Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Aspects of Corporate Organization Operating Policies and Control
Uploaded by
Connie Miole Estrella50%(6)50% found this document useful (6 votes)
2K views3 pagesorganization
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentorganization
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(6)50% found this document useful (6 votes)
2K views3 pagesKey Aspects of Corporate Organization Operating Policies and Control
Uploaded by
Connie Miole Estrellaorganization
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
KEY ASPECTS OF CORPORATE ORGANIZATION OPERATING
POLICIES AND CONTROL
Organization
Organizations can be grouped into one of six major categories:
(1) One-man Operation Most organization start this way. This single
manager may formulate vague strategies and plans, make all decisions on
the basis of experience and limited first-hand knowledge, and issue orders
to all operating personnel.
(2) Father-son or manager Assistant Either one or more sons, or one or
more assistant, are used to multiply the efforts of the the boss, who
retains all authority and responsibility and makes all the decisions.
(3) Functional organizations favors significant growth in many direction
for its introduces the concept of delegation of authority and sanctions the
use of professional management. The functional managerssuch as the
financial manager, the purchasing manager, the production manager, the
personnel manager, etc.make all of the necessary and required
operating services.
(4) Functional organization, but with a central headquarters and
geographical dispersion This type of organization is an extension of
the third form just described but permits manufacturing or sales
operations in two or more locations.
(5) Multi-divisional Firm this type permits the firm to cope with disparate
product lines because it has separate divisions for each product line
and/or for each geographical location.
(6) Conglomerate where the central headquarters only maintains financial
control over a number of wholly-owned companies. This is a typical form
of organization where each unit has a different product line and marketing
system.
Operating Policies
Operating policies acts as a lubricant for the effective, efficient, and smooth
operation of the organization.
Policies are often confused with the rules and procedures.
(1) POLICY: A verbal, written or implied guide setting up boundaries and
directions within which
managerial decisions should take place.
Hence, a policy is a guide to decision-making.
(2) RULE: A prescribed course of action which must be followed. Hence, a
rule is a guide to individual action.
(3) PROCEDURE: A sequence of related tasks that make up the chronological
sequence and the establish way of performing the work to be done.
Hence, it is also a guide to action.
Advantages:
(1) Support Continuity
(2) Greatly promote delegation of authority
(3) Promote consistency and reduce arbitrary bases for decisions.
Disadvantages:
(1) Highly confidential and, if distributed among many people, would soon be
available to competitors.
(2) Their effectivity remain even long after they have become obsolete
(3) May permit insufficient discretion to the decision-maker
2 basis sets of operating policies:
(1) General policies are applicable at all levels and in all parts of
organization
(2) Functional policies developed for each functional area of management
Managerial Control Organizations
All other efforts of management are wasted unless a very determined effort is made
to control the many aspects of the operating of the firm.
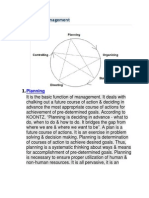
1. Process of managerial control may be thought of as a four-step process:
(1) Setting the standard of the performance present no great difficulty if
management has developed an operational plan. The standards of
performance will be based on that plan, on the policies, objectives and
strategies which were part of the earlier phases of the management cycle.
(2) Measurement of performance may be done at different levels, depending
upon the companys organization and the activity being monitored.
(3) An information system must be established - to get these reports quickly
into the hands of the individual who must compare actual performance
against the predetermined standard and decide whether or not corrective
action is required.
(4) Promt, corrective action without such action, the control process merely
produces a historical record, the process of corrective action itself is a two
process:
First the individual who has control responsibility must determine
the cause of the discrepancy between actual and desired
performance.
Then he must decide on the best corrective action.
2. Management Information system -
dsg
You might also like
- Letter Calling For State Department of Oil and Gas To Investigate Gas LeakDocument4 pagesLetter Calling For State Department of Oil and Gas To Investigate Gas LeakLos Angeles Daily NewsNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Mechanical PlanDocument14 pagesElectrical and Mechanical PlanMarielle Bias MercadoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Learning Filipino StyleDocument8 pagesStrategic Management Learning Filipino StyleMela Vinco100% (2)
- Citadel University CaseDocument11 pagesCitadel University CaseHeinz Reimann Daguinsin Orais0% (1)
- DAF Superstructures BodyBuilders - GuideDocument34 pagesDAF Superstructures BodyBuilders - GuideЮлия Дам100% (1)
- Wallenius Wilhelmsen HistoryDocument28 pagesWallenius Wilhelmsen Historymanayani52100% (1)
- ASTM 6365 - 99 - Spark TestDocument4 pagesASTM 6365 - 99 - Spark Testjudith_ayala_10No ratings yet
- Management Quiz BowlDocument53 pagesManagement Quiz BowlFaye ColasNo ratings yet
- Case Study DMDocument15 pagesCase Study DMtangyna33% (3)
- 6 Job Organization and Information - Christine MancenidoDocument4 pages6 Job Organization and Information - Christine Mancenidojanellavanes100% (1)
- Practical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRDocument84 pagesPractical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRCarlos SoaresNo ratings yet
- Rules For Building and Classing Marine Vessels 2022 - Part 5C, Specific Vessel Types (Chapters 1-6)Document1,087 pagesRules For Building and Classing Marine Vessels 2022 - Part 5C, Specific Vessel Types (Chapters 1-6)Muhammad Rifqi ZulfahmiNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Management ReflectionDocument2 pagesCooperative Management ReflectionFaker Mejia100% (1)
- Role of The State and Its Impact On Business OrganizationsDocument20 pagesRole of The State and Its Impact On Business OrganizationsBaby Joy Bautista100% (3)
- Strategic Planning (Imperial Appliance Plaza)Document18 pagesStrategic Planning (Imperial Appliance Plaza)Samanta SingcolNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Practice of Management in CooperativesDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 8 Practice of Management in Cooperativesalex266100% (4)
- Yamaha Acoustic GuitarsDocument18 pagesYamaha Acoustic Guitarsrusf123100% (5)
- Organizational Behavior and Performance Appraisal 2Document20 pagesOrganizational Behavior and Performance Appraisal 2Ceazar Justine Fulugan100% (3)
- Stability RatioDocument27 pagesStability RatioashokkeeliNo ratings yet
- Key Aspects of Corporate Organization, Operating PoliciesDocument12 pagesKey Aspects of Corporate Organization, Operating PoliciesLou IzNo ratings yet
- 02 Traps Management Service AdminDocument134 pages02 Traps Management Service AdminDonovan RuizNo ratings yet
- Dagdag Puhunan Program in The City Government of Muntinlupa 2 PDFDocument89 pagesDagdag Puhunan Program in The City Government of Muntinlupa 2 PDFjhaeus enaj100% (2)
- Ten Strategies For The Top ManagementDocument19 pagesTen Strategies For The Top ManagementAQuh C Jhane67% (3)
- Human Resource Management: I. Maintenance and Rewarding of EmployeesDocument43 pagesHuman Resource Management: I. Maintenance and Rewarding of EmployeesChriz Chan67% (3)
- SM AssignmentDocument4 pagesSM AssignmentNikita Mallick100% (1)
- Jordan Fernandez Casais BSBA FM 3-DDocument2 pagesJordan Fernandez Casais BSBA FM 3-DJordan Fernandez CasaisNo ratings yet
- Final Research (Villavelez, Villamora, Percil)Document39 pagesFinal Research (Villavelez, Villamora, Percil)Grace AncajasNo ratings yet
- Pestle Analysis For Cebu AirlineDocument9 pagesPestle Analysis For Cebu AirlineKevo KarisNo ratings yet
- Hbo - Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesHbo - Prelim Examray100% (1)
- Summary of Educational TourDocument14 pagesSummary of Educational TourChin Tatoy DoloricaNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Delaying Payments Towards Home Credit Philippines 1Document13 pagesRationale of Delaying Payments Towards Home Credit Philippines 1Katrina De LeonNo ratings yet
- Quality and Quantity ControlDocument9 pagesQuality and Quantity ControlSaji Jimeno100% (1)
- Reaction Paper 7-10 FinalDocument3 pagesReaction Paper 7-10 FinalJomari Gingo SelibioNo ratings yet
- Chapters 2 To 5 Complete PDFDocument87 pagesChapters 2 To 5 Complete PDFElizabeth N. BernalesNo ratings yet
- Case Study EdsaDocument4 pagesCase Study EdsaAnne CuraNo ratings yet
- Thesis About SalariesDocument33 pagesThesis About SalariesChristoper TaranNo ratings yet
- HouskeepingDocument18 pagesHouskeepingJay ArNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire-Checklist "The Effects of Expensive Tricycle Fare in Antipolo, City"Document2 pagesQuestionnaire-Checklist "The Effects of Expensive Tricycle Fare in Antipolo, City"Kristle R BacolodNo ratings yet
- Case of StudyDocument5 pagesCase of StudyRenz Charles Tenebro100% (1)
- Case Study 1 HRM in PandemicDocument2 pagesCase Study 1 HRM in PandemicKristine Dana LabaguisNo ratings yet
- STRAMADocument22 pagesSTRAMAMilaine ZilabboNo ratings yet
- Different Job TermsDocument2 pagesDifferent Job TermsGLenda Enrica A. Sy100% (4)
- Answer To Module 8Document1 pageAnswer To Module 8Jose Emmanuel DaeltoNo ratings yet
- Opto, Charles Jan M. Chap. 7. Dist. Mngt.Document2 pagesOpto, Charles Jan M. Chap. 7. Dist. Mngt.Charles Jan Mosquera Opto100% (1)
- MGT Man Is Called To Served GODDocument3 pagesMGT Man Is Called To Served GODAllan AgpaloNo ratings yet
- MALELANG - Narrative Report TaxDocument4 pagesMALELANG - Narrative Report TaxRoseanneNo ratings yet
- Types and Categories of CooperativesDocument4 pagesTypes and Categories of CooperativesIsaac Riego100% (1)
- Module 9.the Global Org'l., MKTG., Manufacturing, Acctg. and SCDocument47 pagesModule 9.the Global Org'l., MKTG., Manufacturing, Acctg. and SCaybe jedNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management of Stakeholder RelationshipsDocument18 pagesStrategic Management of Stakeholder RelationshipsAlyssa Hallasgo-Lopez AtabeloNo ratings yet
- Total Environment of A FirmDocument2 pagesTotal Environment of A FirmIrdo Kwan75% (4)
- Module 1 Introduction To Business PolicyDocument54 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Business Policycha11100% (1)
- Garcia, Rochene I - Reaction Paper For Group 1's PresentationDocument4 pagesGarcia, Rochene I - Reaction Paper For Group 1's PresentationRochene GarciaNo ratings yet
- Level of Motivation Among The Lgu Personnel in The Municipality of IguigDocument3 pagesLevel of Motivation Among The Lgu Personnel in The Municipality of IguigPrincess Liban Rumusud100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Good GovernanceDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Good GovernanceKath Dayag100% (1)
- Chapter 3-Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentDocument23 pagesChapter 3-Challenges in The Internal EnvironmentMulong Cabrillas100% (1)
- CASE StudyDocument26 pagesCASE Studyjerah may100% (1)
- Reflection 2-Capital Markets VideoDocument2 pagesReflection 2-Capital Markets Videojonald almazarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Public Policy Vision For CSRDocument4 pagesStrategic Public Policy Vision For CSRLouelie Jean AlfornonNo ratings yet
- Company Vision and MissionDocument2 pagesCompany Vision and MissionEloisa EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Bureaucracy Reflection EssayDocument3 pagesBureaucracy Reflection EssayAbhiraj Singh67% (3)
- PA 215 - ReportDocument6 pagesPA 215 - Reportarniel somilNo ratings yet
- Functions of Management: PlanningDocument46 pagesFunctions of Management: PlanningKharen JaneNo ratings yet
- 200 HoursDocument5 pages200 HoursRegine Del Moro Arinaza0% (1)
- HRD 6 7Document3 pagesHRD 6 7Stephanie SyNo ratings yet
- Quality of Service of Courier CompanyDocument7 pagesQuality of Service of Courier CompanyRowell DiazNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Course OutlineDocument2 pagesPublic Finance Course Outlinetuffoman100% (1)
- Preparation of The Project Feasibility: January November Activities Project Conceptualization and Identification DecemberDocument1 pagePreparation of The Project Feasibility: January November Activities Project Conceptualization and Identification DecemberMarnelli PerezNo ratings yet
- Corporate Organization PDFDocument25 pagesCorporate Organization PDFlarraine aguimatangNo ratings yet
- Strategy 4 TH UnitDocument21 pagesStrategy 4 TH UnitElango VSNo ratings yet
- RF Power Meter v2: Preliminary Operator's ManualDocument10 pagesRF Power Meter v2: Preliminary Operator's Manualsalvatore dalessandroNo ratings yet
- のわる式証明写真メーカー|PicrewDocument1 pageのわる式証明写真メーカー|PicrewpapafritarancheraNo ratings yet
- Ogm 25Document1 pageOgm 25azimsabudinNo ratings yet
- Practice - Creating A Discount Modifier Using QualifiersDocument37 pagesPractice - Creating A Discount Modifier Using Qualifiersmadhu12343No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 7 Steps in Developing HRM StrategyDocument11 pagesHuman Resource Management 7 Steps in Developing HRM StrategyjaysoreNo ratings yet
- Python Setup and Usage: Release 2.7.8Document57 pagesPython Setup and Usage: Release 2.7.8dingko_34No ratings yet
- Heatsink Calculation and Examples: Application NoteDocument3 pagesHeatsink Calculation and Examples: Application NoteAmador Garcia IIINo ratings yet
- Gambar SuspensiDocument1 pageGambar SuspensiMashiro HikariNo ratings yet
- Presented by Name: Kanu Ikechukwu Department:Chemistry MATRIC NO:DE:2014/2707 REG NO:ITA/2015/122568Document13 pagesPresented by Name: Kanu Ikechukwu Department:Chemistry MATRIC NO:DE:2014/2707 REG NO:ITA/2015/122568chdiNo ratings yet
- Urethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)Document2 pagesUrethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)CriVe OffeNo ratings yet
- China Chassis Cj14Document1 pageChina Chassis Cj14David Argote BellidoNo ratings yet
- Códigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTDocument8 pagesCódigos de Fallas de Problemas Específicos de PEUGEOTJesus GarciaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For CNIP IndustriesDocument42 pagesBest Practices For CNIP IndustriesSaurabhDubeyNo ratings yet
- EVSDocument7 pagesEVSsubhas9804009247No ratings yet
- Apache Derby DatabaseDocument4 pagesApache Derby DatabaseJohn KrcmarikNo ratings yet
- Silica Analyzer, Series 5000, Model 6000-Intrument Manual PDFDocument136 pagesSilica Analyzer, Series 5000, Model 6000-Intrument Manual PDFAdhy Priyo Pambudi100% (1)
- Light Runner BrochureDocument4 pagesLight Runner Brochureguruprasad19852011No ratings yet
- Workbook Answer Key Unit 9 Useful Stuff - 59cc01951723dd7c77f5bac7 PDFDocument2 pagesWorkbook Answer Key Unit 9 Useful Stuff - 59cc01951723dd7c77f5bac7 PDFarielveron50% (2)
- J030 J032 Eu Aa V1.00Document41 pagesJ030 J032 Eu Aa V1.00gkalman_2No ratings yet
- Expansion JointsDocument29 pagesExpansion Jointsvarma101100% (1)
- Intel® Desktop Board DP35DPDocument84 pagesIntel® Desktop Board DP35DPAnticristo69No ratings yet