Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7 5
Uploaded by
sarasmile2009Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7 5
Uploaded by
sarasmile2009Copyright:
Available Formats
Section 7.
5 • Systems of Inequalities 137
Name______________________________________________
Section 7.5 Systems of Inequalities
Objective: In this lesson you learned how to sketch the graphs of
inequalities in two variables and to solve systems of
inequalities and how to use systems of inequalities to model
and solve real-life problems.
Important Vocabulary Define each term or concept.
Solution of an inequality An ordered pair (a, b) is a solution of an inequality in x and
y if the inequality is true when a and b are substituted for x and y respectively.
Graph of an inequality The collection of all solutions of the inequality represented
on the Cartesian plane.
Linear inequalities An inequality written in the form ax + by < c.
Solution of a system of inequalities A point (x, y) that satisfies each inequality in the
system.
Consumer surplus The area of the region that lies below the demand curve, above
the horizontal line passing through the equilibrium point, and to the right of the p-axis.
Producer surplus The area of the region that lies above the supply curve, below the
horizontal line passing through the equilibrium point, and to the right of the p-axis.
I. The Graph of an Inequality (Pages 541−542) What you should learn
How to sketch the graphs
To sketch the graph of an inequality in two variables, . . . of inequalities in two
replace the inequality sign by an equal sign, and sketch the graph variables
of the resulting equation. Use a dashed line for < or > and a solid
line for ≤ or ≥. Then test one point in each of the regions formed
by the graph of equation. If the point satisfies the inequality,
shade the entire region to denote that every point in the region
satisfies the inequality.
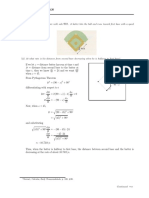
The solution points for the inequality y < 3x + 5 lie below
the line y = 3x + 5.
Example 1: Sketch the graph of the linear inequality y ≥ 2 . y
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
138 Chapter 7 • Systems of Equations and Inequalities
II. Systems of Inequalities (Pages 543−545)
What you should learn
To sketch the graph of a system of inequalities in two How to solve systems of
inequalities
variables, . . . first sketch the graph of each individual
inequality (on the same coordinate system) and then find the
region that is common to every graph in the system.
To find the vertices of the solution region for a system of three
linear inequalities, . . . solve the three systems of
corresponding equations obtained by taking pairs of equations
representing the boundaries of the individual regions.
III. Applications of Systems of Inequalities (Pages 546−547) What you should learn
How to use systems of
The consumer surplus is a measure of the amount that consumers inequalities in two
would have been willing to pay above what they variables to model and
solve real-life problems
actually paid . Producer surplus is a measure of the
amount that producers would have been willing to receive
below what they actually received .
y y y
x x x
y y y
x x x
Homework Assignment
Page(s):
Exercises:
Larson/Hostetler Precalculus/Precalculus with Limits Notetaking Guide IAE
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Section 12.5 The Area Problem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.5 The Area Problem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.8 Graphs of Polar Equations: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.3 The Tangent Line Problem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 11.2 Vectors in Space: NameDocument2 pagesSection 11.2 Vectors in Space: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: NameDocument2 pagesSection 12.4 Limits at Infinity and Limits of Sequences: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.5 Rotation of Conics: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.5 Rotation of Conics: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.9 Polar Equations of Conics: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: NameDocument2 pagesSection 11.3 The Cross Product of Two Vectors: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate SystemDocument2 pagesAnalytic Geometry in Three Dimensions: Section 11.1 The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systemsarasmile2009100% (1)
- Section 10.6 Parametric Equations: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.6 Parametric Equations: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products: NameDocument2 pagesSection 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: NameDocument2 pagesSection 8.3 The Inverse of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 10.3 Ellipses: NameDocument2 pagesSection 10.3 Ellipses: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 9.6 Counting Principles: NameDocument2 pagesSection 9.6 Counting Principles: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 7.6 Linear Programming: NameDocument2 pagesSection 7.6 Linear Programming: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: NameDocument2 pagesSection 8.4 The Determinant of A Square Matrix: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: NameDocument2 pagesSection 9.5 The Binomial Theorem: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 7.1 Linear and Nonlinear Systems of EquationsDocument4 pagesSection 7.1 Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equationssarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas: NameDocument4 pagesSection 5.5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 6.2 Law of Cosines: NameDocument2 pagesSection 6.2 Law of Cosines: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.4 Sum and Difference Formulas: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: NameDocument2 pagesSection 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Section 4.8 Applications and Models: NameDocument2 pagesSection 4.8 Applications and Models: Namesarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Analytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental IdentitiesDocument2 pagesAnalytic Trigonometry: Section 5.1 Using Fundamental Identitiessarasmile2009No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- LSTM PDFDocument48 pagesLSTM PDFAZEDDINENo ratings yet
- Transaction Costs and Non-Markovian Delta HedgingDocument14 pagesTransaction Costs and Non-Markovian Delta HedgingpostscriptNo ratings yet
- MB0048 Set1 & Set2Document13 pagesMB0048 Set1 & Set2sarojda9No ratings yet
- Discrete B-Splines and Subdivision Techniques in Computer-Aided Geometric Design and Computer Graphics PDFDocument26 pagesDiscrete B-Splines and Subdivision Techniques in Computer-Aided Geometric Design and Computer Graphics PDF姜豪No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TOnLINEAR PROGRAMMINGDocument9 pagesINTRODUCTION TOnLINEAR PROGRAMMINGPrincess Amber0% (2)
- Fundamentals of CFDDocument276 pagesFundamentals of CFDSainath SatishNo ratings yet
- Limit TheoremsDocument20 pagesLimit Theoremssvillejohn05No ratings yet
- COR 005 Assessment (F1F2A1A2B1)Document12 pagesCOR 005 Assessment (F1F2A1A2B1)AnoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document5 pagesLecture 25Syeda Farkhanda Batool NaqviNo ratings yet
- Spinrad. Graph Theory (Book Draft)Document7 pagesSpinrad. Graph Theory (Book Draft)lecuongttbkNo ratings yet
- Ad ReferDocument53 pagesAd ReferHoàng Duy ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Uc1.b4064632 368 1588311712Document1 pageUc1.b4064632 368 1588311712vigneshwaran50No ratings yet
- Maths2A 75 - 75 March 2023Document14 pagesMaths2A 75 - 75 March 2023sai mukeshNo ratings yet
- School - Data - ADIS1 - Assignment - 20511 - Grade 10 Revision Worksheet 1 Term 1 - NewDocument4 pagesSchool - Data - ADIS1 - Assignment - 20511 - Grade 10 Revision Worksheet 1 Term 1 - Newsharon VijuNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 - Math 212Document1 pageExam 1 - Math 212Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- Função de GudermannDocument3 pagesFunção de GudermannElaine MoratoNo ratings yet
- An Application of Approximation Theory To Numerical Solutions For Fredholm Integral Equations of The Second KindDocument7 pagesAn Application of Approximation Theory To Numerical Solutions For Fredholm Integral Equations of The Second KindIL Kook SongNo ratings yet
- Simplex Economic InterpretationDocument34 pagesSimplex Economic InterpretationVinayak SinglaNo ratings yet
- Fisher Information and Cram Er-Rao Bound: Lecturer: Songfeng ZhengDocument12 pagesFisher Information and Cram Er-Rao Bound: Lecturer: Songfeng Zhengprobability2No ratings yet
- h1 Cse548 Spring2012Document4 pagesh1 Cse548 Spring2012stonethumbNo ratings yet
- Schmid and Henningson (2001) - Stability and Transition in Shear Flows PDFDocument561 pagesSchmid and Henningson (2001) - Stability and Transition in Shear Flows PDFJim67% (3)
- 09-Digital Control SystemsDocument2 pages09-Digital Control Systemssanjy_69No ratings yet
- Grphics Viva Question:: Plain Scale Diagonal ScaleDocument4 pagesGrphics Viva Question:: Plain Scale Diagonal ScaleAvinash GuptaNo ratings yet
- DSP-1 (Intro) (S)Document77 pagesDSP-1 (Intro) (S)karthik0433No ratings yet
- Ex# (3.1-3.2-3.4) First Year StepDocument11 pagesEx# (3.1-3.2-3.4) First Year StepAqeel AbbasNo ratings yet
- MCQS Module 2 RGPV Mathematics IiiDocument8 pagesMCQS Module 2 RGPV Mathematics IiiMohit BhalekarNo ratings yet
- Pre University h2 Further MathematicsDocument22 pagesPre University h2 Further MathematicsLeng RyanNo ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer T-Chart CompletedDocument2 pagesGraphic Organizer T-Chart Completedapi-312390227No ratings yet
- 03 09 020 Related RatesDocument2 pages03 09 020 Related RatesKirz SerranoNo ratings yet
- Lec9 PDFDocument5 pagesLec9 PDFrishitNo ratings yet