Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lithium With Mania Generally Show 1. Effects On Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Chelsea ValdezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lithium With Mania Generally Show 1. Effects On Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Chelsea ValdezCopyright:
Available Formats
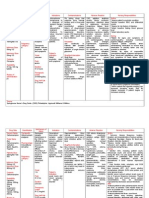
NOTES
LITHIUM
CLINICAL RESPONSE
Patients presenting
with mania generally show
at least partial response to
lithium within the first 2
weeks of therapy
For patients presenting
with depression, the
timeframe is considerably
longer. It would be 4-6 weeks
to see the response.
INDICATION
Drug of choice for the
treatment and prevention of
bipolar disorder
Lithium carbonate and
citrate are the two clinically
relevant salt forms
Lithium carbonate
Lithium citrate is available
as liquid and helpful in
patients who are
noncompliant with tablets or
capsules
Indications:
As prophylaxis in
preventing both mania and
depression
ADMINISTRATION & DOSAGE
Daily dose: 600-3600mg
among different individuals
Majority requires: 15001800 mg/d
Almost always necessary to
give Lithium in divided doses
to avoid gastric distress when
initiating treatment
Medication is best taken
with or shortly after meals
Maintenance Therapy:
Patients who have one or
more episodes of illness per
year are candidates for
maintenance treatment
MOA
1. Effects on
neurotransmitters
Inhibit NE release and
accelerate its metabolism
May increase presynaptic
re-uptake of NE and 5-HT
2. Effect on second
messengers and G
proteins:
Inhibits conversion of IP to
inositol
leads to depletion of PIP2
PIP2 IP3 and DAG
For both a-adrenergic and
muscarinic transmission
Adjunct to TCAs & SSRIs
in patients who do not
respond fully to
antidepressants alone
Schizoaffective disorders
Schizophrenic symptoms
plus altered effects in the
form of depression and
excitement
should be in combination
with antipsychotics
Lithium alone is rarely
successful in treating
schizophrenia
Effect on G-proteins
involved in receptor
desensitization, in
modulating membrane
structure events, in
regulating transcription, in
mediating immune
responses, in regulating cell
growth, and in learning,
mood and memory
Bipolar Disorder:
Mild Mania:
Lithium alone is effective
Carbamazepine is useful
when manic episodes are not
controlled by lithium alone
Severe mania
Always add clonazepam /
lorazepam and often give one
of the anti-psychotic drugs
Depression
Requires concurrent use of
antidepressants
ADVERSE EFFECTS
Neurologic and Psychiatric
Tremor
Choreoathetosis, ataxia,
dysarthria, motor
hyperactivity, aphasia
Psychiatric disturbances
(confusion)
Thyroid function
Decreased thyroid activity
(hypothyroidism)
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTIONS
Decrease Lithium conc:
Methylxanthines
Osmotic Diuretics
Pregnancy (3rd trimester)
Urine alkalinizers
Increase Lithium conc:
ACE inhibitor
NSAIDs
Thiazides
Dehydration
Postpartum
Renal
Polyuria, polydipsia
reversible
Lithium-induced diabetes
insipidus
Treatment: amiloride
Long term renal dysfunction:
Chronic interstitial nephritis
Minimal change
glomerulopathy
Pregnancy
Lithium is transferred to
nursing infants through
breastmilk
Lithium toxicity in newborn:
lethargy, cyanosis, poor suck,
hepatomegaly
Increase in frequency of
cardiac anomalies (Ebsteins
anomaly)
Miscellaneous:
Acneiform eruptions
Folliculitis
Leukocytosis
OVERDOSE
Therapeutic overdose is
more common than
accidental ingestion due to
accumulation of lithium (eg.
use of diuretics , NSAIDs)
Any value over 2 mEq/L
must be considered as
indicating potential toxicity.
Normal Lithium serum
concentration:
0.6 1.4mEq/L
VALPROIC ACID
An anticonvulsant that is
Mechanism is unknown
DOSE-RELATED SIDE
Drugs known to increase VPA
You might also like
- Real Estate Broker Licensure ExaminationDocument47 pagesReal Estate Broker Licensure ExaminationErica Patricia Lao100% (13)
- Drugs in Psychiatric NursingDocument38 pagesDrugs in Psychiatric NursingJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument20 pagesAminoglycosidesHassan.shehri100% (5)
- Dog Breeding CourseDocument5 pagesDog Breeding CourseChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Compounded Sterile Products Stability Compendium-AntineoplasticsDocument0 pagesCompounded Sterile Products Stability Compendium-AntineoplasticsRahmalia 'lia Cudby' PrihanantoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in PsychiatryDocument94 pagesPsychopharmacology in PsychiatryOslo SaputraNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY 10 NCPDocument46 pagesCASE STUDY 10 NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (8)
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Drug Study Mother TDocument14 pagesDrug Study Mother TEuzelle Jeena ArandaNo ratings yet
- Anti Manic DrugsDocument19 pagesAnti Manic DrugsVickyEliseFinandaNo ratings yet
- Fitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine 8ed PDFDocument3,190 pagesFitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine 8ed PDFBernadetta Dewanty100% (2)
- Mood Stablizing AgentsDocument15 pagesMood Stablizing AgentsDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- Cataract Consent FormDocument4 pagesCataract Consent FormHitesh Sharma100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - MakamisaDocument3 pagesLecture 18 - MakamisaChelsea Valdez100% (2)
- Great Sperm RaceDocument19 pagesGreat Sperm RacefrjesNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing: Narayan Swami College of NursingDocument10 pagesPediatric Nursing: Narayan Swami College of NursingAnkit KotnalaNo ratings yet
- Dystolic Dysfunction Ppt. SalmanDocument42 pagesDystolic Dysfunction Ppt. SalmanMustajab MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug StudyJennyLapitan80% (5)
- Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes MellitusDocument32 pagesPharmacotherapy of Diabetes MellitusGhilli Jaya PrakashNo ratings yet
- REBLEX Reviewer 2016Document138 pagesREBLEX Reviewer 2016Elias Buenavente20% (5)
- LithiumDocument4 pagesLithiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesTreatment of Diabetes MellitusIrfan IdealistNo ratings yet
- Synthroid (Levothyroxine)Document2 pagesSynthroid (Levothyroxine)E100% (2)
- Casas - Mood StabilizersDocument16 pagesCasas - Mood StabilizersKarl Kuis SantanderNo ratings yet
- Seminar 6 - Psychopharmacology - EctDocument108 pagesSeminar 6 - Psychopharmacology - EctA. TivieanNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilizing AgentsDocument21 pagesMood Stabilizing AgentsHamze Abdullah Al-ShawaheenNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugmmmartinez1583No ratings yet
- A Mood stabiliz-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesA Mood stabiliz-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- Antimaniac & Mood Stabilizing DrugsDocument13 pagesAntimaniac & Mood Stabilizing DrugsNikhat KadriNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilisers by NavinaDocument91 pagesMood Stabilisers by NavinaNavina SureshNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilizers-Amanat Ali-1Document33 pagesMood Stabilizers-Amanat Ali-1Syed Sanan shahNo ratings yet
- 16-12-2020 Mood Stabilizers Practice Teaching-1Document61 pages16-12-2020 Mood Stabilizers Practice Teaching-1VARSHANo ratings yet
- 22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument5 pages22 Psychotherapeutic AgentsAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- 3 - Bipolar DisorderDocument20 pages3 - Bipolar DisorderrazAn swNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants DESKTOP MHAO1SHDocument19 pagesAntidepressants DESKTOP MHAO1SHjanemwanza003No ratings yet
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocument2 pagesDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Antimanic DrugsDocument24 pagesAntimanic DrugsAlina AnwarNo ratings yet
- Lithium: Agnes May Cayco Ma. Golda Meir MassalangDocument13 pagesLithium: Agnes May Cayco Ma. Golda Meir MassalangCayx CaycoNo ratings yet
- CCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Treat Bipolar Disorder: By: DR Satar OstadhadiDocument31 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Bipolar Disorder: By: DR Satar OstadhadiSattar OstadhadiNo ratings yet
- ANTIDEPRESSANTS MaterialDocument5 pagesANTIDEPRESSANTS MaterialxyzNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants MaterialDocument5 pagesAntidepressants MaterialxyzNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document5 pagesModule 8Yuki Xairah TunayNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Lithium ToxicityDocument28 pagesLithium ToxicityReejan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Obesity Muhammad Fajri Labdul 821417146 C-S1 2017Document20 pagesObesity Muhammad Fajri Labdul 821417146 C-S1 2017Putry ReginaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Manic DrugsDocument16 pagesAnti-Manic Drugsanaya khan StudentNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDocument41 pagesDrugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDivya JoyNo ratings yet
- Diabetes PharmacologyDocument14 pagesDiabetes PharmacologyRich JeongNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Study - Metropolol Tartrate (Neobloc)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Metropolol Tartrate (Neobloc)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug StudyDocument19 pages8 Drug StudyLoyloy D ManNo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugDocument25 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugANI SAMNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilizing Agents For Bipolar DisorderDocument29 pagesMood Stabilizing Agents For Bipolar DisorderDaniyal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil 2Document14 pagesPropylthiouracil 2Magdy Ali ELsherbenyNo ratings yet
- Psych MedicationsDocument6 pagesPsych Medicationsash00se7enNo ratings yet
- Antimanic DrugsDocument30 pagesAntimanic DrugsTJ Ng100% (4)
- (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or GreaterDocument3 pages(BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or GreaterRackyNo ratings yet
- 175 Anaesthesia and Psychiatric Drugs Part 2 Mood Stabilisers and Antipsychotics PDFDocument6 pages175 Anaesthesia and Psychiatric Drugs Part 2 Mood Stabilisers and Antipsychotics PDFWahyu Permata LisaNo ratings yet
- Obesity and DiabetesDocument41 pagesObesity and DiabetesHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Description: Four Types of Mood EpisodesDocument4 pagesDescription: Four Types of Mood EpisodeskhinayoNo ratings yet
- For Drug Recitation 1Document33 pagesFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Psychiatrypoisoning E.ODocument24 pagesPsychiatrypoisoning E.OZeenat JunaidNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineDocument2 pagesDrug Dosage Action Indication Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Chlorpro MazineJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- BPAD FinalDocument31 pagesBPAD FinalZANo ratings yet
- Sandomigran PiDocument6 pagesSandomigran PiNexi anessaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- GWA CalculatorDocument2 pagesGWA CalculatorChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ace RX OutlineDocument3 pagesAce RX OutlineChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Quaratine PlanDocument2 pagesQuaratine PlanChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Canada VisaDocument8 pagesCanada VisaChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Visa CanadaDocument6 pagesVisa CanadaChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Physeo RuntimesDocument9 pagesPhyseo RuntimesRubayet Tasfin AlifNo ratings yet
- Us Mle Content OutlineDocument34 pagesUs Mle Content OutlineMariela LopezNo ratings yet
- Merritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleDocument75 pagesMerritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Complexo and Gravi NotesDocument8 pagesComplexo and Gravi NotesChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Merritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleDocument75 pagesMerritt's Dedicated Step Study ScheduleChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics of CardiologyDocument14 pagesMnemonics of CardiologyRaouf SolimanNo ratings yet
- Imidazole Imidazoline: Common Heterocycles Within Drug MoleculesDocument13 pagesImidazole Imidazoline: Common Heterocycles Within Drug MoleculesChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Timeline Date MilestoneDocument3 pagesTimeline Date MilestoneChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper ExtremitiesDocument1 pageBones of The Upper ExtremitiesChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- ACR Guidelines For Screening, Treatment, and Management of Lupus Nephritis PDFDocument12 pagesACR Guidelines For Screening, Treatment, and Management of Lupus Nephritis PDFJavier Saldaña CamposNo ratings yet
- Scalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitDocument4 pagesScalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Nmat Bulletin of InformationDocument16 pagesNmat Bulletin of InformationBrian SoanNo ratings yet
- Scalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitDocument4 pagesScalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Scalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitDocument4 pagesScalar Vector: LAW Involved Formula Unit LAW Involved Formula UnitChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- CMG P ReportDocument32 pagesCMG P ReportChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- ICH Q9 - Guideline PDFDocument23 pagesICH Q9 - Guideline PDFLuis CárdenasNo ratings yet
- Drug Adminitration Indication MOA Adverse Effect 1. NitratesDocument1 pageDrug Adminitration Indication MOA Adverse Effect 1. NitratesChelsea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Palmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlDocument41 pagesPalmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlGeekWireNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Thermal Camera For Use in Preclinical Detection of Diabetic PeripheralDocument8 pagesLow Cost Thermal Camera For Use in Preclinical Detection of Diabetic PeripheralEDGAR ISMAEL REYES DEZANo ratings yet
- 681 FullDocument6 pages681 FullKurnia AnharNo ratings yet
- Perkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusDocument3 pagesPerkutan Kateter Vena Sentral Dibandingkan Perifer Kanula Untuk Pengiriman Nutrisi Parenteral Ada NeonatusmuslihudinNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument54 pagesEctopic Pregnancypatriciaatan1497No ratings yet
- Demography Using Cemetery DataDocument5 pagesDemography Using Cemetery DatamjbdobleuNo ratings yet
- Legends About The Discovery of Fire Key IncludedDocument2 pagesLegends About The Discovery of Fire Key IncludedSilvia MontesNo ratings yet
- IELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Practice Test 30Document14 pagesIELTS Recent Actual Test With Answers Practice Test 30Ferris Wheel GuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - The Brainstem and Cranial NervesDocument8 pagesChapter 9 - The Brainstem and Cranial NervesJess PeltraNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan CBT COMBO 3Document802 pagesPembahasan CBT COMBO 3Sari Dewi WiratsihNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaDocument17 pagesMedicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Anti Stress Effects of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC Root Extract On Clinical Patients A Psycological EstimationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Anti Stress Effects of Nardostachys Jatamansi DC Root Extract On Clinical Patients A Psycological EstimationESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Public Health Reasoning and Epidemic Modelling 2005Document332 pagesInterdisciplinary Public Health Reasoning and Epidemic Modelling 2005Nadhira KarimaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Airline PilotsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Risk Factors in Airline Pilotsluis11256No ratings yet
- Curs 1 Introducere EndodontieDocument24 pagesCurs 1 Introducere EndodontieVlahul VladNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and DkaDocument6 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy and Dkajames garciaNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Catholic Doctors in The Changing World - 15th AFCMA Congress 2012Document218 pagesChallenges of Catholic Doctors in The Changing World - 15th AFCMA Congress 2012Komsos - AG et al.No ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Microorganisms (Continuation)Document2 pagesChapter - 2 Microorganisms (Continuation)ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Curs de Limba PortughezaDocument16 pagesCurs de Limba PortughezaMădălina TodincaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Research Paper OutlineDocument6 pagesAlcohol Research Paper Outlineafmctmvem100% (1)
- Glucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsDocument31 pagesGlucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsnikenNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoDocument8 pagesEfficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoANA CRISTINA MENDEZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- Emerys IepDocument15 pagesEmerys Iepapi-300745138No ratings yet