took 15ms to reach
the destination Host
Ping 203.213.34.194
Ping test Unsuccessful!
Pinging 203.213.34.194 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 203.213.34.194:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
All packets were lost
The result will indicate either:
Customer heavily utilising the link with downloads
(Increase ping times w 5000, continuous ping t, netstat)
Denial of Service (DoS Attack)
Faulty ADSL Router
Faulty ADSL Line
Trojan on Customer PC or Network or
Host machine (i.e. PC or Router) has a Firewall blocking ICMP request
13
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
tracert 203.213.34.194
OK!
Tracing route to 203-213-34-194-nsw.tpgi.com.au [203.213.34.194] over a
maximum of 30 hops:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
15 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
16 ms
<10 ms
32 ms
<10 ms syd-ibo-zeu-1-fe-6-1.tpgi.com.au [203.29.157.1]
<10 ms syd-pow-ibo-zeu-ge-2-0.tpgi.com.au [202.7.167.130]
<10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-ero-pos-6-2.tpgi.com.au [202.7.162.202]
<10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-tit-2-ge-1-0.tpgi.com.au [203.58.24.131]
<10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-l3-ge-0-1.tpgi.com.au [220.244.226.8]
<10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-ero-1-ge-2-0.tpgi.com.au [220.244.229.129]
<10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-twe1.tpgi.com.au [220.244.229.14]
<10 ms 172.31.43.37
31 ms 203-213-34-194-nsw.tpgi.com.au [203.213.34.194]
tracert 203.213.26.110
Tracing route to 203-213-26-110-nsw.tpgi.com.au [203.213.26.110] over a maximum
of 30 hops:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
<10 ms
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
<10 ms <10 ms syd-ibo-zeu-1-fe-6-1.tpgi.com.au [203.29.157.1
<10 ms 15 ms syd-ibo-aph-1-gig-0.tpg.com.au [203.12.160.97]
<10 ms 16 ms 10.20.23.58
<10 ms 15 ms syd-nxg-ibo-ero-1-ge-2-0.tpgi.com.au [220.244.229.129]
16 ms <10 ms syd-nxg-ibo-twe1.tpgi.com.au [220.244.229.14]
*
15 ms 172.31.41.37
* Request timed out.
* Request timed out.
172.31.41.37 reports: Destination host unreachable.
* Request timed out
* Request timed out
Unsuccessful!
Either the destination
has a firewall or it
doesnt know how to
get there.
Hop 6 knows how to
reach the destination
but cannot get to it.
The result will indicate either:
The Forward path and the Reverse Path might be different
Routing Loops (generally caused by problems on a devices routing table, these can occur at any
point in a network (anywhere there are routers).
Timeouts on every hop until 30 hops has been reached (Generally caused by packet filters,
routing issues.
Speed Issue (customer flooding the link by downloading a lot, customer being DoS attacked or by Trojans)
Heavily utilised link within our backbone.
Congestion with upstream provider.
Issue outside our network/control
Note (acceptable latency):
Maximum of 100ms to Australian sites.
Maximum of 350ms to US sites.
Customer Traversing through Telstra ADSL Network to us is 20ms
14
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
FILTERS AND SPLITTERS
Once installation of ADSL is complete, the frequency on the service number is increased.
The Internet works on the higher frequency range. Each device working on the same
ADSL service number like phones, fax machine etc. need to use a filter to block the high
frequency allowing only the low frequency to pass.
Devices that operate on the low frequency that may work on the same phone number as
the Internet includes:
1. Phones (regular or cordless)
2. Fax machines
3. EFPOS Electronic Funds Point Of Sales - Used for credit card or non-cash
payments. Usually for businesses.
4. Back-to-Base alarm systems - Some alarm systems will use the phone line to call
and to alert the customer if their alarm system gets triggered. This line is hard wired into
the alarm system by the technician.
5. Foxtel Digital - Cable TV service. The set top is connected to a phone line for
interactive features.
6. PABX - Phone system installed by a certified company which allows for multiple phone
extensions to be used in the office, similar to what we have at TPG
NOTE: PABX and Back-to-Base Alarm systems need to be filtered by a Central Splitter
installed by licensed technicians. Other devices can be filtered using basic or central
filters.
There should be NO MORE than 3 devices working on the Broadband Service number.
A fax machine may take up the place of 2 devices.
Since the Internet works on a higher frequency range, the modem/router must NOT be
filtered under any circumstance.
15
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Having no filter or incorrect filter attached will cause Internet problems like:
- No sync No ADSL signal on the modem/router
- Intermittent sync No ADSL signal at times
- Browsing
- Speed and
- Authentication
With each modem/router sent out from TPG, it comes with a CENTRAL filter. Additional
central filters can be purchased.
1. Basic Filter
End labelled LINE gets connected to the phone jack
End labelled PHONE connects to a device
Used for Non-cordless phones, Fax, Foxtel Digital, EFPOS
Basic filter and its installation.
2. Central Filter
End labelled LINE gets connected to the phone jack
End labelled PHONE connects directly to a device
End labelled MODEM connects to the ADSL modem/router.
Used on cordless or regular phones, Fax, Foxtel Digital, EFPOS or when the
modem/router and a device need to share the same phone jack. (there is only 1 phone
socket)
Central filter and its installation.
16
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
3. Central Splitter
Needed when:
- there are more than 3 devices, like phones, fax etc.;
- there is a back to base alarm system; OR
- there is a PABX/Commander system running on the ADSL service number
TPG do not sell Splitters, customer needs to contact a licensed technician to get one
installed
Once installed, there is no need to have filters on each device.
There will be filtered and unfiltered ports on a splitter. The technician will wire the
premise in such a way that there are:
1. Filtered ports from the splitter - connection to wall sockets that need to have a device
connected
2. Unfiltered port from the splitter - connection to wall socket where the modem/router
would be connected.
Central filter and its installation.
PABX/Commander System
PABX Private Automated Branch Exchange. These systems allow for a single access
number to offer multiple lines to outside callers while providing a range of external lines to
internal callers or staff. It is installed on a specific landline.
If a customer already has a PABX on a specific phone number, they CANNOT nominate
this same service number for ADSL. If they do without realizing this, the ADSL application
will be rejected.
If an organization requires an ADSL and a PABX, it is recommended to lease 2 separate
lines (numbers) from Telstra, one for the PABX/Commander system and the other for
ADSL
When a customer first gets ADSL then installs PABX, the correct way to filter the PABX is
by using a CENTRAL SPLITTER
Our responsibility is not to understand how the PABX is filtered, that is the technicians
responsibility. We need to make sure the customer understands when sharing one
number for ADSL and PABX, their PABX MUST be filtered using a CENTRAL SPLITTER
17
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ISOLATION TEST
An isolation test is to remove or disconnect all telephony devices like phones, fax, back to
base alarm system, EFPOS, Foxtel Digital and PABX system that work on the ADSL
service number. Leaving the modem/router the only device directly connected (with no
filters/double adapters in front) to the ADSL service number. Also, making sure that the
phone cable to the modem/router is less than or equal to 3m in length.
Note: Customers with Back to Base Alarm Systems OR PABX Systems may need to contact the
respective company or the people that installed the Central Splitter to Isolate it from line.
WHY DO WE ASK CUSTOMERS TO DO AN ISOLATION TEST?
We ask customers to do an isoation test to determine whether:
the problem is caused by other devices using the ADSL service number. Thus, filters may
not be installed.
the problem is caused by filters or double adapters installed. Filters may not be installed
on all devices, placed incorrectly or faulty, or the incorrect filter is used for the device.
Customers may have miscalculated and they have more than 3 devices running on the
ADSL Service number. Double adapters may be faulty or corroded.
there is an internal wiring issue. (customer's premise)
there is a line issue. (Telstra line)
the problem is caused by a faulty modem or equipment.
HOW DO I EXPLAIN TO THE CUSTOMER HOW TO PERFORM AN
ISOLATION TEST???
1. First you need to know how many and what kind of devices are operating on the ADSL service
number. Also determine the number of phone sockets in the premise. You can ask the following
questions:
NOTE: There could be devices operating on the ADSL service number which are located
outside the building or house for example in a Granny Flat, garage or shed.
How many phone sockets do you have on the ADSL service number?
Do you have any telephones operating on the ADSL service number (01) 2345 - 6789?
Are any of these phones cordless?
Is there a Fax machine operating on this number?
Do you have an EFPOS machine operating on the ADSL service number?
Do you have Foxtel Digital? If so does that also work on the ADSL service number?
Is there a PABX or Commander system installed on this ADSL service number?
Do you have a Back to Base Alarm system that may be connected to the ADSL service
number?
2. If you follow the phone cable from the phone jack at the wall to the router/modem, is there a
filter on that line? If there is please remove it
18
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
3. Are you talking to me on a phone operating on the ADSL service number? If so, I will explain
how to do an Isolation Test, please do this after we hang up. If your Internet doesnt resume back
to normal please call us back for further troubleshooting
4. As well as doing the Isolation Test, please ensure that the length of the phone cable
connecting from the phone jack at the wall to the router/modem is less than or equal to 3m
5. The Isolation Test involves disconnecting all the devices that you have mentioned that are
operating on the ADSL service number (01) 2345 6789 (inside or outside the immediate
premises) and leaving only one phone line <=3m connected to the ADSL router/modem with no
filter. If you have a Back to Base Alarm or a PABX/Commander system, you may need to contact
the relevant company or the people who installed your Central Splitter to isolate it from the line.
6. If the customer have other phone sockets in the premise, you may ask them to try the other
phone sockets and do the same procedure. Ask the customer to call us back for the results.
600 SERIES SOCKET
RJ 11 SOCKET
ADSL TOOLS
In CSWEB, under ADSL, you can access Quick SQs, Check Telstra Reference Numbers, Check
Service Configurations and the TPG DSLAM Manager.
19
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Quick SQs
Service Qualification is done to ensure that the nominated number is compatible for ADSL/2+.
Reasons for failed SQ:
a. Pair Gain/RIM a technology that 'splits' a copper telephone line so as to allow for the
provision of more than one telephone service over that line. We allow customers to apply for
ADSL1 even if their exchange is ADSL2+ ready.
b. Attenuation too high this would mean that they are too far from the exchange and so there
would be signal degradation. The application for ADSL would be rejected, as there would be no
fix for this.
A customer may be found on a sub-exchange, although this is ok for ADSL it is not for
ADSL2+. Again customer can apply for ADSL1.
Check Telstra Reference Numbers
With Telstra Reference Numbers, you can query the status of a new installation, an upgrade, a
churn, etc. The reference number can be found in IAS under ADSL installation status:
Get the reference number in IAS and you can view the status of the installation in Telstra
reference number check.
20
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Check Service Configurations
Service configurations checks if there is TPG ADSL service on the nominated number or in other
words, if there's TPG CODES on the line.
ADSL 1
ADSL2+
TPG DSLAM Manager
In the TPG DSLAM Manager you will be able to query a username and it returns detailed
information about each ADSL2+ customer.
Section 1: Customer Details
Line Profile: This tells the profile of the customers line. It is possible to force the
customers line to different speeds and change line settings from the DSLAM Manager,
however, access to change this is restricted . For example the customers line may be
forced to an ADSL1 connection. These changes are not performed or requested by
Level1.
Service Number: Number on which ADSL2+ is installed.
Cable Length: This is the distance between the customers premises and the exchange
in meters.
Status: Tells if ADSL2+ is installed on the service number.
Section 2: Radius Details Authentication Information
Status: Tells if customer has authenticated, if so it says Alive. If not it says Stop.
IP: If customer has authenticated, this is the IP address.
Connected: Tells when the customer authenticated last.
Current Session: Tells the how long the customer has been authenticated since the last
connection.
Section 3: DSLAM Details Sync Information
Exchange Name: The exchange at which the customers line is connected.
Last Connected: Tells when the customer last got SYNC.
Last Disconnected: Tells when customer last lost SYNC.
Current Session: Tells how long the customer has been in SYNC since the last
connection.
Downstream Rate: This is the download speed (in Kbit/sec) the customer is Synced up.
Upstream Rate: This is the upload speed (in Kbit/sec) the customer is Synced up.
21
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Sync History Bar: Read from right to left. This shows the sync history for the past 4 days
whether the customer lost sync or not. It does not record the customer's authenticated
sessions. Note: A customer may be in sync but not authenticated. Each block
represents 1 hour and may have a number in it to represent the number of times a
customer has lost sync during the one-hour block. Hovering the cursor
over the number will give a tool tip for the recorded session of the block. Clicking on the
number will bring up the sync details for that block. It will show when the sync was lost,
for how long and when the sync resumed.
Section 4: Sync Reliability Test Last 24 hours
Looking under the section of <ATU-R>
Count of all blocks received with un-correctable errors: This should be less than 500.
If more than this, it means possible modem issues. Suggest customer to try another
modem if possible.
Section 5: RVOP Remote View On Port
Standard in port training: Tells what modulation the customer is connected.
Downstream channel rate (Kbps): Rate of download the customer is Synced up.
Downstream max. attainable rate (Kbps): Maximum rate of download the line is
capable of.
Downstream channel SNR margin (dB): Should be between 5 and 6.
Downstream channel attenuation (dB): Refer to attenuation table.
Upstream channel rate (Kbps): Rate of upload the customer is Synced up.
Upstream max. attainable rate (Kbps): Maximum rate of upload the line is capable of.
Section 6: Port State Test
Activating: Customer doesnt have sync yet from the DSLAM.
Activated: Customer has sync from the DSLAM.
Testing: Try again in a little bit.
Deactivated: Port is INACTIVE, NO SYNC POSSIBLE. Consult FS or TL.
22
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL2+ installation process for a new customer
From the day the customer submits the request for ADSL2+ installation, it takes approximately
3-5 working days for the installation to be complete.
1. Registration (allow 1 working day) - TPG receives the completed ADSL Registration
form and verifies that the customer has completed all relevant sections.
2. Verification/line qualification (SQ) - Usually same day unless further testing is required.
A Service Qualification is done to ensure the service number nominated is compatible for
ADSL. Reasons for failed SQ:
a. Pair Gain/RIM: Customers have 3 options:
1. Applying for ADSL1 is the only way they can get transposition (removal of pair
gains). Customers may wish to go ahead with the transposition. Once the request
is received, we apply for the transposition to take place. After transposition is
done there is no guarantee that the customer can upgrade to ADSL2+.
2. If a client wishes to try to have ADSL connected on a different telephone number
the Logistics team SQ the new number and proceeds with the required course of
action
3. If a client wishes to cancel their application it is automatically removed from our
database. Setup fee and the first month charge is refunded
b. Attenuation too high: The application for ADSL would be rejected, as there would be
no fix for this.
Note: A customer may be found on a sub-exchange although this is ok for ADSL it is
not for ADSL2+. Again customer can apply for ADSL1.
Customers are notified by Logistics through email outlining their options regarding the
failed SQ.
When the SQ is done, if a customer is far from the exchange but not far enough for the
application to be rejected, chances are they may have issues with their Internet
connection for example speed or dropout. These customers are said to be 6D customers.
We recommend the customer use the NB1 modem or the RTA1320 to reduce their
chance of having issues in the future.
3. Initial charging - Usually same day unless further investigation is required. After
qualification is successful TPG bills the customer for:
Set-up cost (if applicable)
Equipment (e.g. modem/router if purchased through TPG)
Equipment delivery fee (if applicable)
The first subscription fees are billed monthly, quarterly or another term as
specified for the customers plan.
Note: Billing period will commence when the service is first activated. Installation will
proceed upon receipt of payment. Allow 5 working days for direct debit processing.
IAS account will be created. Customer will now be given a Username.
4. Line order submitted by Logistics: Service Activation Request (allow 3 working days) Physical provisioning of the ADSL service and configuration of the customers requested
line.
23
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
5. Shipment of Equipment and / or Configuration Sheet - Allow 1-2 working days
Modems will be configured by TPG and dispatched via overnight bag.
6. Installation of Service - Customer and Dealer will be advised of installation by e-mail.
Please Note: working days do not include National or Public holidays and weekends
ADSL1 installation process for a new customer
The same process is executed for ADSL customers with some minor differences.
1. Registration - TPG receives the completed ADSL Registration form and verifies that the
customer has completed all relevant sections.
2. Verification/line qualification (SQ) - SQ may fail due to Pair Gain or Attenuation too high.
3. Initial charging - Usually same day unless further investigation is required
4. Now Logistics will submit the application to Telstra. At this point, Telstra can still have
problems completing the installation. The reason for this may be:
a. There were no ADSL ports available at the customers local exchange.
Again the customer is notified by Logistic via email.
There is no guarantee if or how long it will take for ports to become available.
The customer can wait or cancel. IAS will usually show some more information
on the matter.
If there is an ETA, advise the customer of this else the customer can check with
us in about a months time.
If you see a release date this means the customer will be given a port. If the
customer is given a release date, they should expect to get service within 5 days
of this date. If its delayed, please advise the customer to wait another week
b. Network Build. This means the current cable into the exchange is not able to carry the
ADSL signal. There could be 2 statuses for this:
1. Under investigation: Telstra may be thinking of replacing the cabling, they havent
decided yet
2. Underway: Telstra is actually doing work on the cabling at the moment. There
could be an ETA given by Telstra for the completion
5. Shipment of Equipment and / or Configuration Sheet
6. ADSL gets installed on the nominated service number between 3-5 working days from
the day Logistics submits the request to Telstra, if there were no delays like no port
availability, pair gain or network build issues.
24
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Churn (Fast transfer from another ISP to TPG)
The process of churning is to simply move from one ISP to another.
Customers can move from another ISP directly to TPG ADSL or ADSL2+. For ADSL2+,
customers must be eligible for TPG ADSL2+ (TPG ADSL2+ enabled exchange)
Customers who wants to churn to TPG must meet the following requirements:
1. Customer is coming from an ADSL/2+ churn participant. This list can be found at:
http://www.tpg.com.au/products_services/churn_list.php?type=adsl for ADSL1
http://www.tpg.com.au/products_services/churn_list.php?type=adsl2 for ADSL2+
2. Customers current ADSL/ADSL2+ connection must remain active for the churn to
happen. So customers must not cancel the current connection with current ISP until the
transfer to TPG has been completed.
3. Customers must churn/transfer their ADSL/ADSL2+ connection to the same
telephone number and address.
The churn process will take a minimum of 3 working days to complete from the time
logistics makes the submission
Customers can request a CRD (Customer Request Date) where customer nominates the
date for the transfer. This can be done at registration time. CRD must be more than 3
working days but less than 10 working days
A brief downtime of 4 hours during the churn/transfer process may be experienced. This
will alert customers that the churn is in progress, and that it is time to change their
connection settings.
Upgrade
Customers can upgrade from ADSL to ADSL2+ by simply applying for a change of plan
online.
This process takes approximately 3-5 working days.
Customer will only experience a short 30 minute downtime.
ADSL 2+ Migration
Migration is the process of moving selected ADSL1 customers to ADSL2+. TPG have
selected a number of exchanges around Australia to be included in the Migration plan. A
number of selected customers were invited via email to join this scheme.
Customers have the choice to take this offer by going to a special URL by a certain date
mentioned in the email else a default plan will be selected for them to move to. If
customers do not want to migrate to ADSL2+ they must still go to the link and select this
option.
Once they accept the offer (or the default plan was selected), they will be found in the
TPG DSLAM Manager with the Status as MIGRATION. If they dont accept the offer,
they will not be included in the Migration.
25
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Once customer has made a plan selection, the order is placed with Telstra to move the
customer to ADSL2+. From the day of submission, it takes 3-5 working days for
installation to be complete. At this point you should see the codes in ADSL2+ and a
record of the customer in the DSLAM Manager.
During the installation process, the customer will experience a short down time of 30
minutes. Up until this point, the customer still can use their ADSL connection.
Note: If it has been more than 30 minutes since the downtime and there is ADSL2+
codes on the line, normal troubleshooting must be performed.
Mirror Plans
For some customers on certain old plans (called Layer 3 which were another type of
ADSL1 plans on Telstra infrastructure/equipment), mirror plans were created to migrate
customers to Layer 2.
These mirror plans are the copy of the customers old plan in terms of monthly cost,
download speed and download quota but they are setup in Layer 2 PPPoE.
There are 2 types of mirror plans:
1. Mirror plans on Telstras infrastructure
- These plans would have an abbreviation starting with A1L2M in IAS
- These are Layer 2 connections on ADSL1 Telstra infrastructure
2. Mirror plans on TPGs infrastructure
- These plans would have an abbreviation starting with A2L2M in IAS
- Although the customer would be on our DSLAM, they are not ADSL2+
customers. They do not get up to 24Mbps speeds!
- Customer on A2L2M plans will be throttled so as download speeds on the line
will match their old plan (either 1.5, 256 or 128K)
- You can still use the DSLAM Manager to look at customer line details like sync,
speeds, authentication etc
- Customer should be treated as an ADSL1 customer when troubleshooting but
since customer is on our DSLAM, some ADSL2+ troubleshooting techniques may
apply
Example:
A1L2M118 = ADSL1 Layer 2 PPPoE copy of plan 118 (old Layer 3 plan) on Telstra infrastructure
A2L2M118 = ADSL1 Layer 2 PPPoE copy of plan 118 (old Layer 3 plan) on TPG infrastructure
26
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
Before you start troubleshooting, it is important to know the following:
Be aware of the service location (ADSL Parameters in IAS or Service Configurations in
CSWEB). There may be outages or issues in that area. Always check TPG service
status, your email and Telstras Service Status:
http://telstra.com/ServiceStatus/wholesale (for ADSL outages only)
Is the customer using a modem or router? What is the make and model? We only
support configuration/reconfiguration of modem/routers listed on the TPG Helpdesk page:
http://helpdesk.tpg.com.au. Manuals on how to do this are also found here.
How is the modem/router connected to the PC? USB? Ethernet? Wireless?
Is the customer close to the computer?
Be aware of what kind of connection the customer has i.e. Layer 2 (2D or 2F)
Ask the customer about the activity of the lights on the router or modem (power light,
ethernet/usb light, sync light)
Here is an example of the front panel of an ADSL modem/router (DSL302g):
And on the rear panel of the router is where all the physical connections are made.
27
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
1. No power on modem/router
Power light on the modem/router is not lit up.
a. Does the router have an external power supply?
Check power adapter/cable/outlet.
Make sure customer is using the correct power supply.
Power cycle.
Suggest to send back modem for testing if and only if they meet our conditions.
b. Is this a USB only modem?
Check USB cable/port.
Reboot the PC.
Reinstall driver on another USB port.
Check power management on PC.
Suggest to send back modem for testing if and only if they meet our conditions.
2. Ethernet or USB light is not lit up
The Ethernet or USB cable connected to the PC and the respective light on the modem is not lit
up. On some modems/routers these lights may flash to indicate data flow.
a. Make sure the power light is lit up on the modem/router.
b. Is the customer using Ethernet connection?
Check the cables; reseat the cables.
Try other Ethernet ports on the router. (if available)
Is the NIC responding? Is it enabled?
Make sure the cable between PC and the modem is a straight through cable.
Power cycle the modem.
Replace the cable.
c. Is the customer using USB connection?
Power cycle the modem/router and PC.
Check the USB connections. Make sure nothing is loose.
Uninstall and reinstall the driver on another USB port.
Try using Ethernet connection. (if possible)
d. Could be modem/router issue. Suggest to send back modem for testing if and only if they
meet our conditions.
28
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Conditions for modem/router or filter testing:
Customer must have bought the modem or filter from TPG.
If the modem or filter is found to be faulty, it will be replaced if it is still under 1 year
warranty.
Older modems/filters can be tested but if it is found to be faulty it will not be fixed or
replaced.
The warranty period will not restart when a replacement unit is issued.
There is no extra fee for testing by TPG.
Ask the customer to write a note with:
Name and Surname
Username
Short explanation of why they are returning the equipment
Customer must send the modem and the note to:
TPG Internet
Attention ADSL Engineer,
65 Waterloo Rd, North Ryde
NSW 2113
If they choose to use Australia Post, advise them to use registered post. As in the past,
there have been modems that have gone missing. By registering the post, if we did not
receive the equipment, Australia Post can track the parcel.
Customer can deliver the modem in person between 9am-5pm, Monday to Friday (not
including public holidays)
Customer is responsible for getting the modem to TPG including cost. TPG is responsible
for returning the modem including cost. We use the courier company Australian Air
Express: www.aae.com.au
Depending on when we receive the equipment, testing should be done by the end of the
business day. AAE picks up deliveries from TPG every business day late afternoon to
make the delivery to metro areas by the next morning.
Deliveries to regional areas may be done by the next business day afternoon.
No replacement modem is sent out while the customers modem is being tested as per
Terms and Conditions.
Equipment is not tested over the weekend or public holidays.
29
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
1. No Sync
Sync is given to the modem/router when it is connected to a phone line that has ADSL
installed.
On the modem/router it is labeled as the Link or ADSL or DSL light.
No Sync is when this light is completely off or continuously flashing with no rest.
When a modem/router is powered on, the sync may flash for a few seconds as it is in
training. After this the sync light should stabilize.
On some modem/ routers, once the training is complete, the sync light may be flashing
when there is data flow.
a) Make sure that the modem is connected to the phone line. Make sure that the phone
cable is not loose.
b) Check if the customer has connected the modem/router to the correct phone line (where
ADSL is installed). Confirm the service number (IAS>ADSL Parameters). Some
customers may have more than one telephone number.
c) Check that ADSL or ADSL2+ is completely installed on the nominated number. Check for
codes on the line using Service Configurations tool in CSWEB.
NOTE: If there are no codes on the line, we need to understand why the codes
have been dropped. Possible reasons are:
Has there been a change of address or a change of service number? Both falls under
change of location. If so, ADSL will be affected. Transfer customer to CS or they need
to email adsl_admin@tpg.com.au for reconnection of ADSL codes.
Has there been a change of lessee/ownership on the service number. If so, ADSL will
be affected. Transfer customer to CS. This will take 2 working days and there is no fee if
it is submitted within 7 days of the change of lessee
Has the customer changed phone providers? Even though the customer may have
changed phone providers, the physical line may still be owned by Telstra but not always.
Customer can try to get reconnected. Transfer customer to CS they will check to see if
the reconnection is possible.
Did the customers telephone line recently disconnected due to non-payment or
Telstra work? Even after the phone service gets reconnected, ADSL will be affected.
Customer needs to email adsl_admin@tpg.com.au for reconnection of ADSL codes. It
will take 3-5 working days and the customer will be charged for a reconnection fee.
Is this customer going through a Churn? Maybe the churn has not taken place yet.
d) Does the phone line connected to the modem/router have dial tone? To check, have the
customer plug a phone and listen for the dial tone. If there is no dial tone, the
modem/router will not be able to pick up the sync.
If the customer has any issues with their dial tone, try other wall sockets around the
premises. If there is still no dial tone they need to report this to Telstra.
e) If the customer has more than 1 phone socket, can the customer try to plug the
modem/router into another phone socket? Possible phone socket issues. See if the
customer knows which wall socket is the main one in the premises and try this one.
f)
Power cycle the modem/router. Turn the modem off, wait for 10 seconds and turn it back
on.
30
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
g) Identify the devices running on the ADSL number. Name these devices: phones, fax,
back to base alarm system, EFPOS and Foxtel Digital and PABX.
h) Ask the customer if all these devices are filtered or not. If not, they must filter all devices
that work on the ADSL Service number. Ask if the customer has a cordless phone. These
phones need a Central Filter.
i)
Try different phone cables. The phone cable connecting the modem/router to the phone
socket is less than or equal to 3 meters.
j)
Make sure the customer hasnt placed a filter on the modem line i.e., no filter between the
modem and the phone socket.
k) Ask the customer to do an Isolation Test. If the customer still doesnt get sync back, we
need to continue with troubleshooting.
l)
If the customer gets the sync back, then this could mean that:
filters were placed incorrectly or they missed filtering a device
a filter could be faulty or incorrect type of filter was used
Physical phone line issue (eg: too long) etc
m) If the isolation test did not help, reset modem to factory defaults and reconfigure.
Change modulation to G.dmt (if using an ADSL2+ modem). If its a USB connection,
uninstall and reinstall the driver.
Note: Setting the modulation to G.dmt mode will cap the speed to 8Mbps.
n) Does the customer say that the only time they can get sync is when the phone is in use?
This is called a High Open/High Resistance case. Do an Isolation Test and replicate
the problem. Ask the customer to call Telstra for a Metallic Loop Line Test (make sure not
to mention anything about internet or ADSL). Lodge a No Sync Fault and make a note
that this is a High Open or High Resistance case.
o) Ask the customer to try a different modem or try the modem on a different location, or try
upgrading the firmware (should be asked if possible, but never impose). For firmware
upgrade, the customer can either do this themselves or speak to the manufacturer (not
applicable for VOIP routers: Zyxels, NB9W and RTA 1046VW).
p) Still having problems?
For ADSL customers: Lodge a No Sync FAULT. ADSL Engineering Team will be
handling the case now.
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a
call.
REMEMBER!!!
No codes on the line, you cannot lodge a fault!
Find out why there are no codes on the line.
31
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
2. Intermittent Sync
When the ADSL service works and then drops out due to the sync light dropping off either
at predicted or random times, it is referred to as Intermittent Sync.
On some modems/routers it is normal to see the link light flash a little. This indicates data
flow. But the norm is that it should be steady most of the time.
a) For ADSL2+ customers, you can see how often the customer has lost sync in the past 4
days. In the DSLAM Manager, check the Sync History Bar.
b) For ADSL 2+ customers, run the Sync Reliability Test on the DSLAM manager. Click on
Last 24 hours. Looking under the section of <ATU-R>. Check Count of all blocks
received with un-correctable errors this should be less than 500. If more than
this, it means possible modem issues. Suggest to try another modem if possible.
c) Go through the No Sync checklist. Make sure you check:
The phone cable connecting the modem to the phone socket is less than or equal to 3m.
Try different phone cables.
There should be no filter between the phone socket and the modem.
Try another phone socket (if available). See if the customer knows which is the main
phone socket in the premises and try this one.
Ask how many devices the customer has on the ADSL service number. There should be
no more than 3 devices (not including the modem/router).
Are all devices filtered correctly? Cordless phones need a central filter.
Reset and reconfigure modem/router. Reinstall any drivers.
Change modulation to G.dmt (if using an ADSL2+ modem)
Advise customer to do an ISOLATION TEST
d) Ask the customer to try a different modem or try the modem on a different location, or try
upgrading the firmware (should be asked if possible, but never impose). For firmware
upgrade, the customer can either do this themselves or speak to the manufacturer (not
applicable for VOIP routers: Zyxels, NB9W and RTA 1046VW).
e) Still having problems?
For ADSL customers: Lodge an Intermittent Sync FAULT. ADSL Engineering Team
will be handling the case now.
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a call.
Be sure that you get the following information from the customer before you lodge a fault
or escalate:
- How often does the customer loose sync?
- Have they noticed some sort of pattern? Any particular time of the day?
- When they loose sync, how long does it take for the service to resume?
32
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
3. Authentication Issues
Authentication takes place after sync is established by the modem/router.
On some modems it is labelled as the PPP light.
Authentication issue is when the customer has sync yet their username and password is
being rejected.
a) Make sure there is Sync on the modem/router (ADSL light should be solid. For ADSL2+
customers, the DSLAM Manager can also tell is the customer has sync). Check for ADSL
codes using Service Configuration Tool in CSWEB.
b) Is the account status active? If not transfer the customer to CS.
c) Check authentication attempts. To check from our end if an ADSL or ADSL2+
customer is authenticated, run VPDN Tool through the Helpdesk Tools page. For
ADSL2+ customers, the DSLAM Manager can also tell you if the customer has
authenticated.
d) Power cycle the modem and check VPDN again. Please note that some modems may
take up to 20sec to authenticate.
e) Make sure the PPPoE settings are correct. Re-type the Username and the Password. If
the customer is using a modem/router, access the interface of the router. If the customer
has a USB only modem (DSL200), double click on the dialler.
For USB only modem, check for error message (usually would get error 691 or 678). For
Error 678, try plugging the modem onto other USB port available. Make sure to shut
down the computer before disconnecting the USB cable from the computer.
f)
Check if the Password is correct via Call Tracking. Make sure the customer has the
correct Username extension. For ADSL1 customers, UN must end with
@L2TP.tpg.com.au (2F) or @PPP.tpg.com.au (2D). This is not case sensitive. For
ADSL2+, no extension. For all new customers, the UN and PW are the same.
For ADSL1 customers, try the alternative extension e.g. if the customer is using PPP
try L2TP and vice versa.
g) If fails, run the Radius Test to make sure there are no authentication issues on TPGs
behalf.
h) Reset the modem/router back to factory defaults and reconfigure. If customer is
using a USB only modem, uninstall and reinstall drivers.
i)
Configure the modem/router in Bridge Mode then create a PPPoE dialler through
Network Connections (for XP and Vista). If customer is using a USB only modem,
uninstall and reinstall drivers in Bridge Mode then create a PPPoE dialler.
j)
Reset the password. Reconfigure the router with the new PW. Tell them to wait 15min. f
the customer has a USB only modem, change the PW on the dialler.
k) Check how many devices there are running on the ADSL service number. Make sure
these devices are filtered.
l)
Advise the customer to do an Isolation Test.
33
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
m) Ask the customer to try a different modem or try the modem on a different location, or try
upgrading the firmware (should be asked if possible, but never impose). For firmware
upgrade, the customer can either do this themselves or speak to the manufacturer (not
applicable for VOIP routers: Zyxels, NB9W and RTA 1046VW).
n) Still having problems?
For ADSL customers: Lodge an Authentication Fault. ADSL Engineering Team will be
handling the case now
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a call.
4. No Dataflow
When a customer's modem has sync and is authenticated but cannot send or receive any
data (this includes not being able to browse or send and receive email), it is referred to as
No Dataflow.
a) Make sure the modem has power, has sync, authenticated and the ethernet or USB
light is ON depending how their connection is setup. Make sure the customer is not
using wireless connection. If so ask the customer to connect using Ethernet.
b) Run VPDN. Check UN extension. For ADSL1 customers, UN must end with
@L2TP.tpg.com.au (2F) or @PPP.tpg.com.au (2D). This is not case sensitive. For
ADSL2+, no extension. Connecting on the wrong domain may cause browsing issues.
c) Make sure the PPPoe settings are correct. NAT should be enabled.
d) Power cycle the modem/router. Run VPDN again. Make sure they are online and have a
public IP address assigned. If customer is using a modem/router, access the interface to
check. If customer is using a USB only modem (DSL 200), make sure they see the
connection on the Task Bar. Ipconfig will show you the IP address received. For ADSL2+
customers, you can also use the DSLAM Manager to check.
If the customer is on 2F, make sure there are no other connections reported on VPDN, if
so remove it and reset the password. Advise the customer to try again in 15min.
e) Check the configuration on the customers computer. Ask them to do an ipconfig.
Customer must have a Private IP, GW and SM.
f)
Do they have a firewall running? Check the Task Bar and suggest disabling it.
g) If the customer is on a network, power cycle any other devices like hubs and switches. If
there is still no data flow, remove any device between the modem and the PC and
connect the PC directly to the ADSL modem/router before you continue with
troubleshooting.
h) If the customer is using DSL200 modem:
34
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Go to Network Connections
Right click on the DSL200 dialler and go to properties
Double click on TCP/IP
Click on Advanced in the General Tab
Make sure there is a tick in the box for Use default gateway on remote network
i)
Run ping tests. Ping Gateway, URL (www.tpg.com.au) and IP (203.12.160.187 TPG
website)
j)
If ping test of URL passed:
Optimize browser settings ( delete cache, cookies, and history, lower security settings,
set privacy to allow cookies).
Remove proxy settings.
Try different browser or computer
Reset TCP/IP:
netsh int ip reset resetlog.txt (Windows 2000 and XP)
netsh winsock reset catalog (XP SP2)
Possible malware issues (virus/spyware). Run Netstat to check and suggest to scan the
PC for possible virus or spyware.
k) If ping test of URL failed:
Try to browse using IP(203.12.160.187 TPG website)
Assigne DNS to TCP/IP:
203.12.160.35 and 203.12.160.36
l)
Reset the modem/router back to factory defaults and reconfigure. If customer is
using a USB only modem, uninstall and reinstall drivers.
m) Configure the modem/router in Bridge Mode then create a PPPoE dialler through
Network Connections (for XP and Vista). If customer is using a USB only modem,
uninstall and reinstall drivers in Bridge Mode then create a PPPoE dialler.
n) Ask how many devices are running on the ADSL service number, there should be no
more than 3 devices (excluding the modem/router). Are all these devices filtered
correctly?
o) Advise the customer to do an isolation test.
p) Ask the customer to try a different modem or try the modem on a different location, or try
upgrading the firmware (should be asked if possible, but never impose). For firmware
upgrade, the customer can either do this themselves or speak to the manufacturer (not
applicable for VOIP routers: Zyxels, NB9W and RTA 1046VW).
q) Still having problems?
For ADSL customers: Lodge a Data Flow Fault. ADSL Engineering Team will be
handling the case now
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a call.
35
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
When a customer cannot browse, always remember the troubleshooting flow!!!!!
NOTE:
If the customer is using a USB connection on a modem/router:
The customer would be using a USB cable as apposed to an Ethernet cable.
Keep in mind customer is no longer using a NIC, they would have a separate icon
created once the driver is installed in Network Connections.
To check TCP/IP settings you would go to the properties of this icon.
Since it is a modem/router, to configure the router you still have to access the interface
once the driver has been installed.
If the customer is using a USB only modem (DSL 200):
There is no interface, modem is configured by installing the driver.
When it is recommended to reconfigure the modem, you would reinstall the driver.
DSL200 in particular can only be setup in Bridged or PPPoE since its only an ADSL
modem
5. Intermittent Dataflow
Intermittent dataflow is when a customer always has sync. They can send and receive
data most of the time, but either regularly or irregularly, they cannot send and receive
data (this includes not being able to browse or send and receive email).
Be careful customer makes sure they had sync at the time of the problem as this issue
may be a sync/int sync problem. If there is a sync problem and the customer is not aware
of this, to them it looks like a dataflow issue.
Another way you can identify Intermittent Dataflow is by pinging the customers public IP
continuously. You will see a number of packets timing out (packet loss) while some pings
may reply. This will be evident at the time of the problem.
a) Make sure the customer always has sync and authenticated. If a customer has
Intermittent Sync issues it may seem like an Intermittent Data Flow.
36
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
b) You can check for ADSL 2+ customers, if they have Intermittent Sync issues by checking
the Sync History Bar in the DSLAM Manager. If so, go through Intermittent sync checklist.
c) Make sure the customer is not using wireless connection. If so, ask the customer to
connect using Ethernet.
d) Go through NO DATAFLOW checklist.
e) Still having problems?
For ADSL customers: Lodge an Intermittent Dataflow fault. ADSL Engineering Team
will be handling the case now.
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a call.
6. Speed Issues
A customer is having Speed issues when they are not getting the correct download
and/or upload speed they are suppose to get. For example if the package is 512/128, this
means the customer should be getting download speeds of ~50Kbytes/sec and upload
speeds of ~12Kbytes/sec.
At any time the customer can use the TPG Download Speed Test to check the rate of
download. This can be accessed via the TPG home page > Helpdesk > Download >
Speed Test.
PLEASE NOTE: The following suggestions may be considered for both ADSL and ADSL
2+ customers. However, please keep in mind additional number of factors that can slow
down an ADSL2+ customers connection like distance from the exchange, line quality,
EMI and equipment used. We can use tools like the TPG DSLAM Manager to check for
the speed on the customers line.
a) Check for speed throttling/shaping.
Most of our packages have a monthly download limit and if this limit is exceeded, the
download and/or upload speed is reduced. If the customer is throttled, there will be a log
in IAS, under View Log (Full) and Display Current Usage.
ADSL and ADSL2+ plans get throttled to as low as 64kbps, for both download and
upload, depending on the plan. Throttling gets lifted on the first day of the next billing
month.
If the customer's throttling is lifted but are still on slow speeds (can be verified by doing a
download speed test), ask them to power cycle the modem. If this does not help, bring it
to the attention of Floor Supports or TL.
b) Make sure the customer is not using wireless connection. If so ask the customer to
connect using Ethernet.
c) Make sure the customer is not running any sort of program in the background that uses
the Internet connection, like updates.
37
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
d) For ADSL customers, check Service Configuration (codes) to make sure the speed
reported is the one matching with the package that they are actively on (compare IAS and
LOLIG).
e) For ADSL 2+ customers, check the distance between the customer and the exchange
using the TPG DSLAM Manager. Consult the ASDL2+ distance/speed graph to see the
potential maximum speed achievable according to the distance from the exchange. This
graph is quite generous! Whatever the graph indicates, if you take away approximately
1-2Mbps, this is what the customer would typically sync up at and this figure should be
displayed in the DSLAM manager.
Be aware of what kind of modem/router they are using:
Remember ADSL1 modems are capable of getting a theoretical speed of 8MBps
Remember ADSL2 modems are capable of getting a theoretical speed of 12MBps
Remember ADSL2+ modems are capable of getting a theoretical speed of 24MBps
f)
For customers on the Telstra 8MB plans, use the Quick SQ to see how far the customer
is from their exchange. Consult the ASDL1 distance/speed graph to see the potential
maximum speed achievable according to the distance from the exchange. This graph is
quite generous!Whatever the graph indicates, customers expected speed when doing a
download from the TPG download Speed Test should be 1-2Mbps less.
Acceptable speed for 8MB plan is 110Kbytes/sec download and 17Kbytes/sec upload.
If the customer is getting at least this, then it is not a fault. The best you can do is normal
troubleshooting.
These are ADSL1 customers provided by Telstra with no cap. They will not be found on
the DSLAM Manager.
g) Download Speed Test: Get the customer to download the Speed Test from the TPG
website to confirm that they in fact have a download speed problem. Make sure the
customer is not doing any downloads like updates.
For ADSL1 and 8MB plan customers:
Advise the customer to go to TPG website>Helpdesk>Downloads>Speed Test>ADSL.
Save the file to the desktop so as they can observe the download rate.
As the download is being done, the customer needs to look at the speed reported and
see where it stabilizes. (The transfer rate is in kilobytes. Multiply it by 10 to have it in
kilobits.)
For ADSL1, compare download speed test to package. For 8MB plan, compare it to the
graph.
For ADSL 2+ customers:
Advise the customer to go to TPG website>Helpdesk>Downloads>Speed Test>ADSL2+.
This file is much bigger than the one for ADSL1 allowing for more accurate results.
Download speed should be the same as the one reported in the DSLAM Manager.
Please get the initial speed then cancel the download. (This will be deducted from the
monthly quota.) Compare download speed test to DSLAM Manager and the graph.
Upload Speed Test: Get the customer to upload a large file to their free web space using
an FTP client. You can suggest using Cute FTP client.
If the customer gets the correct speeds when doing these tests then the problem could be
coming from the server side where the customer is downloading/ uploading the file.
If the customer gets the incorrect speeds then continue with troubleshooting.
38
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
h) A lot of speed issues are a result of a virus. Initial checks would be to look for excessive
dataflow on the connection by double clicking on the connection icon in the Task Bar.
Make sure there are no downloads or uploads being done at this time. Advise customer
to update their antivirus definitions and do a full scan of the PC.
i)
Disable any firewalls as they may block ports, programs or networks.
j)
For ADSL 2+ customers, run the Sync Reliability Test on the DSLAM manager. Click on
Last 24 hours. Looking under the section of <ATU-R>. Check Count of all blocks
received with un-correctable errors this should be less than 500. If more than
this, it means possible modem issues. Suggest to try another modem if possible.
k) Reset and reconfigure the router. Check the modulation. If using an ADSL modem,
reinstall the driver.
l)
Ask how many devices are running on the ADSL service number, there should be no
more than 3 devices (excluding the modem/router). Are all these devices filtered
correctly?
m) Advise the customer to perform an Isolation Test and run the Download Speed test
while the line is in Isolation.
n) Ask the customer to try a different computer or browser.
o) Ask the customer to try a different modem or try the modem on a different location, or try
upgrading the firmware (should be asked if possible, but never impose). For firmware
upgrade, the customer can either do this themselves or speak to the manufacturer (not
applicable for VOIP routers: Zyxels, NB9W and RTA 1046VW).
p) Still having issues?
For ADSL customers: Lodge a Speed fault. ADSL Engineering Team will be handling the
case now.
For ADSL2+ customers: ESCALATE the case. Level 2 will be handling the case now.
They can run tests on the line and change line profiles (if necessary) to see if this will fix
the problem.
Remind the customer: (Include this in your case documentation.)
1. Leave their modem on for the next 48 working hours.
2. Possible fee for service if the problem was found to be from customer premises.
3. As soon as we have further information about their case, customer will receive a call.
When you are lodging a fault or escalating through Call Tracking, along with the usual
details you report make sure you also include:
- What kind of speed fault are you lodging Download or Upload?
- What was the result of the Download Speed Test or the Upload rate?
Including these rates are extremely important as the case cannot go further without this
information.
REMEMBER!!!
When troubleshooting ADSL or ADSL2+ connections you need to
identify the type of issue first. ALWAYS check the lights on the
modem/router and check for:
1. Sync
2. Authentication
3. Data Flow
39
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
WIRELESS CONNECTIONS
Wireless connections have become very popular and you will come across customers who are
having Internet problems when using wireless connection. Remember that wireless is another
way for your router to communicate with PCs in your Local Area Network (LAN). Although
wireless is not in the HD troubleshooting scope, we still need to provide basic troubleshooting.
Wireless Adapter
To have a wireless connection, your PC must have a wireless card/adapter. Some customer may
already have this built in their PC/notebook.
If customer does not have a wireless adapter they can purchase this from TPG:
USB wireless adapter for PC and notebooks
PCI wireless adapter for PC
PCMCIA wireless adapter for notebooks
For the adapter to work, you need a utility like drivers or the XP wireless utility, which comes with
all XP machines.
If a customer needs assistance to install the USB adapter bought from TPG, then we can do this.
Please follow the manual on the helpdesk page under ADSL. Other adapter installations need to
be done by the customer.
Scanning and connecting to your wireless router
When the PC has a wireless adapter installed and enabled and the routers wireless feature is
also enabled, your PC should be able to scan for your networks SSID (name of your network
access point - wireless router).
To do this you double click on the wireless adapter icon in the Task Bar and scan for networks
close by. You can refresh the network list by clicking on Refresh Network List on the left.
40
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Your SSID should appear if there is reasonable signal strength. Select your SSID and click on
Connect at the bottom. Your PC will attempt to connect to the wireless router.
Once your PC has connected to the wireless router, you should see the Connected status.
If your router asks for a password or key, this means there is encryption setup.
Encryption
This defines security for your wireless connection. Because there is no physical connection
between the router and your PC, anyone else that comes in close range to the router, will be able
to connect to your network and use your Internet.
To prevent this from happening, your PC and router must share a password or a key. This way
only those who know this key will be able to join the network.
Although we do not support wireless or encryption setup, it is good to know about it so as we can
guide the customer into the right direction.
Encryption is something that we strongly recommend for the customer to enable and so it would
be good to have some basic knowledge about it. When the customer buys a wireless router from
TPG, the instructions for setting up security should be included.
To setup this key, you first need to access the router interface and go to the wireless setup area.
Standard settings for encryption are:
Network Authentication Open
WEP Encryption Enabled
Encryption Strength 64bit
41
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Key you would enter your choice of 5 ASCII characters or 10 Hexadecimal digits (using letters
a-f and digits 0-9). Some routers may already have a default key at factory defaults for example
the NB5+4W has key as a1b2c3d4e5
Once the key has been set in your router, your PC needs to use this key to be able to connect to
the router. You can either manually enter this key every time you want to make a connection to
our router or have your PC remember it. Most people would have this set on their wireless
adapter. To do this you go to Control Panel -> Network Connections and right click on the
wireless card and go to Properties
Please note: We need to be careful when suggesting to customers to
disable the security, since it will leave their connection vulnerable to
unauthorized users.
After Connection
Once the PC has connected to the router, it will receive a dynamic IP (by DHCP) from the same
range as the router, For example, if your router has a 192.168.1.1 address (LAN side), your PC
will get something between 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.1.254.
You should be able to ping your router from your PC, just like how you would with an Ethernet
connection
TROUBLESHOOTING WIRELESS ISSUES
BASIC RULE: If the Internet works when using Ethernet then customer has wireless
issues. We can provide the customer with basic troubleshooting to show the customer
direction.
***Our first priority is to make sure the Internet works on Ethernet***
1. Check for Internet connectivity
Identify why the customer cannot use the Internet, is it a wireless issue or Internet is not
working?
a. Check the Sync on the router. If there is no sync go to No Sync checklist, etc.
b. Is the customer connected? Use VPDN. If not, go to Authentication checklist.
Power cycle the router and check if the internet is working.
Ask the customer to connect using Ethernet and see if this is an Internet problem or
wireless connectivity issue.
If the customer can use the Internet using Ethernet, then explain to the customer that the
reason why they cannot use the Internet is because they have a wireless issue and not
an Internet problem. If the Internet does not work on Ethernet then troubleshoot as usual
Advice the customer: HD is not trained to support wireless issues however I can
give you some simple instructions to try.
2. Check if customer can search for the SSID from the PC
When you go to Network Connections, can customer see the SSID of the router? If not then:
Make sure the router is on.
Refresh the network list.
If signal strength is too low, try to reposition the PC closer to the router.
Could be that the router settings are set to hide the SSID. To enable this, you need to go
back on Ethernet and log into the router to check.
42
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
3. Connection to the router from PC wirelessly
Once you have confirmed that the customer can get Internet access via Ethernet and they can
see their SSID in Network Connections, follow on:
Low signal strength? Put the cursor on the wireless icon in the Task Bar and check.
Having low signal strength will cause the customer to have Internet issues. Factors that
can affect wireless signal strength:
- Too many walls in-between the PC and router.
- Other wireless devices close by.
- Position of the router.
- Is the router far from the PC/notebook? If possible move them closer.
- Customer can use a signal booster. (bought from computer/electronic shops)
Try another wireless adapter or reinstall USB drivers (if using USB adapter)
Could be issues with their encryption.
- Are they using the right key? Is it a customer specified key?
- Is the key saved in the wireless adapter? It could be wrong.
- You can log into the router using Ethernet and change the key.
REMEMBER!!!
TPG Helpdesk has limited support for wireless issues, our first
priority is to make sure the Internet works on Ethernet.
If the Internet works on Ethernet, then it is a wireless issue.
CHANGING CUSTOMER PASSWORD
Customers can change their password by going to the Your Account section on the home page
or you can change the password using IAS under Modify user details.
Changing the password can take up to 1 hour to take effect for the email inbox and 10 to 15
minutes for the Internet connection.
Passwords must be letters and numbers only. Customers going to the Your Account section of
the TPG home page are asked to provide a new password that is between 6-8 characters long
and contain at least 1 numeric number. However, changing the customer password through IAS>
Modify user details does not hold this rule very strict.
Password changes are allowed up to 3 times in 1 day.
When changing a customers master account password, remember that there are many services
that are reliant on this password.
1. Internet Connection
Once customer has changed the password with TPG, their session will continue on their
old password until after the 10-15 minutes.
After 10-15 minutes time, if/when the customer loose the session because they might
have lost sync or power cycled the router, customer will notice connection issues.
This is when the customer must reconfigure the modem/router and change the password
to the new one.
If customer is using a modem, they must dial up with the new password next time they
want to connect to the internet.
43
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
2. Master Email Account
If customer is using the Post Office to access emails, they need to log into their account
with the new password.
If customer is using an email client like Outlook express, customer also needs to change
the password to the new one.
3. Free Web Space
Customers will need to use their new password to be able to FTP to their free web space.
4. VoIP
If the customer has VoIP services, their VoIP password needs to be changed in the
router. Customers need to log into their router to do this.
5. Softphone
If the customer has a Softphone account registered under the master account, then by
changing the password it changes the access to the softphone service.
6. IPTV
If the customer is using the free IPTV service, then by changing the password it changes
the access to the IPTV viewer page.
When To Change Customer Password
Please ensure that you do not use the change of password troubleshooting step as an
easy way out or to get the customer off the phone
Changing password should only be done if:
1. It is a step recommended in this manual (it must be noted that there is a reason why
password resets are done more towards the end of the HD Authentication checklist, so
the stage you do this is important)
2. Customer insists.
3. Customer password has been compromised (someone else may know it).
4. Customer has completely forgotten their current password and has already exhausted
all possibilities.
5. Customer is still using their default password (same as their UN) as generated by IAS
during registration.
REMEMBER!!!
There are many services that rely on the master account password:
1. Internet Connection
2. Master Email Account
3. Free Web Space
4. VoIP
5. Softphone
6. IPTV
Make sure you change the password on the modem/router or advice
the customer about this.
44
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL ENGINEERING TEAM
Handles faults and lodges any fault to Telstra, including ones submitted by HD
Level1(ADSL1) and HD Level2 (ADSL2+).
As Telstra do their tests, they report back to the ADSL Engineering team with updates
and possible instructions they want the customer to carry out. The ADSL Engineer then
updates the logs, which can be found by clicking on the link in Call Tracking.
When Telstra updates the engineer on the situation, the ADSL Engineer will contact the
customer and pass this information on.
The ADSL Engineering team also organize TTFs if necessary
The ADSL Engineering team is open from 8am 6pm (Sydney Time) Monday to Friday.
FAULT PROCEDURES:
When a Helpdesk officer lodges a fault for an ADSL customer, they should advise the
customer:
1. To leave their modem on for the next 48 hours. (It may take up to 48 working hours
until Telstra comes back with a response. During this time, line testing is done. The line
cannot be tested if the modem is off.)
2. Possible Fee for Service by Telstra if they find the problem was in the
customers premise
3. A TPG Engineer will contact them as soon as we have further updates about the
case
When a fault is lodged, it is called an OPEN FAULT. Other faults cannot be lodged if
there is already an existing open fault including Residential Line Faults. This type of
fault is lodged by the customer directly to Telstra when their phone line has a problemnothing to do with ADSL- for example customer has no dial tone. If there is a residential
line fault and the problem is fixed according to the customer, they need to make sure that
it gets closed first before we can lodge an ADSL fault.
ETA for Faults. Telstra usually give us ETAs (estimated time of arrival) every time we
lodge a fault. There is no set period, as it all depends on the area, recent occurrences
(lighting storms) or how much backlog of other faults there are.
The standard ETA is always 48 hours, but many times it does run over. When Telstra
have finished their testing, they will always ring us.
Faults do take time to get fixed. When customers inquire about the status of the faults,
often times we have no updates as yet. From small home users to big businesses, all
faults are handled in the same way.
45
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
If the customer calls Helpdesk, it is the responsibility of each call agent to be able to
identify if the customer has an open fault. Afterwhich, you need to contact the
Engineering Team for immediate transfer to the Engineer in charge of the fault (or
anybody from the Engineering Team if the Engineer in charge is unavailable).
If an immediate transfer is not possible, arrange a callback with the customer. Take note
of the caller's name, callback number and availabitlity time/date for callback and send an
email to:
Email: adsl_faults@tpg.com.au (Do not give this address to the customer)
Subject Format: Fault Update: <username> Attention: <engineer's login name>
CC: Engineer in charge of the fault
When the problem is fixed the FAULT IS CLOSED or it is a CLOSED FAULT.
Sometimes open faults have a COB. This stands for Close of Business (usually 5pm
Sydney time), this is when the fault will be closed. Once the fault is closed, Telstra will not
revisit this case unless another fault is lodged.
46
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
If a Closed Fault reoccurs within 20days with the same issue, the case can be re-lodged
immediately. The original escalated case will be reopened and case ownership will
automatically be given to the last ADSL engineer who held case ownership.
Initial troubleshooting should still be done to identify if the case is of the same nature as
the previously escalated case. Proper documentation of the findings and
recommendation for immediate re-endorsement to Engineering must be included in the
case notes. Immediate escalation to ADSL Engineering must be done through an email.
Email: adsl_faults@tpg.com.au (Do not give this address to the customer)
Subject format: Fault Re-escalation < CID >.
A note must be included in the body in regards to the details of the re-escalation. The
contents must be able to answer the following questions:
1. Is the case within the 20 day monitoring period?
2. Is the service experiencing the same symptoms as compared to the previously closed
fault?
What if a Telstra Tech calls the HD?
When Telstra Tech's need to contact ADSL Engineers to update on an ADSL customers fault,
they call the Telstra Queue on 02 9850 0811. However, sometimes the tech might call the ADSL
queue (unlikely the dial up queue).
Please follow these instructions if you get a call in the HD Queues from Telstra Tech's. Please
DO NOT try to handle the call.
If you get a call from Telstra:
A. Monday - Friday: 8am - 6pm Sydney Time
Get the service number of the customer that the tech has called about
Look up the service number in IAS to find the username
See if an ADSL Engineer is available to take the call then transfer
Log the call in Call Tracking
B. Other times After 6pm Sydney time or anytime over the weekend
Please advise them that the ADSL Engineering department is now closed
Give them the following number 02 9850 0811. This is the Telstra Queue. Advise them to
either:
1. Call back during the opening hours to talk to an Engineer or
2. The Telstra Tech can actually leave a message on the answering machine and
the ADSL Engineer, if needed, will call the Telstra Tech on the next business day
Get the service number of the customer that the tech has called about and look up the
service number in IAS (ADSL Service Number) to find the username
Log in Call Tracking to say that you advised the tech to call back during opening hours or
leave a message on the answering machine
Send an email to:
Email: adsl_faults@tpg.com.au
Subject Format: Fault Update: <username> Attention: <engineer's login name>
CC: Engineer in charge of the fault
47
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
GENERAL RESPONSES FROM TELSTRA
Here are some common terms used during investigation:
Appointment
Issue is not certain to be considered as a line problem. Service needs to be proven
further. Customers are advised to be at the premise but they too should be aware of any
possible FFS.
Typical appointment times are: 8am-12 noon, 10am-2pm or 1pm-5pm (customers local
time)
BBHD, Broadband Help Desk
Telstra Staff 1st level who generally lodges faults and inform us of any updates to faults.
COB, Close of Business
Usually 5pm Sydney time. This is when the fault will be closed.
Commitment
When line problem is evident. Field Technician is assigned to check on the customer's
line condition. As Telstra has advised, it is not necessary for the customer to be at the
premise while line checks are being done.
FFS, Fee for Service
Fee for service is usually charged if Telstra has already been to the NBP and they make
an onsite visit
Fee for service is not charged if it is a Telstra issue, i.e. line quality issues
Fee for service will be charged if it is any other kind of issue i.e. filtering issue, modem
issue, user configuration, premises wiring issues, alarms, PABX/Commander systems
NBP, Network Boundary Point
It is the point that separates Telstra equipment and the customer. This would be the point
where the main line gets connected to the premises. When a TTF is sent, they start at the
local exchange and move closer to the NBP. The technician has to prove service is
working before he leaves the NBP (i.e. pings)
Rebuild
Reprograms all the information at the exchange
Usually performed by the specialist after 24-hour monitoring of the connection
Reset
A line reset is generally performed when the fault is lodged
It resets the link between the gateway at the exchange to the point just before our routers
SP, Telstra Fault Specialist
2nd level staff that does the ADSL testing remotely.
Target Restoration Date
This means that the Telstra specialist will have had a look at the fault by this time but
does NOT necessarily mean a fix has been found.
TTF, Tech to Field
Telstra will first go to the exchange and see if they can get the service working. If they
need to do further investigation, they may possibly need to go inside the premises
(onsite visit)
A Telstra technician will try to go out to the network boundary and try to prove service is
working from there.
48
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
When a TTF is set, it is required to have a person over 18 years at the premises.
When a TTF is set, an onsite visit is not always done, only if the technician feels it is
required.
When the TTF goes onsite, they do not help the customer set up. They plug in their own
equipment and laptop. If it works, they show it to the customer and informs us that it
works (pings) and leaves. Fee for service may be charged. This charge will appear on the
customers next Telstra bill.
Typical appointment times are: 8AM-12NN, 10AM-2PM or 1PM-5PM (customers local
time).
Please note: If the customers original appointment is set for the following and wants to
reschedule:
8:00AM -12:00NN (customers local time) they must let us know by 18:00 (Sydney time)
the day before
10:00-14:00 (customers local time) they must let us know by 8:00 (Sydney time) the
same day
13:00-17:00 (customers local time) they must let us know by 10:00 (Sydney time) the
same day
ESCALATION TEAM: LEVEL 2
Telstra no longer take responsibility for ADSL2+ customers Internet faults, unless Telstra
is at fault. This would have to be proven by Level2 or TPG ADSL Engineers.
Level 2 will run tests and take necessary action to get the problem fixed. They will even
call the customer to see if what they have done has fixed the problem or not.
If Level 2 sees an obvious Telstra issue or simply cannot fix the problem, it needs further
attention of the ADSL Engineering Team.
- If our TPG ADSL Engineers cannot get the connection working, they will either request
for a TPG TTF in the customers city to go out (Our engineers in Australia will be assigned
this task) or if it was an obvious Telstra issue, they would lodge a fault to Telstra.
- If a TPG TTF is to be set, our engineers in Australia will contact the customer to
organise a time and day.
- The TPG TTF will visit the exchange and/or NBP. If there is a need to visit onsite,
customer will be contacted.
- At the moment there is no fee for service although we still tell customers that it may
apply.
ESCALATION PROCEDURES:
When a Helpdesk officer escalates the case for an ADSL 2+ customer, they should
advise the customer:
1. To leave their equipment on for the next 48 working hours for testing to be done.
2. A TPG Level 2 Technician will contact them as soon as we have further updates about
the case.
49
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
If the customer calls Helpdesk, it is the responsibility of each call agent to be able to
identify if the customer has an Open Escalation. Afterwhich, you need to contact the
Escalation Team for immediate transfer to the L2 in charge of the Escalation (or anybody
from the Escalation Team if the L2 in charge is unavailable).
If an immediate transfer is not possible, arrange a callback with the customer. Take note
of the caller's name, callback number and availabitlity time/date for callback and send an
email to:
Email: orchidl2@tpg.com.au (Do not give this address to the customer)
Subject format: Escalation Update: <username> Attention: <L2's login name>
CC: L2 in charge of the escalation
If a Level 2 Case reoccurs within 20days with the same issue, the case can be reescalated immediately. The original escalated case will be reopened and case ownership
will automatically be given to the last escalation staff that held case ownership.
Initial troubleshooting should still be done to identify if the case is of the same nature as
the previously escalated case. Proper documentation of the findings and
recommendation for immediate re-escalation to Level 2 must be included in the case
notes.
Immediate re-escalation to Level 2 can be done through the escalate folder in call
tracking.
Please remember that if the customer has any issues with their phone line quality, they
must report this first to Telstra. For example when the customer has no dial tone from any
wall socket in the premises or when the line has static even when the modem is not
connected to the line.
Please note that it may be possible for the line to have no dial tone yet the Internet
remains unaffected. In this case customer must report no dial tone to Telstra.
Examples of when customers must speak to Telstra first:
1. Customer has no dial tone or intermittent dial tone.
2. Customers line has static and it effects their Internet when this static begins.
3. Customer has Internet but no dial tone.
4. Customer cannot receive or make phone calls (whether or not there is an issue on the
Internet side)
50
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL ADMIN AND LOGISTICS
The roles of ADSL Admin:
Billing of ADSL customers
Receive customer requests for:
1. Relocation
2. Package Changes Speed changes possibly
3. Cancellation
4. Purchasing of ADSL equipment
5. ADSL Reconnections
Process any fees for certain requests made
Forward appropriate requests to ADSL Logistics processing
For most of these processes, customer must email ADSL Admin at
adsl_admin@tpg.com.au
The Logistics Team:
The Logistics Team has many different roles. Many of which involves:
1. Submitting to Telstra the installation for new ADSL and ADSL2+ account holders.
2. Submitting to Telstra changes that the customer wants to make to their account.
Nearly all changes to a package need to be done by Telstra. Except changes that leave
the customer on the same speed, location and ISP.
For most of these changes, the customer must email ADSL Admin so as the account can
be billed accordingly. Once that has been done, ADSL Admin may request Logistics to
submit this change to Telstra.
The Logistics Team has a queue. This is an INTERNAL queue/department only.
Customers do not talk to Logistics. If you have a query, place the customer on hold
and talk to a Logistics agent (*03010) or send an email to
orchid_logistics@tpg.com.au.
For existing ADSL and ADSL2+ customers ADMIN and Logistics are involved with the
following:
1. Change of Lessee
When the customer changes the name on the Telstra bill it may effect the codes on the
line and so the Internet.
Customers need to talk to CS to apply for a reactivation of the line.
Normally takes 1-2 working days.
2. Change of Location (COL) - ADMIN process these
Moving the ADSL service to another number or location. This includes:
1. Changing their service number and moving address or
2. Changing the service number but staying at the same address or
3. Moving address but keeping their service number. Customer needs to move their
number first (Telstra does this) and then they apply for COL with TPG.
Customers must first email adsl_admin@tpg.com.au with their request.
Admin will process the application. Once Admin receives the request:
- They submit this to Telstra. It will take 3-5 working days from this day for the completion.
- Once completed, the customer gets billed for the COL.
- IAS Parameters will be changed.
51
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
- The old number/location will loose the ADSL service automatically.
If the customer is doing case 1 or 2 they would not loose their old Internet connection
(This is called Zero Downtime). This is assuming the old number is still active. Remember
if there is no line, there is no ADSL!
If they are doing case 3 - Moving address but keeping their service number customer
will loose the Internet since the phone line was disconnected and moved to a new
location.
3. Reconnection
When the phone line with the ADSL Service number gets disconnected by Telstra and
reconnected again, ADSL service will be interrupted.
For example, Telstra disconnects the line that has ADSL installed due to the customer
not paying their Telstra bill, ADSL service will be dropped.
The customer needs to email adsl_admin@tpg.com.au to go through the reconnection
process.
ADSL Admin will then get Logistics to submit for reconnection.
This process incurs a fee and can take 3-5 working days after Logistics makes the
request from Telstra.
4. Cancellation
When the customer has applied to cancel the account, Logistics will then submit to
Telstra to get the codes cancelled on the line.
The customer needs to email adsl_cancel@tpg.com.au to go through the cancellation.
5. Speed changes
For ADSL1 customers only.
These changes take place because the customer moves to a package that may have a
different speed. (ADSL to ADSL)
There is no downtime for this.
To submit a package change, the customer can talk to CS, apply online or email
adsl_admin@tpg.com.au with their request. Customer may be charged a fee for this.
Once the billing is done, ADSL Admin will request for Logistics to submit the change with
Telstra.
For all these changes, it will take 3-5 working days from the date of submission by
Logistics
6. Churns
Churn to: Customers who want to move their ADSL service from another participating
ISP to TPG. TPG take care of customers who are churning to TPG.
Churn from: Customers who want to move their ADSL service to another ISP
Customer who wants to move to TPG must be eligibleto join TPG ADSL/ADSL2+.
Customers who wants to churn to TPG must meet the following:
1. Customer is coming from a participating ISP. The list can be found at:
www.tpg.com.au/products_services/churn_list.php (for ADSL);
http://www.tpg.com.au/products_services/churn_list.php?type=adsl2 (for ADSL2+)
2. Customers must churn/transfer their ADSL/ADSL2+ connection to the same telephone
number and address.
3. Customers current ADSL/ADSL2+ connection must be active for an ADSL/ADSL2+
Churn to happen. Customers must not cancel the current connection with current ISP
until the transfer to TPG has been completed. Customers must not have a pending ADSL
cancellation order OR a pending service order for any work or additional services on the
telephone line.
The churn process will take a minimum of 3 working days to complete from the time
Logistics submits the application.
52
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Churning to ADSL is free of charge. For ADSL2+, churning will be free to customers who
agree to a minimum of 18 months contract.
Customers can request a CRD (Customer Request Date) where customer nominates the
date for the transfer. This can be done at registration time. CRD must be more that 3
working days but less than 10 working days.
Customer may experience a brief downtime of 4 hours during the churn/transfer process.
This will alert you that the churn is in progress, and that it is time to change connection
settings to TPGs.
7. Modem and Filter dispatching
This is done in the Sydney office.
When the customer purchases a modem/router, Admin will charge the customers
account and send the request to Logistics for dispatching.
All modem/routers are sent with one central filter (Except for the Linksys AM300 which
comes with a basic filter). Customers can purchase any additional filters.
Any equipment purchased is sent to the billing address by default not the site address.
TPG uses the couriers Australian Air Express for modem/router deliveries. Their site
http://www.aae.com.au/ can be used to track and trace the equipment with the
Consignment Number found in the ADSL Installation Status logs.
TPG uses Australia Post if the customer has ordered a filter only.
8. Equipment Testing
This is done in the Sydney office.
During troubleshooting, by following the guidelines for any type of problem, you may find
that the problem may be with the equipment. If so, you must make sure the customer
meets our requirements before they send the modem back for testing.
In all circumstances, you must troubleshoot all possible aspects of the problem by
following the troubleshooting guideline before you assume there may be an equipment
fault. This even includes lodging a fault if necessary. If in doubt please ask your TL or
Floor Supports before you ask the customer to send the equipment for testing.
Please remember we do not test modems that were not bought from TPG.
The Logistics Team returns modem/routers that are tested.
TPG VoIP PRODUCTS
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a revolutionary new technology that
allows users to make telephone calls using a broadband Internet connection (IP to IP
voice communication).
VoIP converts the voice signal from your telephone into a digital signal. This digital signal
travels over the Internet then converted back to voice signal at the other end.
In general, phone service via VoIP costs less than equivalent service from traditional
sources.
To create a VoIP network, a PABX server must be used to connect IP to IP calls. Our
PABX server uses the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
Currently TPG offers these VOIP products:
1. VPC Service
2. ADSL VoIP Service
3. Softphone VoIP
4. Naked DSL VoIP
5. $1 International Call Cap
53
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
VPC
VPC stands for Virtual Phone Card, it is a prepaid phone card service, which can be used
from any landline telephone.
VPC is similar to phone cards that can be purchased from retail outlets however the
details will be issued electronically to customers.
VPC utilizes VoIP technology to convert calls made on the PSTN into digital signals,
which are transmitted over the Internet. This is different to a VoIP service that requires a
call to be made from a computer.
Customers are not required to have Internet connection with TPG to have VPC.
VPC is currently available to anyone located in the locations where there is a VPC
Gateway. Metro areas are the capital cities of the States in Australia. Regional areas are
other cities in each state where we offer this service.
The VPC record is shown in IAS under VoIP details. VoIP usage can be viewed through
the Display usage link.
How to use VPC
Step 1: Dial your local TPG Virtual Phone Card Gateway Number
Step 2: Listen to the prompts, then enter your Access Code and PIN followed by hash(#) key
Step 3: Dial the Destination number
- Eg: For overseas calls, dial: 0011 + country code+ area code + local number + #
- Eg: For STD calls within Australia, dial: area code + local number + #
Gateway Numbers
If customers are located in one of these cities, they dont need to dial the area code for
the Gateway:
54
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Registered Numbers
When the customers number is registered, their Access Code and PIN is automatically
accepted every time they call a VPC Gateway from that registered number. The customer
will then hear an invitation to dial the destination number.
The number that they register cannot be a private or silent number it must be a listed
number in the phone book.
Once there is a registered number, the VPC service will only work on the registered
number.
Registering a number is done by clicking Modify under VoIP Details and entering a
phone number.
Changing PIN
Changing PIN is done by clicking Modify under VoIP Details and entering a new fourdigit PIN.
Advise the customer to wait 15 minutes for the new PIN to take effect.
The only way to check the PIN of a VPC service is to try to login with the Access code
and PIN in the Your Account section of the VPC website.
You can also send a confirmation email to the customer (VoIP Details>Modify>Resend
Confirmation Email). This sends the customer their Access code, PIN and account
balance.
Rates
National Call Rates
For International Call Rates check http://www.tpg.com.au/vccard/callrates.php
55
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
VPC TROUBLESHOOTING
Common VPC problems:
1. If the client is constantly prompted to re-enter their Access Code and Pin (assuming the
number they are calling from is not registered)
Query the Access Code in IAS and confirm the status of the VPC is active.
Make sure that the customer inputs the number not too quickly. If they enter this very
quickly, the VPC gateway will not recognise the access code and PIN.
Did the customer hear a full tone when pressing the numbers on the phone?
If the number is not registered, this means the customer has to enter the access code
and PIN every time they call the Gateway. Make sure the customer enters their access
code and pin in full, followed by the hash key.
Reset the customers PIN via IAS and advise to try again in 15mins.
2. Client hears a prompt saying, "You can not dial this number"
Most likely the customer is trying to dial a number that is not supported on the VPC
service. Remember when calling:
a. Local number in Australia, you must always include the area code first.
b. International numbers, you must dial 0011 to get a line out of Australia, then dial the
country code followed by area code and the number.
c. Mobile numbers, you simply dial the mobile number. There is no prefix.
Ensure the telephone number can be dialled through our VPC service through the VPC
website. Go to http://www.tpg.com.au/vccard/calling_rate.php to do a Quick Search.
Query the number the customer is trying to dial (international, national or mobile). If you
can query this, it will either give you an error message that this number is not supported
on the VPC service or it will tell you the cost involved which means this number is
accessible on theVPC service so make sure that the customer is dialling the correct prefix
and number followed by the # key.
3. Client hears nothing after dialling the VPC Gateway Number
Check if the customer has problems dialling other non-TPG numbers. If this is the case,
this means they have problems with their phone line, nothing to do with the VPC service.
Please ask them to contact their telephone provider.
Check if there is a current outage.
4. Customer hears: "Your Account Balance is too low to make a call
Query the customers Access Code in IAS. Under the VoIP Details section:
a. Check the VPC balance. If there's no more balance, transfer to CS.
b. Make sure the status of the VPC is Active.
If the customer has just spoken to CS and has already topped up their VPC account and
they are still getting a message, please make sure they have waited 15 minutes for the
system to update.
Make sure there are no VPC issues.
56
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
5. Customer hears: "Your Access Code or PIN Number is Invalid"
Query the Access Code in IAS and confirm the status of the VPC is active.
Possible that the customer has incorrectly entered their access code or PIN.
Check the customers access code and PIN by logging in with their credentials at the
"Your Account" section of the VPC website.
If you are successful then the Access code and PIN is correct. Get the customer to try
again making sure they are pressing the numbers correctly on the phone followed by #.
If they have already done, this reset the PIN using IAS If you are not successful then the
Access Code and PIN are incorrect. Reassign a new PIN using IAS - 4 digit number.
Please remember, PIN changes take up to 15 minutes to go through.
6. Still having problems? VPC Fault Escalation
Email: vpc_faults@tpg.com.au
Please make sure you ask and collect the following information from the Customer before
emailing:
- Customer's name and contact details (email as well if possible)
- Customer Access code and PIN
- Which Gateway was the customer calling (eg: Sydney, Melbourne)
- The phone number customer was trying to call
- Time of customer's call
- Any error messages received
TPG ADSL VoIP Service
ADSL VoIP uses an ADSL VoIP modem/router to connect to the TPG VoIP network.
When customers join any one of our ADSL VoIP packages, they need to purchase the
VoIP modem/router from TPG. TPG overrides the factory default firmware with our own
version.
TPG currently sells the Dynalink RTA1046VW when customers choose to have our VoIP
product. TPG have sold 4 other models: Zyxel 2602H, Zyxel 2602HWL 61C, Zyxel
2602HWL 61, and Netcom NB9W.
We use the G.723 or G.729 codec for voice compression and so any device that
connects to our VoIP service must support these codecs and SIP protocol.
The VoIP phone number is the same as the ADSL service number. Customer connects a
phone (standard or cordless) to the VoIP modem/router to make/receive VoIP calls. No
need for filters. All other phones/devices running on the ADSL service number needs to
be filtered since they will be using the Telstra PSTN service.
Remember: This product is a cost saving product to the customer but does not replace
the regular PSTN service.
ADSL VoIP service count towards the monthly usage. As a rough estimation, using VoIP
consumes 0.6 Megabyte for every 10 minutes of conversation, assuming Standard
(G.729) voice compression.
VoIP Details
All customers who register for VoIP should have a VoIP record in IAS.
57
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
This would tell you which SIP server the customers VoIP registration is found. Customer
must use this information in the VoIP configuration. Currently we have 6 SIP servers,
aphone1 to aphone6.
VoIP usage can be viewed through the Display usage link under VoIP Details. Free
VoIP calls made to other TPG VoIP customers are not recorded in the system.
Every VoIP customer has an Access Code however this is not used for VoIP purposes
and customers are not advised of this code.
Set-up
To be able to make VoIP calls, the modem/routers VOICE side has to be configured and
connected to the voice servers (Aphone). The normal username and password is
needed to be able to do this no need for the PPP or L2TP extension. The WAN side
must still hold the customers UN (with extension if for ADSL) and password for the
connection.
All VoIP modem/routers purchased from TPG are sent to customers pre-configured on
both the WAN side (for the Internet connection) and the VOICE side (for VoIP).
Example:
SIP Registration Address = aphone4.tpg.com.au (found in IAS under VoIP details)
SIP Outbound Proxy = aphone4.tpg.com.au
SIP Proxy Server Address = aphone4.tpg.com.au
Phone Number = TPG Username (without PPP or L2TP extension)
Caller Name = TPG Username
Username = TPG Username
Password = Current TPG password
Dial Tone
PLEASE NOTE: The VoIP dial tone and PSTN dial tone are very different. Please ensure
customers realize this before making calls and they realize which service they are using.
Make sure you mention this every time you are dealing with VoIP customers. Generally,
the VoIP dial tone is deeper than the PSTN. In the case of the RTA 1046VW, the VoIP
dial tone is choppy unlike PSTN which is a continuous tone.
58
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
PSTN Lifeline
By default, the phone connected to the VoIP router is for VoIP calls only. The PSTN
Lifeline is a feature on a VoIP router that allows users to make and/or receive PSTN calls
on the phone connected to the VoIP router. The phone connected to the VoIP router will
operate on the PSTN line when the VoIP router is off or when the call is coming from
another PSTN. In this case, they will not be using the VoIP services. Telstra would
charge for any calls made.
Making Calls & Call Rates
TPG ADSL VoIP Service cannot be used to make calls to numbers starting with 1800,
1900, 0500, 13 numbers or for operator-assisted calls.
Using the TPG VoIP service, customers are unable to dial 000 - for emergency
When making a call to:
- Any landline in Australia - 10cents flat rate
dial <area code><phone number>
- International Numbers - Great international rates to selected countries
dial 0011 <destination country code><area code><phone number>
- Australian mobiles 28cents per minute
dial <mobile number>
- Another TPG ADSL VoIP user FREE
dial <area code><phone number>
TPG ADSL/VoIP and ADSL2+/VoIP bundle packages
Customers on bundle plans must purchase the VoIP modem/router offered at the time.
Comes with Free talk time minutes (500) each month.
Customers can use free minutes to call Sydney, Melbourne, Perth, Adelaide, Brisbane
and Canberra.
Customer cannot use these free minutes to call Australian mobile numbers or overseas.
Free calls are calculated with a minimum call time of 10 minutes and thereafter in 1
minute increments.
TPG will debit customers credit card $20 for prepaid call credit to cover calls outside the
free calls, e.g. international and mobile calls.
Once this falls below $5.00, their account gets topped up again with $20. With each top
up, credits are valid for 12 months.
Add-on VoIP Plan
For existing TPG ASDL or ADSL2+ customers; no need to change to a VoIP plan if
current plan does not come with VoIP; not offered to customers with other providers.
Customers registering for Add-on VoIP plan must still purchase the VoIP modem/router
offered at the time if they have not purchased a VoIP modem/router from TPG in the past.
Does not come with free talk time.
Same rates apply for VoIP calls that are bundled with ADSL/2+ plans.
No lock-in contract, customer can cancel the Add-on VoIP without affecting their Internet.
No extra fees - no monthly access fee.
TPG will debit customers credit card $20 to use to pay for the calls made. Once this falls
below $5.00, their account gets topped up again with $20. With each top up, credits are
valid for 12 months.
59
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
VoIP Modem
Codec
SIP/Aphone server
Lifeline
VoIP to PSTN
Zyxel 2602H
(non-wireless)
G.723
Aphone 1 & 2
None
None
G.723
Aphone 1 & 2
Zyxel 2602HWL 61C
(with 1 antenna)
V-cable
Green: Lifeline
Gray: DSL
Dial * OR 0000
V-cable
Gray: Lifeline
Black: DSL
Dial * OR 0000
G.729
(with sticker)
Aphone 3 to 6
Zyxel 2602HWL 61
(with 2 antenna)
G.729
Aphone 3 to 6
Netcomm NB9W
G.729
Aphone 3 to 6
Labeled Line
Dial ##
Dynalink RTA1046VW
G.729
Aphone 3 to 6
Labeled PSTN
Dial ## - you will hear no
PSTN dial tone after
60
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
VOIP TOOL
The VoIP Tool is used to see if a VoIP customer is connected to the VoIP servers.
(Frontoffice>Misc>Help Desk Tools>VOIP Tools)The customer must have a VoIP Record in IAS
under Service Type.
1. Customer is registered/connected to a voice server
Example: UN: sony1309
[aphone1]...
[aphone2]...
[aphone3]...
sony1309/sony1309
60.242.90.69
5060
OK (62 ms)
[aphone4]...
[aphone5]...
[aphone6]...
This shows that the VoIP is currently connected on aphone3. In IAS, you will see that Service
Type is aphone3 and so in the modem/router settings it should have aphone3.tpg.com.au.
2. If you were to search a username and you found no results:
61
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
[aphone1]...
[aphone2]...
[aphone3]...
[aphone4]...
[aphone5]...
[aphone6]...
If the customer does not have VoIP record in IAS, they need to talk to CS.
If the customer does have a VoIP record in IAS, reset the password to something different.
3. Customer is not registered/connected to a voice server
Example: UN: kamran78
[aphone1]...
[aphone2]...
[aphone3]...
kamran78/kamran78
(Unspecified)
UNKNOWN
[aphone4]...
[aphone5]...
[aphone6]...
This shows that the VoIP is not currently connected on aphone3. However, if you look in IAS, you
will see that Service Type is aphone3 and so the modem/router settings should have
aphone3.tpg.com.au.
4. Customer is experiencing bad quality VoIP
Example: UN: liukim83
[aphone1]...
liukim83/liukim83
60.240.191.113 D
5060
LAGGED (2744 ms)
[aphone2]...
[aphone3]...
[aphone4]...
[aphone5]...
[aphone6]...
VOIP TROUBLESHOOTING
62
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
1. No/Busy Dial Tone OR Cannot make any VoIP calls
a) Check if the customer has sync, authenticated and can browse. If not, follow normal
troubleshooting. Make sure the customer can use the Internet before you continue.
b) Check if customers VoIP is registered.
If customer is not registered:
Check VoIP settings on the modem/router
- Make sure the customer has the correct aphone server address. Check IAS.
- Make sure the UN is correct (no extension required)
- Verify the PW in Call Tracking
Get the customer to re-enter VoIP settings and try again
Reset and Reconfigure the modem/router (both WAN and VOICE) from factory defaults
Reset the customers password to something different through IAS do not forget to
change the PW on the WAN and VOICE side as they are the same.
If customer is registered:
Power cycle the modem
Check the brand of the modem/router and the codec it supports
Make sure IAS has assigned the correct aphone server for the customer. If this is wrong,
talk to your TL to get it fixed then re-enter the correct server name in the VoIP settings of
the router
Check VOIP settings on modem/router if you have not done so
Try plugging phone into a different port at the back of the modem/router
Try plugging in a different phone
For the Zyxel 2602HWL 61C, check that Phone port light on modem/router if it flashes
when you pick up the phone handset If it does not, then possible modem issue.
Reconfigure from factory defaults
If no results:
Check if customer has a VoIP record in IAS. Make sure you see the VoIP Details
If customer does not have a voice record or it shows a VPC record instead of VoIP
record in IAS, consult your TL or Transfer the customer to CS to get this fixed Customer
can try again in about an hour or so.
Once the record has been created, the customers modem/router should connect to the
VoIP service.
If customer has a VoIP record in IAS and still Helpdesk Tools is not returning a result:
- Reset the password in IAS to something different. Do not forget to change the
password in the modem/routers WAN and VOICE side.
- Customer would need to wait up to 15 minutes and try again
c) Consult your TL or Floor Support or send an E-mail to vpc_faults@tpg.com.au
2. Customer cannot make outgoing VoIP calls to a particular number
a) Check that customer is using the correct prefix
Metro / Regional / VoIP to VoIP area code is needed
National Calls (Destinations outside Metro and Regional areas) call needs to be made
with international prefix: 0011 61 <area code> <number>
International calls - 0011 <country code> <area code> <number>
Mobile calls - does not need a prefix
b) Check for any outages
63
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
c) For Zyxel routers, reduce the Dialling Interval in the router from default value 5 to 3
seconds. This is the time the modem/router waits before it dials the numbers pushed on
the phone handset.
d) Can the customer make the call using Telstras service? Possible destination issues.
e) Is the customer trying to call another TPG VoIP customer? Is this customer also
connected to VoIP? Do they have any issues with their Internet/VoIP?
f) Check if this number is valid on the VoIP service.
3. Customer cannot make/receive PSTN calls through the VoIP router
This would usually indicate issues with the Lifeline
a) Zyxel 2602H
This model does not support this function. If the modem/router is off or there is no internet
connection, the phone connected to the router cannot be used for PSTN.
b) Zyxel 2602HWL 61C (Wireless + Lifeline + 1 antenna)
Check that cable is connected correctly
- Gray (ADSL) line is unfiltered, Green (PSTN) line is filtered
- Customer can use a basic filter with a double adapter OR use a central filter
Make sure the Green line is not loose or unplugged
Can the customer get a dial tone? If not, refer to issue #1.
Try to make a PSTN call from the Zyxel router:
1. Manually:
- Press the star key (*) or dial 0000 on the phone handset. This prefix can be
changed in the routers Lifeline section
- Wait for 5 seconds and you should hear the PSTN dial tone
- The line goes back to VoIP once the phone is placed back on the cradle
NOTE: You can specify phone numbers that will automatically use PSTN when dialled
from the VoIP phone. This way, it is not necessary to dial the PSTN prefix before dialling
the number.
2. Or the router needs to be switched off or not online for a PSTN call to be made from
the phone thats connected to the router
Try to connect the phone to the other phone port at the back of the modem/router
Try to connect another phone to the router
c) Zyxel 2602HWL 61 (Wireless + Lifeline + 2 antenna)
The functionality and setup of the lifeline is the same as the Zyxel 2602HWL 61 except
that the Lifeline cable is GRAY (must be filtered) and the DSL sync line is BLACK
(must not be filtered).
Follow the suggestions as above.
d) Netcomm NB9W (Wireless + Lifeline)
There are 2 ports labelled LINE and ADSL. The LINE cable must be filtered. This
connects on the Phone port on the Central Filter.
The ADSL cable gives sync and must not be filtered. This connects on the ADSL or
Modem port on the Central Filter.
The same can be achieved by using a basic filter and a double adapter.
64
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
e) Dynalink RTA1046VW (Wireless + Lifeline)
There are 2 ports labelled PSTN and DSL. The PSTN cable must be filtered. This
connects on the Phone port on the Central Filter.
The DSL cable gives sync and must not be filtered. This connects on the ADSL or
Modem port on the Central Filter.
The same can be achieved by using a basic filter and a double adapter.
4. Poor quality VoIP calls
a) Check if there is an issue caused by the ADSL connection e.g. intermittent sync, data
flow, and speed issues?
b) Is the customer throttled? This will affect the VoIP quality since they have low connection
speeds.
c) Check for high bandwidth being used. Disable any uploads or downloads being done.
This might be the cause of the problem. In the VoIP Tools, if you see the status
LAGGED instead of OK, this means that the voice service is being affected most
probably because of high bandwidth being used. Make a note of the milliseconds (ms)
reported and the status.
d) Check for any outages
e) Move the VoIP phone away from the modem/router
f) Virus issues on the PC?
g) Try to connect and use another phone possible phone issues.
h) Can the customer hear other VoIP customers conversations? Consult your TL or Floor
Support or send an E-mail to vpc_faults@tpg.com.au
5. Customer gets prompted for Access Code and PIN after they pick up the phone that is
connected to the router
All VoIP customers have access to the TPG VPC service although this is not advertised
as part of their package. They have an Access Code and PIN which can be found in IAS
under VoIP Details.
If the customer gets prompted for this Access Code and PIN, by pushing these numbers
on the phone the customer should get connected to VoIP service, however this is not
normal. The reason this happens is because the routers VOICE side is not connected to
the Voice servers.
a) Make sure customer can get Internet access if not troubleshoot this first.
b) Make sure the customer has the correct type of VoIP Service record in IAS. If not, then
your TL can help to get this fixed.
c) Check that SIP1 is the selected account.
d) Check VOIP settings on the router. Check the username and password on the VOIP
settings on the router.
- Make sure the UN is correct (no extension required)
- Verify the PW in Call Tracking
- Get the customer to re-enter and try again
e) For Zyxel routers, make sure that Send Caller ID is checked.
f) Hard reset then reconfigure the router (both WAN and VOICE).
g) Try resetting customers password to something different through IAS do not forget to
change the PW on the WAN and VOICE side, as they are the same.
h) If the customer still cannot get registered, consult your TL or Floor Support or send an Email to vpc_faults@tpg.com.au
65
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
TPG SOFTPHONE
TPG Sofphone service is a software that is to be installed in the customer's PC, similar to
Skype. When customers register for Softphone, they would need to download the
Softphone client from the TPG website. It is approximately 2.5MB in size.
Suitable for existing broadband users (TPG or non-TPG) with a minimum speed of
512kbps download and 128kbps upload.
Microphone and speakers or headset is required.
Requires Windows operating system.
Ethernet connection is recommended.
Customer will have a VoIP record in IAS under VoIP details.
When customers register, TPG will initially debit $20 for VoIP pre-paid call credit to cover
calls outside the free calls. When the VoIP call credit falls below $5.01, TPG will top up
the customers prepaid call credit by automatically debiting the customers credit card $20.
TPG will send the customer electronic confirmation of any such automatic debit.
Any unused call credit will expire 12 months after service activation. However, each top
up of call credit will commence a new 12-month period. Expired call credit will not be
refunded.
The customer will have a phone number so as other TPG Softphone customers can
call. This phone number will be zero (0) followed by the Customer ID. For example, if the
Customer ID is 2594769 then the phone number is 02594769.
Softphone services counts toward the monthly usage. It uses the G711 codec and
approximately consumes 600KiloBytes per minute each way conversation.
For existing customers of TPG, the password is the same for both Internet access and
Softphone. If this gets changed, it affects both Internet and VoIP services.
To use Softphone, customer needs to authenticate:
ACCOUNT = Customer ID with a leading zero (0).
- For existing TPG customers it would be their current Customer ID, they CANNOT
use their Internet username.
- For non-TPG customers it would be the Customer ID given at registration time.
PASSWORD:
- For existing TPG ADSL/2+ customers it would be their current Internet Password.
- For non-TPG customers it would be what they nominated at registration time.
NOTE: Customer has the option to save their credentials so as next time they run the
Softphone client, it will not ask for these details.
66
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
There cannot be more than one Softphone record under one Customer ID since this
would cause authentication issues. If a customer is already registered and wants to
register the second Gphone account, it would be found under a different Customer ID.
Customers can use the Softphone and PSTN service at the same time since calls made
on the Softphone service uses broadband connection. Your telephone provider will
charge calls made when using your PSTN line. Calls made using the TPG VoIP
Softphone service will be charged by TPG.
If the customer is an existing TPG customer by default, their VoIP record is found under
the same Customer ID as their Internet. If the Internet account is inactive for some reason
but the GPhone account is active and still has credit, customers are allowed to use the
VoIP service as long as they have access to Internet connection that meets our
requirements
Making Calls & Call Rates
Softphone is for making outgoing calls. At the moment the rules for making calls is
exactly like TPG ADSL VoIP, i.e. Metro, Regional, Other areas in Australia with
international format, mobile and overseas. The costs are the same. TPG Softphone to
TPG Softphone is for free.
Using Softphone to call TPG ADSL VoIP Access code or Customer ID cannot be done.
Calling 1800, 1900, 0500, 13 numbers or operator-assisted calls and 000 for emergency
is not supported. Customers are advised to keep their current fixed phone line. The TPG
Softphone VoIP Telephone Service is NOT a substitute for a standard (PSTN) telephone
service.
To call another TPG Softphone customer:
- Dial the start key (*)
- Dial zero (0) followed by the Customer ID
- Press the Dial icon
To make a call to a non-TPG Softphone customer:
- To call an Australian fixed line (Metro and Regional), dial
<Area Code> <8 Digit number>
- To call an Australian fixed line (non Metro and non Regional), dial
0011 61 <Area Code> <Number>
- To call an Australian mobile, dial
<Mobile Number>
- To call an International number, dial
0011<Country Code><Area Code> <Number>
- After you have finished collecting the numbers, press the Dial icon
67
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Factors that can affect the Softphone service
TPG Softphone VoIP service is subject but not limited to a number of factors that may be beyond
our control. These factors include:
Customers broadband internet connection
Broadband speed issues
Other carriers
Electrical supply to the router
Congestion and other factors beyond control of the service provider
Computer, operating system, hardware issues
If the customer has any problems with their Internet service and they are not with TPG,
you do not help them in any way. Advise to speak to their ISP.
VoIP TOOL
We have a VoIP Tool that works very similarly to the current VoIP tool for ADSL VoIP. By
querying the Customer ID, you are able to check if the customer is connected to the GPhone
server. There is only 1 GPhone server.
1. Successful connection:
gphone1...
02527333
60.240.29.234
1265
OK (90 ms)
UNKNOWN
1265
2. Customer not online:
gphone1...
03140506/03140506 (Unspecified)D N
3. No GPhone record:
gphone1
4. VoIP Quality Issues:
gphone1...
02527333
60.240.29.234
LAGGED (90 ms)
Multiple Sessions of Softphone Client using the same account
Customers will be allowed to install the Softphone client on more than one Windows
computer/notebook being used on their network. Multiple sessions/logins are allowed at
the same time using the same account to make calls outside your network. Credits will be
deducted from the account with each use of the service.
Please remember that this service is not a PABX system, it is not designed to make calls
to other specific softphone clients in a network. If the clients are all connected using the
same account and if the customer calls their Softphone phone number, the only client
that would ring would be the last that registered.
68
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
SOFTPHONE TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Voice Quality Issues - If the customer has voice quality issues this may be caused by IP path
to the TPG VoIP server is dropping or excessively delaying packets.
Make sure customer is not on wireless (between modem/router and PC).
Check for any VoIP outage.
Does the VoIP tool show lagged?
Ask the customer to stop any Internet activity including downloads on the computer
check for programs running - and try to make a call
Is the customer experiencing any Internet issues? Speed issues? Speed shaping?
Close the softphone program and reopen.
Possible microphone issues?
Possible speaker issues?
Speakers too close to the microphone?
2. Authentication Issues
Check the status of the VoIP record in IAS, if inactive transfer to CS.
Is there credit on the account? If not transfer to CS.
Make sure customer is not on wireless (between router and PC).
Ask the customer to run the Softphone client and click on the Account PIN icon.
Check the Customer ID, make sure there is a zero (0) in front.
Look up the Customer ID (with no zero in front) in Call Tracking and check the Password,
else use cyberstore or Your Account to try to log on with the credentials. If you can log in
then this is the right PW.
Ask the customer to re-enter the correct Password as confirmed through Call Tracking, in
the PIN field and click Logon to try again.
Reset the password through IAS. This will take approximately 10 minutes to propagate.
Please remember if this is an existing ADSL/2+ customer, you must advise them that
their Internet password will also change. If the customer has a router, you must help the
customer to reconfigure their router with the new password.
Close the softphone program and reopen.
Uninstall the client and reinstall again. May be better to get a fresh copy from the TPG
Download site.
Consult your TL, Floor Supports or Email ata_faults@tpg.com.au if still cannot
authenticate.
3. Problems with making calls
Is the Softphone connected?
Make sure customer is not on wireless (bet modem/router and PC).
Is the customer dialling the numbers correctly? What number is being dialled? Is it in the
correct format?
Tyring to call another Softphone customer?
Is the other person connected and the Softphone working properly?
Are they dialling the right Customer ID with a leading * and zero?
Suggest for power cycle on the friends end.
Could be a speaker issue, customer cannot hear the person they are calling. Speakers
off or low?
Could be microphone issue, other side cannot hear the customer. Mic on mute?
If the customer is using their Softphone Phonebook or selecting a recent number that was
dialled from the drop down menu? Ask the customer to manually enter the numbers in the
box and click with the mouse the Dial button.
69
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
ADSL CONNECTIONS WITH ADDITIONAL IPS
Customers on a 2F plan can purchase additional public IP addresses to set up their own
subnet since they may be running web, email or game servers.
Customer needs to have a router
Customers can purchase blocks of 4,8,16,32 or 64 IPs
Additional IP is shown in IAS under Service Details.
The first IP in the block is called the Network ID
The last IP in the block is called the Broadcast ID
The Network and Broadcast ID are not used and whatever remains become usable IP
As a rule of thumb, the next IP after the Network ID is the Subnet Gateway. For example
a block of 8 IP:
60.241.246.232
Network ID
60.241.246.233
Subnet Gateway
60.241.246.234
60.241.246.235
60.241.246.236
IP Addresses that can be assigned to PCs
60.241.246.237
60.241.246.238
60.241.246.239
Broadcast ID
Subnet Mask for these IPs will depend on the number of IP in the block that it came from
Block
4
8
16
32
64
128
256
Subnet Mask
255.255.255.252
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.128
255.255.255.0
Subnet Breakdown
255.255.255.11111100
255.255.255.11111000
255.255.255.11110000
255.255.255.11100000
255.255.255.11000000
255.255.255.10000000
255.255.255.00000000
The starting IP (Network ID) and the subnet mask to be used is found in IAS>ADSL
Parameters under User subnet Address and Netmask respectively.
70
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
SETUP OF ADDITIONAL IPS
1. Make sure the WAN configuration of the ADSL Router is configured with the UN and PW.
2. Make sure NAT function is disabled.
3. Configure the LAN interface of the router to the first usable IP within the range of purchase
(Subnet Gateway). This IP on the LAN interface will act as a gateway IP for all the devices
running off the router.
4. Also make sure the Subnet Mask used is the one assigned to the Additional IP Range.
5. All of the devices connected to the router should be configured with an IP address of the
second usable in the set of Additional IP range and onwards.
6. All devices pointing to the router have their gateway assigned as the LAN IP of the router.
Therefore each device should have the same gateway, which is the IP assigned on the LAN
interface of the router.
Example:
UN: adsl1234@PPP.tpg.com.au
PW: secret
Starting Additional IP Range: 203.120.36.34
Ending Additional IP Range: 203.120.36.41
Subnet Mask for Additional IP Addresses: 255.255.255.248 (as this is a block of 8)
The final result of the setup would look like:
Internet World
TPG Network
Telstra
WAN
UN:
adsl1234@PPP.tpg.com.au
PW: secret
ROUTER
IP: 203.120.36.35
Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.248
PC1
IP: 203.120.36.36
SM: 255.255.255.248
GW: 203.120.36.35
LAN
PC2
IP: 203.120.36.37
SM: 255.255.255.248
GW: 203.120.36.35
PC3
IP: 203.120.36.38
SM: 255.255.255.248
GW: 203.120.36.35
71
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
a) Check IAS Installation Status to make sure the additional IPs have been assigned to the
customer and has not expired.
b) Make sure the customers ADSL connection is working fine
Check they have sync
Check they have authenticated use VPDN
c) If any of the above fail, you must first do normal troubleshooting to ensure customer has
sync and they can authenticate.
d) Make sure the LAN side of the router holds their Subnet Gateway.
e) Ping the Subnet Gateway IP. This should be pingable but if not make sure the LAN side
of the router is correctly configured.
f)
Make sure NAT is disabled on the router.
g) Ping the PC that has been assigned with an IP in the range of IPs purchased.
h) If it is not pingable, check the NIC TCP/IP settings for IP, Gateway and Subnet Mask.
Make sure all these are correct. Subnet Mask must be corresponding to the number of
IPs they purchased (see above table)
i)
Try to hard code the DNS settings on the modem/router
j)
If still no data flow, you can try to put the modem/router back to factory defaults then,
Configure router as per normal (without subnet)
Make sure customer can sync up and authenticate
Check for browsing, if they can browse then the problem could be with subnet
Now try to setup the subnet
k) If it does not work with the subnet (but there was data flow with no subnet) consult your
TL or Floor Support. There could be some sort of routing issue on our end as it is TPG
that should route Layer 2 customers subnet to their Fixed IP.
72
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Naked DSL (ULL)
Naked DSL (also known as ULL - Unconditional Local Loop) is a type of ADSL Internet
connection without having a voice service, service number or a dial tone attached to their copper
line. This means no more ongoing monthly bills for a PSTN service from the telephone provider.
Customers who rent a phone line only for Internet purposes would benefit from this product most.
TPG Naked DSL
When a customer joins a TPG Naked DSL plan, Telstra will physically transfer their
existing phone line into an ULL line and connect this to TPGs DSLAM, allowing for
ADSL2+ speeds. At the time of the transfer, the customer will loose the voice service on
their phone line.
NOTE: Customers registered on Naked DSL can achieve download speeds of up to
24Mbps (Mega bits per second) and 1Mbps upload, depending on many factors such as
distance from the local telephone exchange, EMI (Electromagnetic Interference), the
quality of the copper phone line and broadband equipment used.
Once Naked DSL has been installed, the telephone line becomes a data only line. Dial
tone will be lost and the phone number will be disconnected automatically. No need for
the customer to contact their phone provider.
If customers have any contractual obligations with their phone provider, customers must
call them and ensure the account gets closed after installation.
Once Naked DSL is installed, customers are not able to run any device that requires a
dial tone to operate. This includes: Phones, Fax machines, Back to Base alarm systems,
EFPOS, PABX, Dial security cameras, 56K Dial up modem and Digital Pay TV (for
example Foxtel, will still be ok however services like voting or purchasing box office
movies will not work since these services need a landline phone service).
Since the line will be used only for data, there will be no need to use filters, as there is
nothing to filter. Customer will not have a filter sent when they purchase a router from us.
Who is eligible for Naked DSL?
At the moment this service is for non-TPG customers (also available to TPG DU customers) who
have an active service number that may or may not have DSL service on the line. Customers
must meet the following requirements before signing up:
Must be TPG ADSL2+ eligible
Must have a Telstra line or be part of the Telstra network
Must not have any complex product on the line when order is placed with Telstra
Complex Products
Telstra has a list of products that they call Complex and these services should not be on the
customers nominated Naked DSL number when the application goes to Telstra.
Common Complex products are: ADSL2+, PABX, Securitel (alarm system), Faxsteam Duet (2
numbers on 1 physical line one for the phone and other for fax).
Full list of complex products are available on Telstras site, however most of these will not be
applicable to most customers.
http://telstrawholesale.com//products/docs/teba/networkaccess_ull_productlist.xls
73
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Applying for Naked DSL online
During the rego, customer will be asked if they have any complex product on the Naked DSL
nominated number. They would answer Yes or No. They will be advised not to remove any
complex product from the line UNTIL AFTER a successful SQ result is obtained at which time
customer will be emailed. Customer should expect this email within 24 - 48 hours after the rego
has been submitted.
After the application is submitted by customer:
An SQ check will be done to ensure customer is Naked DSL compatible first.
Within 24 48 hours customer will receive an email with results.
If SQ passes:
- Customers who have indicated that they have a complex product will be given 3
working days to have this removed.
After 3 working days, it will be assumed that the service has been removed and the
application will proceed to Telstra, no need for customer to call or email to confirm.
Telstra will reject applications if the complex product was not removed. Customers are
advised in the email of possible charges if Telstra rejects application however these
charges are not implemented.
Any rejected cases will be handled by Logistics.
- Customers who indicated that they do not have a complex product, will be advised
that their application will immediately proceed to Telstra for ordering.
Once the application has been sent to Telstra, installation is expected to take 10-20
working days later
If the SQ failed, customer will be sent a rejection email and application will be cancelled.
Customers will be asked to agree to the ULL T&C. They need to confirm that they are the lessee
of the line and that they understand that they will no longer have voice service on the nominated
number once Naked DSL is installed.
Scenario 1: Customer has ADSL1 connection with another provider on their service
number.
Remember that ADSL1 is NOT a complex product.
Customer can apply for Naked DSL with TPG.
They do NOT need to cancel the ADSL1 service before application is sent to Telstra.
The disconnection of ADSL1 and installation of Naked DSL will be done at the same time
by Telstra. When Telstra converts the line to ULL, they will notify the customers current
ISP of the move. It is still the customers responsibility to ensure contractual obligations
are finalised with their current provider.
Scenario 2: Customer has ADSL2+ connection with another provider on their service
number.
ADSL2+ IS a complex product.
Customers ADSL2+ service MUST be cancelled before we can send the Naked DSL
application to Telstra.
Customers are not encouraged to cancel their ADSL2+ service before they start the
registration since its after submitting a rego, an SQ is done.
After customer submits their registration, if SQ passes, customer will receive an email
advising to remove the ADSL2+ service from the line. Its important for customer to talk to
their provider to ensure codes are removed within 3 working days of this email. After 3
working days it will be assumed the removal is complete and the application will proceed
to Telstra. If codes were not removed in these 3 days, Telstra will reject the application
and logistics would contact the customer to ask for removal again.
Scenario 3: Customer has an active service number but no DSL connection on this
number.
Customer can apply for Naked DSL with TPG. Customer must meet the requirements.
74
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Scenario 4: Existing TPG ADSL1 and ADSL2+ Customers
Naked DSL is currently not offered to existing TPG ADSL customers.
The reason behind this is because, for existing TPG ADSL2+ customers to apply for
Naked DSL, they would need to cancel their existing service. This means they are giving
up their port and there may be a chance that they will not be able to get another port
reassigned to them if exchange capacity is a problem. In the near future we will have a
port reservation system to allow our existing customers to easily move to Naked DSL.
Making Calls
Since Naked DSL customers will not have voice service on their ULL line, to be able to
make voice calls they need to have access to:
- A mobile phone
- Another landline OR
- TPG VoIP (softphone/Naked DSL VoIP)
NOTE: All existing Softphone rules will apply. Please remember that TPG Softphone has
restrictions when trying to call certain numbers like 000, 1300, 1800, 0500 and operator
assisted calls. This is why its advised that customers have access to another type of
phone service.
After Naked DSL cancellation
If a customer cancels the Naked DSL service, and they would like to get their old service
number back, they can talk to their Telco to see if this is possible.
Looking up the Reference Number
Once ULL application has been submitted, Telstra will respond with a Reference Number
similar to ADSL/2+. This number will be made up of only a few digits (not as long as
ADSL/2+ reference numbers).
You can find the Reference Number in IAS>ADSL Installation Status, under Comments
From Logs.
For example:
N:20091015 174141:sys:Submitted via LOLO by TPG Processing: Ref 8769
You can use the current Telstra Reference Checker in CSWEB to view the status of the
order.
Under the heading Details, you can find information about this account
1. Customer ID
2. Created when the order was placed with Telstra
3. Status status of the application
4. Updated date where the latest log was created. If the above status is Closed this
would be the installation date.
5. ULL Request ID same as the Telstra Reference Number
6. ULL Identifier since there is no Service number after installation, each customer
gets an Identifier. Just another way for Telstra to identify the customer on our DSLAM
since they dont have a service number anymore. This number will replace the SN field in
IAS once the installation is done.
75
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Under the heading Status Updates, you will see logs for:
An order notification is first sent to Telstra
IULL_Notification
- This tells you when TPG requested for the IULL order
- Includes the service number here
IULL_Receipt_Advice
- Confirmation that Telstra has received our request
IULL_Confirmation_Advice
- Confirmation of order
- ULL Identifier is returned
TPG requesting the initial customer cut-off date (installation date)
IULL_Cutover_Notification
- TPG request/ sets the cutover date and time (time and date of the installation
to take place)
- Time is always set bet 8-12noon
- Date is always 6 business days
IULL_Cutover_Receipt
- This indicates that Telstra have received our set cutover notification
IULL_Cutover_Confirmation_Advice
- This indicates that Telstra has accepted the cutover date
TPG retargeting cut-off date (installation date)
IULL_Retarget_Notification
- TPG sets new cutover date and time
- Time is always set bet 8-12noon
IULL_Retarget_Receipt
- This indicates that Telstra have received our set cutover notification
IULL_Retarget_Confirmation_Advice
- This indicates that Telstra has accepted the cutover date
Other logs
IULL_Rejection_Advice
- Application rejected by Telstra
IULL_Withdrawal_Notification
- Indicates TPG has sent a withdrawal notification
IULL_Withdrawal_Confirmation
- Indicates TPG has sent a withdrawal notification and Telstra have confirmed
it
IULL_Completion
- Sent by Telstra to confirm order is now done
- Customer should have sync on the DSLAM
76
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting ULL customer will be done the same way as any other ADSL2+
customer except please remember that these customers do not have a dial tone and so
do not use any telephony devices on the line (like phones, fax, B2B alarm).
However, for verification, we ask customers if they have a dial tone. As there have been
cases that customers still have dial tone and has been causing problems on the internet.
In addition, we also ask if the customer had any problems with their phone line (before
Naked DSL was installed). Take note when it happened and if they reported it to Telstra.
Also take note if the customer is connected to an MDF or not.
There will be no codes to be looking up in Service Configurations, as there is no service
number after installation.
Use the Telstra Reference Number checker we have in CSWEB to look up the status of
the order. ULL Telstra Ref numbers are also known as ULL Request ID. This number can
be found in IAS under ADSL Installation Status.
Normal ADSL2+ DSLAM tools will be available. You can access the customers DSLAM
Manager using the CID or UN.
If all troubleshooting steps according to HD rules and guidelines has been done, lodge a
fault to the Engineering Team. Same fault procedures apply. Include the following in your
case notes (Call Tracking):
- if there is a dial tone.
- if customer had problems with the phone line (before Naked DSL was installed) and if
they reported this to Telstra.
- if customer is connected to an MDF.
Naked DSL VoIP
Naked DSL VoIP uses the Soul VoIP network. Hence, some of the current TPG VoIP
rules/tools may not apply. At the moment, only Naked DSL with VoIP customers will get
the VoIP service through Soul VoIP network (customers dont need to know this).
Naked with VoIP will still be subject to Naked ADSL2+ availability.
Customers will receive a DID (Direct In Dial) phone number. This is a normal phone
number, with area code. Numbers will be assigned according to customers location and
cannot be chosen by the customer. It will be assigned once payment is taken and
customers internet IP is assigned. Having this number means Naked DSL customer can
receive and make calls.
Such a section will be created in IAS that would display the DID number (Phone
Number) and allow for usage to be displayed:
When customers receive a DID number, this is associated with their Internet IP. They can
only use the VoIP service when on an internet connection that uses this IP.
SIP server name will be: tpgvoip.tpg.com.au for all Naked DSL VoIP customers.
77
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Rates
Current VoIP deposit still applies. TPG will debit customers credit card $20 and tops-up
after it reaches $5.
Naked DSL VoIP customers will get 500 free minutes per month. Current free minute
rules apply.
Local and national calls Australia wide
Mobile calls Australia wide
Emergency Calls (000)
18/1800 numbers
13/1300 numbers
Directory Assistance 1223 numbers
- 10 flat
- 28/min (billed by second)
- Free
- Free
- 30 flat
- $1.10 per call
TPG Naked DSL VoIP to TPG Naked DSL VoIP will be FREE (ie DID to DID only)
1900, 19 and 0500 numbers are still NOT supported
ADSL1/2+ VoIP to DID number will NOT be free (unless its part of customers free
500mins)
Router Setup
The INTERNET side will be set-up as per normal.
Setup on the VoIP side will be slightly different:
SIP Registrar Address = tpgvoip.tpg.com.au
SIP Outbound Proxy = tpgvoip.tpg.com.au
SIP Proxy Server Address = tpgvoip.tpg.com.au
Phone Number = DID phone number (found in IAS)
Caller Name = DID phone number
Username = DID phone number
Password = VoIP PW (nominated during rego)
78
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Preferred codec MUST be G729. Customers who has BYO VoIP router must ensure that
their router can support 711 codec as secondary. Normally routers that support G729 will
also support G711.
The Dynalink VoIP router that we sell will be configured to 729 as default and can support
711.
When customer receives and/or makes calls, they could either be using the 729 or 711
codec and so the usage will depend on this fact.
When making and receiving calls customers monthly quota is used. This could be
between 14 40Mega Bytes per hour conversation being deducted from the customers
usage quota.
A recent firmware upgrade was released for the Dynalink RTA1046VW router. This is
needed. When customers buy the router from TPG after the launch of Naked with VoIP,
they will get the one that has the latest version. However, older customers who changes
to this plan will need to update the firmware to ensure correct functionality.
VoIP Tools and Troubleshooting
Normal VoIP troubleshooting rules should apply just remember that the lifeline feature is
not applicable anymore.
We cannot use current VoIP tools through Frontoffice. Instead we have the following
specifically for Naked DSL with VoIP customers (for their VoIP issues only):
a. Change VoIP PW through IAS
- Through the Mobile and VoIP Phone Menu> Change Service Conditions
b. Bar/unbar calls
- Through the Mobile and VoIP Phone Menu> Change Service Conditions
- Outgoing long distance, mobile and international calls.
- This action takes effect immediately when submitted
c. VoIP Usage
- Through IAS under VoIP Details> Display Usage
d. Checking VoIP setup (currently not yet available)
- This will allow you to confirm customer has been setup on the correct IP
- Will show if you customer is authenticated on the VoIP server
Customers are also able to view their VoIP usage, change their VoIP PW and bar/unbar
calls through the Your Account tool.
If a Naked DSL VoIP issue cannot be resolved by Level1 HD, escalate to L2 (remember
this is a VoIP issue not a Naked DSL issue). If the issue is related to Internet connectivity
(Naked DSL issue) current escalation procedures should apply (fault).
79
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
IPTV
IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) allows customers to watch selected TV channels via
their PC/Notebook which are delivered through TPG ADSL2+ connection, without the
need to purchase additional expensive equipment - most ADSL 2+ modems are
compatible for IPTV.
TPG is offering FREE IPTV service to ADSL2+ customers (at selected IPTV enabled
exchanges).
At present we are offering our customers a selection of news, entertainment and lifestyle
channels with a strong worldwide focus allowing customers to view news/programs from
their mother countries.
IPTV will not work on wireless connection.
Requirements:
Must have ADSL2+ connection and sync speed not lower that 3.5Mbits/sec.
Should be on an IPTV enabled exchange.
Modem should support permanent virtual circuit (PVC) and Internet Group Management
Protocol (IGMP).
Computer must be faster than Intel Pentium IV 2Ghz(or any equivalent) and have at least
128MB of RAM.
Registration:
When a customer meets the basic requirements for IPTV, they need to register/sign-up
for the IPTV service.
You may consider disabling any firewall or security software during the registration
process.
The registration process is as follows:
1. Customer must sign-in with their TPG UN and password.
2. Customer must confirm that they meet the minimum hardware requirements and must
agree with the Terms and Conditions.
3. The Video Lan Client (VLC) must be installed. Make sure that the Mozilla plug-in and
the ActiveX plug-in is ticked. The customer will see a test image if the VLC software is
installed properly.
4. Customer must choose a modem and configure it accordingly. If their modem is not on
the list, they should know if their modem supports multiple PVC and IGMP and configure
it accordingly.
5. Once configured, they must confirm that the modem has been properly configured.
They will be able to see another test image and will be directed to the IPTV viewer page.
6. Customer will be logged off automatically and will need to re-login. The registration is
finished and IPTV is ready to use.
80
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Customers can switch channels by clicking the program they want to watch under Your
Channels at the right side of the viewer page.
When a customer registers their IPTV service, it is tied up to their ADSL service number
and address. Hence, the IPTV service will not work on a different location even if it's TPG
internet.
Before registration, an X mark appears right next to IPTV in the DSLAM Manager. It
means that the customer is not provisioned for IPTV. However, seeing a check does not
automatically mean that the customer is already registered. It may also mean that the
customer only tried to register.
If a customer is already registered and an X mark still appears, email the customer's UN
to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au to remove the customer on the registered list. Once
removed, customer can try to register again.
Firewall Issues
Currently we have 9 specific firewall confirmed to interfere with the IPTV service. It is not an
issue with IPTV nor with the Firewall. It is only a matter of allowing IGMP packets to pass through
to ensure IPTV will work and avoid conflicts. Firewalls name are as follows:
AVG
COMODO
KERIO
KASPERSKY
NORTON
SYGATE
ZONE ALARM
Windows XP and VISTA firewall
Windows Defender (Vista)
DISCLAIMER: We do not recommend turning off firewalls. We do this only to show that IPTV will
work when it is shut down. That would prove that the firewall is blocking IGMP Packets, and it is
the reason why the IPTV service is having problem working. We strongly recommend to
customers to contact the firewall vendor to allow IGMP packets to pass through to avoid conflict
with the service.
81
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
IPTV Modem Configuration and Settings
For supported modems, emulators are available at KB. Manuals are available at
http://www.tpg.com.au/iptv/download.php.
NOTE: These are general settings that can be found in most modems. It may differ from one
brand to another. If unsure, we advise the customer to contact their modem manufacturer.
Create a new connection in the modem user interface
Service name: IPTV
Connection/Mode: bridge mode
Encapsulation/Multiplexing: LLC
VPI: 0
VCI: 35
ATM/QoS: UBR
PVC: enabled
An option for IGMP proxy, or multicast proxy should be enabled
VLC Software
The latest VLC software can be downloaded from the VLC site: http://www.videolan.org.
However, IPTV only works properly on VLC version 0.9.9 or lower. Other version of VLC
can be found at: http://download.videolan.org/pub/videolan/vlc/ .
It is recommended to download the VLC version found on the TPG site:
http://www.tpg.com.au/iptv/download.php
Please remember that when installing the VLC software, the Mozilla plug-in and the
ActiveX plug-in must be ticked.
Channel Subscription and Parental Control
Currently, channel subscription applies to the censored channels. When a customer
clicks on the censored channel they will be asked for a Parental Lock. By default, the
parental lock is the same as the TPG account password.
During the subscription process, customers can change the parental lock. By doing this,
customers would need to enter the new parental lock everytime they access the censored
channel. This change will not affect the Internet or the email password.
Customers can unsubscribe the channel by going to the Your Subscriptions tab on the
IPTV viewer page.
When a customer forgets the parental lock, they would need to unsubscribe the channel
then re-subscribe to be able to nominate a new parental lock.
IPTV on Mirror Plans
IPTV service will work on mirror plans that are located on the TPG DSLAM (A2L2)
provided they meet the minimum sync speed requirement of 3.5Mbps.
IPTV on MAC
Always ensure that the customer has the VLC Software installed properly and that the
mac computer is using the right specific plug-ins.
For Mac OS, there is Intel Based and PowerPC Based. We need to verify that the right
plug-ins are installed depending on the type of Mac OS that the customer is using. Intel
based will only work with Intel web plug-ins. While PowerPC based will only work with
PowerPC based web plug-ins.
For specific plug-ins, refer the customer to:
http://www.videolan.org/vlc/download-macosx.html
82
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
IPTV TROUBLESHOOTING
1. Check the minimum requirements:
Check if the customer is on an IPTV enabled exchange. To check go to:
http://www.tpg.com.au/iptv/exchange.php
Must have an ADSL2+ connection with a minimum sync speed of 3.5Mbps. Check if the
line profile has been changed.
Computer must be faster than Intel Pentium IV 2Ghz(or any equivalent)
Modem should support multiple PVC and IGMP.
- For supported modems, emulators are available at KB. Manuals are available at
http://www.tpg.com.au/iptv/download.php .
- For unsupported modems, make sure that the modem supports multiple PVC and
IGMP.
- Below is a list of modems that have been tested for IPTV.
Modem
IPTV
TPG Internet
Supported
IPTV
TPG Internet
Supported
Asus
No
Yes
No
Modem
LinksysAM300
No
Yes
No
Belkin F1PI-241Gau
Yes
Yes
No
I-connect
Yes
Yes
No
Billion 7300
Yes
Yes
No
NetgearModem s
No
Yes
No
Billion 74xx Series
Yes
Yes
No
Netcom m NB1
Yes
Yes
Yes
Billion 5210S
Yes
Yes
No
Netcom m NB5
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dlink Dsl502T
Yes
Yes
Yes
Netcom m NB5Plus4
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dlink Dsl504T
Yes
Yes
Yes
Netcom m NB5Plus4W
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dlink Dsl G604T
Yes
Yes
Yes
Netcom m NB6
Yes
Yes
No
Draytek Vigor 2500
No
Yes
Yes
Netcom m NB6plus4
Yes
Yes
No
Draytek Vigor 2700
Yes
Yes
No
Netcom m NB6plus4W
Yes
Yes
No
Draytek Vigor 2800
No
Yes
No
Netcom m NB9W
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dynalink RTA1320
Yes
Yes
Yes
Speedstream 4100
No
Yes
No
Dynalink RTA1025/1025W
Yes
Yes
Yes
Speedstream 4200
No
Yes
No
Dynalink RTA1046VW
Yes
Yes
Yes
Speedstream 510
Yes
Yes
No
LinksysWAG54GV2&3
Yes
Yes
No
Webexel AL-2108p
Yes
Yes
No
LinksysAG241
Yes
Yes
No
Zyxel(TPGSupplied)
No
Yes
Yes
2. Check if the customer is already registered. Verify if IPTV was working before. Customer
may need to re-register.
3. Check if VLC software is installed and working. If there is no image, uninstall and reinstall
VLC software. Software can be downloaded on the following link depending on the Operating
System being used.
Windows Link: TPG Download Site:
VLC 0.8.6d http://www.tpg.com.au/res/programs/activex/vlc-0.8.6dwin32.exe
For OTHER Operating System:
http://www.videolan.org
4. Suggest to disable firewall. Check if the customer did any OS or any Security software
updates. Disable or check the firewall setting to ensure that IGMP packets are not being blocked
on the machine.
NOTE: Don't forget to mention a disclaimer about firewall/s. We are doing firewall/s check as an
extended help and we must set customers' expectation to a point that they'll understand our
scope of support.
5. Check the video card driver. In some cases it needs to be updated. Display adapter driver
release date should at least be 2005 and up.
To check:
Go to Device Manager
Click the + sign beside Display adapter
Right click on the Display adapter and select properties
83
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Click on the Drivers Tab check the Driver release date.
Or Click Start>Run>type dxdiag
Click on the Display Tab
Check the Driver Release Date
6. DirectX version should be updated. DirectX driver should not be lower than version 8.1 and
better if higher. IPTV and the VLC 0.8.6d requires version 9.0c or higher.
To check: Click Start>Run>type dxdiag
7. Check modem configuration and firmware version. You may need to reset the modem and
reconfigure. Emulators are available at KB. Manuals are available at
http://www.tpg.com.au/iptv/download.php .
We can advise the customer to check if there are new firmware versions for their modem.
8. If the customer already updated the firmware and already used all VLC version and still having
problems, escalate the case. Send an email to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au and provide the
following information:
User name
Exchange
Modem model number
Modem firmware Version
Operating System
Problem encountered
84
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
Common Issues
1. No Image and waiting for IPTV Stream
Check internet connection. Customer should be able to browse.
Power cycle the modem and the computer.
Check DSLAM for sync speed. It should not be lower than 3.5 Mbps.
Check VLC Software. Try playing video from files.
Check computer for firewall. Double check firewall setting and/or disable it.
Check modem configuration.
Re-create IPTV profile.
Escalate to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au.
The DSLAM Manager shows when IGMP packets are being sent. Under Display IPTV
PVC Configuration>Downstream. It will generally display a high value when IGMP
packets are requested.
Run perfmon command to see if IGMP packets are received by the computer. Before
doing this, press stop on the IPTV viewer.
1. Click Start>Run>type perfmon. Look under System Monitor.
2. In the horizontal row of icons, click the plus [+] icon.
3. In the Add Counters dialog window: Select Use local computer counters.
Choose the Performance object: Network Interface.
4. Select the counter: Packets Received Non-Unicast/Sec
Select: All instances of network interfaces.
5. Click the Add button.
6. Now press a channel on the viewer page to start the IPTV stream.
7. You should notice the graph jump up, which means that IPTV data is being
received by the computer. If the IPTV viewer is not displaying the image, it is
evident that some sort of security software is preventing IGMP packets.
85
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
2. Unable to download/install the VLC software/ Browser keeps crashing
Check internet connection. Customer should be able to browse.
Make sure firewall is turned off in the computer.
Optimize browser settings:
- Check browser version
- Clear cache and delete cookies
- Ensure that there is no proxy enabled
- Make sure there is no anti-spyware or pop-up blocker enabled on the computer
Power cycle modem and restart the computer.
Go back to the registration part to install VLC software again.
Try another browser.
Escalate to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au.
Check DirectX and ActiveX driver version.
- Check video card driver version. Both has to be the updated versions depending on the
video card brand.
- Ensure that correct web plug-ins are installed if using a MAC OS or Windows.
Refer to OEM or local tech for further assistance.
3. Losing Internet connection when IPTV is configured on the modem
Power cycle the modem and restart the computer.
Disable firewall, anti-spyware and pop-up blocker software in the computer.
Re-create the IPTV profile.
Change the modem local IP address (ex. From 192.168.1.1 change it to 192.168.20.1)
- Power cycle the modem
- Release and renew computer IP address then check if the new IP range took effect.
Assign static IP and DNS on the computer. Disable DHCP service of the modem.
Reset and reconfigure the modem.
Escalate to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au.
4. Not saving settings
Optimize browser settings:
- Clear cache and delete cookies
- Ensure that there is no proxy enabled
- Make sure there is no anti-spyware or pop-up blocker enabled on the computer
Power cycle modem and restart the computer
Reset and reconfigure the modem
Check the modem firmware version, suggest firmware upgrade.
Try another browser or modem.
Refer to OEM.
When sending an email to iptv-escalation@tpg.com.au , please provide the following information:
User name
Exchange
Modem model number
Modem firmware Version
Operating System
Problem encountered
86
ADSL TRAINING MANUAL
EDITING: VERSION CONTROL
Date
24 May 2005
27 June 2005
14 July 2005
18 July 2005
2 September 2005
8 September 2005
26 October 2005
2 November 2005
16 December 2005
31 January 2006
18 May 2006
6 July 2006
15 November 2006
12 December 2006
26 March 2007
27 April 2007
30 May 2007
20 September 2007
23 October 2007
16 November 2007
October 2009
December 2009
Version
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Who
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Ivan Mitrovic
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Eileen Assatoury
Lester Abarabar
Lester Abarabar
87
You might also like
- DSLDocument20 pagesDSLZatin Gupta100% (1)
- X DSLDocument8 pagesX DSLTushar SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber LineDocument91 pagesDigital Subscriber LinePrabudh BansalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Adsl: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber LineDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Adsl: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Linepsingh_sunnyNo ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber LineDocument10 pagesDigital Subscriber LineNissan SkylineNo ratings yet
- Mile From The Exchanges To The End-User's Home or BusinessDocument5 pagesMile From The Exchanges To The End-User's Home or Businessgvr11No ratings yet
- Broadband & Data Services-MtnlDocument69 pagesBroadband & Data Services-MtnlRakesh Vishwakarma100% (1)
- Lesson Notes AdslDocument5 pagesLesson Notes Adslෂර්ලොක් හෝම්ස්No ratings yet
- DSLDocument5 pagesDSLAljon AbriamNo ratings yet
- BB TrainingDocument17 pagesBB TrainingJayaramsai PanchakarlaNo ratings yet
- How Stuff WorksDocument10 pagesHow Stuff WorksGábor Krémer100% (1)
- Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line - GneDocument4 pagesAsymmetric Digital Subscriber Line - GneDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)Document54 pagesDigital Subscriber Line (DSL)Mehmud Ali100% (1)
- Is A Digital Subscriber LineDocument67 pagesIs A Digital Subscriber LinehafezakilNo ratings yet
- What is broadband? Understanding speeds, technologies and moreDocument27 pagesWhat is broadband? Understanding speeds, technologies and moreakshaymandawaria2009No ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber LineDocument11 pagesDigital Subscriber LinePooRav TaiLorNo ratings yet
- DSL Technology and DSLAM: An Overview: Authored by Rajul SrivastavaDocument4 pagesDSL Technology and DSLAM: An Overview: Authored by Rajul Srivastavarajuls2512No ratings yet
- BB Concepts-20150713-000904119Document37 pagesBB Concepts-20150713-000904119ankit1844No ratings yet
- DSLDocument27 pagesDSLgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Adsl Prsentation 1Document16 pagesAdsl Prsentation 1Sunil PillaiNo ratings yet
- How VDSL Works by Jeff TysonDocument5 pagesHow VDSL Works by Jeff Tysonchaidar_lakare100% (1)
- Wired and Wireless Connections of BroadbandDocument49 pagesWired and Wireless Connections of BroadbandgjagadeeshNo ratings yet
- DSL Technology GuideDocument18 pagesDSL Technology GuideItishree Pati100% (1)
- Digital Subscriber Line - DSLDocument14 pagesDigital Subscriber Line - DSLpppptttNo ratings yet
- Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line - WikipediaDocument18 pagesAsymmetric Digital Subscriber Line - WikipediaChinni Pravallika100% (1)
- Analogue Modem: 33 K 56 K Conventional Modem ConnectionDocument17 pagesAnalogue Modem: 33 K 56 K Conventional Modem ConnectionMohit ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DSL:-: How Fast Is DSL?Document26 pagesIntroduction To DSL:-: How Fast Is DSL?Abdullah AlsaggafNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Is A Family of Computer Networking Technologies For Local Area Networks (Lans)Document12 pagesEthernet Is A Family of Computer Networking Technologies For Local Area Networks (Lans)rbd101512No ratings yet
- Presentation On Fast Access Technologies: By:-Gurpreet RathoreDocument25 pagesPresentation On Fast Access Technologies: By:-Gurpreet RathoreDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- High Speed LinesDocument6 pagesHigh Speed Linesgouthami26No ratings yet
- IAP12 DigitalSubscriberLine (DSL)Document46 pagesIAP12 DigitalSubscriberLine (DSL)rizwan ahmedNo ratings yet
- If-Modes F Connctng 2 InternetDocument2 pagesIf-Modes F Connctng 2 InternetAnkit SingodiaNo ratings yet
- What Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleDocument9 pagesWhat Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleIas Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- What Is DSL?: Figure 1: Common Type of XDSLDocument8 pagesWhat Is DSL?: Figure 1: Common Type of XDSLm rauf tabassumNo ratings yet
- Adsl BasicsDocument5 pagesAdsl BasicsSuyash PrakashNo ratings yet
- Working of InternetDocument4 pagesWorking of InternetYogesh Bansal100% (1)
- ASDKLNASDDocument29 pagesASDKLNASDanon_965614693No ratings yet
- BB PPT Complete PresentationDocument56 pagesBB PPT Complete PresentationVishwanand ThombareNo ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Advances: Prepared By, Pow Jun Jiang (EE 071271)Document35 pagesDigital Subscriber Line (DSL) Advances: Prepared By, Pow Jun Jiang (EE 071271)pramtejkumarNo ratings yet
- Data Communications With Standard Telephone Lines and ModemsDocument13 pagesData Communications With Standard Telephone Lines and ModemsIfraheem Hassan Muhammad Aslam100% (4)
- ADSL Final PresentationDocument10 pagesADSL Final PresentationHaris UmairNo ratings yet
- Adsl PresentationDocument15 pagesAdsl PresentationbikashhhNo ratings yet
- DSL: An Introduction To ADSL: What Is It?Document32 pagesDSL: An Introduction To ADSL: What Is It?BibinMathew100% (1)
- DSL Copper Telephone ModemDocument3 pagesDSL Copper Telephone ModemAbhijeet KeshryNo ratings yet
- Types of Internet Connections - ppt1Document27 pagesTypes of Internet Connections - ppt1singhrichaNo ratings yet
- DslamDocument2 pagesDslamIslam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wired Broadband TechnologiesDocument22 pagesWired Broadband TechnologiesVindya ImbulpitiyaNo ratings yet
- Fast Guide To DSL: How It WorksDocument5 pagesFast Guide To DSL: How It Worksrohanr18No ratings yet
- DSL & Its TypesDocument24 pagesDSL & Its TypesahmedNo ratings yet
- Describing DSL Technology: Teleworker ConnectivityDocument31 pagesDescribing DSL Technology: Teleworker ConnectivityrajkumarlodhNo ratings yet
- 3 - What Is ADSL PDFDocument33 pages3 - What Is ADSL PDFlolitoNo ratings yet
- XDSL TechnologiesDocument23 pagesXDSL TechnologiesSuglo kwabena SolomonNo ratings yet
- DSL: An Overview: by M. V. Ramana MurthyDocument9 pagesDSL: An Overview: by M. V. Ramana Murthyvijay_786No ratings yet
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)Document17 pagesDigital Subscriber Line (DSL)Junaid InamNo ratings yet
- ADSLADSLADSLDocument83 pagesADSLADSLADSLKrishnan Unni GNo ratings yet
- Introduction to DSL Technologies and StandardsDocument36 pagesIntroduction to DSL Technologies and StandardsBereketeab ZinabuNo ratings yet
- Data Communication: Cable Modem, ADSL, XDSL and Multi Channel AccessDocument24 pagesData Communication: Cable Modem, ADSL, XDSL and Multi Channel AccessJonald BualNo ratings yet
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Albert PikeDocument6 pagesAlbert Pikeapi-302575383No ratings yet
- EA Flora 1Document3 pagesEA Flora 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- (The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)Document72 pages(The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)BlackFlix Legendas em PortuguêsNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusDocument7 pagesPhilippine Politics and Constitution SyllabusIvy Karen C. Prado100% (1)
- British and American Culture Marking RubricDocument5 pagesBritish and American Culture Marking RubricAn Ho LongNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxides Semiconductor CeramicsDocument14 pagesMetal Oxides Semiconductor Ceramicsumarasad1100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Citrix XenAppDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts of Citrix XenAppAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Appraisal Sample PDFDocument22 pagesAppraisal Sample PDFkiruthikaNo ratings yet
- Flight Instructor Patter Ex17Document1 pageFlight Instructor Patter Ex17s ramanNo ratings yet
- معامل الاسفلتDocument32 pagesمعامل الاسفلتMohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Quarter I - Module 2Document26 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Quarter I - Module 2Katrina TulaliNo ratings yet
- Chick Lit: It's not a Gum, it's a Literary TrendDocument2 pagesChick Lit: It's not a Gum, it's a Literary TrendspringzmeNo ratings yet
- Footprints 080311 For All Basic IcsDocument18 pagesFootprints 080311 For All Basic IcsAmit PujarNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisDocument9 pagesGabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisGabrielNobredeSouzaNo ratings yet
- DelhiDocument40 pagesDelhiRahul DharNo ratings yet
- EDUC 5 - QuestionairesDocument7 pagesEDUC 5 - QuestionairesWilliam RanaraNo ratings yet
- OB HandoutsDocument16 pagesOB HandoutsericNo ratings yet
- Pengkondisian Kesiapan Belajar Untuk Pencapaian Hasil Belajar Dengan Gerakan Senam OtakDocument9 pagesPengkondisian Kesiapan Belajar Untuk Pencapaian Hasil Belajar Dengan Gerakan Senam OtakSaadah HasbyNo ratings yet
- Karan Chawla and Joshua Lee November 21, 2016 MEDS 3020 - Fall 2016 Dr. Rosevear, Dr. Cartwright, Dr. LiebermanDocument2 pagesKaran Chawla and Joshua Lee November 21, 2016 MEDS 3020 - Fall 2016 Dr. Rosevear, Dr. Cartwright, Dr. LiebermanJeremy DelaneyNo ratings yet
- Njhs Application EssayDocument4 pagesNjhs Application Essaycjawrknbf100% (2)
- Padmavati Gora BadalDocument63 pagesPadmavati Gora BadalLalit MishraNo ratings yet
- Adapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumDocument3 pagesAdapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumVini PezzinNo ratings yet
- Balzac and the Little Chinese Seamstress: A Journey During the Cultural RevolutionDocument4 pagesBalzac and the Little Chinese Seamstress: A Journey During the Cultural RevolutionRogona 123No ratings yet
- 2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilDocument2 pages2021.01.28 - Price Variation of Steel Items - SAIL Ex-Works Prices of Steel - RB-CivilSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- JKR Specs L-S1 Addendum No 1 LED Luminaires - May 2011Document3 pagesJKR Specs L-S1 Addendum No 1 LED Luminaires - May 2011Leong KmNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFDocument15 pagesPembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFArdi Ansyah YusufNo ratings yet
- Compabloc Manual NewestDocument36 pagesCompabloc Manual NewestAnonymous nw5AXJqjdNo ratings yet
- Cat IQ TestDocument3 pagesCat IQ TestBrendan Bowen100% (1)
- The Golden HarvestDocument3 pagesThe Golden HarvestMark Angelo DiazNo ratings yet
- 1 CAT O&M Manual G3500 Engine 0Document126 pages1 CAT O&M Manual G3500 Engine 0Hassan100% (1)