Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormonal disorders guide
Uploaded by
ritik shuklaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hormonal disorders guide
Uploaded by
ritik shuklaCopyright:
Available Formats
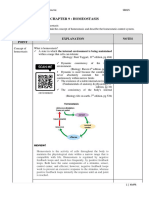
List of Hormonal disorders
Disorders due to hormone deficiency (Hyposecretion)
Name of disorder
Hyposecretion of
Acromicria (in adults)
Somatotrophin
Addisons disease
Aldosterone
Cretinism (in children)
Thyroxin
Diabetes insipidus
Vasopressin (ADH)
Diabetes mellitus
Insulin
Dwarfism
Somatotrophin
Myxoedema (in adults)
Thyroxin
Tetany
Parathormone
(PTH)
Eunuchoidism
Testosterone
Symptoms
Bones of the face and extremities are small and delicate.
Hypertension, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, low blood
sugar, low plasma Na+, high plasma K+, increased
urinary Na+ and bronze like pigmentation of skin.
Retarded growth, low intelligence, delayed sexual
maturity.
Enormous secretion of urine (polyuria), excess thirst
(polydypsia) etc
Hyperglycemia (high sugar level in blood), glycosuria
(sugar in urine), polyphagia (overeating), polydypsia
(excess thirst) and polyuria (frequent urination).
Short in stature.
Physical sluggishness, mental dullness, low metabolic
rate, dry and coarse skin and puffy face.
Steep drop in blood calcium level, abnormal rise in
excitability of nerves and muscles, sustained and violent
contraction of muscles of face, larynx, hands and feet.
Lack male secondary sexual characters, sterility etc
Disorders due to excess hormone (Hypersecretion)
Name of disorder
Hypersecretion of
Acromegaly (in adults)
Somatotrophin
Adrenal virilism (in female)
Sex corticoid
Conns syndrome
Aldosterone
Symptoms
Abnormal growth of bones of face, lower jaw, hands and
feet. Enlargement of internal organs such as lungs,
spleen etc
Masculanization of females such as growth of beards and
moustaches and male voice etc.
Headache, Excessive urination at night, Excessive
thirst, Excessive urination, Increased volume of
blood,Increased blood sodium level, High alkalinity of
10.
Cushings syndrome
Cortisol
Exophthalmic goiter (Graves
disease)
Thyroxin
Gigantism (in children)
Somatotrophin
Hyperglycaemia
Glucagon
Insulin shock
Insulin
Kidney stone
Parathormone
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
Parathormone
blood and body fluids,
High blood sugar, obesity, deposition of fat in the face,
neck etc. rise in plasma Na+ and high BP. In acute
condition it leads to mental depression and impotency.
Hypertrophy of thyroid gland, increased metabolism, high
rate of heartbeat, bulging eyeballs, restlessness,
nervousness and loss of weight.
Excessive height, extreme bone, muscle and organ
growth.
Polyphagia, Polydipsia, Polyuria, Blurred vision, Fatigue
(sleepiness), Weight loss
Poor wound healing (cuts, scrapes, etc.), Dry mouth, Dry
or itchy skin, Tingling in feet or heels, Erectile
dysfunction, Recurrent infections, external ear infections
(swimmer's ear), Cardiac arrhythmia, Stupor, Coma,
Seizures
Abnormal lowering of blood glucose (hypoglycemia),
sudden fall of body temperature, fatigue, tremors and
unconsciousness.
Accumulation of calcium in blood and it precipitate with
phosphates to form kidney stones.
Calcification of soft tissues like blood vessels
You might also like
- Vitamins Table with Functions and Deficiency SymptomsDocument3 pagesVitamins Table with Functions and Deficiency SymptomsthomasqilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine NursingDocument2 pagesEndocrine NursingUnclePorkchop94% (34)
- Endocrine SystemsDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemsRean T. DeAndreasNo ratings yet
- Diagn Approach of Abdominal PainDocument53 pagesDiagn Approach of Abdominal PainNuriNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Disorders - Adrenal Disorders - Thyroid DiseasesDocument207 pagesPituitary Disorders - Adrenal Disorders - Thyroid Diseasesnurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Interview Pa Tool.Document5 pagesInterview Pa Tool.Raisah Bint AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Baluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesDocument6 pagesBaluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesdave_1128No ratings yet
- Clinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7Document36 pagesClinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7aparish10100% (1)
- CSF Protection & Flow of the BrainDocument25 pagesCSF Protection & Flow of the BrainchintyamontangNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam LamDocument7 pagesPsychotherapeutic Drugs: Pam Pam Lamchubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- GI Signs and SymptomsDocument40 pagesGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeNo ratings yet
- Medical Guide to Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (PoTSDocument12 pagesMedical Guide to Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (PoTSAttis PhrygiaNo ratings yet
- Decena, Cyrille Justine A. BSN-4A: Competency AppraisalDocument4 pagesDecena, Cyrille Justine A. BSN-4A: Competency AppraisalJohn Glenn Balacano100% (2)
- Comprehensive H&PDocument2 pagesComprehensive H&PjwwisnerNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rahim Bin Mohamad Nor C 111 10 871: Prof - Dr.Peter Kabo, PHD, SPFK, SPJP (K), Fiha, FasccDocument38 pagesAbdul Rahim Bin Mohamad Nor C 111 10 871: Prof - Dr.Peter Kabo, PHD, SPFK, SPJP (K), Fiha, FasccAis KonorasNo ratings yet
- AhafinalheadtoeDocument4 pagesAhafinalheadtoeapi-620081868No ratings yet
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocument16 pagesCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1No ratings yet
- Case Analysis Tool Worksheet: Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument4 pagesCase Analysis Tool Worksheet: Squamous Cell CarcinomaDina KristevaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Document47 pagesPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument2 pagesCranial NervesakexisNo ratings yet
- 100 Essential Drugs1Document8 pages100 Essential Drugs1Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology 2Document108 pagesEndocrinology 2Sofijanovic JasminNo ratings yet
- Ninja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1Document42 pagesNinja On Fleek - Fern Charts MT1pp100% (1)
- H. OncologyDocument27 pagesH. OncologyGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Secondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageSecondary Amenorrhea Testing AlgorithmpolygoneNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument5 pagesDiabetes InsipidusFazalJaturieNo ratings yet
- Vindicate For LBPDocument10 pagesVindicate For LBPShaun TylerNo ratings yet
- FINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSDocument1 pageFINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSronique reidNo ratings yet
- PCP Exam Topics in Major Medical SpecialtiesDocument1 pagePCP Exam Topics in Major Medical SpecialtiesBobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- Piuitary DisordersDocument40 pagesPiuitary DisordersSuliman GarallehNo ratings yet
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocument10 pagesMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationDocument55 pagesPhysical Examinationdakshpanchal26369No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diagnostic Tests & Procedures.Document25 pagesCardiovascular Diagnostic Tests & Procedures.Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Study GuideDocument4 pagesEndocrine Study GuideNursingSchoolNotes100% (1)
- Cell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of ActionDocument3 pagesCell Wall Inhibitors and Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Antibiotics Mechanisms of Actionyanks1120No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesPathophysiology of Endocrine SystemRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 50 Questions & AnswersDocument28 pagesEndocrine 50 Questions & AnswersBrooke Susac100% (1)
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- Endocrine ChartDocument28 pagesEndocrine ChartNiki NikolićNo ratings yet
- Review in AUBFDocument37 pagesReview in AUBFMichelle T. MabasaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notes - Part 2Document10 pagesEndocrine Pathophysiology Nursing Notes - Part 2grad_nurse_2015100% (1)
- Physio Reviewer Renal To Acid BaseDocument11 pagesPhysio Reviewer Renal To Acid BaseNicole ChanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsDocument3 pagesLecture 29 30 Thyroid TherapeuticsAhmed MashalyNo ratings yet
- Metabolic and Endocrine ManagementDocument42 pagesMetabolic and Endocrine ManagementAlyssa MontimorNo ratings yet
- 55 ENDOCRINE Tutorial Week 5ADocument9 pages55 ENDOCRINE Tutorial Week 5AChristian Versola-Macapulay Valle100% (1)
- Approach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesApproach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- MS Exam 2Document34 pagesMS Exam 2David LopezNo ratings yet
- Renr Practice Test 11Document17 pagesRenr Practice Test 11Aaron Wallace92% (12)
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- General Medicine Diagnostic PointsDocument14 pagesGeneral Medicine Diagnostic PointsUsman AR VainceNo ratings yet
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Checklist (Masroni)Document13 pagesHead To Toe Checklist (Masroni)hillary elsaNo ratings yet
- 3-Major Veins of The BodyDocument26 pages3-Major Veins of The BodyTJPlayz100% (1)
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDocument35 pages1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy Medicines for Breast Cancer TreatmentDocument2 pagesChemotherapy Medicines for Breast Cancer Treatmentr_mckenrick0% (1)
- Lab Values and Vital SignsDocument4 pagesLab Values and Vital SignsWole Olaluwoye100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Headache NotesDocument3 pagesNeurology - Headache NotessarahNo ratings yet
- Kaplan All SubjectsDocument8 pagesKaplan All Subjectssarmad_bayatliNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-AnswersDocument2 pagesDisorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answersapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Neuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Document9 pagesNeuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Johanna Hamnia PobleteNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Causes, Signs, Symptoms and InterventionsDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances: Causes, Signs, Symptoms and InterventionsmkninnyNo ratings yet
- HF Management GuideDocument49 pagesHF Management GuideJabraan Jamil100% (1)
- 201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pages201103-Fkg-Drugs Act On Cardiovascular SystemEidelen Lovani Sembiring100% (1)
- Pain MedicationsDocument2 pagesPain MedicationsimirelaNo ratings yet
- Sign and SymptomsDocument8 pagesSign and SymptomsCaral Grace Gatdula-PenalbaNo ratings yet
- Impactednurse Nurses Reference PackDocument2 pagesImpactednurse Nurses Reference PackRaenell CurryNo ratings yet
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFDocument2 pagesNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia vera clinical presentation and treatmentDocument5 pagesPolycythemia vera clinical presentation and treatmentPrisbert W. AlejoNo ratings yet
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Water Metabolism and Edema FormationDocument7 pagesDisorders of Water Metabolism and Edema FormationlalitrajindoliaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument18 pagesHomeostasisEmelia DeeNo ratings yet
- Guideline, Management of HypernatremiaDocument9 pagesGuideline, Management of HypernatremiaLia Safitri Leloly100% (1)
- Garrahy 2020Document13 pagesGarrahy 2020Ana Elizabeth Gangotena CoralNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE-BOARD REVIEW Dr. SchearDocument57 pagesENDOCRINE-BOARD REVIEW Dr. SchearNayara PataroNo ratings yet
- Aimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Document360 pagesAimee M. Abide, Catherine Margaret Kuza, Michael T. Vest - Self-Assessment in Adult Multiprofessional Critical Care (2022, Society of Critical Care Medicine) - Libgen - Li 2Gibran HolmesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Water Metabolism and Diabetes InsipidusDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Water Metabolism and Diabetes InsipidusSteffi AraujoNo ratings yet
- PosttestDocument6 pagesPosttestBelleNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes: George A. HarwellDocument29 pagesElectrolytes: George A. HarwellWho Knows100% (1)
- Insights Into Veterinary Endocrinology - Diagnostic Approach To PU - PD - Urine Specific GravityDocument4 pagesInsights Into Veterinary Endocrinology - Diagnostic Approach To PU - PD - Urine Specific GravityHusnat hussainNo ratings yet
- Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance ChapterDocument7 pagesWater, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance ChapterSteve MizzoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Deprivation TestDocument3 pagesFluid Deprivation TestsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- OsmometryDocument6 pagesOsmometryVERMADEEN0% (1)
- MCQ1Document11 pagesMCQ1Yuda Lutfiadi100% (1)
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: MetabolismJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- SGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationDocument1 pageSGD - Polyuria in Pediatrics: Clinical ExaminationREnren ConsolNo ratings yet