Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AMRITSAR
Uploaded by
Suparna DasguptaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AMRITSAR
Uploaded by
Suparna DasguptaCopyright:
Available Formats
PUNJAB
DISTRICT
MAP
AMRITSAR, PUNJAB INDIA
AMRITSAR
LOCATION & SIZE
410 KM N-W DELHI
228 km west of Chandigarh
Altitude :- 230 m from ASL
LATTITUDE:-31.6167 N,
LONGITUDE :- 74.8500E
CITY MUNICIPAL AREA :- 114 SQ. KM
Population:25,00,000 (2011)
Density/km2:-928 persons
Sex ratio:-889 per 1000 male
Literacy Rate (2011)-76.27
Population
DISTRICT FORMS AN INTERNATIONAL distributionBORDER WITH PAKISTHAN
occupation wise
Population
distribution-age
wise
TOPOGRAPHY &
PHYSICAL FEATURES
CITY DEVELOPMENT THROUGH STAGES
1581
1573-77
Guru Amar
Das found a
township a
sacred tank
dug
Ramdaspur
township
established
1628- Township of
Ramdaspur around
the sarovar
CLIMATE
SEMIARID
CLIMATE,
ABOUT 230 M ABOVE
MEAN SEA LEVEL
LOCATED IN THE ALLUVI
AL PLAIN OF RAVI & BEAS
RIVER
FORMS BOWL SHAPED
PLAIN HENCE FLOODS
CERTAIN AREAS WITH EVEN
SMALL RAINFALL
AMRITSAR-NETWORKS
1809-1831
1849
Gobind gahr
fort & palace
by local king
British
took
over
1919
Jallianwala
Bagh
massacre
1947
Post
partition
riots
1802
Organic growth.
1900, The settlement spilled
Walled city came into
existence and it became outside the fort area. British
settlements developed outside
densely populated.
and away from the core.
1962
1984
59
development
schemes
proposed
Destruction
around
Golden
Temple
1962
Walled city discarded
by Punjab
development of
damaged area act
1947, Amritsar expanded in all
directions. New settlements along
the GT Road and the Railway lines
1984
1986
Large scale
redevelopment
project -300m
around
Golden Temple
Dairies /goods
transport
booking
agencies
shifted out of
city
2000, The densely populated.
planned and the organic
development has generated a
complex growth pattern.
LAND USE PATTERN
MIXED LAND USE 50% RESIDENTIAL,510 % COMMERCIAL.
COMMERCIAL
ON
GROUND/(LOWER)
FLOORS
RESIDENTIAL ON
UPPER FLOORS
ALONG THE MAIN
ROADS
IMPORTANT
EDUCATIONAL
INSTITUTIONS
ALONG THE MAIN
ROADS, INDUSTRIES
ALONG TRADING
ROUTES
AMRITSAR DISTRICT MAP
GOVT. BUILDINGS
TO THE WEST
RECREATIONAL
SPACES AT THE
OUTSKIRTS
CITY EXPANDED
IN AL DIRECTIONS
WITH TIME KEEPING
THE WALLED CITY IN
CENTER,
ECONOMIC BASE
A trade and religious tourism centre
Potentials to have vibrant and
sustainable economic activities
agriculture, live stock production,
industries and trade.
WORK FORCE PARTICIPATION
Work participation rate 34.33 %
89% of the people are engaged in the
Secondary and tertiary sector
Trading sector absorbs 59% of the workforce
MAJOR INDUSTRIES & THEIR TYPES
Large scale Industry-TEXTILE
Small scale Industry-MACHINE
TOOLS, CHEMICALS FOOD
PRODUCTS,
& Others like PLASTIC GOODS, RUBBER
GOODS, MUSICAL INSTRUMENT,
SHOES AND LEATHER, GEMS AND
JEWELS, ROPE MAKING etc
UNDERSTANDING A CITYS PLANNING
INTERVENTION THROUGH REFERENCE STUDY
Suparna Dasgupta
13AR60R38
SOLIDWASTE MANAGEMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL SERVICES (PHYSICAL
INFRASTRUCTURE)
The water supply system operated by the MCA
comprises a total of 260
tube wells, pumping water directly to distribution
mains on an intermittent basis.
many households, commercial/ institutional
organizations and industries
have installed their own private motorized tube wells
Disinfection by bleaching powder solution.
WASTE WATER DISTRIBUTION
sewerage
pumping station
at Mahlan(32%)
sewerage
pumping
station
Fatehpur(63%)
Glass
Source
WASTE WATER MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
70% of the population enjoy access
to an underground sewerage system
South zone
STORM WATER DRAINAGE
open storm water drains or nallahs
Segregation of Waste at
Not in domestic water supply
45 % of the commercial, institutional and
industrial connection meters
North zone
no sewage treatment at domestic level
Industrial effluents treated to an extent (specified by PCB)
25-30 %
Generation of Solid Waste
450 Metric Tonnes (MT) of solid waste
is generated
50-55%
Local residents,
Construction
,
Commercial areas and vegetable
markets,
Biodegradable
Households,
30 %
Industries
Hotels and restaurants,
Hospital and dispensaries,
Domestic and stray animals,
5%
Wood/ 5%
Floating population
furniture
1%
WATER SUPPLY
80% of the population has access to the piped
drinking water system.
Water Quality:
Water metering
SEWAGE TREATMENT
Industrial
Most households rely on
itinerant scavengers for
segregation of waste- houseto-house collection
arrangements
Stored in dustbins
Chhehartta
(WEST of the city)
sewerage
pumping station
Gumanpura
1%
Metal
Plastic
SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE
EXISTING & PROPOSED SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE
EDUCATION
EXISTING
PROPOSED
NURSERY SCHOOL
191
628
PRIMARY SCHOOL
626
152
Sr SECONDARY
116
88
INTEGRATED SCHOOL
95
20
HANDICAPPED
SCHOOL
46
COLLEGE
Transported to landfills HEALTH
HOSPITAL
Bhagatawala (8.1 ha) GENARAL
INTERMEDIATE HOSPITAL
Fatahpur (5.8 ha )
MATERNITY &CHILD
WELFARE HOSPITAL
Bharaiwal (2.65 ha)
172
Tung Dhab
(NORTH)
Ganda
Nallah
(SOUTH)
Hudiara Drain
Ravi
river
UN-SEWERED AREAS
Around the outer fringes of
the city
URBAN FINANCES
6
80
32
131
DISPENSERIES
112
VETERNARY
DISPENSERIES
16
STUDY OF SAI CONSULTANCY ENGINEERS PRIVATE
LIMITED
Nearest nallah
Hudiara Drain
TRAFFIC & TRANSPORTATION
NH15
GRAND
TRUNKROAD
Growth of vehicle
AIRPORT
AH 2
0
2KM
AH15
NH15
AMRITSAR- IMPORTANT ROADS
NH -1 connects the city to Jallandhar through Beas (east)
Road safety
NH-15 links the region with Tarn Taran District (south)
good linkage to Lahore, Pakistan through Wagha Border
radial-cumcircumferential road network
G.T. Road passes through the centre of the city
ACCOMODATION ARRANGEMENTS FOR
EMPLOYED PEOPLE
Problems in traffic &
2%
transportations
HOUSE TYPE
Independent AMRITSAR-RAILWAYS
Houses
2% 6%
Flats
15%
Chawlbustees
21%
25% of road network of the city is
77%
in poor condition
Others
Insufficient parking areas
77%
Insufficient public transport
system leads to high
The survey covered workers engaged in four sectors of employment viz. Registered
Factories, Electricity Generating and Distributing Establishments, Public Motor Transport
percentage of privately owned
own accommodation arrangements Undertakings and Railways. The total number of working class families covered during the
vehicles in the city
survey was 432.
House Tax
Walled city narrow roads
employers dwellings
Food
% EXPENDITURE PATTERN
widths
10% on Rental Residential of
relatives / friends
10%
congested roads, Lack of road
38%
total annual rent.
Housing
22%
side amenities
15% on self commercial or
Unplanned intersections
Education
15%
rental commercial units.
15%
Transport
5% fire cess on total tax, which
slow down the overall traffic speed
is implacable on above both
cases.
Health
HOUSE HOLD SURVEY CES 2011
AVERAGE HOUSE HOLD INCOME-Rs 17392
AVERAGE HOUSE HOLD INCOME-Rs 14734
TOURISM IN AMRITSAR
A rebate of 10%(if paid within
stipulated time)
Sr.
Plot Area
No
(sq. yds.)
.
Minimum Height
Site
F.R.
front set permissib
coverage
R.
back
le
Upto 100
sq. yds.
80%
5'-0"
38'-6"
01:0
2.
Above
100 to
150"
75%
6'-0"
38'-6"
1:1'.
90
Above
150 to
200"
38'-6"
01:0
2.
Above
200 to
300"
Above
300 to
500"
Above
500"
70%
65%
60%
50%
7'-0"
10'-0"
15'-0"
20'-0"
38'-6"
01:0
2.
38'-6"
01:0
2.
38'-6"
01:0
1.
TOURIST PLACES in & AROUND AMRITSAR
Golden Temple(Harmander
Sahib)
Durgiana Temple (Lakshmi
Narain Temple)
Wagah Border
Ram Bagh
Ram Tirath
NUMBERS
Pul Kanjari
HOTELS NO. OF
Samadhi of Guru Angad Dev
ROOMS
Ji
Jama Masjid Khairuddin
DHARMA
Samadh of Shravan
SHALAS NUMBERS
Khoo Kalyanwala
NO. OF
The Historical Banyan Tree(
ROOMS
Shaheedi Bohr)
HOUSING & SERVICES FOR
URBAN POOR
Estimated average age in the slums is
about 16 years 36% and the total
population (about 6.45 hectares)
Many of these pucca houses but are
quasi-legal and/or lack major services.
Proposal: An amount of Rs. 70 Crores
(98%) have been earmarked for Urban
Poor Housing
and services.
PROBLEMS OF URBAN POOR
Increasing trend of slum population
Land encroachment
Inadequate infrastructure, unhygienic
environment
Improper accessibility
Improper street light
BASIC SERVICES: ACCESS AND NEEDS
Amritsar is not visited by too many intra
state visitors but visited by a commendable
no. Of interstate & international visitors.
About 70000 visitors visit the place every
day which adds to the floating population
of the place
BUILDING BYELAWS (HOUSING)
An international airport, on
Ajnala road 15 km from the
Amritsar railway station
Well connected to Delhi,
Srinagar and Chandigarh by
regular domestic flights.
International flights are mainly
destined to Afghanistan,
Birmingham, China, Singapore,
Toronto etc.
Water supply in 61% of slum areas
sewerage to 52% of slum areas
65% provided with open drains
68% with brick paving
24% streets have street lighting
THE WALLED CITY OF
AMRITSAR
GROUP HOUSING, MULTI-STOREYED BUILDINGS/APARTMENTS:
Maxim
Sr.N Minimum Plot
um
o. size
Site coverage F.A.R. Maximum Height
59'-6" (excluding
1000 sq. yds.
Not exceeding
parapet water tank, &
1(minimum size) 50%
01:02.0mumty, etc.)
70'-6" (excluding
Above 100 sq. Not exceeding
parapet water tank, &
2yds. plots
50%
01:02.0mumty, etc.)
HOUSES FOR URBAN POORS UNDER
VAMBAY SCHEME
1400 One Room Tenements by
Municipal Corporation Amritsar
CIVIC BODIES INVOLVED
117
2094
6
750
UNDERSTANDING A CITYS PLANNING
INTERVENTION THROUGH REFERENCE STUDY
Suparna Dasgupta
13AR60R38
You might also like
- Sikh ArchitectureDocument3 pagesSikh ArchitectureMandeep Kaur Bains100% (1)
- Public Notice Notification - HMDA (A)Document4 pagesPublic Notice Notification - HMDA (A)Shaik Zayed100% (1)
- S4P Guidance On How To Make A Successful Design SubmissionDocument46 pagesS4P Guidance On How To Make A Successful Design SubmissionITDP India100% (1)
- Landscape Ecology and Enivornment and EiaDocument26 pagesLandscape Ecology and Enivornment and EiaparvathabaskarNo ratings yet
- Town PlaningDocument5 pagesTown PlaningMubasher ZardadNo ratings yet
- Shopping CenterDocument44 pagesShopping CenterineeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Case StudyDocument4 pagesGujarat Case Studysketch up0% (1)
- Karol Bagh & Patel NagarDocument18 pagesKarol Bagh & Patel NagarApu RvaNo ratings yet
- Community HousingDocument45 pagesCommunity HousingTwinkle MaharajwalaNo ratings yet
- Hyderabad MasterplanDocument25 pagesHyderabad MasterplanShirin Hasan100% (1)
- Ud Asgn01 DelhiDocument64 pagesUd Asgn01 DelhiKavitha GnanasekarNo ratings yet
- Landscape Case StudyDocument9 pagesLandscape Case StudyAnil AbduNo ratings yet
- Kathmandu Valley Beautification ProgramDocument102 pagesKathmandu Valley Beautification ProgramBidur KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Civic Culture and Public Spaces of VaranasiDocument39 pagesCivic Culture and Public Spaces of VaranasiShubham Mathur100% (1)
- Infra ReportDocument3 pagesInfra ReportjuniorarkeeNo ratings yet
- Revised Draft Report Volume IDocument75 pagesRevised Draft Report Volume INishith MohanNo ratings yet
- Outer Ring Road For Thiruvananthapuram Compressed 1Document13 pagesOuter Ring Road For Thiruvananthapuram Compressed 1Aswin OwnerNo ratings yet
- Market Research On Lajpat NAGARDocument8 pagesMarket Research On Lajpat NAGARKishan jhaNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Paper JetirDocument4 pagesDissertation Paper JetirVIVEK DESAINo ratings yet
- Constantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDocument12 pagesConstantinos A.Doxiadis: Islamabad - Town PlanningDhari KaranNo ratings yet
- Heritage Conservation and Planning New Development in Bhaktapur NepalDocument18 pagesHeritage Conservation and Planning New Development in Bhaktapur NepalUnited States National Committee of the International Council on Monuments and Sites100% (1)
- Delhi Masterplan ReviewDocument26 pagesDelhi Masterplan ReviewMrigank VatsNo ratings yet
- Ghaziabad ReviewDocument69 pagesGhaziabad ReviewAbhishek Venkitaraman IyerNo ratings yet
- Changing Frontiers: The Peri Urban Interface Hubli-Dharwad, IndiaDocument148 pagesChanging Frontiers: The Peri Urban Interface Hubli-Dharwad, IndiaBest Practices FoundationNo ratings yet
- ChandigarhDocument42 pagesChandigarhPrashant SeenuNo ratings yet
- Gowtham. S (Human Settlement & Planning)Document7 pagesGowtham. S (Human Settlement & Planning)Gõwthàm SNo ratings yet
- DDP Pataudi Haily Mandi-2031 Notification (English)Document20 pagesDDP Pataudi Haily Mandi-2031 Notification (English)Nakul ThakranNo ratings yet
- Human Settlements and Town PlanningDocument11 pagesHuman Settlements and Town PlanningKittur AkshayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Town PlanningDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Town PlanningKripansh Tyagi100% (1)
- Meerut City ProfileDocument4 pagesMeerut City Profileshreyabuddy165No ratings yet
- Rural Study GuidelinesDocument4 pagesRural Study GuidelinespradeepNo ratings yet
- Nagpur City Profile PDFDocument9 pagesNagpur City Profile PDFpradeepNo ratings yet
- Jaipur Real Estate 2013Document20 pagesJaipur Real Estate 2013Radhika VijayNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Master Plan For Kakinada Municipal Corporation Area and Its 5 Kms VicinityDocument23 pagesPreparation of Master Plan For Kakinada Municipal Corporation Area and Its 5 Kms VicinitySathya BobbyNo ratings yet
- Aurangabad - S4P W2 PDFDocument17 pagesAurangabad - S4P W2 PDFITDP IndiaNo ratings yet
- Kahn Riverfront Development: Environmental Planning and Design Cae-1 Assignment 37210901 K. Sri ChaanthanaDocument23 pagesKahn Riverfront Development: Environmental Planning and Design Cae-1 Assignment 37210901 K. Sri ChaanthanaK.SRI CHAANTHANANo ratings yet
- Assessing Urban Open Spaces in Township PlanningDocument13 pagesAssessing Urban Open Spaces in Township PlanningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Article On OAGCDocument11 pagesArticle On OAGCcrdpkerala govNo ratings yet
- Critical RegionalismDocument5 pagesCritical RegionalismSreerag NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Surat DraftDocument34 pagesSurat DraftgercbrdNo ratings yet
- PokharaDocument15 pagesPokharasanam subedi100% (1)
- Chaardham Ghats-A Religious Recreational HubDocument6 pagesChaardham Ghats-A Religious Recreational HubManvi Agarwal100% (1)
- Draft SCP ChandigarhDocument27 pagesDraft SCP ChandigarhSaikhulum NarjaryNo ratings yet
- Town and Country Planning Organisation (TCPO) : ObjectivesDocument2 pagesTown and Country Planning Organisation (TCPO) : ObjectivesVikrant ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument17 pagesReferenceKripansh TyagiNo ratings yet
- UjjainDocument201 pagesUjjainjkkar12100% (1)
- Status of Lakes in HyderabadDocument64 pagesStatus of Lakes in HyderabadNisha PNo ratings yet
- Socio Economic Profile of AurangabadDocument72 pagesSocio Economic Profile of AurangabadShrinath DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Revised City Development Plan For Panaji 2041 2Document392 pagesRevised City Development Plan For Panaji 2041 2ANSAL SALIMNo ratings yet
- Ganga Cypress PuneDocument1 pageGanga Cypress PuneSanjay DuraiNo ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument4 pagesSite AnalysisZarkima RanteNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TYPES OF SETTLEMENTSDocument8 pagesUnit 1 TYPES OF SETTLEMENTSAishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning Profession Education and ResearchDocument20 pagesUrban Planning Profession Education and ResearchNafisa IrinaNo ratings yet
- Argyle Street Streetscape PresentationDocument22 pagesArgyle Street Streetscape PresentationChicago Dept. of TransportationNo ratings yet
- Road Networks of Chandigarh and Gandhi NagarDocument25 pagesRoad Networks of Chandigarh and Gandhi NagarKunal BasistNo ratings yet
- Saarrthi Sovereign Pune - 0Document1 pageSaarrthi Sovereign Pune - 0rajat charayaNo ratings yet
- Amritsar City Development PlanDocument6 pagesAmritsar City Development PlanJersonFerrerasPuaNo ratings yet
- CEEW What Is Polluting Delhi Air Issue Brief PDF 12apr19 PDFDocument44 pagesCEEW What Is Polluting Delhi Air Issue Brief PDF 12apr19 PDFSumit guptaNo ratings yet
- Aadhunik Bhartiya Itihas Evam Samkalin Vishwa Itihas: Bhartiy Itihas Evam Vishva Itihas Ke 550 PrasnaFrom EverandAadhunik Bhartiya Itihas Evam Samkalin Vishwa Itihas: Bhartiy Itihas Evam Vishva Itihas Ke 550 PrasnaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of the Sky Caves: Danger and Discovery on Nepal's Mustang CliffsFrom EverandSecrets of the Sky Caves: Danger and Discovery on Nepal's Mustang CliffsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- Review 3 The Design Process: Materials & TechnologyDocument1 pageReview 3 The Design Process: Materials & TechnologySuparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Design Process-Step - 1: Neighbourhood PlanningDocument1 pageDesign Process-Step - 1: Neighbourhood PlanningSuparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- First We Shape Our Buildings, Then They Shape Us, Then We Shape Them Again-Ad InfinitumDocument3 pagesFirst We Shape Our Buildings, Then They Shape Us, Then We Shape Them Again-Ad InfinitumSuparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document1 pagePresentation 1Suparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Building TypologyDocument2 pagesBuilding TypologySuparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Space Structures - Sydney Opera: Submitted by - SUPARNA DASGUPTA BA08ARC-0037Document10 pagesCase Study of Space Structures - Sydney Opera: Submitted by - SUPARNA DASGUPTA BA08ARC-0037Suparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
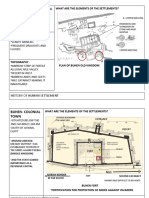
- Buhen-Colonial Town: - Situated Below The 2Nd Cataract, 260 KM South of Aswan, EgyptDocument7 pagesBuhen-Colonial Town: - Situated Below The 2Nd Cataract, 260 KM South of Aswan, EgyptSuparna DasguptaNo ratings yet
- AM2755 - Testing, Commissioning and Handover Template Rev T0Document40 pagesAM2755 - Testing, Commissioning and Handover Template Rev T0Mohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- WSE 2 Marks With AnswersDocument18 pagesWSE 2 Marks With AnswersAravindhan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- GENERAL GUIDE TO THE Polution Prevention PDFDocument97 pagesGENERAL GUIDE TO THE Polution Prevention PDFIsmar JamNo ratings yet
- Concrete Drainage PipesDocument3 pagesConcrete Drainage PipesGoldy PantaranNo ratings yet
- External Building DrainageDocument11 pagesExternal Building Drainagevelayuthan_s9168No ratings yet
- Formulation and Updating of Septage and Sewerage Management OrdinanceDocument111 pagesFormulation and Updating of Septage and Sewerage Management OrdinanceAlvin Lee Cucio AsuroNo ratings yet
- ASTM F412-12 TerminologyDocument18 pagesASTM F412-12 TerminologyMarlon TurnerNo ratings yet
- 01 PDFDocument208 pages01 PDFconcretemadNo ratings yet
- WEPA Updates On Domestic Wastewater 2021Document23 pagesWEPA Updates On Domestic Wastewater 2021Khiara Claudine EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Water-Sewage Investigation Haninge Municipality 201404Document49 pagesWater-Sewage Investigation Haninge Municipality 201404ErSoravNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document12 pagesCH 07baylorguyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1Aljon CabahugNo ratings yet
- Cork Minimum Engineering Requirementsfor Residential Site Development WorksDocument102 pagesCork Minimum Engineering Requirementsfor Residential Site Development WorksJohn DoughNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Registration and Licensing of Meat PremisesDocument21 pagesGuideline For Registration and Licensing of Meat PremisesDulas DulasNo ratings yet
- 1Document16 pages1Eyhr ZeiNo ratings yet
- Vol - 3 Road - 02-08-2021Document106 pagesVol - 3 Road - 02-08-2021Saleem Khan100% (1)
- Catalogues Au MyDocument28 pagesCatalogues Au MyChu Hữu LạcNo ratings yet
- Norms Standards Municipal Basic Services in India NIUADocument41 pagesNorms Standards Municipal Basic Services in India NIUASivaRamanNo ratings yet
- Lagos State Urban and Regional Planning and Development LawDocument72 pagesLagos State Urban and Regional Planning and Development LawDennis GodsmarkNo ratings yet
- Cruz, Leandro Meynard R. Bsce - 3Document10 pagesCruz, Leandro Meynard R. Bsce - 3Mille Alfred AgaloosNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument158 pagesCase StudiesvijkingNo ratings yet
- NASSCO Specification Guideline - Smoke Testing - May 2021Document13 pagesNASSCO Specification Guideline - Smoke Testing - May 2021Khalid KaddouraNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Pipe Fitting: Scheme of The ExaminationDocument4 pagesPlumbing and Pipe Fitting: Scheme of The ExaminationKunbi Santos-ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Ecological Building: Term Project For ME 599Document32 pagesEcological Building: Term Project For ME 599Junaid AnwarNo ratings yet
- Development Application For Ravenswood SubdivisionDocument88 pagesDevelopment Application For Ravenswood SubdivisionThe ExaminerNo ratings yet
- SPC-0804.02-99.02 Rev D2 Preparation of P&I DDocument37 pagesSPC-0804.02-99.02 Rev D2 Preparation of P&I DPadakandla Suman100% (1)
- 9 Plumbing DetailsDocument1 page9 Plumbing DetailsMilan RedosNo ratings yet
- Reference MaterialDocument134 pagesReference Materialsubashini_jaganathanNo ratings yet
- Design ReportDocument28 pagesDesign ReportKip RotichNo ratings yet