Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive System I. Introduction/Overview: Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
Uploaded by
billOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digestive System I. Introduction/Overview: Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
Uploaded by
billCopyright:
Available Formats
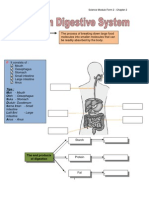
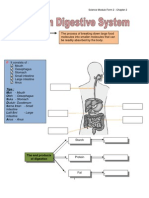
Digestive System
I.
Introduction/Overview
A.
B.
____________________:
1.
Breakdown of ____________________ into small soluble ____________________
2.
Occurs ____________________ and ____________________
____________________:
1.
C.
II.
Taking ____________________ the body of the specific compounds
____________________:
1.
____________________ of materials not absorbed (taken into) the body
2.
____________________
Location of Parts and Function
A.
1.
Teeth
Type of teeth depends on ____________________ type:
a.
____________________: teeth for grasping ____________________ and severing
meat from bones
b.
____________________: flat teeth surfaces for ____________________ plant
fibres
c.
____________________: have a variety of tooth types for both
____________________ and ____________________ matter
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
2.
Structure
a.
Covered by a very hard substance called
____________________
b.
Under this: is the softer ____________________
(bony)
c.
Living part of the tooth is the pulp which contains
____________________ and
____________________ ____________________
d.
3.
B.
Function: ____________________ digestion of food.
Tongue
1.
2 functions:
a.
b.
C.
Teeth fit into ____________________ in the ____________________
____________________
i.
____________________
ii.
____________________
iii.
____________________
iv.
____________________
Help ____________________ ____________________ in the teeth
Salivary Glands
1.
2.
3 pairs:
a.
____________________ on side of face (swell with the mumps)
b.
____________________ (below tongue)
c.
____________________ both in lower jaw
Produce ____________________
a.
Helps forms a ____________________ (food ball)
b.
Begins ____________________ digestion with the
____________________ ____________________
D.
c.
Rinse/____________________ the mouth
d.
____________________ mouth lining
e.
____________________e soluble particles
f.
____________________/lubricate food
Palates
1.
Locate at the ____________________ of the mouth
2.
Both ____________________ (____________________) and ____________________
(____________________)
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
3.
Separates the ____________________ from the ____________________
cavity
4.
E.
End in a flap called the ____________________
Pharynx (#8)
1.
Area between the ____________________ and the ____________________
2.
Pharynx is a ____________________ used for breathing and eating
3.
____________________ (#9) closes off the opening to the glottis (larynx) when food is
swallowed to prevent ____________________
F.
Esophagus (#7)
1.
Muscular tube that pushes the food to the ____________________ by
____________________
G.
Cardiac Sphincter (#10)
1.
____________________ that surrounds the ____________________ at its
junction with the ____________________
2.
H.
____________________ to admit food into the ____________________
Stomach (#6)
1.
____________________ pouch or enlargement of the
____________________ tract
2.
Located slightly ____________________ of center in the body
3.
Capacity: about ____________________
4.
Inner ____________________ lining contains ____________________
glands
a.
____________________ cells to produce ____________________
b.
____________________ cells produce ____________________, which is activated
by ____________________ into
enzyme ____________________
c.
____________________ cells produce mucus to
____________________ the stomach lining
5.
Function
a.
____________________ ____________________ for ingested food (empties in
____________________ hours)
b.
Place for ____________________ ____________________ (pepsin and salivary
amylase) to work
c.
____________________ of small molecules (e.g.
____________________, ____________________)
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
d.
____________________ amount of ____________________
produced:
i.
Extra protein will stimulate lower stomach to secrete hormone called
____________________ which will stimulate the ____________________
____________________ cells to produce ____________________
____________________
I.
Pyloric sphincter (#11)
1.
____________________ that surrounds the ____________________ at its junction with
the ____________________
____________________
2.
Opens to admit ____________________ into the ____________________
____________________
J.
Small Intestine
1.
____________________ meters or 10 feet in length
2.
Walls highly convoluted to ____________________.
3.
Interior folds covered with ____________________: tiny fingerlike projections that further
____________________.
4.
Divided into 3 parts
a.
____________________ (first 25 cm) (#3)
i.
Produces digestive enzymes: ____________________
____________________ ____________________
____________________
ii.
____________________ duct and ____________________ duct enter here
with their secretions.
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
b.
____________________
c.
____________________
5. Functions:
a.
Completes ____________________ ____________________
b.
____________________ of nutrients
i.
____________________, ____________________,
____________________, ____________________ are
transported into ____________________ ____________________, and
diffuse into _________________
ii.
____________________ diffuse into intestinal cells and are deposited in the
____________________ (lymph vessel in the villus)
K.
Liver (#2)
1.
____________________ internal organ in the body
2.
Constant monitoring of the ____________________ contents as the blood comes from the
small intestine via the ____________________ ____________________
____________________
3.
Functions:
a.
____________________ and ____________________ toxic materials
i.
b.
Example: ____________________ detoxification
____________________ extra glucose in the form of ____________________
i.
Will also convert ____________________ to ____________________
when blood sugar levels drop
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
c.
Destroys old red blood cells
i.
Hemoglobin broken down:
1.
____________________ is recovered/sent to bone marrow for use
in new red blood cells
2.
Protein is degraded into bilirubin and biliverdin that are excreted as
____________________
d.
Produces bile
i.
____________________ fluid
ii.
Stored in the ____________________ ____________________
iii.
____________________ fats
1.
Breaks fat drops into ____________________ droplets
2.
Helps fats stay in suspension in ____________________
environment
3.
Increased surface area of the fat aids ____________________
function
e.
Produces ____________________ from breakdown product of
____________________ ____________________
i.
Urea is ____________________ waste
f.
Makes ____________________ proteins
g.
Stores ____________________ and the ________________________________________ vitamins A, D, E and K
h.
Converts ____________________ ____________________ to
____________________ if necessary (____________________)
L.
Pancreas (#5)
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
1.
Produces ____________________ juice (____________________
____________________ and ____________________ ____________________ to
neutralize acidic ____________________)
2.
Produces ____________________, a hormone that influences the cells
____________________ of ____________________ from the ____________________
3.
____________________ juice and ____________________ are produced in response to
the ____________________ ____________________ from the stomach
a.
____________________ triggers the release of the hormones
____________________ and ____________________ (CCK) from the
____________________
i.
____________________ triggers release of
____________________ ____________________
ii.
____________________ triggers release of
____________________
M.
Caecum
1.
____________________ pouch at the end of the small intestine
2.
____________________ ____________________ in humans (vestigial)
3.
In herbivores, the ____________________ is broken down here by microbes that live in
the animal
4.
Appendix (#12) is a ____________________ ____________________-
____________________ growth off the end of the caecum
N.
Large Intestine (#4)
1.
5 parts
a.
____________________ ____________________
b.
____________________ ____________________
c.
____________________ ____________________
d.
____________________ - ____________________
____________________
e.
____________________- muscles close the rectum until release of feces is
appropriate
2.
Functions
a.
____________________ of ____________________
i.
b.
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
____________________ of the daily 10 L of water is removed
____________________ of ____________________
c.
____________________ of some amino acids, growth factors, vitamins B's and K
by E.coli)
3.
E. coli bacteria
a.
____________________ some undigestable material
b.
Produce ____________________ (____________________)
c.
Produce ____________________ ____________________
d.
Produce ____________________
e.
Produce ____________________ factors (proteins that stimulate cell
growth)
4.
III.
Feces is composed of
a.
____________________ food (mainly cellulose)
b.
Dead ____________________
c.
____________________
Digestive Enzymes
A.
Enzymes break down food into small molecules which are then absorbed
Name:
IV.
Source:
pH:
Digests:
Product:
Swallowing and Peristalsis
A.
Swallowing:
1.
Occurs in the ____________________
2.
A ____________________ action
3.
____________________ ____________________ closes off nasal cavities
4.
____________________ covers the opening to the ____________________
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
B.
The esophagus moves the ____________________ into the stomach by ____________________
1.
(defn): a rhythmic, wavelike contraction of the ____________________ and
____________________
2.
Muscle contractions (____________________ muscle) run along the tube and push food
material in
____________________ direction
V.
Insulin (and Glucagon)
A.
Insulin (secreted in response to high glucose levels after eating)
1.
Produced by cells in the pancreas called ____________________ of
____________________, which secrete directly into ____________________
2.
Acts upon the cell membranes of ____________________, ____________________, &
____________________ cells
3.
Insulin receptors on outer membrane open ____________________ proteins in the
____________________, allowing ____________________ to enter the cells from the
blood
4.
Stimulates the ____________________ and ____________________ to convert
____________________ to ____________________, as well as promoting the formation
of fats and proteins
5.
Big Picture: Insulin promotes
_______________________________________________________________________
______________
B.
Glucagon (secreted between meals)
1.
Also produced by cells ____________________ of ____________________
2.
Increases ____________________ glucose levels
3.
Stimulates ____________________ of stored nutrients
4.
Big Picture: Glucagon promotes
___________________________________________________________
Mrs. Kusec Biology 12
You might also like
- Activity Sheet 10 & 11 GenBio1Document6 pagesActivity Sheet 10 & 11 GenBio1Marlou GayaneloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Homeostasis - Tutorial WorksheetDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Homeostasis - Tutorial Worksheetapi-3728508100% (3)
- AUBF QFRs Week 2Document8 pagesAUBF QFRs Week 2Jacquelyn PerezNo ratings yet
- Biomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesDocument19 pagesBiomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- 9th class biology PBA PAPERDocument9 pages9th class biology PBA PAPERhadiabdul56755No ratings yet
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - CLOZE Macromolecules BioACC CH 3 NotesDocument6 pagesKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - CLOZE Macromolecules BioACC CH 3 NotesALEXA CADENANo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Exam OverviewDocument10 pagesBiology Form 4 Exam Overviewmark smithNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Work Book 1Document64 pagesBasic Science Work Book 1Arezoo ZargollNo ratings yet
- SST6Chapter25outline PDFDocument17 pagesSST6Chapter25outline PDFRosemarie CatanoNo ratings yet
- Literacy 1A Homework Set 1Document34 pagesLiteracy 1A Homework Set 1EdwinNo ratings yet
- Home Economics worksheet on food preservationDocument2 pagesHome Economics worksheet on food preservationDaejah Gordon100% (1)
- Test Science 6th HealthyDocument5 pagesTest Science 6th HealthylourdesNo ratings yet
- C8 Study Guide 8-2Document2 pagesC8 Study Guide 8-2LaikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Cellular RespirationCarmenNo ratings yet
- Molecule of LifeDocument19 pagesMolecule of LifeFatin Arishya AqilahNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida Biology, Class Ix Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Resource Sheet 1 (MLP 1)Document4 pagesAmity International School, Noida Biology, Class Ix Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Resource Sheet 1 (MLP 1)Shubham SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Document2 pagesRESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Science No.24 PDFDocument9 pagesScience No.24 PDFPanida Mhew SukkasemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellAveen ShabanNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology WORKSHEETDocument7 pagesCSEC Biology WORKSHEETAnderson Michelle100% (1)
- Unit I. Biomolecules, Respiration and Metabolism Free Radicals and Oxidative StressDocument11 pagesUnit I. Biomolecules, Respiration and Metabolism Free Radicals and Oxidative StressAngie CaragNo ratings yet
- ChapterGuide CellularEnergyDocument14 pagesChapterGuide CellularEnergycorygunther100% (1)
- Science Year 3 AssessmentDocument5 pagesScience Year 3 AssessmentHasenna Liew HasimNo ratings yet
- Starter Pack Activities 2022Document22 pagesStarter Pack Activities 2022Alejandra BarrettNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Let's Time Travel!: Colina, Angela Kathryne V. September 26, 2021 Grade Ix AirDocument2 pagesLet's Time Travel!: Colina, Angela Kathryne V. September 26, 2021 Grade Ix AirF-COLINA, ANGELA KATHRYNENo ratings yet
- 2021 Marking ShemeDocument11 pages2021 Marking ShemediegocmakoNo ratings yet
- 4 - Enzymes ExtendedDocument6 pages4 - Enzymes ExtendedYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Med Faculty HomeworkDocument2 pagesMed Faculty HomeworkLucian AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological Organization Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesLevels of Biological Organization Worksheet PDFasungapeNo ratings yet
- APT 51 Activity 2Document6 pagesAPT 51 Activity 2Velynda JulioNo ratings yet
- Bio - IIDocument12 pagesBio - IIMalitha PeirisNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Test G2Document4 pagesAptitude Test G2fordsbedtrustschoolNo ratings yet
- Cumulative G-4Document3 pagesCumulative G-4Hisham PrimeNo ratings yet
- s2 Final Study GuideDocument12 pagess2 Final Study Guideapi-242868690No ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument12 pagesCell NotesP1No ratings yet
- Biochem Practice Test Nov 2020 No EnzymesDocument4 pagesBiochem Practice Test Nov 2020 No EnzymesWen CenaNo ratings yet
- Biology Review Test - Part 2 - Grade 10Document11 pagesBiology Review Test - Part 2 - Grade 10Arhant KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Grade VI Summer Break Science TasksDocument8 pagesGrade VI Summer Break Science TasksGhulam Rasool MagsiNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4) Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument2 pagesBiology (Form 4) Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellSiti MadihahNo ratings yet
- Bio-Gisell 3Document7 pagesBio-Gisell 3ht7vp7vk2cNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesistrypalanineNo ratings yet
- p.5 Sci Revision Test 2020 Exam Teacher - AcDocument7 pagesp.5 Sci Revision Test 2020 Exam Teacher - AcBartsford job Kato EnockNo ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive System PDFDocument22 pagesExercise Digestive System PDFIzudin Hasan86% (7)
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- Mention The Process, Organ or Nutrient According To The Function in Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesMention The Process, Organ or Nutrient According To The Function in Digestive SystemRida Fatima Azhar - 74894/TCHR/BARNo ratings yet
- Content Review PacketDocument9 pagesContent Review Packetapi-342334216No ratings yet
- P.2-Literacy God CaresDocument4 pagesP.2-Literacy God Caresmutokambare jamesNo ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- 3 Sanitary Procedures That Can Help Reduce Contamination in The Food Preparation Area in A Foodservice Facility (6pts)Document3 pages3 Sanitary Procedures That Can Help Reduce Contamination in The Food Preparation Area in A Foodservice Facility (6pts)Yan Yan YanNo ratings yet
- Cell SpecialisationDocument4 pagesCell SpecialisationAvila VarshiniNo ratings yet
- P6 End of Term I Science 2023Document6 pagesP6 End of Term I Science 2023Kinsambwe Noah100% (1)
- EVS Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesEVS Revision WorksheetBHUVI KUMARINo ratings yet
- 5 0 Biogeochemical CyclingDocument7 pages5 0 Biogeochemical Cyclingapi-222503660No ratings yet
- P. 7 End of Term I ExaminationDocument9 pagesP. 7 End of Term I Examinationkakeetodavid807No ratings yet
- Jim PPS P.2 Lit1 ADocument12 pagesJim PPS P.2 Lit1 AKisaakye LorrinNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Quarter 1 Week 2Document21 pagesAnswer Sheet Quarter 1 Week 2elleniel joy pablicoNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Topic 4 - Ecology Revision Sheet: BackbirdDocument1 pageIB Biology Topic 4 - Ecology Revision Sheet: BackbirdLexieNo ratings yet
- The Stress-Free Guide to Parenting a Child With ADHD: Effective and Proven Strategies for Alleviating Anxiety and Forming Strong Bonds Without the HassleFrom EverandThe Stress-Free Guide to Parenting a Child With ADHD: Effective and Proven Strategies for Alleviating Anxiety and Forming Strong Bonds Without the HassleNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- RECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2Document62 pagesRECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2RadianNasution100% (1)
- % Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodDocument33 pages% Chapter 3: Regulation of Gas Content in BloodK CNo ratings yet
- Byssinosis PDFDocument8 pagesByssinosis PDFFaza AlhinduwanNo ratings yet
- HBCJ Npev Vedw T60B PDFDocument20 pagesHBCJ Npev Vedw T60B PDFAnonymous fPQaCe8No ratings yet
- PDF Sunset and Desire by Paz LatorenaDocument12 pagesPDF Sunset and Desire by Paz LatorenaBebelyn PatricioNo ratings yet
- Development - of - CVS-5Document20 pagesDevelopment - of - CVS-5Ahsan IslamNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPbabycheska08No ratings yet
- Snakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFDocument5 pagesSnakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFhoticeforuNo ratings yet
- Mpla 021 Exam May 2017 P1Document4 pagesMpla 021 Exam May 2017 P1Phindile MavimbelaNo ratings yet
- Amphibian Graphs?Document9 pagesAmphibian Graphs?Anshumaan PatraNo ratings yet
- Individual Behaviour: Biographical CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesIndividual Behaviour: Biographical Characteristicsapi-3792827No ratings yet
- Heat StressDocument39 pagesHeat StressDelando CoriahNo ratings yet
- Hillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial CellDocument8 pagesHillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial Celloli JrNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System For MBBSDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System For MBBSjacobsNo ratings yet
- TRX Force Tactical Kit - Essential Protein for Cellular ReactionsDocument11 pagesTRX Force Tactical Kit - Essential Protein for Cellular ReactionsRafael FilhoNo ratings yet
- Language and BrainDocument23 pagesLanguage and Brainalbino100% (1)
- Physiology Objectives DetailedDocument35 pagesPhysiology Objectives DetailedSOOOS94No ratings yet
- Functional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and StrengthDocument2 pagesFunctional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and Strengthtodd455No ratings yet
- Assessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument15 pagesAssessment of Fluid and ElectrolyteDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- Fat Burn ConceptDocument31 pagesFat Burn ConceptManoj100% (1)
- Biochemistry Notes-Study GuideDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Notes-Study Guidegmanb5100% (2)
- 11.transportation in Plants & AnimalsDocument51 pages11.transportation in Plants & AnimalsReshma ModhiaNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic Painn PDFDocument20 pagesNeuropathic Painn PDFkaktusNo ratings yet
- Neuroparasitology PDFDocument62 pagesNeuroparasitology PDFpsetoNo ratings yet
- Principles & Practice of First AidDocument298 pagesPrinciples & Practice of First AidJoshua100% (2)
- Sleep Disordered Breathing: Ramon Alcira, MD, FPSO-HNSDocument3 pagesSleep Disordered Breathing: Ramon Alcira, MD, FPSO-HNSMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Histological Characteristics of the Lingual FrenulumDocument1 pageHistological Characteristics of the Lingual FrenulumajudNo ratings yet
- Binocular Anomalies - GriffinDocument595 pagesBinocular Anomalies - GriffinAdolph Grey75% (4)
- Chronic UrticariaDocument40 pagesChronic UrticariaeeeeewwwwwNo ratings yet
- Armstrong, Mechele - Blood Lines 05 - Bitter LoveDocument126 pagesArmstrong, Mechele - Blood Lines 05 - Bitter LoveMenahil BasitNo ratings yet