Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quick Nursing Student Notes 2
Uploaded by
Frank KimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quick Nursing Student Notes 2
Uploaded by
Frank KimCopyright:
Available Formats
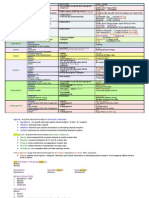
Normal Lab Values
Na+
K+
Cl-
BUN
CO2
Cr
LABS
Sodium
Potassium
Chloride
Bicarb
BUN
Creatinine
Glucose (fasting)
HbA1c
Calcium
Phosphorus
Magnesium
Hematology
Hct (men)
Hct (women)
Hgb (men)
Hgb(women)
MCV
MCH
MCHC
Platelet Count
RBC (men)
RBC (women)
WBC
ARTERIAL BLOOD
pH
pCO2
pO2
HCO3
Glucose
Hgb
WBC
Plt
Name
Type
Function
Assessment
I. Olfactory
Sensory
Smell
Ask clients to identify different odors
using one nostril at
a time
II. Optic
Sensory
Vision and visual fields
Use Snellen chart
to check visual
acuity; conduct
an opthalmoscope
examination
III. Occulomotor
Motor
Parasympathetic
Extrinsic eye movements
Pupillary constriction
and visual focusing
Assess six cardinal
ocular movements
test pupillary reaction to light; test
convergence
IV. Trochlear
Motor
Downward and lateral
eye movements
Assess six cardinal
ocular movements
V. Trigeminal
Sensory
Facial sensation, mastication, anterior tongue
and teeth
Test corneal reflex
Test sensitivity to
pain, touch, warm
and cool temperatures
Ask client to clench
teeth and palpate
muscles, h ave client bite down
VI. Abducens
Motor
Lateral eye movements
Look left and right
VII. Facial
Motor
Sensory
Facial expression
Taste in the anterior
tongue
Smile, frown, puff
cheeks, and close
eyes; raise and
lower eyebrows;
check for symmetry
VIII.
Vestibulocochlear
Sensory
Hearing and equilibirum
Administer hearing
acuity tests, Weber
and Rinne tests
IX. Glossopharyngeal
Motor
Sensory
Swallowing ability and
gag reflex
Taste in the posterior
tongue
Test gag reflex, test
swallowing, confirm
rise and fall of soft
palate and midline
uvula.
Ask client to identify
samples in back of
tongue
X. Vagus
Motor
Sensory
Sensation of external
ear, pharynx, and larynx; swallowing; vocal
cord movement
Test gag reflex; assess clients speech
XI. Accessory
Motor
Head movement,
shoulder shrugging
Push down on shoulders as client tries
to shrug; ask client
to turn head against
resistance
XII. Hypoglossal
Motor
Protrusion of tongue,
tongue movement
Have client protrude
tongue and move it
side to side
Hct
135-145 mEq/L
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
95-105 mEq/L
22-30 mEq/L
5-25 mg/dl
0.5-1.5 mg/dl
70-110 mg/dl
4-6%
9.0-11 mg/dl
2.5-4.5 mg/dl
1.8-3.0 mg/dl
40.50%
36-46%
13.-17.5 g/dl
12-16 g/dl
80-100 um3
26-34 pg
31-37 g/dl
150-400 x 103/mm3
4.6-6.0 x 106/mm3
4.0-5.0 x 106/mm3
4.5-10.0 103/mm3
GAS
7.35-7.45
35-45 mmHg
70-100 mmHg
19-25 mmHg
Insulin
Types of
Insulin
Examples
Onset of
Action
Peak of
Action
Duration
of Action
Rapid Acting
Humalog
(lispro)
Novolog
(aspart)
15 min
30-90
min
3-5 hours
Short-acting
(regular)
Humulin R
Novolin R
30-60
min
50-120
min
5-8 hours
Intermediate
acting
(NPH)
Humulin N
Novolin N
Humulin L
Novolin L
1-3 hours
1-2.5
hours
8 hours
20 hours
7-15
hours
18-24
hours
Lantus
(glargine)
1 hour
Long-acting
Cranial Nerves (CN)
15 min
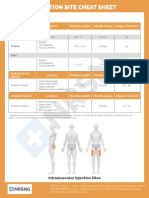
Injections
Intramuscular
Subcutaneous
Intradermal
90
45
15o
none
24 hours
You might also like
- STUDENT-Sickle - Cell-FUNDAMENTAL ReasoningDocument7 pagesSTUDENT-Sickle - Cell-FUNDAMENTAL ReasoningSharon Tanveer0% (1)
- Must Have Nursing Mnemonics PDFDocument50 pagesMust Have Nursing Mnemonics PDFJanus Lazaro100% (2)
- Type Drug ChartDocument3 pagesType Drug ChartKarina Rodriguez100% (3)
- Medication Work Sheet For MedSurgDocument5 pagesMedication Work Sheet For MedSurgRyanMitchell100% (2)
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetabardwell100% (85)
- 5 Nurse NotesDocument1 page5 Nurse Notescarefulgurl420% (3)
- 000 Nursing School Necessities Cheat SheetDocument3 pages000 Nursing School Necessities Cheat SheetRevNo ratings yet
- The Nclex-Pn Cram Sheet: General Test Information Normal Lab ValuesDocument2 pagesThe Nclex-Pn Cram Sheet: General Test Information Normal Lab Valuesroboat96No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDocument11 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideDocument11 pagesNursing Pharmacology Inflammation Study GuideChelsea Smith100% (1)
- 02 NursingInterviewPrepGuide NurseWellVersedDocument7 pages02 NursingInterviewPrepGuide NurseWellVersedOceanNo ratings yet
- Medication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasDocument1 pageMedication Calculation - Commonly Used FormulasAaron AntonioNo ratings yet
- Pre-Op Medication Reference SheetDocument3 pagesPre-Op Medication Reference Sheetsabbo morsNo ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusCassie100% (4)
- Test InformationDocument5 pagesTest InformationCatalina BorquezNo ratings yet
- Entire Medication BundleDocument22 pagesEntire Medication BundleKarina Castillo100% (1)
- Anti-Infectives Course #25Document18 pagesAnti-Infectives Course #25Gina Giammalvo100% (2)
- Med BundleDocument36 pagesMed Bundlejamie sealNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DrugsDocument4 pagesCardiac DrugsIbrahem Al100% (2)
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 pagesNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- PA1 HandoutDocument22 pagesPA1 HandoutIligan, JamaicahNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument6 pagesNursing NotesLinguumNo ratings yet
- Pharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharm 1.11 Insulin Cheat SheetSanobar Charania100% (1)
- Drugs WorksheetDocument16 pagesDrugs Worksheetninja-2001No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocument78 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review NotesLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument13 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentVino MaghirangNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument2 pagesAntidotesYemaya84No ratings yet
- Cs Pharm 022 Injection Site Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCs Pharm 022 Injection Site Cheat SheetEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Study GuideDocument27 pagesMed Surg Study Guidetrifecta31No ratings yet
- Drug Chemical Name Generic Name Trade Name Drug Classification PharmaceuticsDocument5 pagesDrug Chemical Name Generic Name Trade Name Drug Classification Pharmaceuticschubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Med Surg BulletDocument12 pagesMed Surg BulletCham SaponNo ratings yet
- Upload Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsDocument2 pagesUpload Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsnamitaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology & Ekgs: Archer Nclex ReviewDocument59 pagesCardiology & Ekgs: Archer Nclex Reviewdaphne farleyNo ratings yet
- Studying Patho For Nursing School - EasyDocument1 pageStudying Patho For Nursing School - EasyMarie J100% (1)
- Pharmacology NCLEX ReviewDocument128 pagesPharmacology NCLEX ReviewBritanny NelsonNo ratings yet
- Psych ATI Study GuideDocument9 pagesPsych ATI Study GuideJaclyn FugateNo ratings yet
- PN NCLEX Integrated A 1Document75 pagesPN NCLEX Integrated A 1jedisay1100% (1)
- Med Surg Study Guide 41 PagesDocument42 pagesMed Surg Study Guide 41 PagesVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (2)
- Template Drug Card1Document1 pageTemplate Drug Card1Kay TaylorNo ratings yet
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Med Surge 2 Mod 3 Study Guide2Document21 pagesMed Surge 2 Mod 3 Study Guide2Dirk Buckner100% (4)
- OB NRSNG - Com BrainsheetsDocument4 pagesOB NRSNG - Com BrainsheetsD SchwartzlerNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For NursesDocument52 pagesMnemonics For Nursessweetpearl27100% (3)
- 1430 Drug CardsfinalDocument7 pages1430 Drug CardsfinalLizSherman100% (1)
- Bullets Nclex Terms 50Document48 pagesBullets Nclex Terms 50ShazaNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics For NursingDocument35 pagesMnemonics For Nursingbetterdenthat100% (1)
- RemarDocument4 pagesRemarChelle RocoNo ratings yet
- Nurses Note DONEDocument1 pageNurses Note DONEjhenssineNo ratings yet
- EKG Basics1Document16 pagesEKG Basics1Jamie Lemons100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System Acronyms and MnemonicsDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System Acronyms and Mnemonicsdecsag06No ratings yet
- Medication List and InformationDocument9 pagesMedication List and InformationHealthAndFitnessGuyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pneumonics For Infection ControlDocument2 pagesNursing Pneumonics For Infection Controlmrsstrickland100% (1)
- Hesi Med Surg-6Document1 pageHesi Med Surg-6GeorgeNo ratings yet
- A-T-I Endocrine NotesDocument3 pagesA-T-I Endocrine NotesKelseyAnnBarnesNo ratings yet
- Dosage Calculations Packet-WordDocument33 pagesDosage Calculations Packet-Wordspringday_2004100% (1)
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Document27 pagesInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANo ratings yet
- Pep Mock Exam Questions Updated - 2Document84 pagesPep Mock Exam Questions Updated - 2Cynthia ObiNo ratings yet
- Abasaglar Patient Information Leaflet Updated Dec 17Document2 pagesAbasaglar Patient Information Leaflet Updated Dec 17zafemarakiNo ratings yet
- Desired Over HaveDocument14 pagesDesired Over HaveJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- 2017-09-18 in Re Insulin Opinion Interim LeadershipDocument7 pages2017-09-18 in Re Insulin Opinion Interim LeadershipThe Type 1 Diabetes Defense FoundationNo ratings yet
- Tablet Paten: NO Nama Obat Kandungan ED JumlahDocument2 pagesTablet Paten: NO Nama Obat Kandungan ED Jumlahvicki yugasworoNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Long Acting InsulinsDocument3 pagesComparison Between Long Acting InsulinsSiddiq MohammedNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PharmacologyDocument14 pagesDiabetes PharmacologyRich JeongNo ratings yet
- PDF Export 64cce1599ba62Document2 pagesPDF Export 64cce1599ba62joye24hoodaNo ratings yet
- LANTUS XR Label InformationDocument17 pagesLANTUS XR Label InformationMichaelJonatanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Drug With Trade NameDocument5 pagesDiabetic Drug With Trade NameNazmul Alam FarukiNo ratings yet
- A Step-By-Step Guide To Using Your Lantus Solostar PenDocument5 pagesA Step-By-Step Guide To Using Your Lantus Solostar Penraval anil.uNo ratings yet
- Types of Insulin: NOTE: Exact Onset, Action, and Duration Are Dependent On The Generic/brand UsedDocument3 pagesTypes of Insulin: NOTE: Exact Onset, Action, and Duration Are Dependent On The Generic/brand Usedask1400No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Management Guideline in PHCDocument80 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Management Guideline in PHCAnna TkachenkoNo ratings yet
- LindeTechnology 1-04 Biotechnology EngDocument6 pagesLindeTechnology 1-04 Biotechnology EngTarif_87No ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Drugs: Case StudyDocument31 pagesPancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Drugs: Case StudyMae Lislie Canonigo - FloresNo ratings yet
- Patient With DM Type 2: Valentina Dwi Hartati TambunanDocument31 pagesPatient With DM Type 2: Valentina Dwi Hartati TambunanValent TambunanNo ratings yet
- A. BCGDocument17 pagesA. BCGkassahunNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Health Care IndustryDocument120 pagesPharmaceutical Health Care IndustryJanella Garcia50% (2)
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFDocument74 pagesPharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFGlenn Perez71% (7)
- Master List 008 HPP 130518 PDFDocument23 pagesMaster List 008 HPP 130518 PDFHan Siang KuNo ratings yet
- Nclex ReviewDocument27 pagesNclex ReviewNicole Chadwick100% (4)
- Classifications of Insulin2Document116 pagesClassifications of Insulin2loglesb1No ratings yet
- Insulin Case Studies AACE 5-20-05Document56 pagesInsulin Case Studies AACE 5-20-05Leanne Shepherd100% (2)
- DCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesDocument5 pagesDCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesNabihah BarirNo ratings yet
- TH Trung ThauDocument224 pagesTH Trung ThauLinh TrọngNo ratings yet
- CH 67Document14 pagesCH 67john mwangiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and MassageDocument23 pagesDiabetes and MassagemassagekevinNo ratings yet