Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Organelles
Uploaded by
jcatrett8306Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Organelles
Uploaded by
jcatrett8306Copyright:
Available Formats
BIO 103
THE CELL
STRUCTURES IN CYTOPLASM
The following are found in the cytoplasm of most cells. Your textbook contains more extensive explanations of these
structures.
1.
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
An organelle consisting of an extensive system of channels and compartments
a. rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) - ER with ribosomes on its surface; usually involved in the synthesis of
proteins
b. smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) - ER with no ribosomes on its surface; usually involved in the
synthesis of lipids and other macromolecules
2.
ribosomes
The site of protein synthesis in the cell. It is not considered an organelle because it is not enclosed by a membrane.
This structure can be associated with the ER or they can be free in the cytoplasm.
3.
Golgi Complex (Golgi or Golgi Apparatus)
An organelle that collects, modifies, packages, and distributes molecules.
4.
vesicles
An organelle that consists of a small membrane bound sac that stores substances in a cell.
ex. lysosome - A vesicle that contains a mixture of digestive enzymes which are capable of breaking down
macromolecules. They are sometimes called suicide sacs.
5.
mitochondria (plural) (mitochondrion - singular)
The powerhouse of the cell. The site of cell respiration or oxidative metabolism. Extracts energy from
macromolecules in the presence of oxygen. Mitochondria have two membranes-an outer and an extensively folded
inner membrane. The folds of the inner membrane are called cristae. The interior of the mitochondria is called the
matrix. (Note: DNA is found in the mitochondria and is called mitochondrial DNA. It is only passed from mother to
offspring)
6.
cytoskeleton
A matrix of protein fibers that supports the shape of the cell and anchors organelles. It is a very extensive network.
7.
flagella
A fine, long, threadlike organelle that is used by a cell for locomotion and/or feeding. Cells can have various numbers
of flagella.
8.
cilia
An organelle similar to flagella but usually more numerous, shorter, and in dense rows. They may be used for
locomotion, to assist feeding, or used to move substances across the surface of the cell.
9.
centrioles
An organelle found only in animal and protist cells (not in plants) that assemble and organize microtubules. They
influence cell shape, move chromosomes during cell division, and provide functional internal structure for cilia and
flagella.
STRUCTURES FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS
10. plastids
Organelles in plants cell that store pigments or macromolecules.
ex. chloroplast - A plastid that contains chlorophyll and is the site of photosynthesis. It has an outer and an inner
membrane but it also has inner membranes. These inner membranes form the membranes around the thylakoids.
Thylakoids are flattened sac like membranes formed by the inner membrane. Grana are stacks of thylakoids.
Stroma is the semifluid substance around the thylakoids and inside the inner membrane. Lamella connect adjacent
grana.
11. cell wall
A nonliving layer outside of the plasma membrane in plant cells. It is composed primarily of cellulose.
12. vacuoles
A fluid filled sac, an organelle, that may contain a variety of substances. Plant cells have a large, central vacuole that
pushes other organelles, including the nucleus, toward the plasma membrane. Because of this, you will not be able to
see the nucleus in a plant cell.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Morals and Ethics of Using Stem CellsDocument2 pagesMorals and Ethics of Using Stem Cellssfe sfgNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 4 - Absorption of Roots Biology: Book Name: Selina ConciseDocument17 pagesClass X Chapter 4 - Absorption of Roots Biology: Book Name: Selina ConciseMallikarjuna MuthyaluNo ratings yet
- Fragrance With Antiaging Benefits: Naturals-Driven Functionality For Added ValueDocument6 pagesFragrance With Antiaging Benefits: Naturals-Driven Functionality For Added Valuejasminai_17No ratings yet
- Human Chromosomes and GenesDocument2 pagesHuman Chromosomes and GeneshomamunfatNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NOTESDocument11 pagesMitosis Meiosis NOTESCaden DiazNo ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument38 pagesEPITHELIUMAstridNo ratings yet
- Regents Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesRegents Protein Synthesisabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- NecrosisDocument12 pagesNecrosisAneeza AhmadNo ratings yet
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document15 pages٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular Biology20304105Document8 pagesCell and Molecular Biology20304105مروة صلاحNo ratings yet
- Eoc Review Packet 2018Document25 pagesEoc Review Packet 2018api-375285021No ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument21 pagesBiotechnologyShivangi Mishra50% (2)
- Anthony D. Woolf, Kristina Akesson Osteoporosis An Atlas of Investigation and Diagnosis 2008Document166 pagesAnthony D. Woolf, Kristina Akesson Osteoporosis An Atlas of Investigation and Diagnosis 2008Stefania NicuNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- CLS 715 Immunological Synapse 2023Document14 pagesCLS 715 Immunological Synapse 2023Heba LahhamNo ratings yet
- New Lipid PowerpointDocument113 pagesNew Lipid PowerpointMadane Jamila Amerol SaminNo ratings yet
- Botany DU 2820947q23Document45 pagesBotany DU 2820947q23Janus MalikNo ratings yet
- NLRP3 InflammasomeDocument11 pagesNLRP3 InflammasomeUmmuNo ratings yet
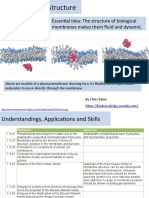
- 1.3 Membrane StructureDocument31 pages1.3 Membrane StructureEthan MaysonNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument17 pagesPROTEINSAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- MSC Biotechnology Syllabus FINALDocument53 pagesMSC Biotechnology Syllabus FINALdeepakNo ratings yet
- Xun Xu The Genomic Sequence Chinese HamsterDocument8 pagesXun Xu The Genomic Sequence Chinese HamsterAbhishek NaikNo ratings yet
- Sasakawa 2010Document15 pagesSasakawa 2010Kavyarani RathodNo ratings yet
- The Cell Biology PDFDocument66 pagesThe Cell Biology PDFSamina PachaNo ratings yet
- Durham-Moore Edible Cell Project and RubricDocument2 pagesDurham-Moore Edible Cell Project and Rubricmindmover0003100% (1)
- Epidermal Permeability Barrier Defects and Barrier Repair Therapy in Atopic DermatitisDocument12 pagesEpidermal Permeability Barrier Defects and Barrier Repair Therapy in Atopic DermatitisMisaeldpdNo ratings yet
- BIO230 Exam ReviewDocument24 pagesBIO230 Exam ReviewRomo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- BEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Diagnostic - Animal Cell or Plant CellDocument5 pagesBEST - BCL - 1 - 2 - Diagnostic - Animal Cell or Plant CellmtauhidNo ratings yet
- 1st Lec On Endo Physiology by DR RoomiDocument24 pages1st Lec On Endo Physiology by DR RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Hema 1-Module 2 - Topic 2-Answer SheetDocument3 pagesHema 1-Module 2 - Topic 2-Answer SheetKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet